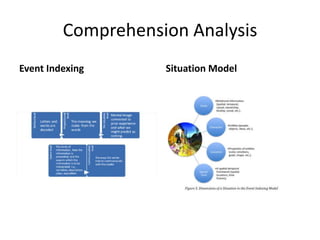
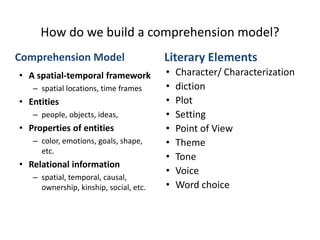
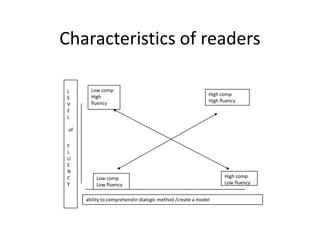
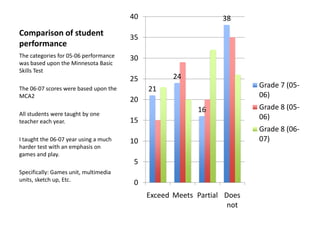
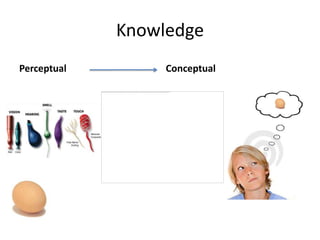
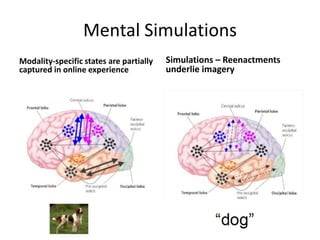
The document discusses research on instruction that emphasizes congruent sensorimotor experience and visualization. This type of instruction has been found to improve comprehension, reading fluency, and problem solving abilities. The document also discusses how perceptual knowledge is transformed into conceptual knowledge and schema through identifying affordances of action and potential actions. This allows students to construct situation models to understand context, meaning, and usage.