The document discusses Composer, a dependency manager for PHP that simplifies the process of managing libraries and their dependencies in a project. It covers installation, usage, autoloading strategies, and configuration files such as composer.json and composer.lock. By leveraging Composer, developers can easily define, install, and manage package versions, enhancing the efficiency of their development workflow.




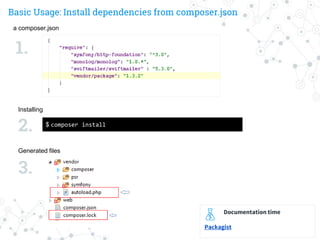




![Autoloading using classmap
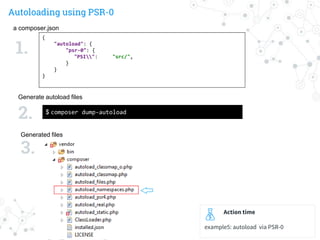
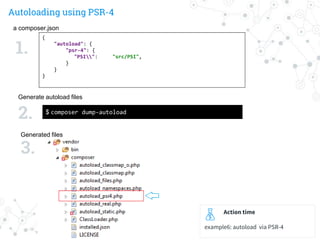
a composer.json
$ composer dump-autoload
Generate autoload files
Generated files
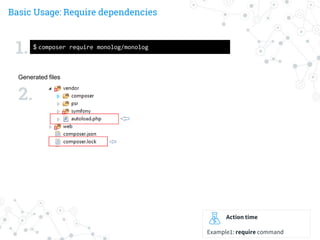
1.
2.
3.
Action time
example4: autoload classmap
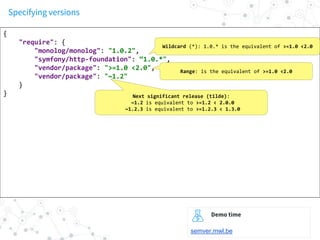
{
"autoload": {
"classmap": ["src/", "lib/", "Something.php"]
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/composernamespacing-160927155448/85/Composer-namespacing-14-320.jpg)