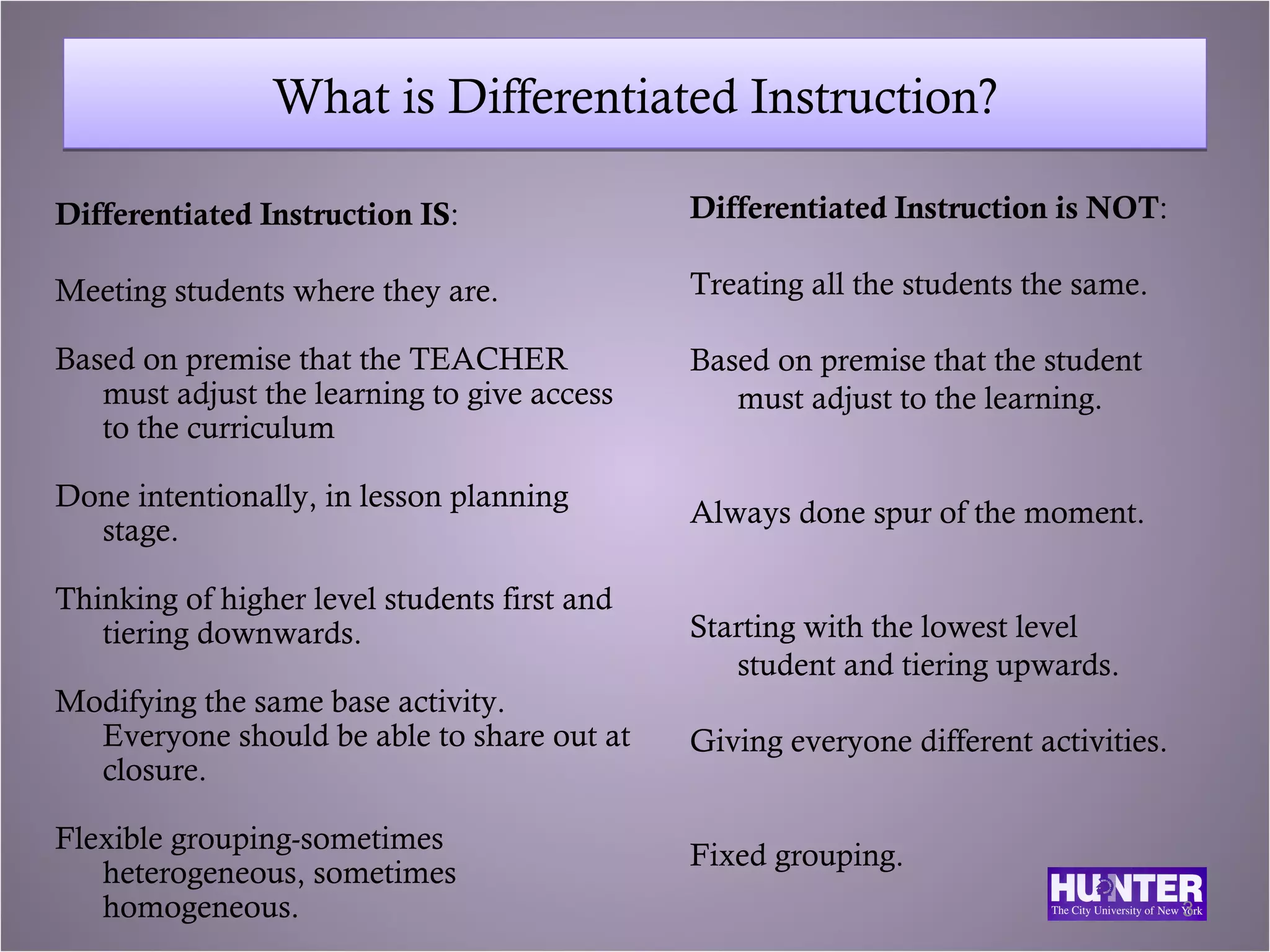
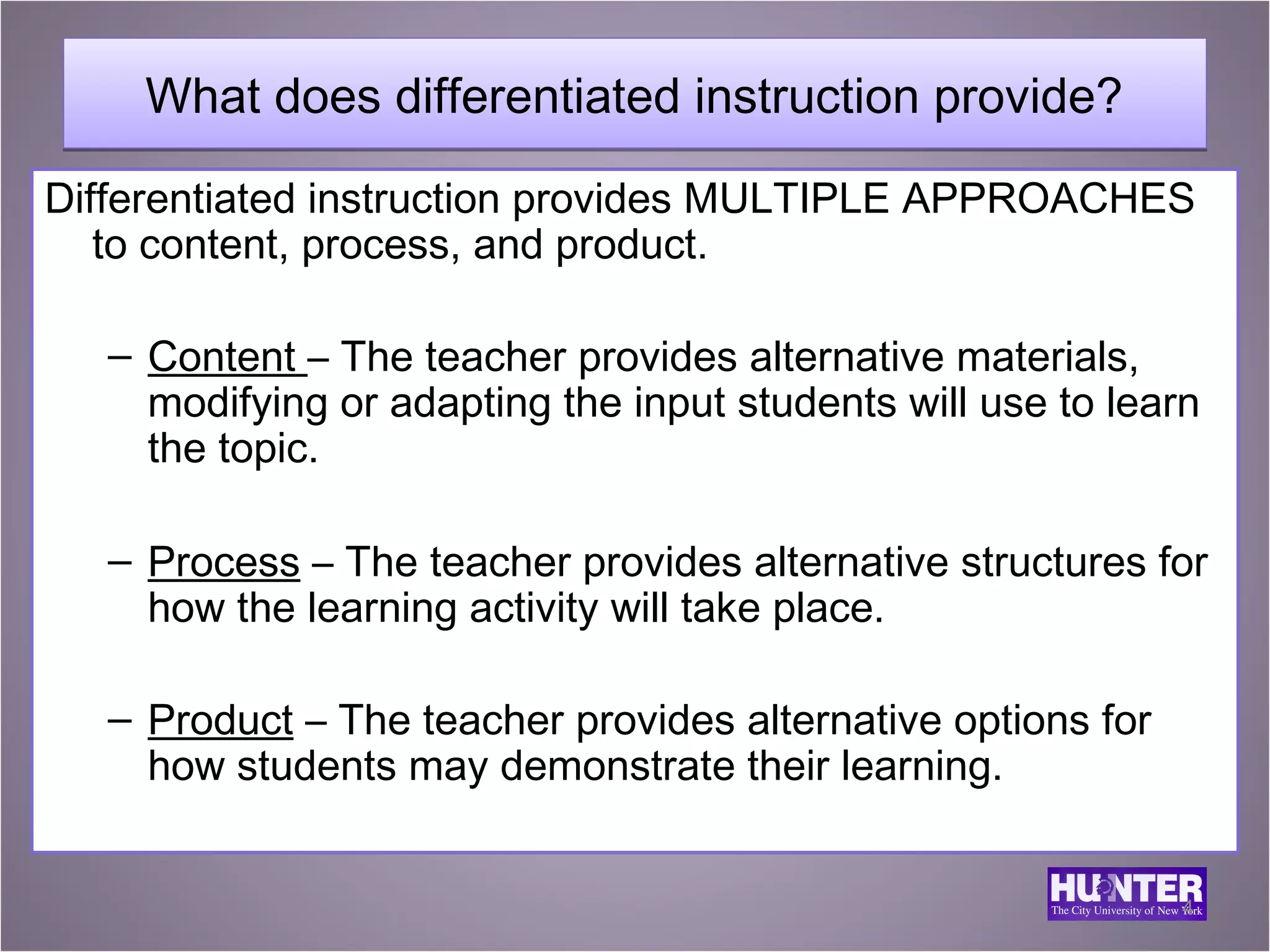
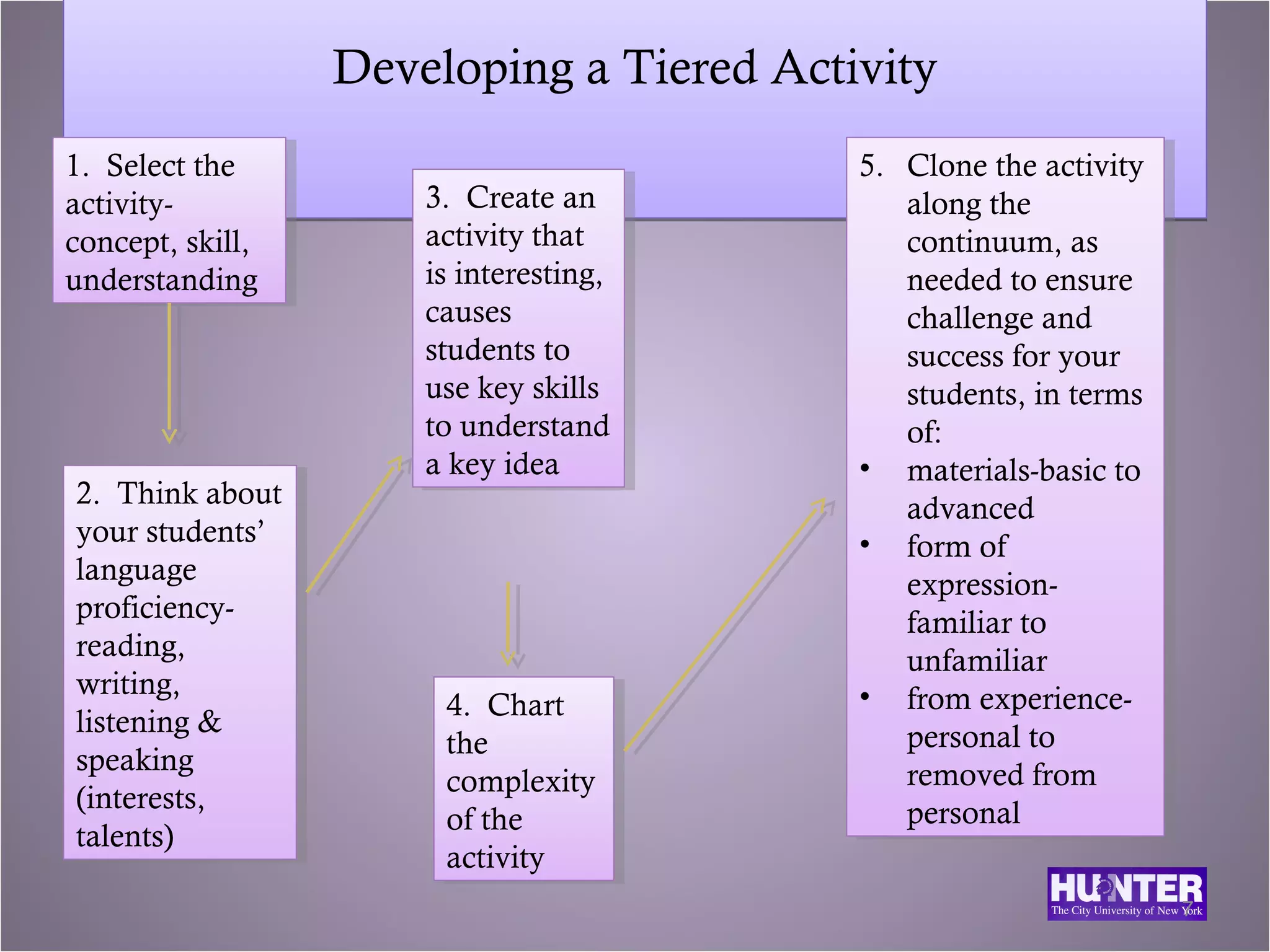
This document discusses differentiated instruction for English language learners. It defines differentiated instruction and contrasts it with uniform instruction. It explains that differentiated instruction involves modifying content, processes, and products based on student needs, interests and learning profiles. The document provides examples of how to differentiate speaking, listening, reading and writing activities for students at different proficiency levels through adjusting materials, support, and expectations.