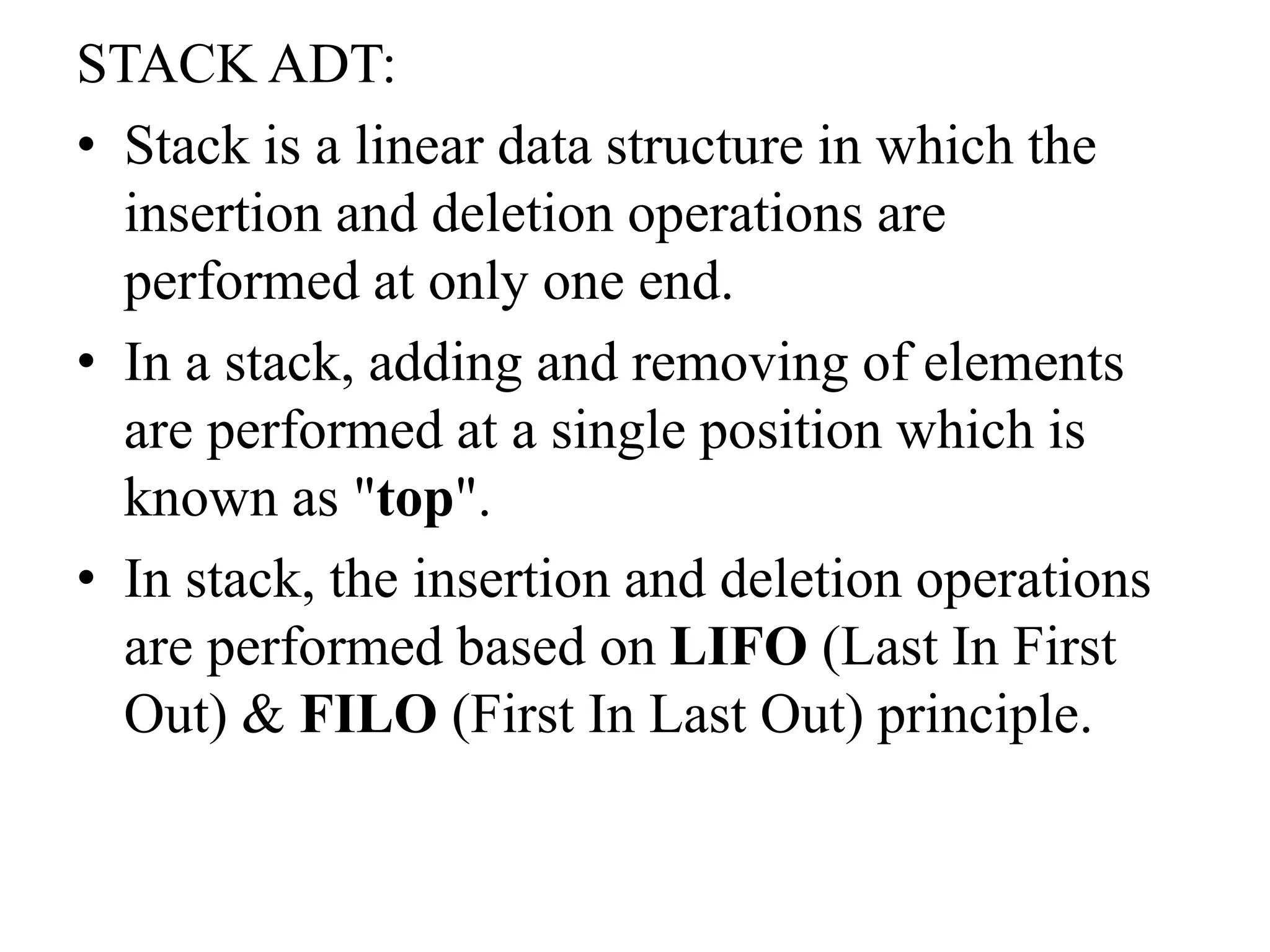
The document defines and describes a stack data structure. A stack follows LIFO (last in, first out) and FILO (first in, last out) principles. Elements can be inserted using push and deleted using pop. Stacks have only one end for insertion/deletion and can be implemented using arrays or linked lists. The document provides code examples to implement stacks using arrays and linked lists and describes some applications of stacks like evaluating expressions and balancing symbols.


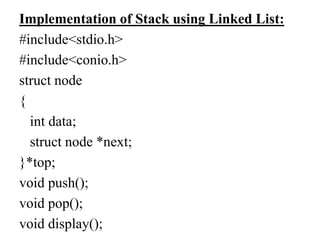
![Implementation of Stack using Array:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define SIZE 10
void push(int);
void pop();
void display();
int stack[SIZE], top = -1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitii-210524101009/85/CS8391-Data-Structures-Unit-2-4-320.jpg)


![void push(int value)
{
if(top == SIZE-1)
printf("nStack is Full!");
else
{
top++;
stack[top] = value;
printf("nInsertion success!!!");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitii-210524101009/85/CS8391-Data-Structures-Unit-2-7-320.jpg)
![void pop()
{
if(top == -1)
printf("nStack is Empty!");
else
{
printf("nDeleted : %d", stack[top]);
top--;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitii-210524101009/85/CS8391-Data-Structures-Unit-2-8-320.jpg)
![void display()
{
if(top == -1)
printf("nStack is Empty!!!");
else
{
int i;
printf("nStack elements are:n");
for(i=top; i>=0; i--)
printf("%dn",stack[i]);
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitii-210524101009/85/CS8391-Data-Structures-Unit-2-9-320.jpg)