Embed presentation
Download to read offline



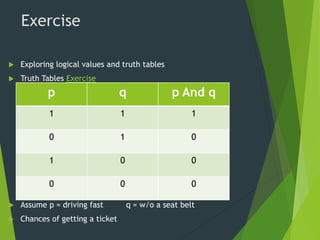

Logical operators allow programmers to create complex conditional statements by combining two or more simple conditional statements using logical operators like AND, OR, and NOT. This is more efficient than writing multiple separate conditional statements. Logical operators evaluate statements in a certain order - AND statements require both statements to be true, while OR statements require only one to be true. Truth tables can be used to explore the logical values that result from combining statements with different logical operators.




