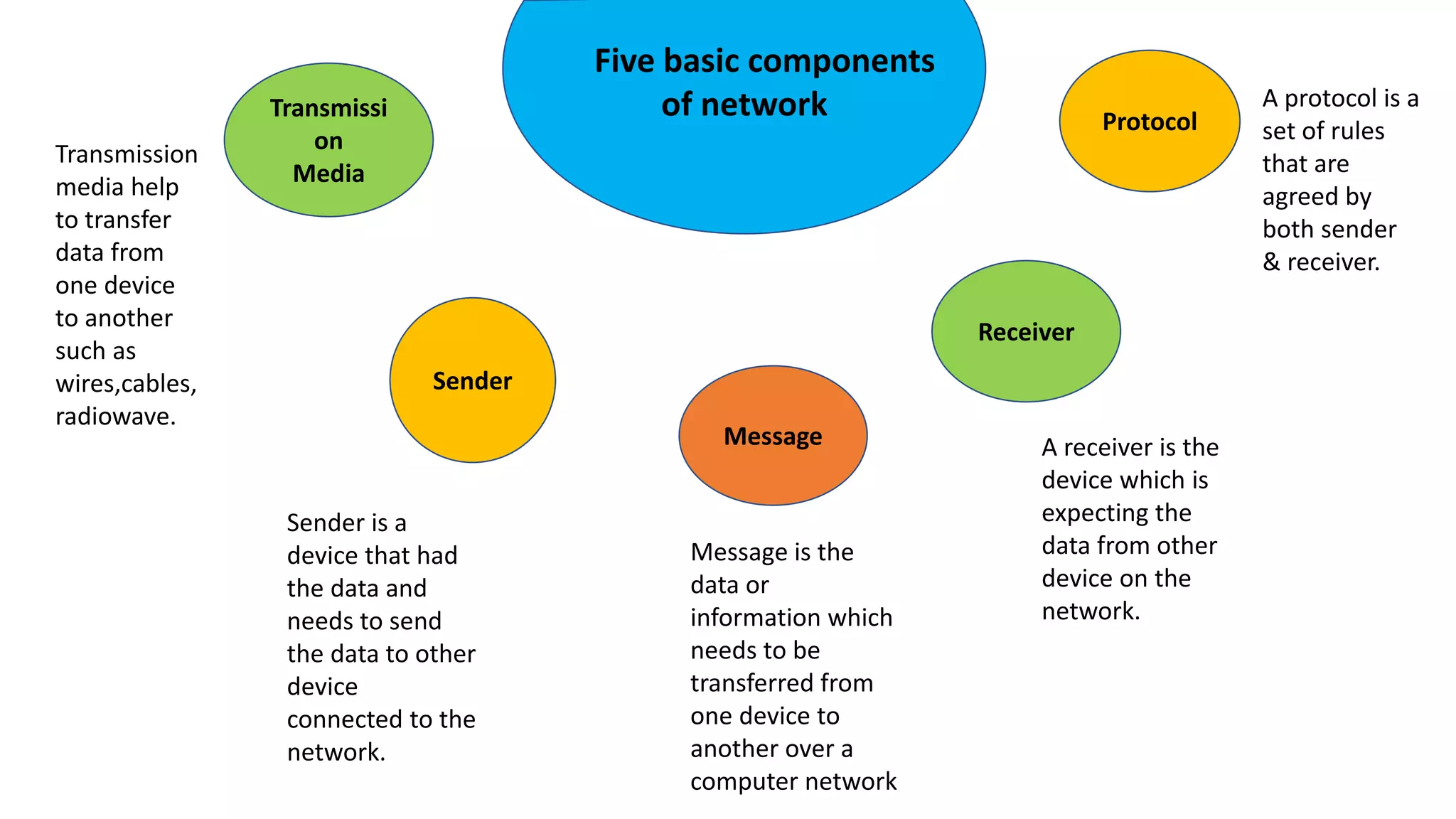
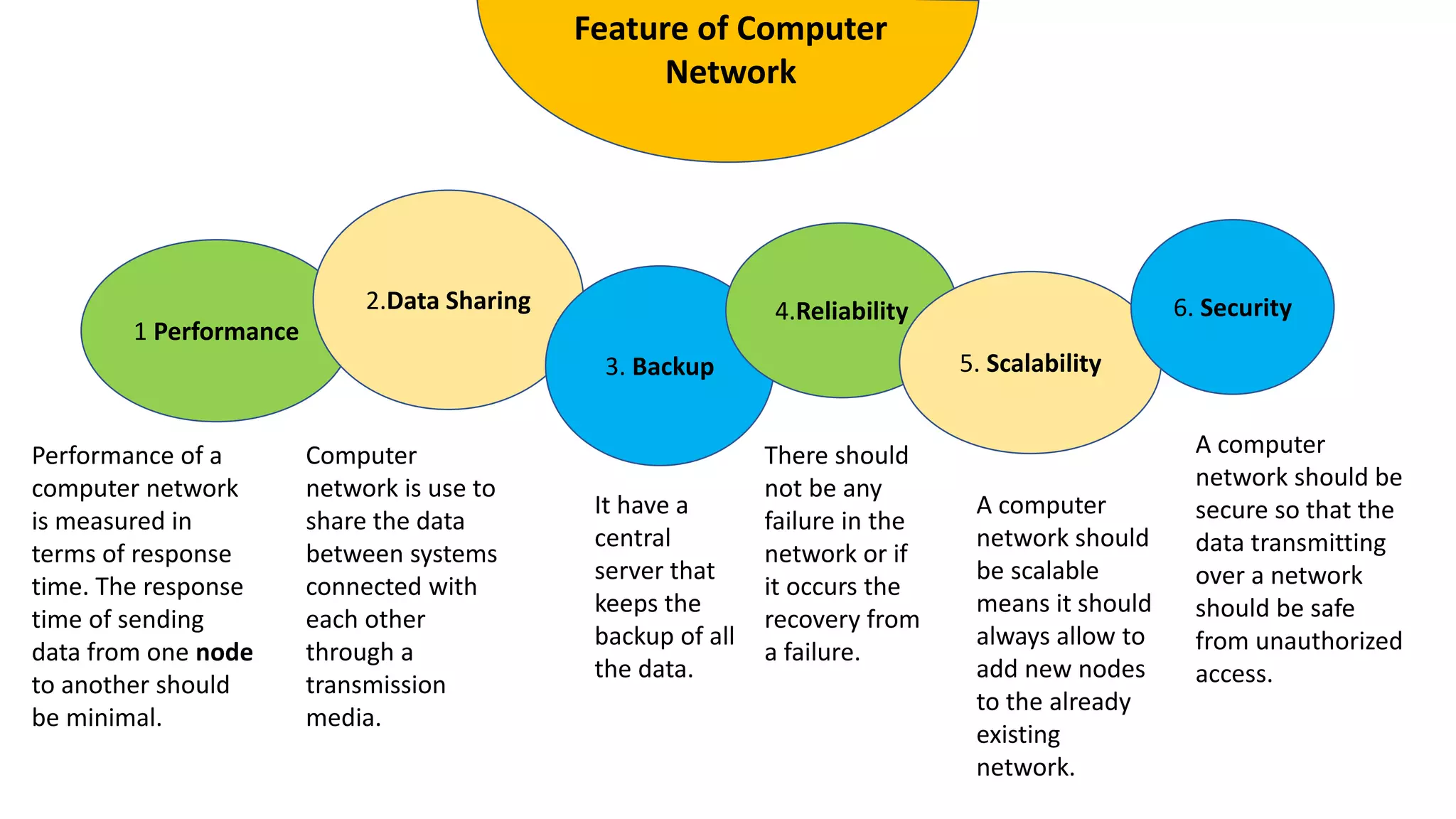
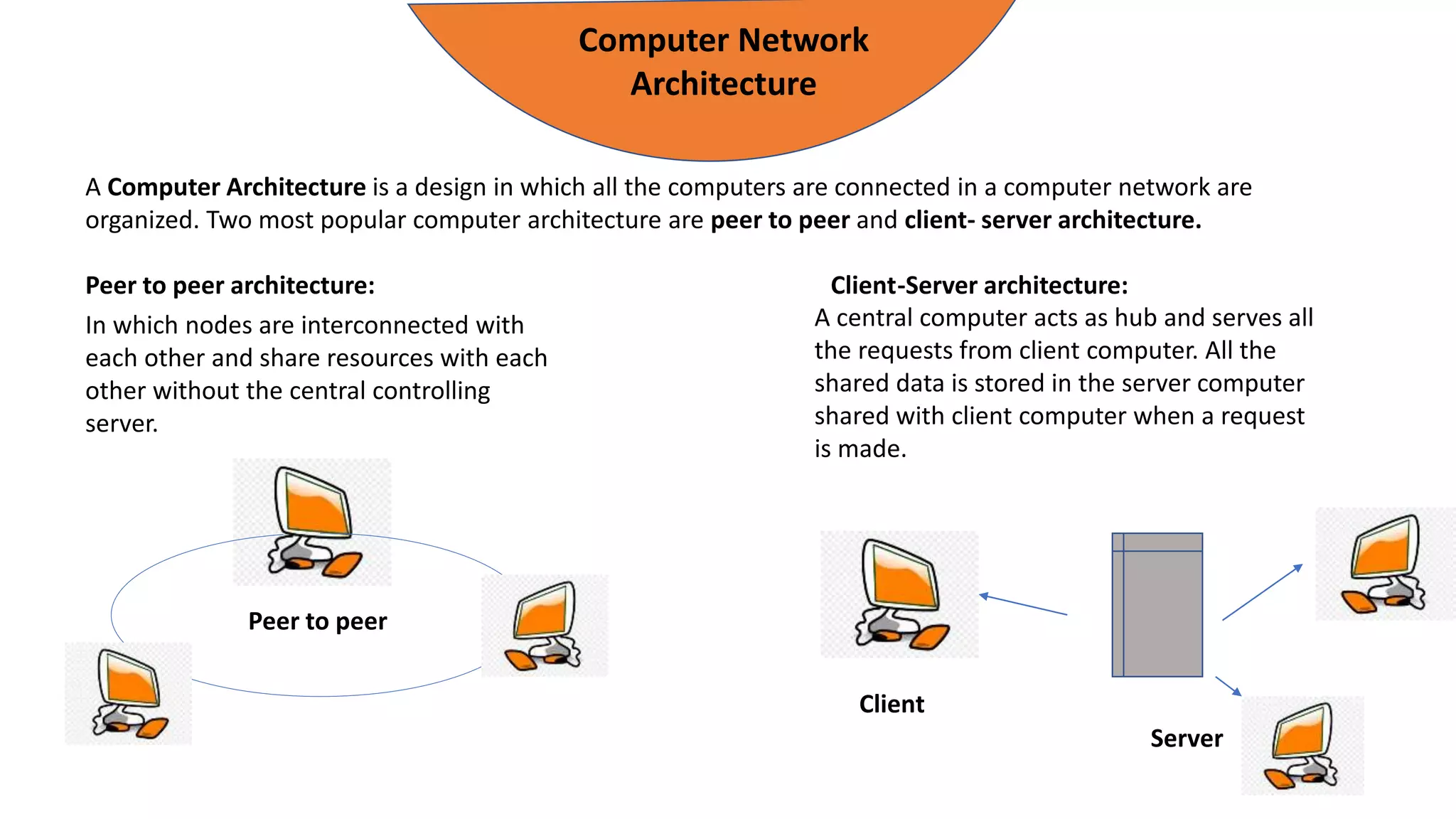
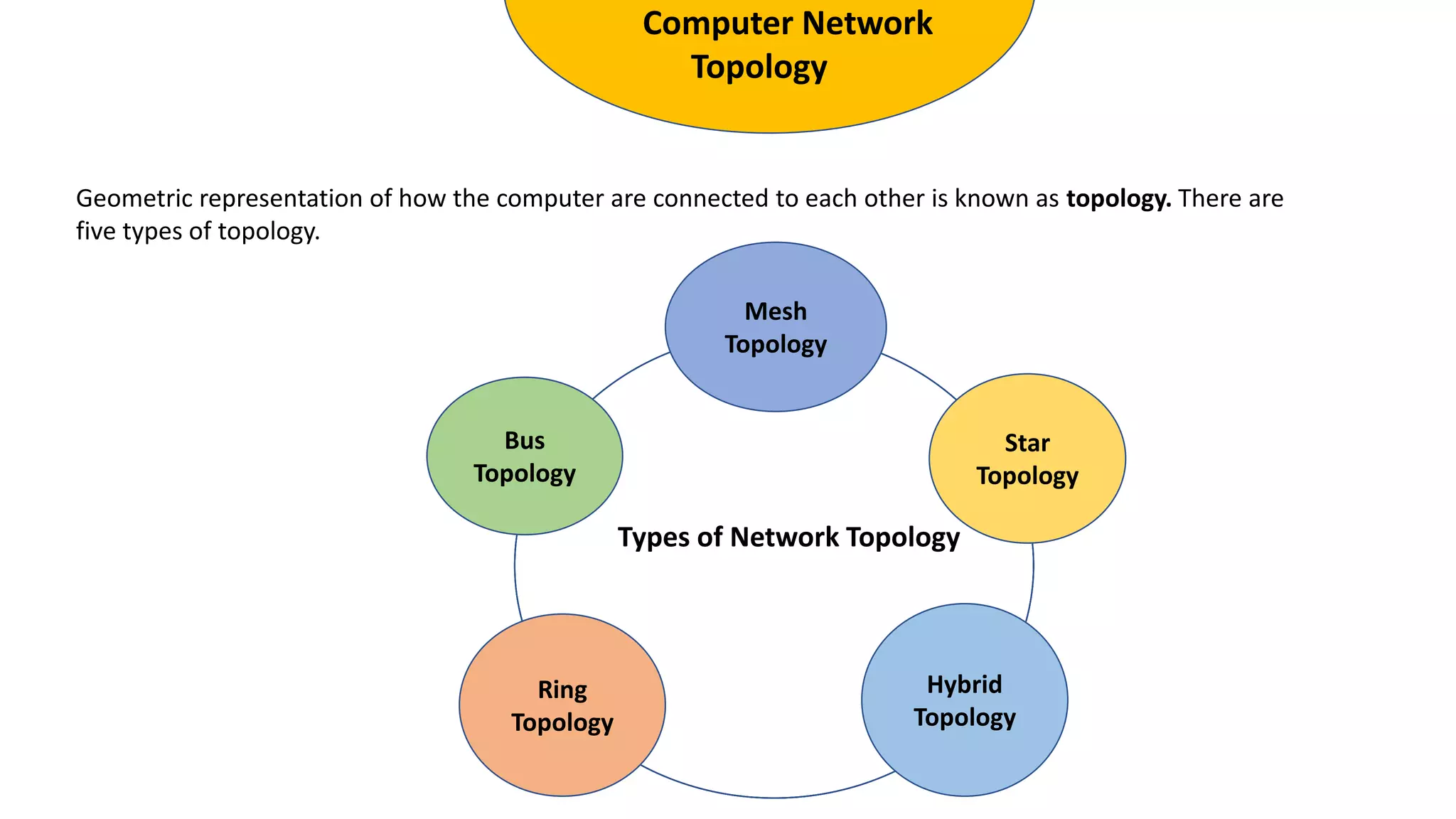
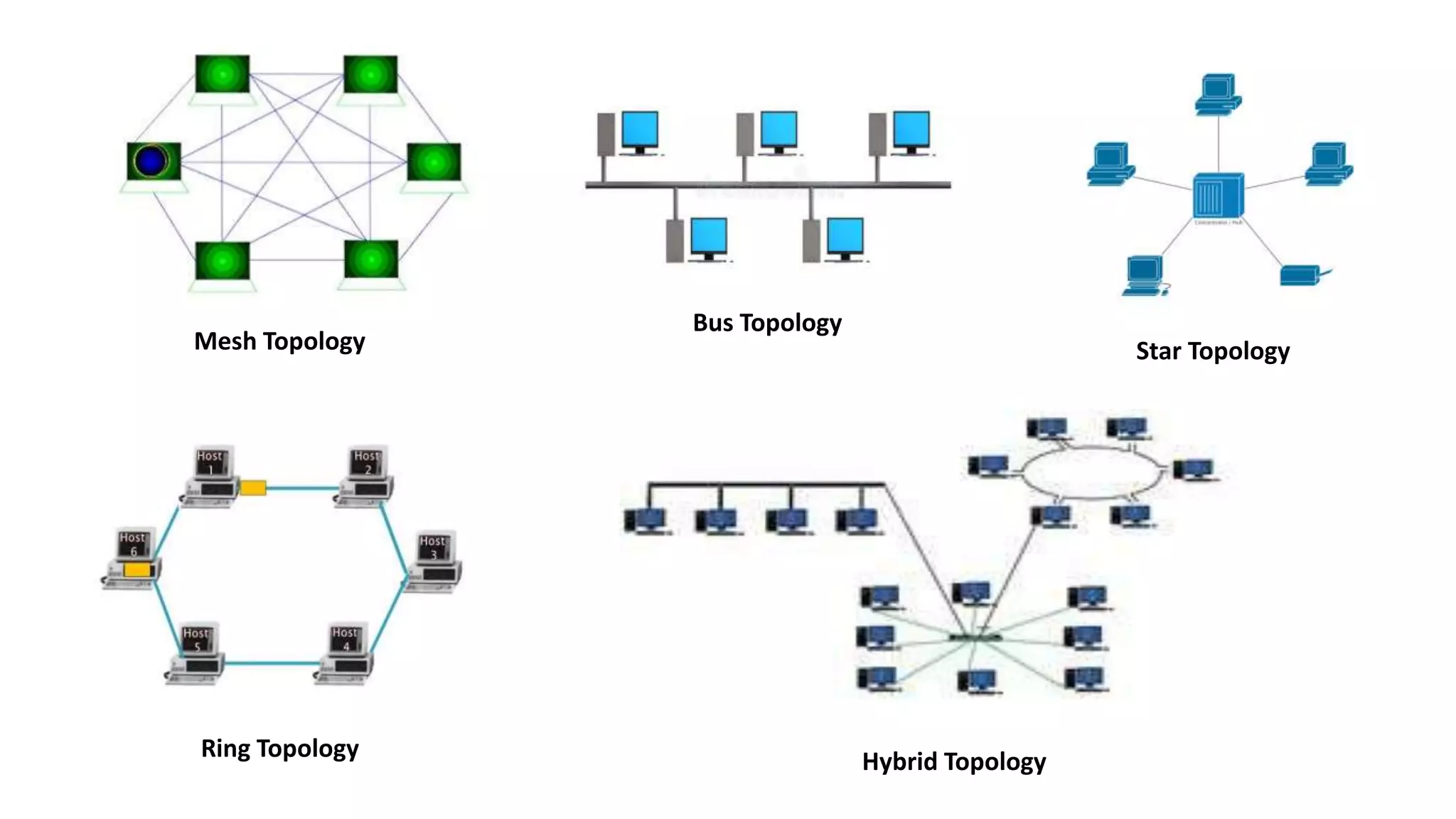
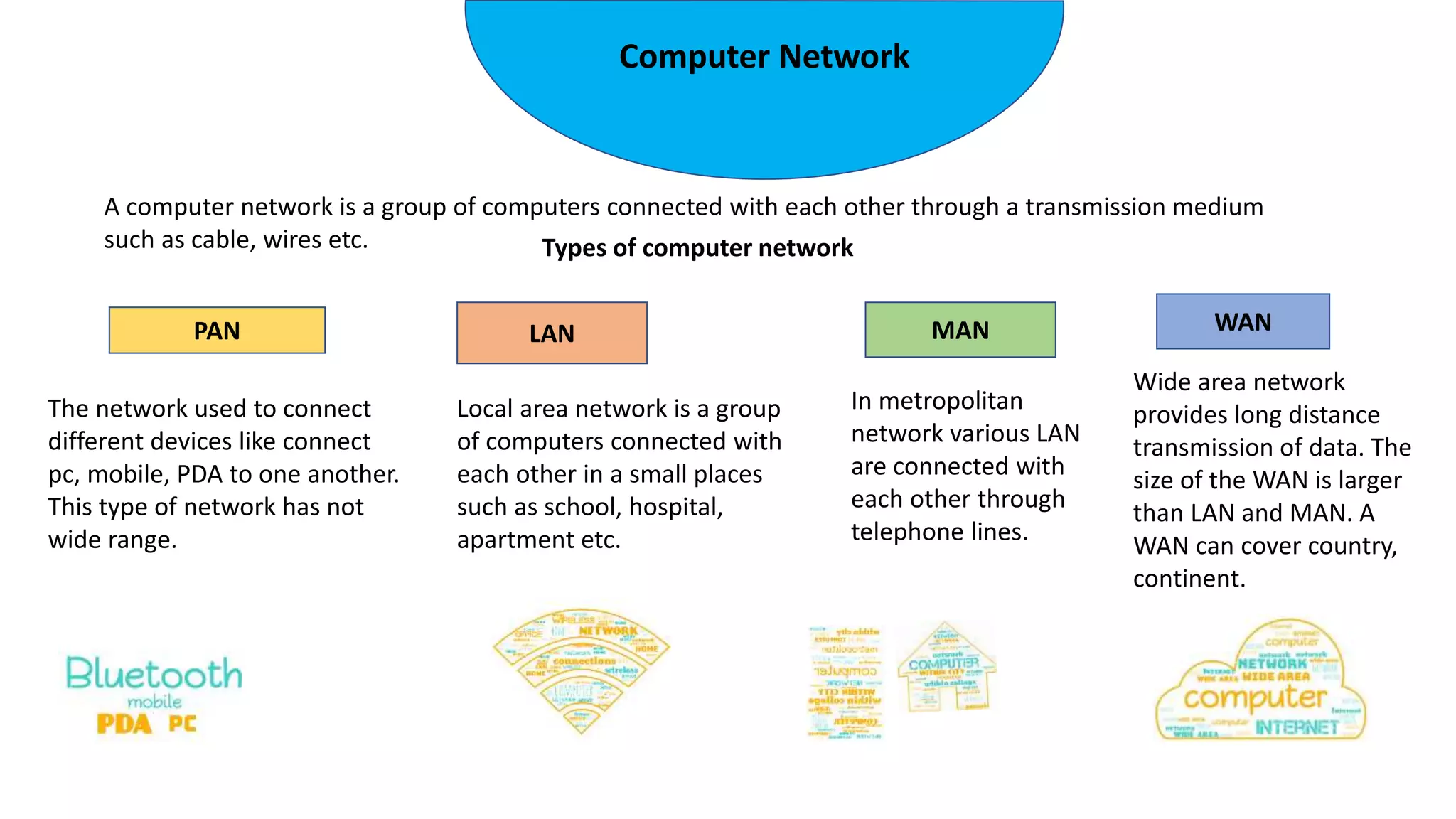
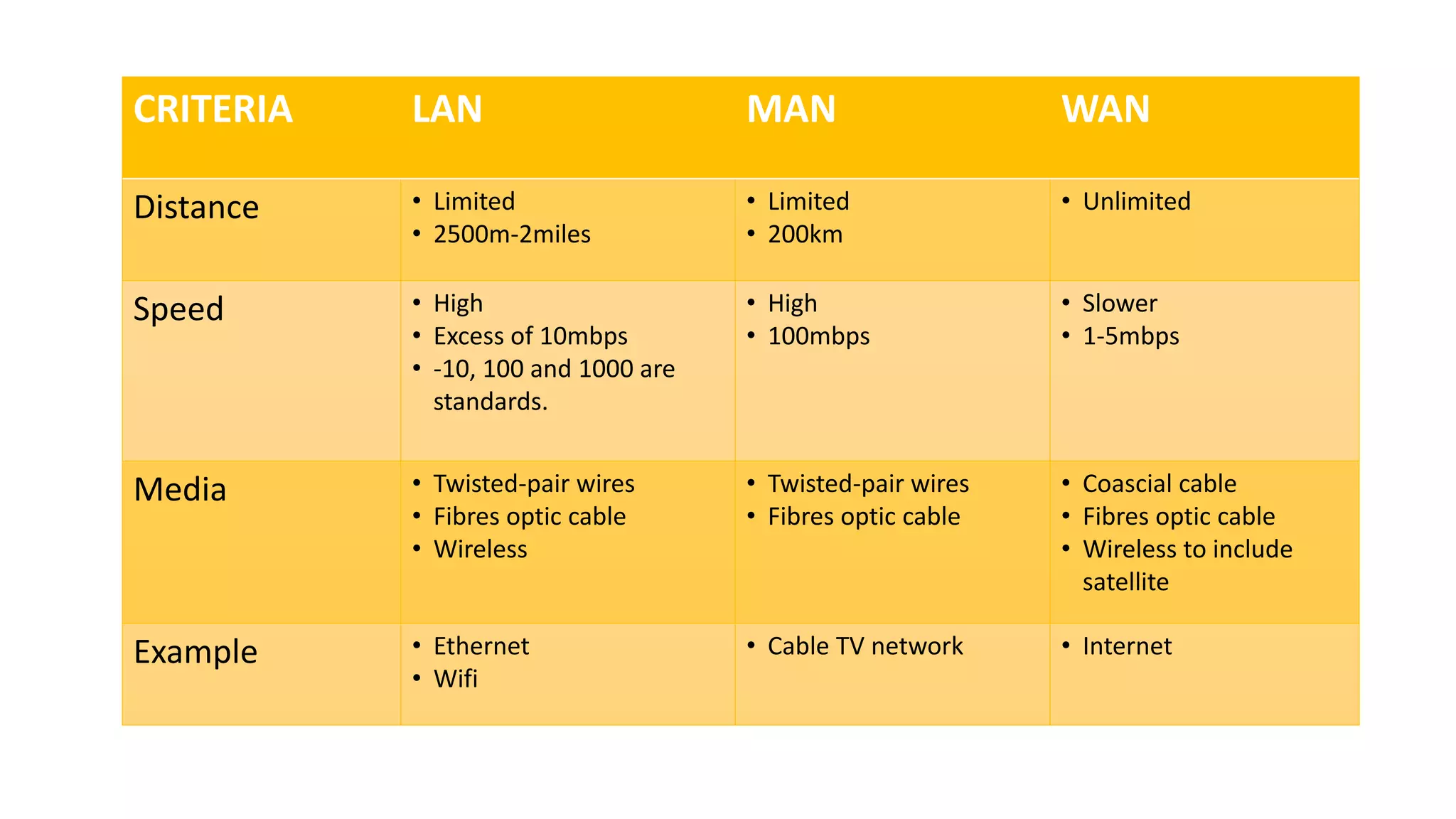
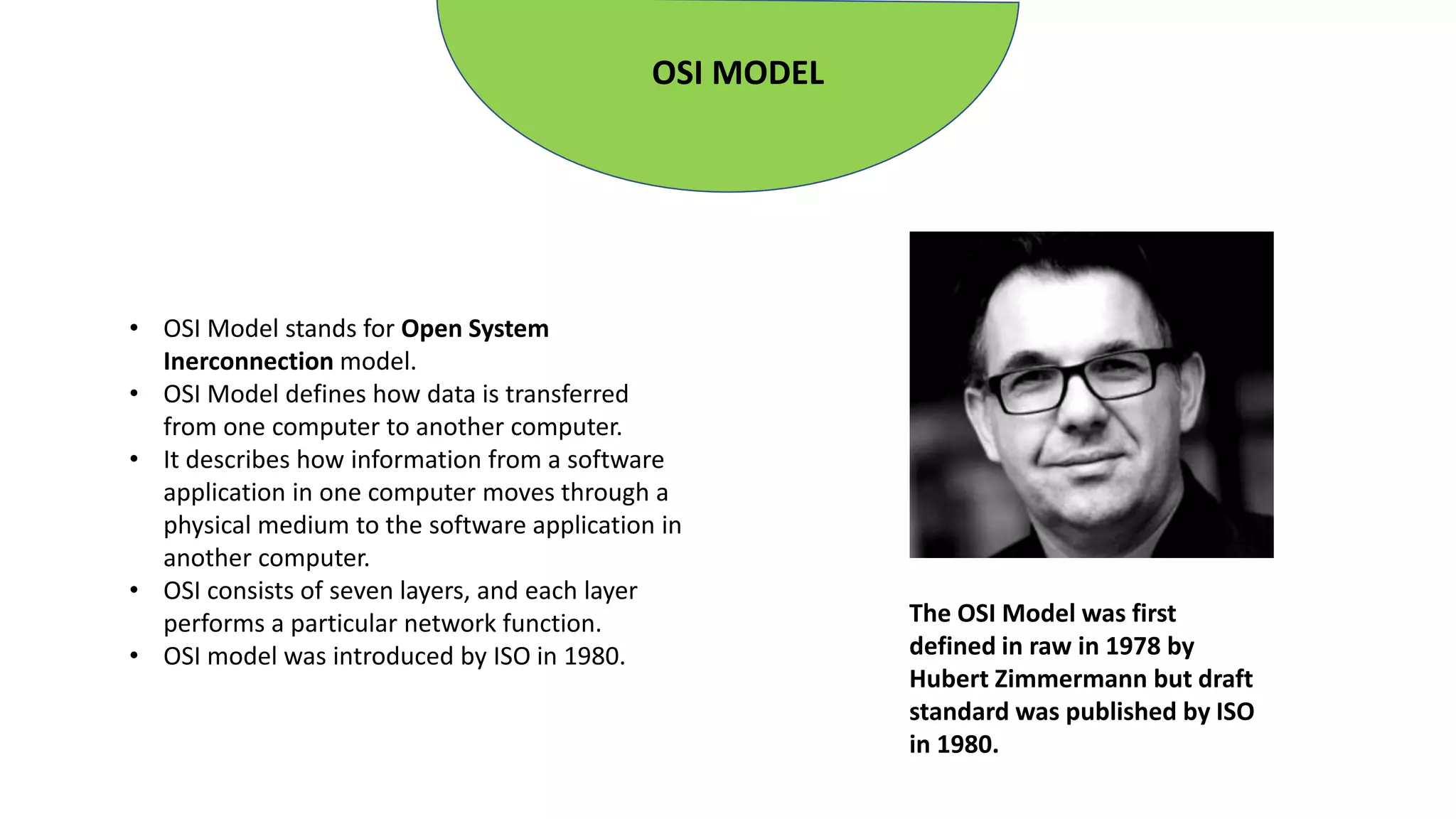
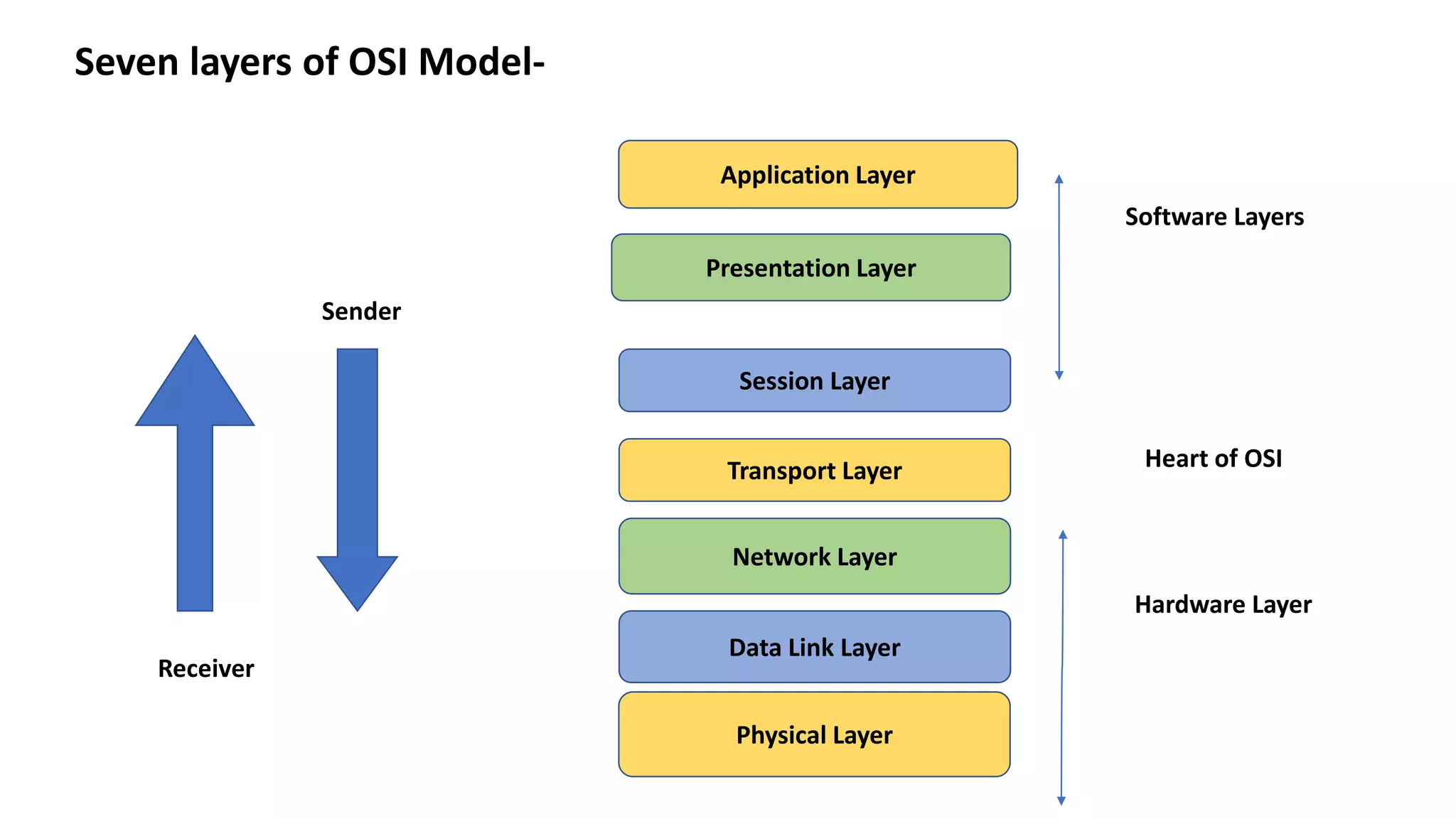
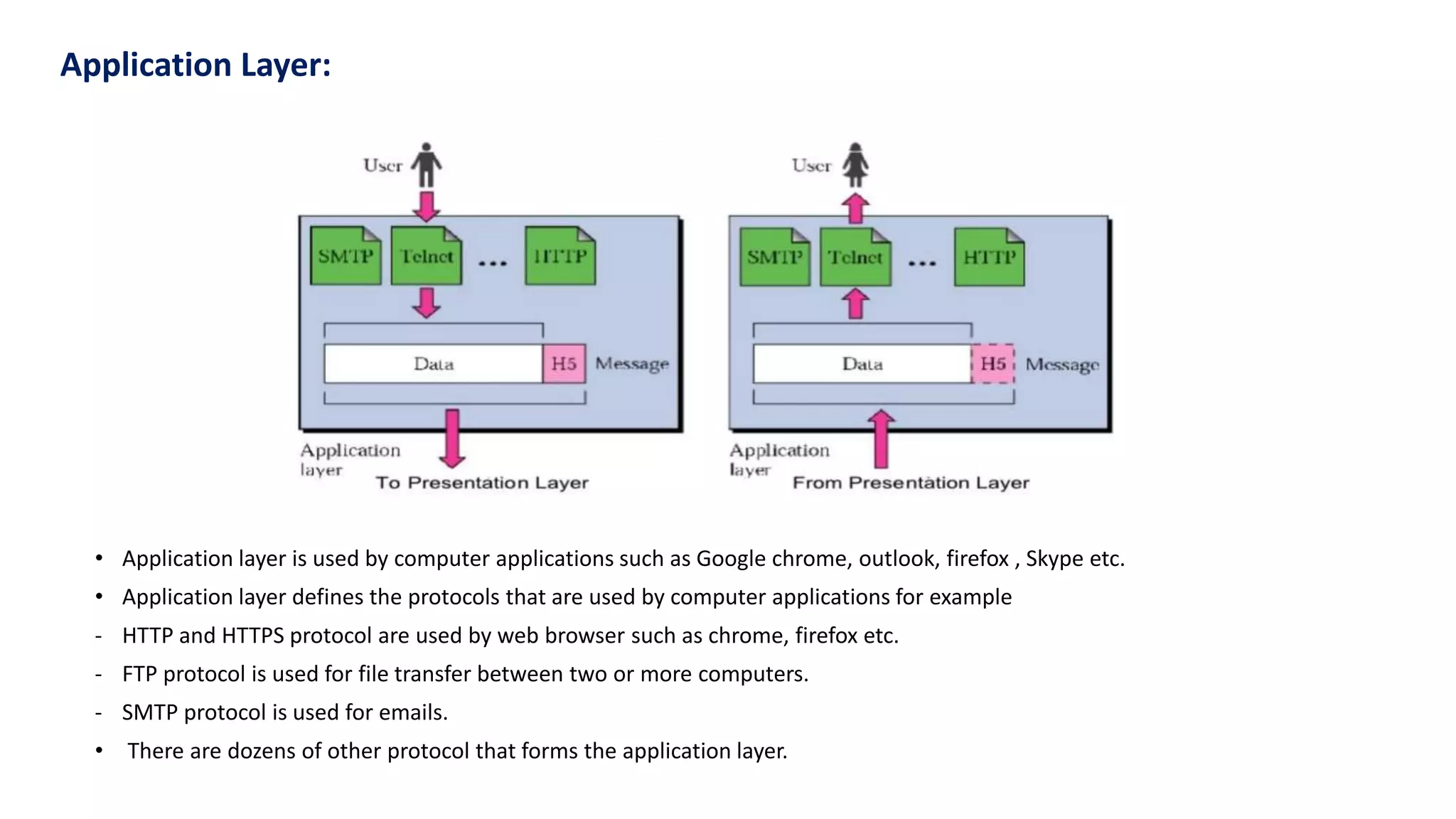
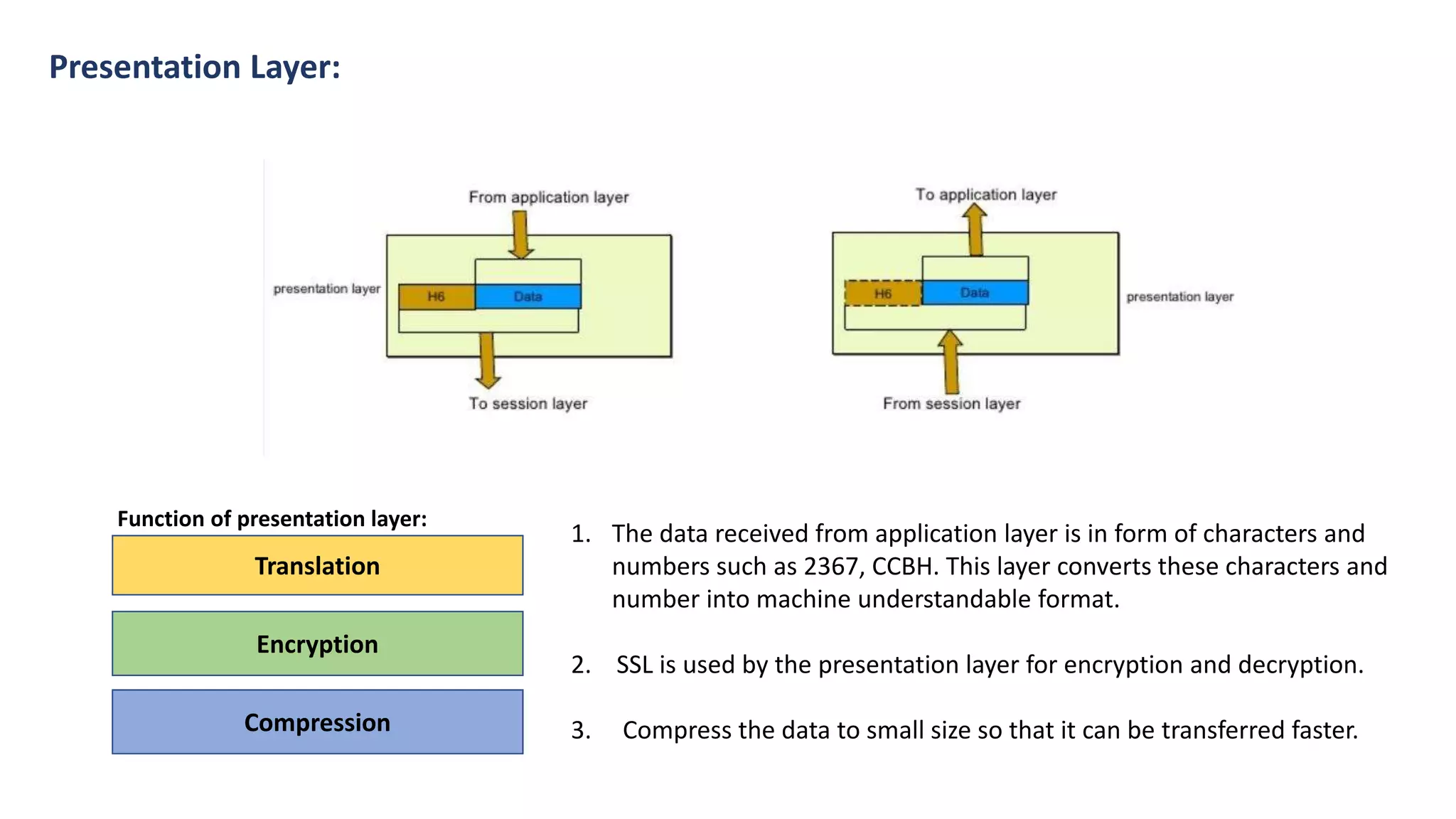
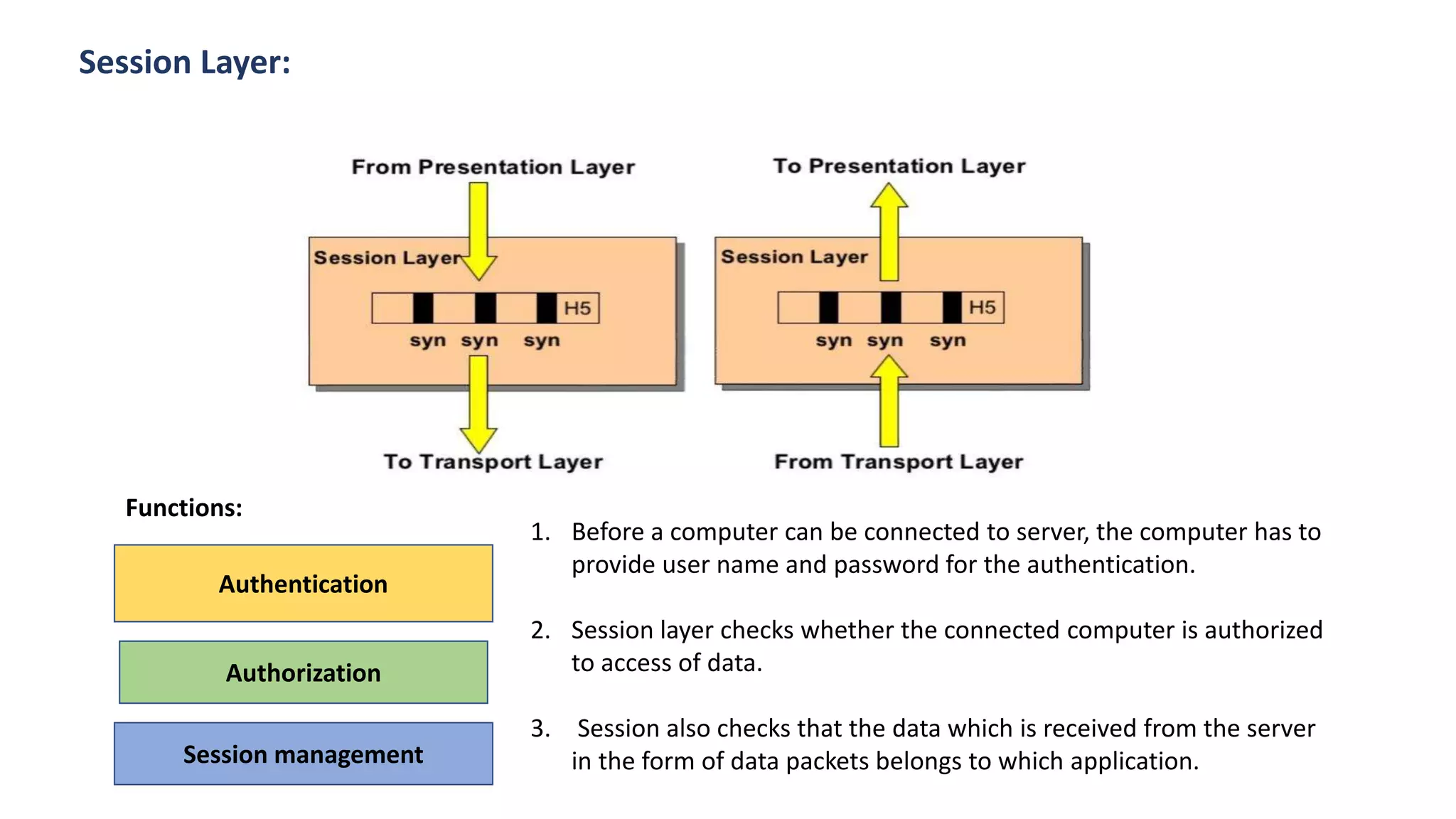
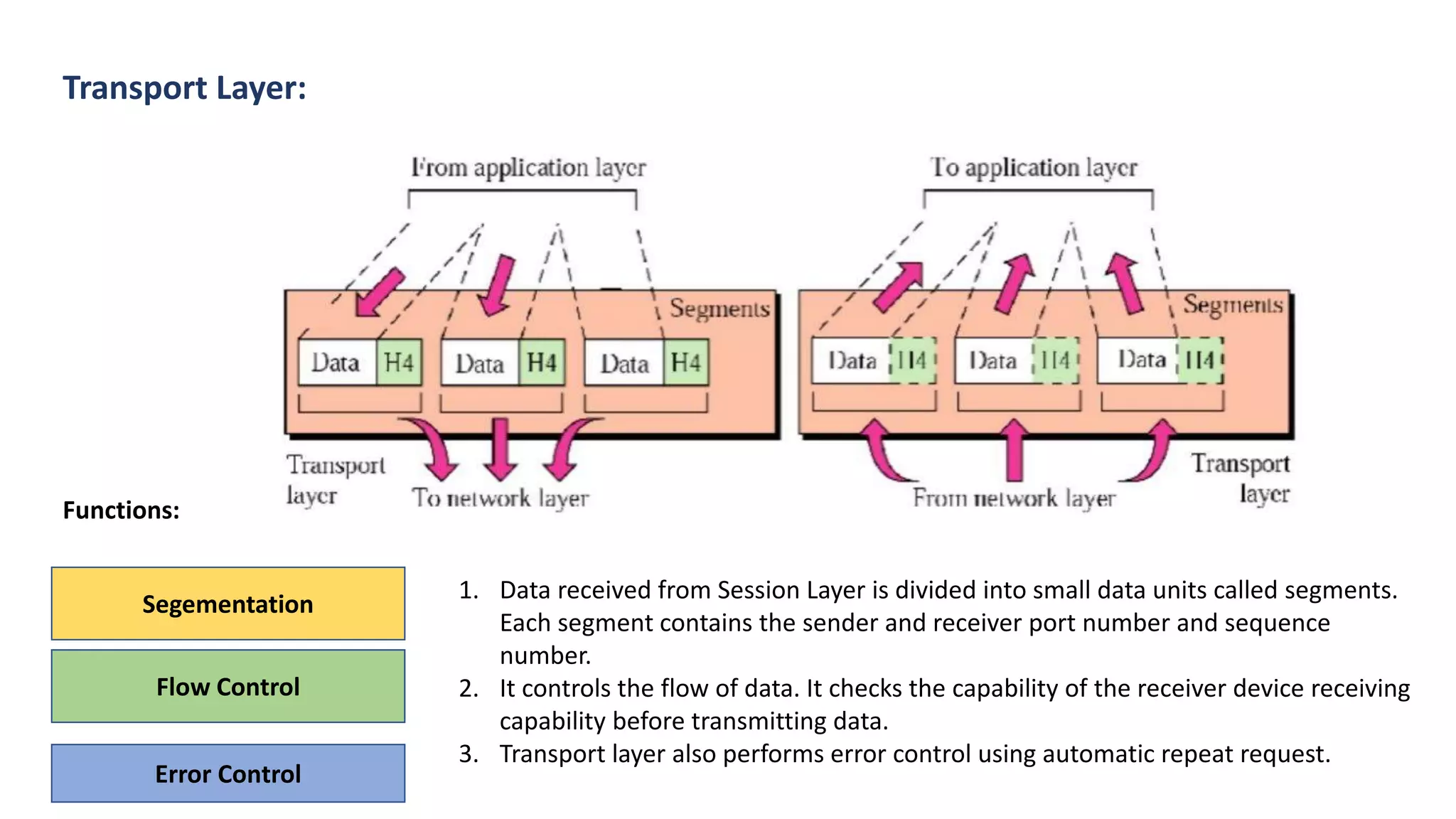
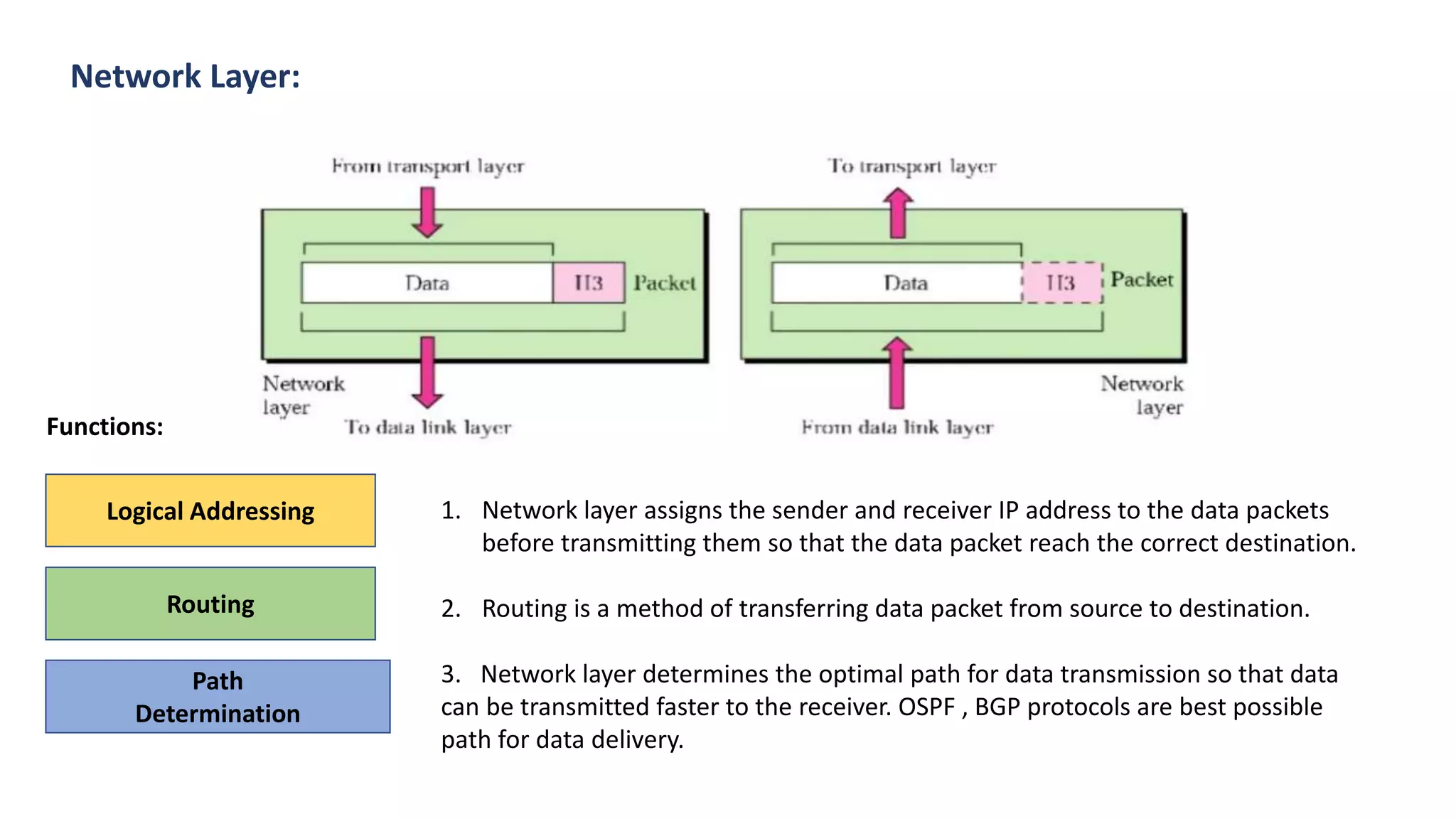
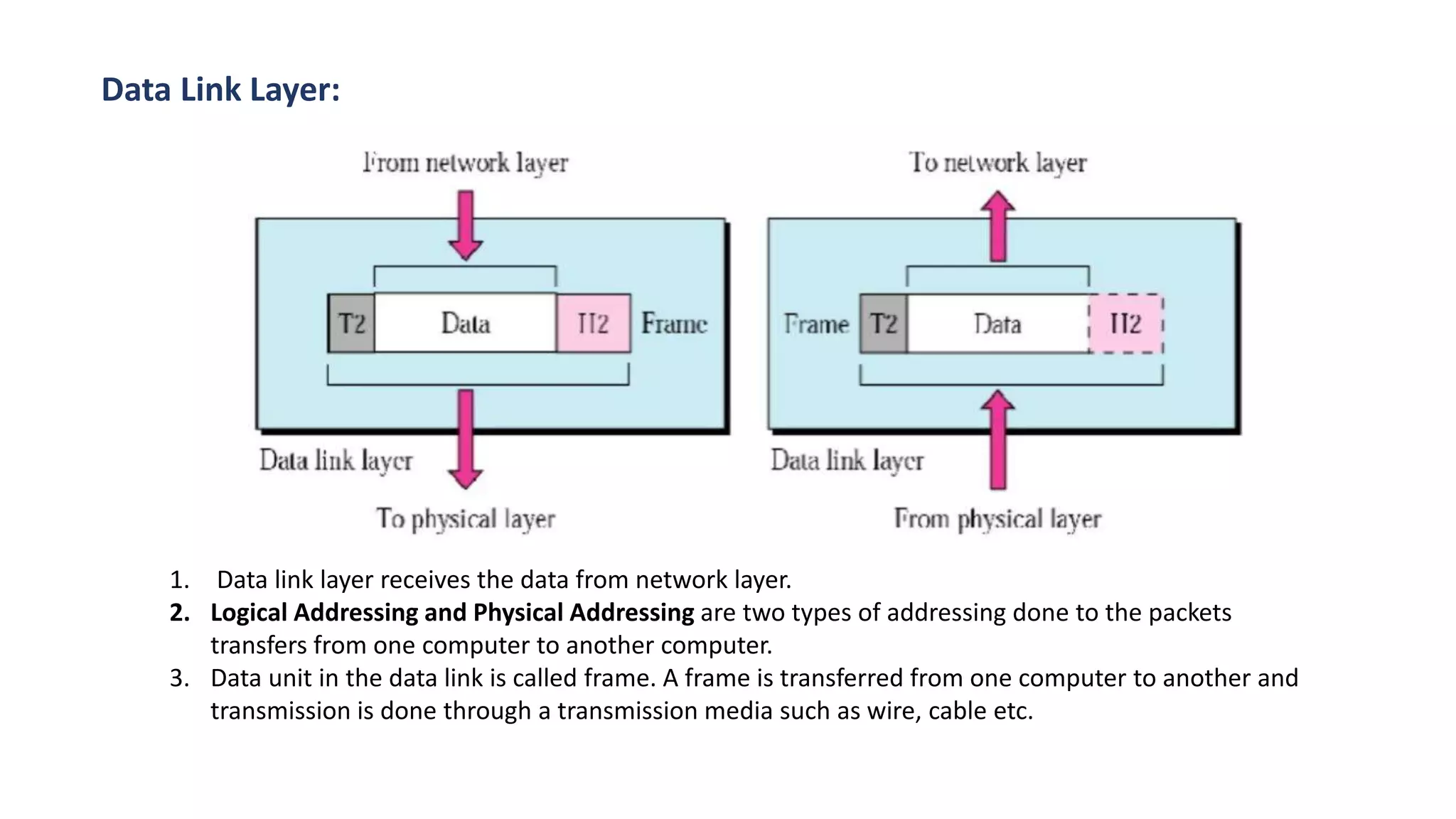
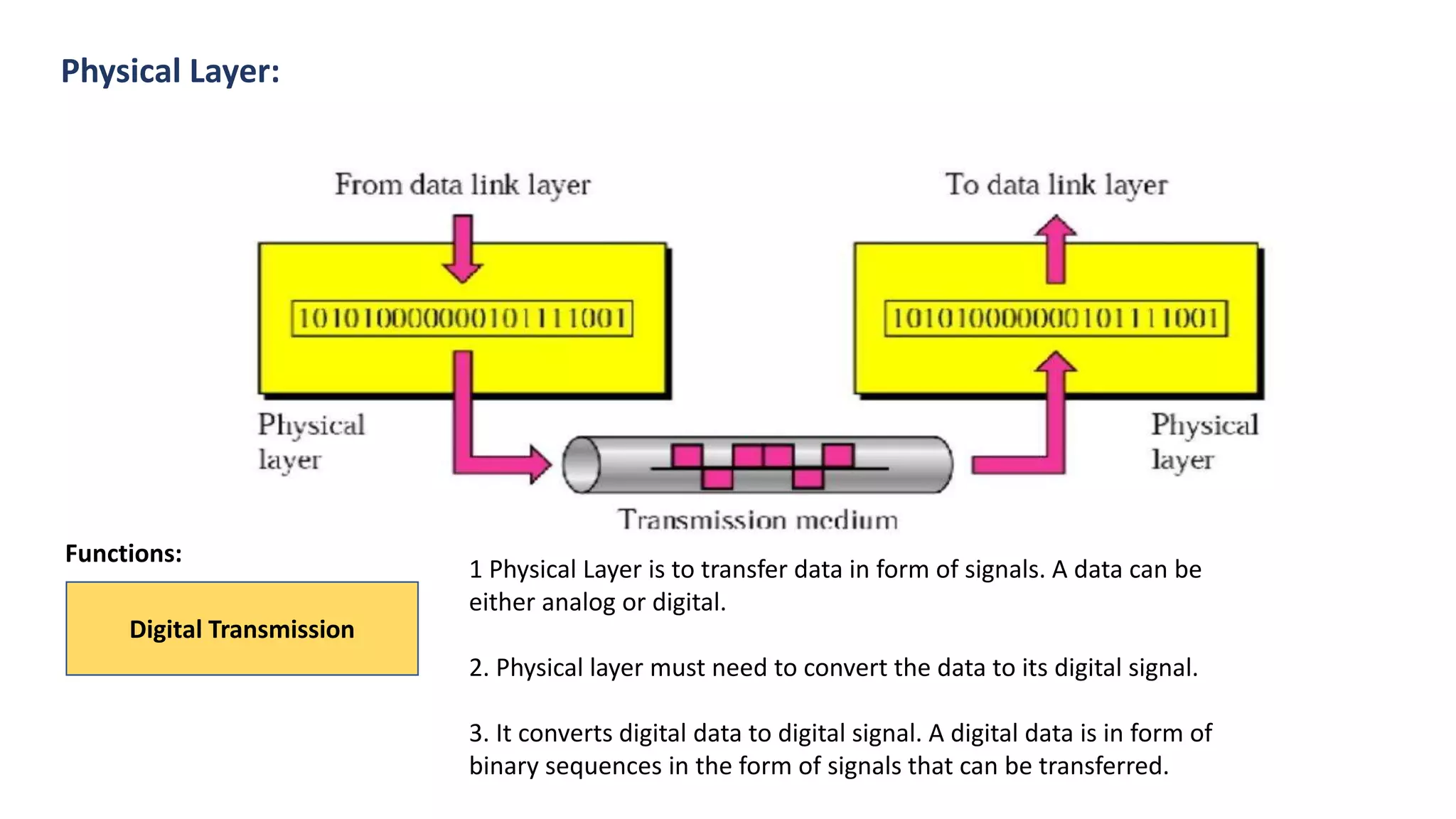
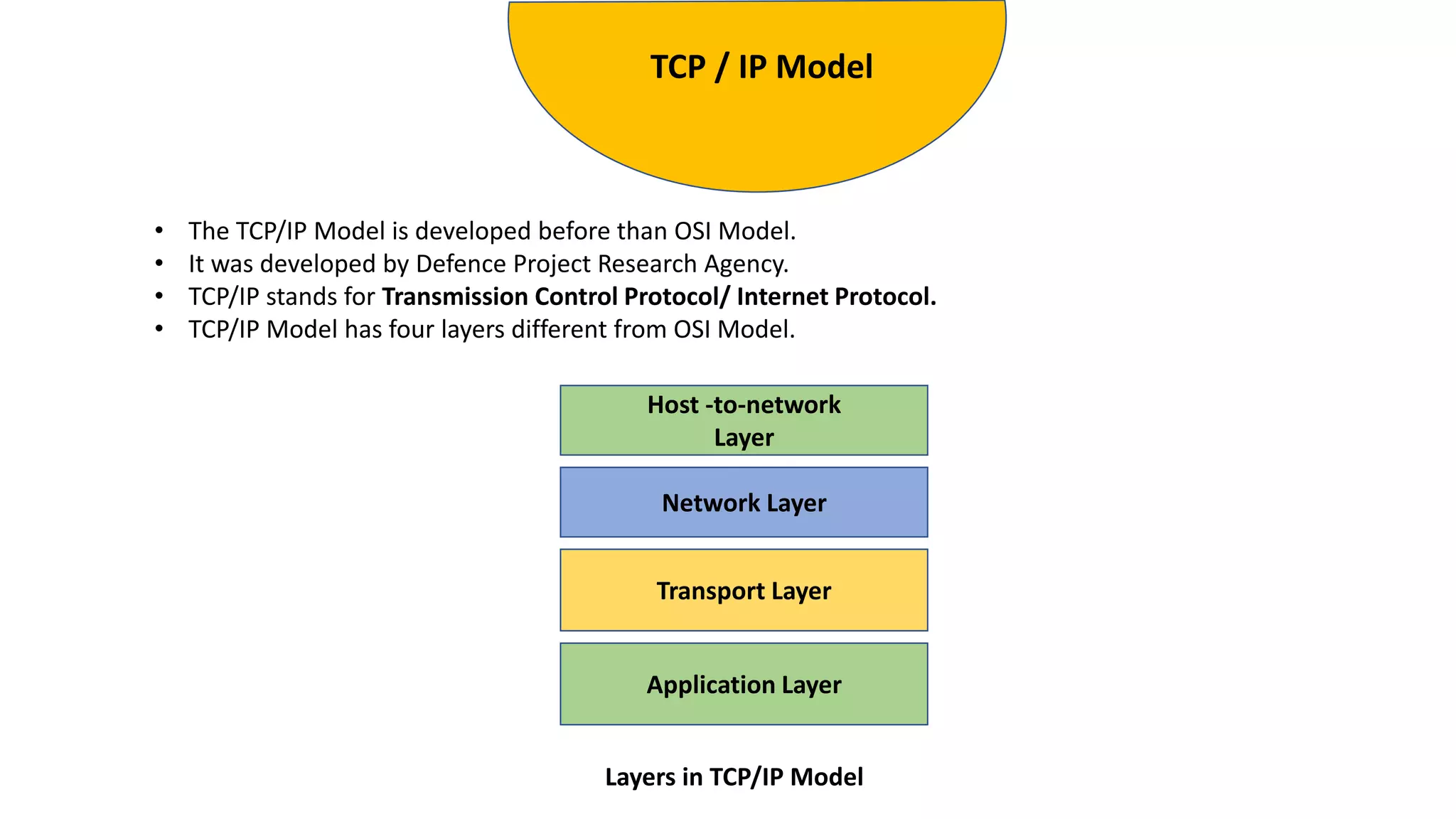
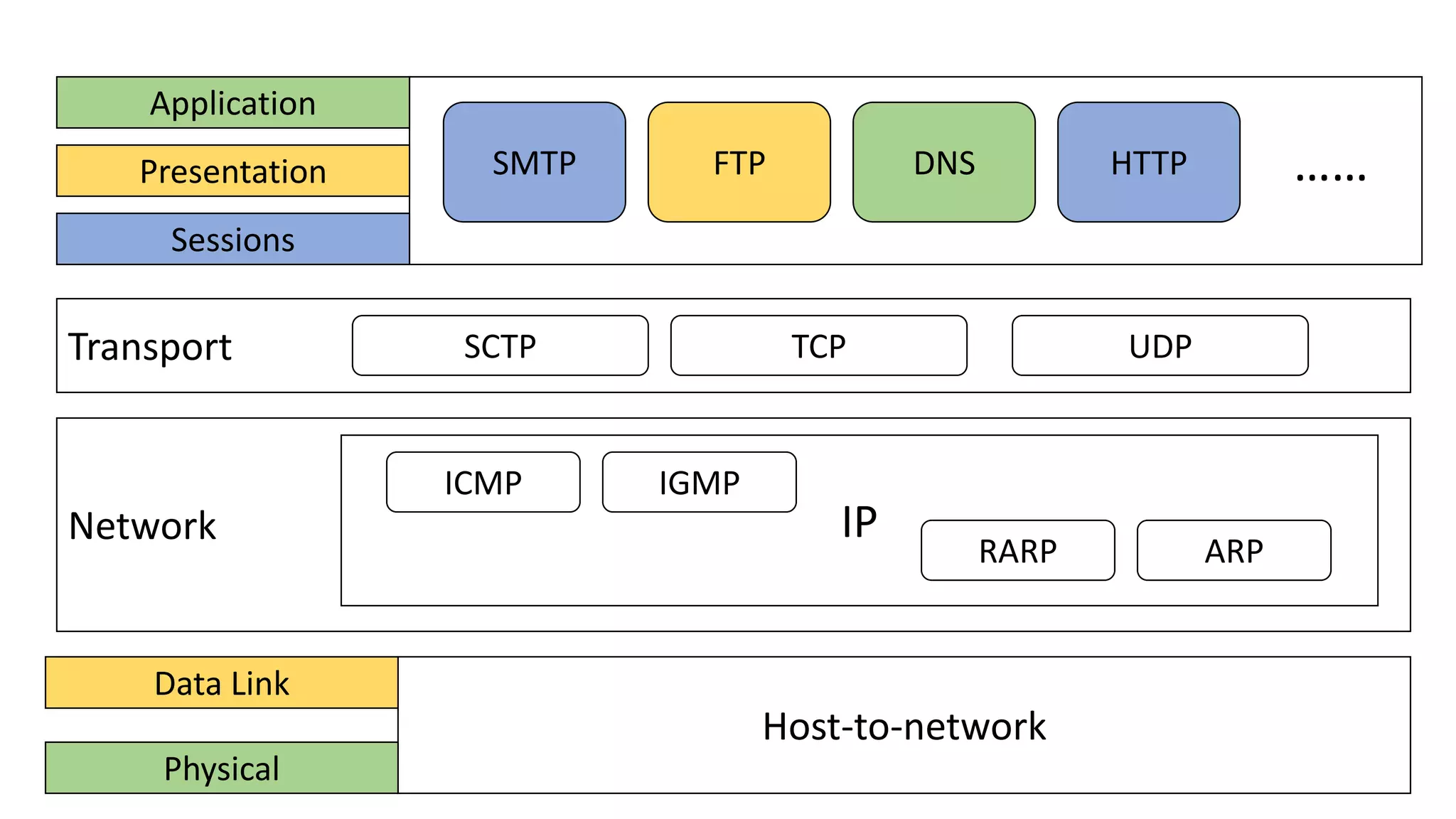
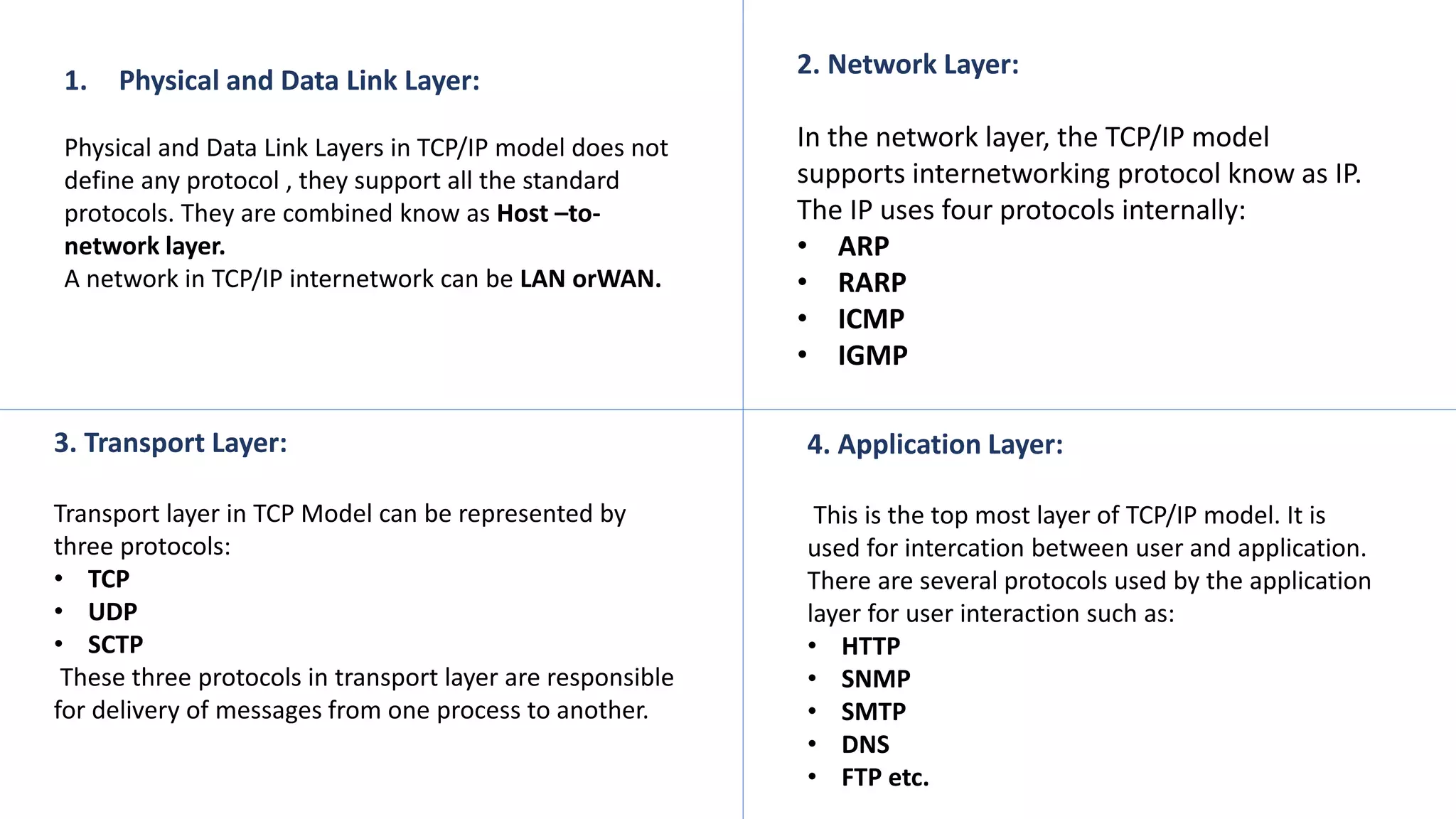
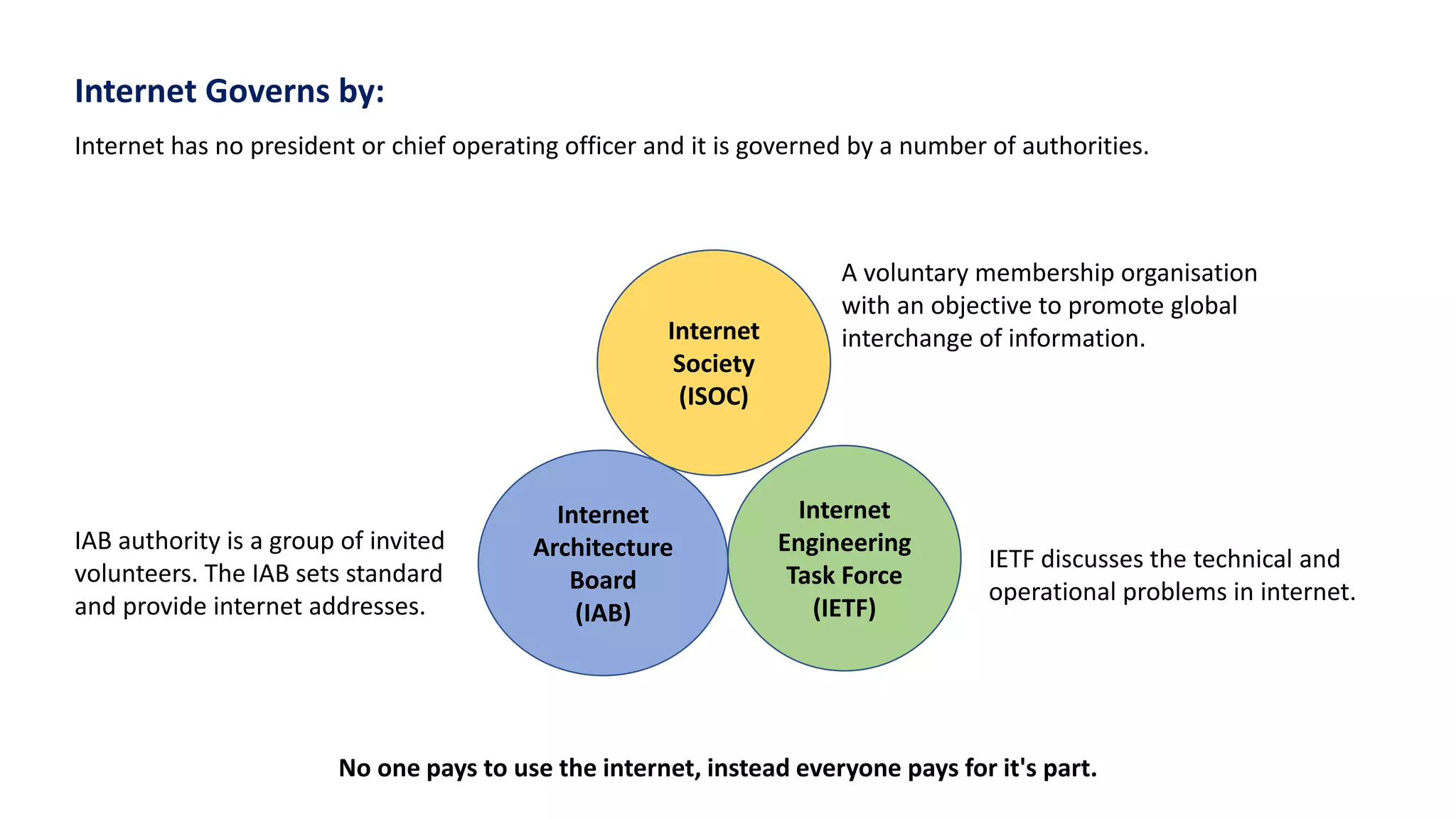
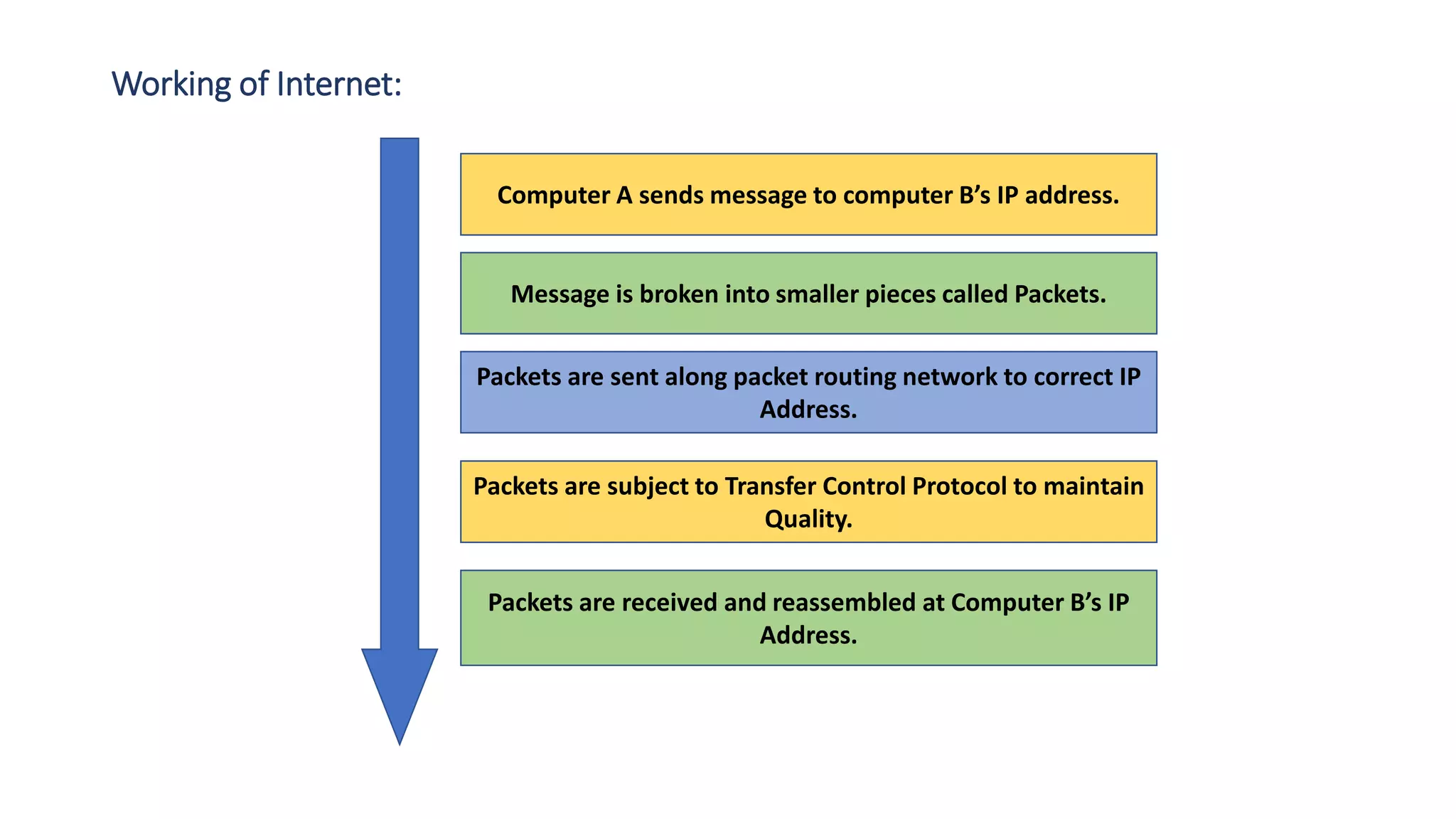
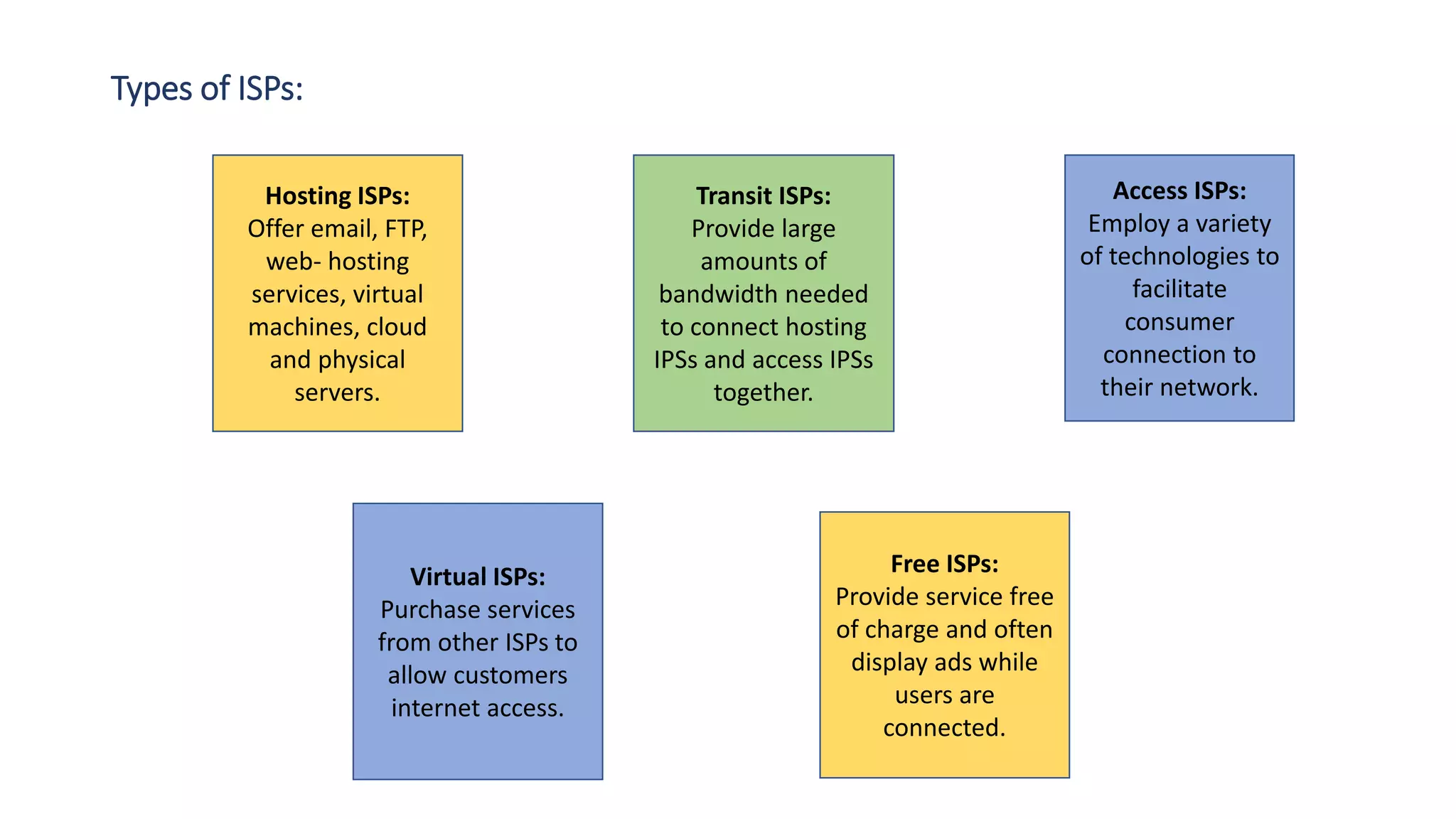
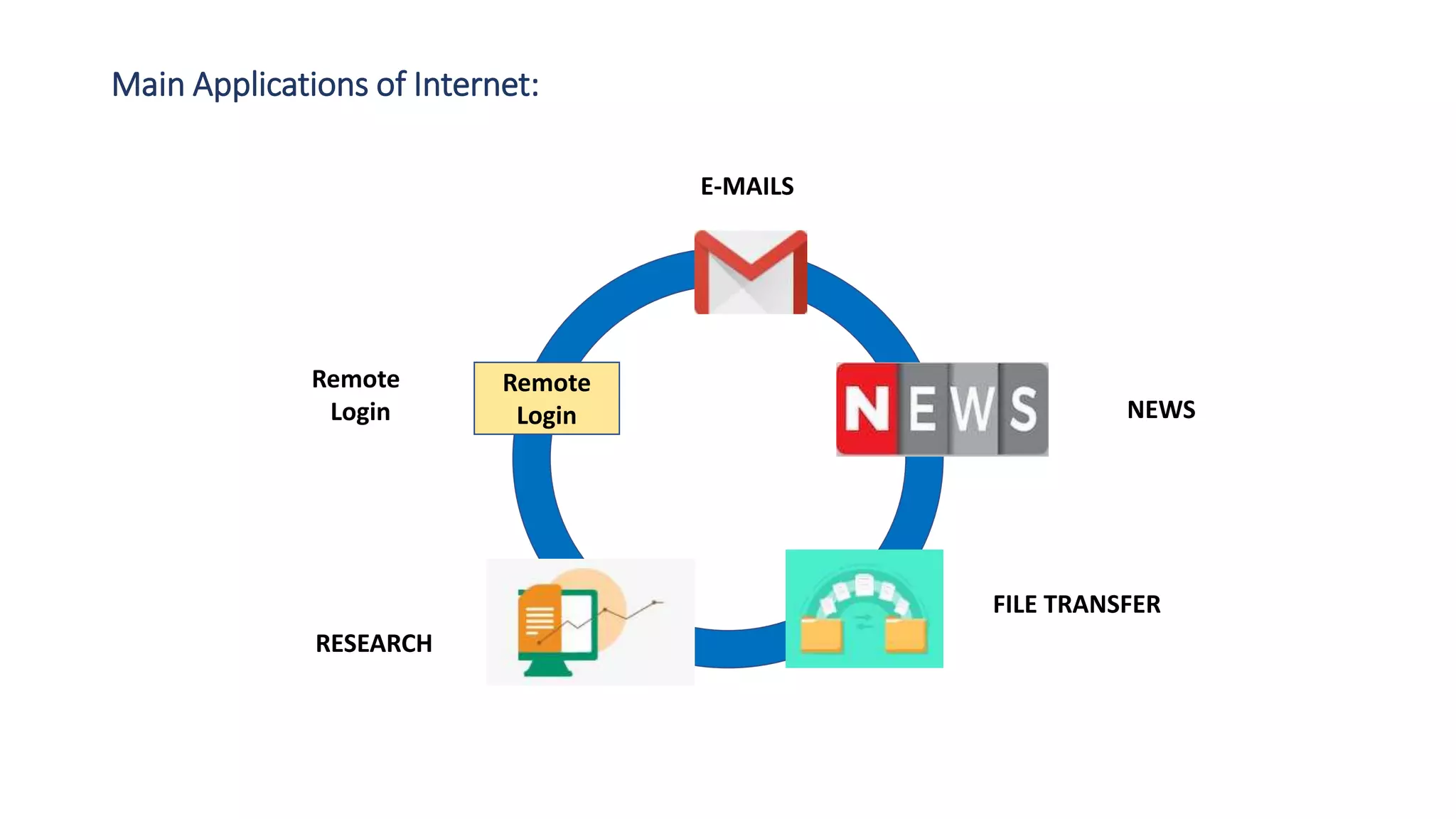
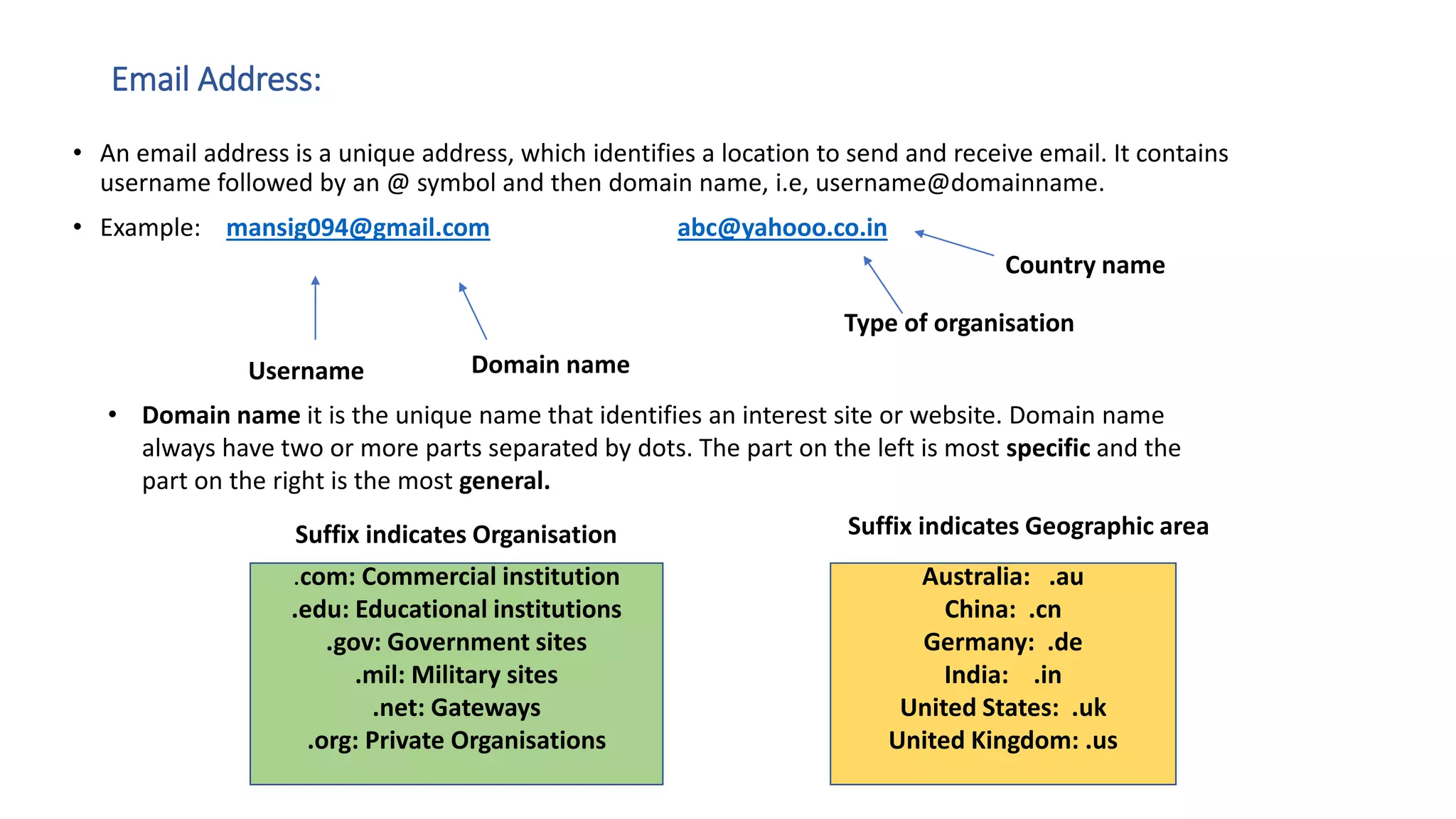
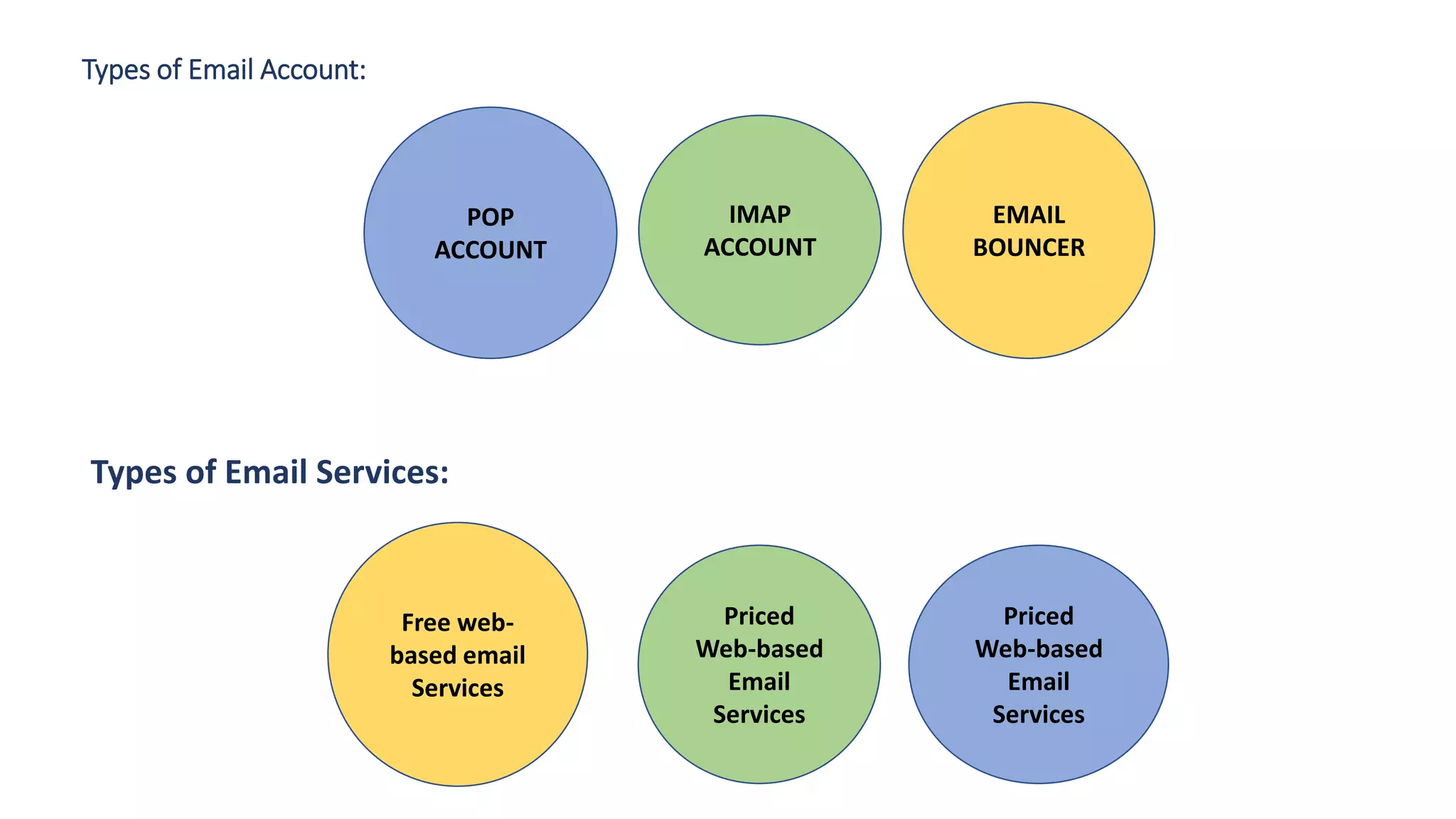
The document provides an overview of computer networks, including their architecture, types, and protocols such as the OSI and TCP/IP models. It discusses key components like transmission media, sender, and receiver, as well as various network topologies and the functionalities of different layers within the OSI model. Additionally, it outlines the concept of the internet, its governance, Internet Service Providers (ISPs), and applications like email.