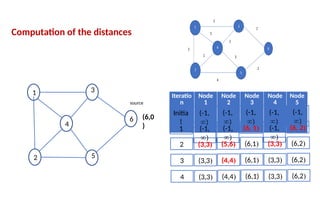
The document discusses the implementation of the Bellman-Ford algorithm for finding the shortest path in a network, detailing its operation at the network layer and its ability to handle negative edge weights. It outlines how the algorithm iteratively updates routing information to determine the minimum distance from a source node to all other nodes and includes sample Java code for its implementation. The document also provides example outputs demonstrating the algorithm's functionality, including handling cases with negative edge cycles.





![Program 6: Write a program to find the shortest path between vertices
using bellman-ford algorithm.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BellmanFord
{
private int D[];
private int n;
public static final int MAX_VALUE = 999;
public BellmanFord(int n) Constructor of the class
{
this.n=n;
D = new int[n+1]; Creates an array D to hold the distance information
}
public void shortest(int d, int A[][])
{
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
D[i]=MAX_VALUE; Initially all n values in D is set to infinity which is 999](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bellemford-240926091342-8262c08e/85/computer-networks-lab-program-Bellman-Ford-pptx-9-320.jpg)
![D[d] = 0; Distance from destination to itself is set to zero
for(int k=1;k<=n-1;k++)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(A[i][j]!=MAX_VALUE) for every node distance is updated in array D, if an
alternate path is available path through a neighbor
which is better than the current
if(D[j]>D[i]+A[i][j]) {
D[j] is the current distance value, D[i]+A[i][j] is the
D[j]=D[i]+A[i][j]; new path through neighbor i
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bellemford-240926091342-8262c08e/85/computer-networks-lab-program-Bellman-Ford-pptx-10-320.jpg)
![for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(A[i][j]!=MAX_VALUE)
{
if(D[j]>D[i]+A[i][j]) The same condition which was tested in the previous loop is
checked, if it is true here the graph contains negative edges
{
System.out.println("The Graph contains negative egde cycle");
return;
}
}
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
System.out.println("Distance from " +i+ “ to destination " +d+ "is " + D[i]); Finally array D will
have the computed distance from all
} the vertices to the destination vertex
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bellemford-240926091342-8262c08e/85/computer-networks-lab-program-Bellman-Ford-pptx-11-320.jpg)
![public static void main(String[ ] args)
{
int n=0,d;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of vertices");
n = sc.nextInt();
int A[][] = new int[n+1][n+1];
System.out.println("Enter the Weighted matrix");
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
A[i][j]=sc.nextInt(); read the weighted matrix A
}
System.out.println("Enter the destination vertex");
d=sc.nextInt(); select the destination node
BellmanFord b = new BellmanFord(n); create an object of the class
b.shortest(d,A); Call the shortest function
sc.close();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bellemford-240926091342-8262c08e/85/computer-networks-lab-program-Bellman-Ford-pptx-12-320.jpg)

