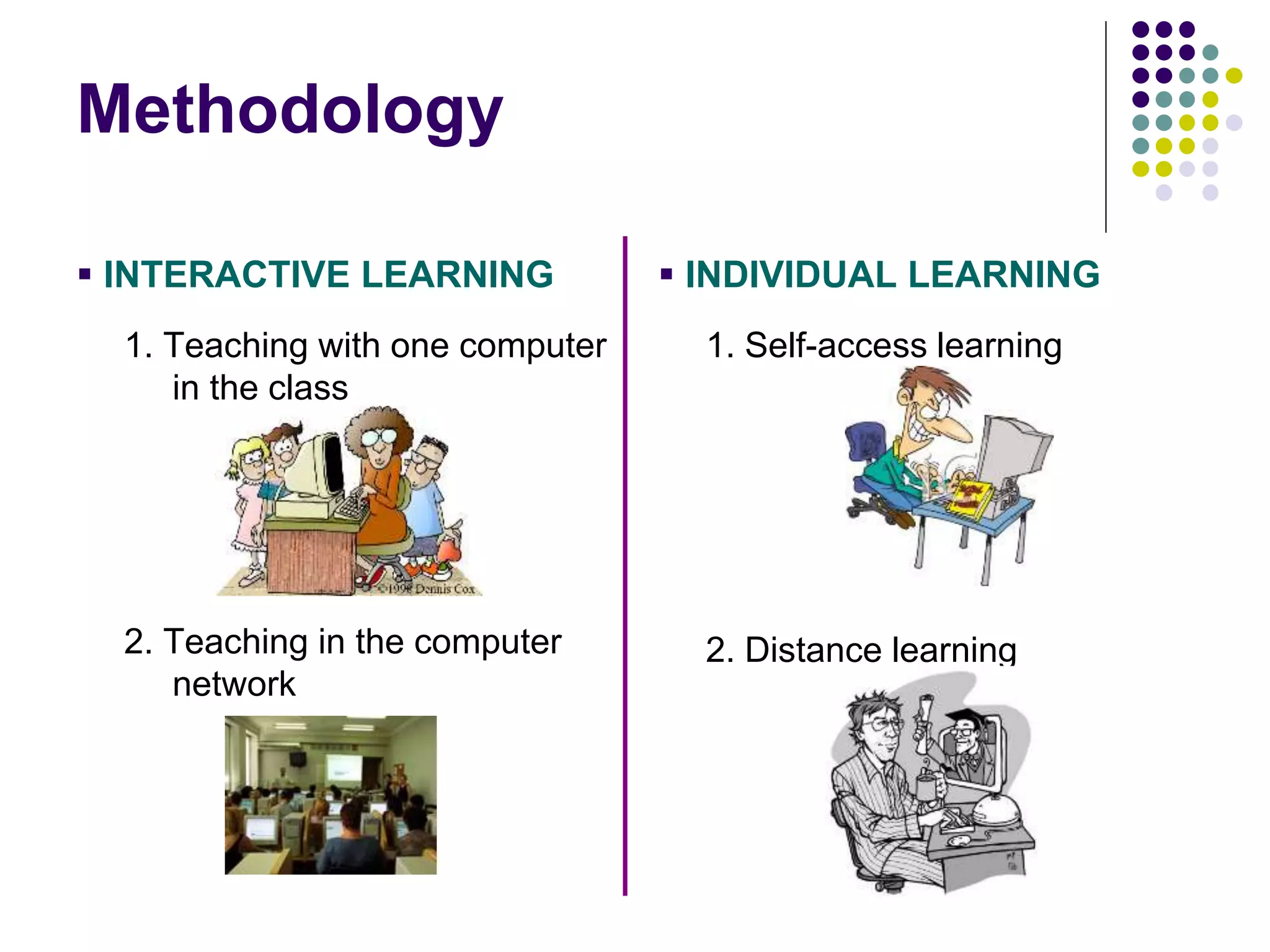
Computer-assisted language learning (CALL) uses computers to aid in language teaching and learning. CALL originated from computer-assisted instruction where computers helped teachers, but CALL is more student-centered with interactive lessons allowing independent learning. CALL has evolved through different periods from behaviorist CALL in the 1950s-1980s, to communicative/cognitive CALL in the 1980s-1990s, to current integrative/explorative CALL utilizing multimedia and the internet. Behaviorist CALL used drill-based repetition, communicative CALL focused on language use over analysis, and current CALL integrates language skills into tasks and projects using multimedia technologies. CALL can be used interactively in the classroom or individually for self-access or distance learning.