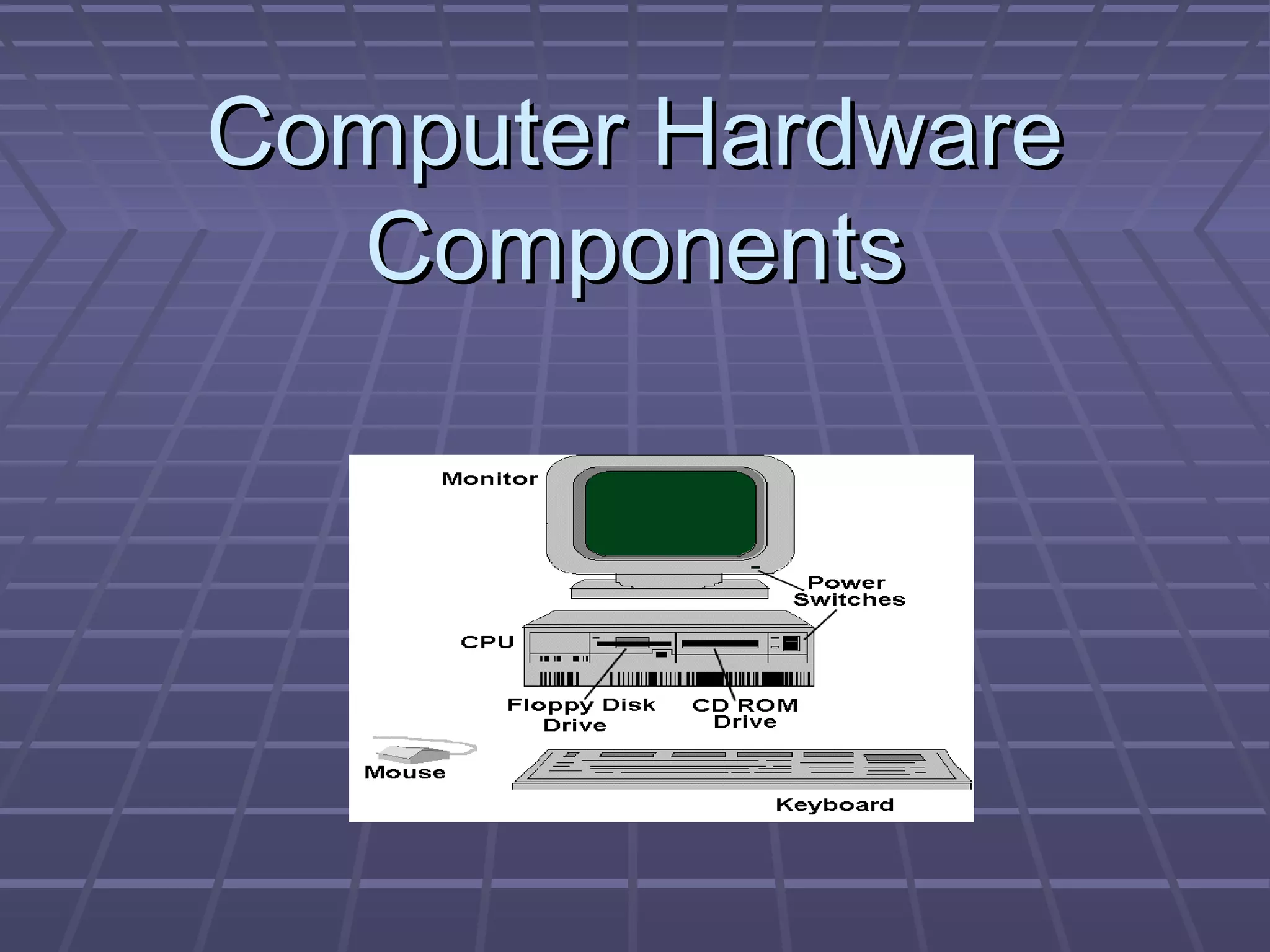
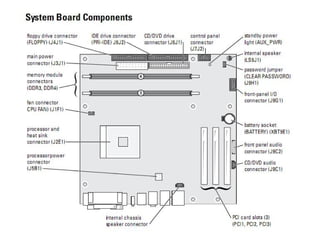
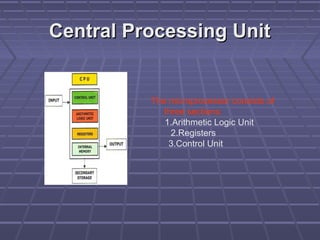
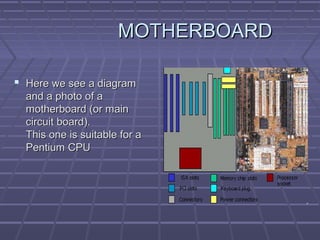
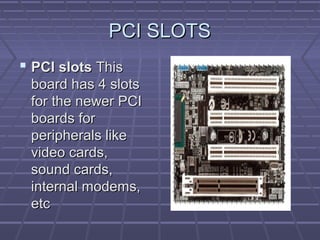
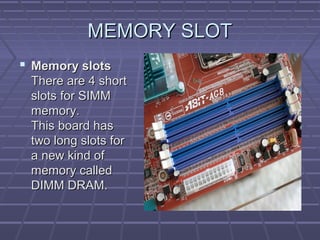
The document discusses the main components of a computer hardware system. It describes the central processing unit (CPU), motherboard, memory, storage devices like hard disk drives, floppy drives, CD-ROM drives, and DVD drives. The motherboard contains connectors for attaching these components and controlling peripheral devices like the keyboard, mouse and monitor. It provides power connections and slots for the CPU, memory and expansion cards. Storage devices vary in speed, capacity and cost, with hard drives being fastest and highest capacity, and floppy drives smallest and cheapest.