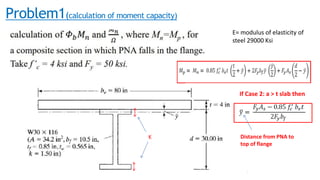
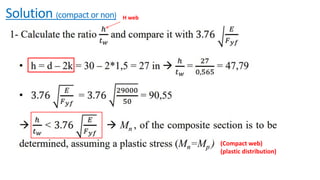
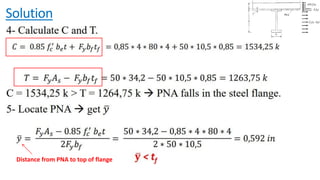
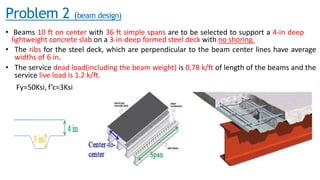
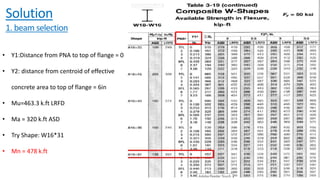
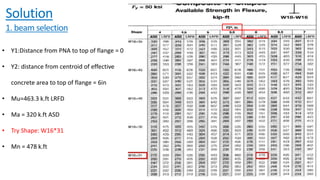
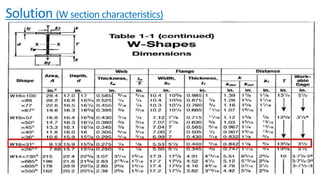
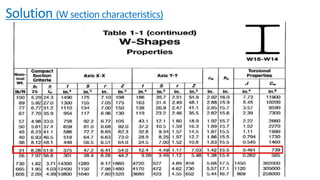
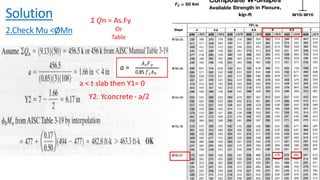
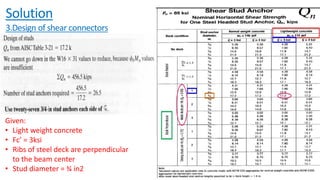
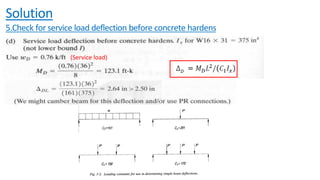
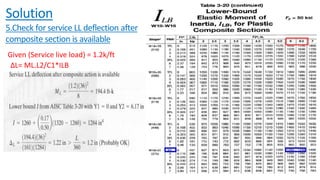
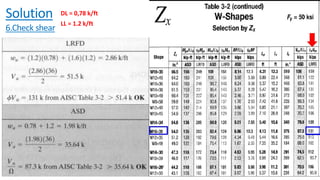
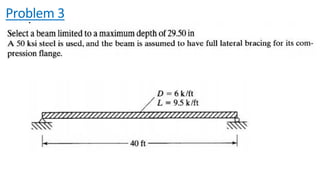
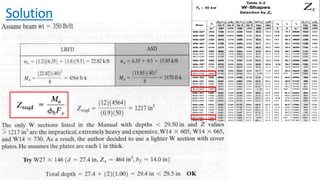
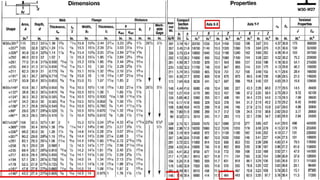
The document discusses composite beam design and calculations in structural engineering, presenting solutions for various problems related to moment capacity and beam selection. Key factors include the analysis of a lightweight concrete slab supported by steel beams, examining service loads, shear connectors, and deflection checks. It also cites references for further reading in structural steel design.