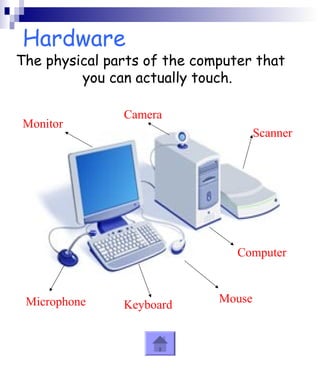
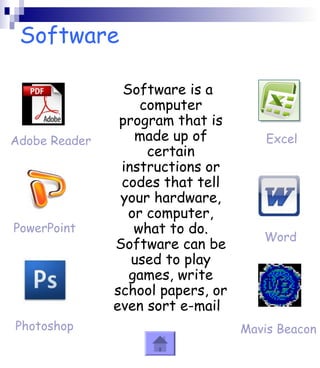
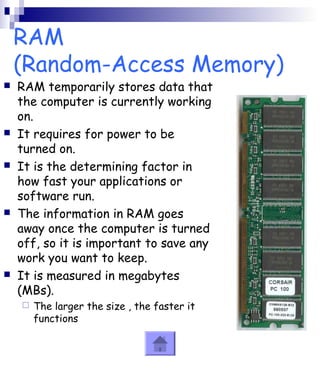
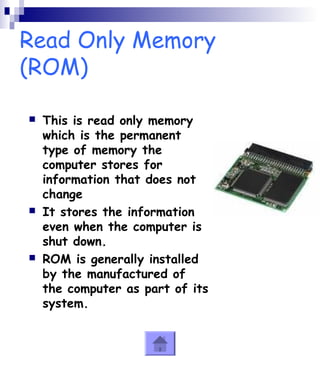
This document provides an overview of the key components of a computer system. It discusses both hardware components like the CPU, RAM, motherboard and storage devices, as well as software components like operating systems and programs. Peripherals that can input or output data are also covered. The document is intended to explain the basic parts and functions of a computer to a reader.