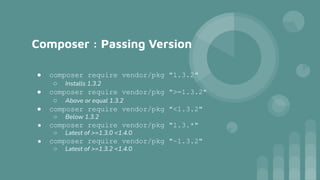
Composer is a tool for managing PHP dependencies. It allows declaring project dependencies in a composer.json file. Composer will install and update these dependencies. Important Composer commands include install, update, require, and remove for managing dependencies. Composer best practices include not running update on production and instead using install, and thoroughly testing updates on development before deploying. Composer allows specifying dependency versions using operators like >= and <. Tilde and caret operators define compatible version ranges for updates.