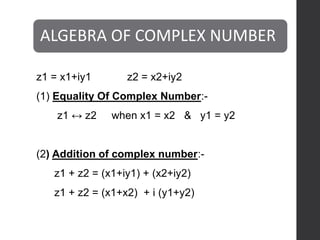
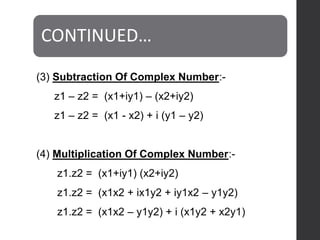
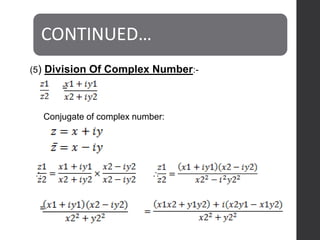
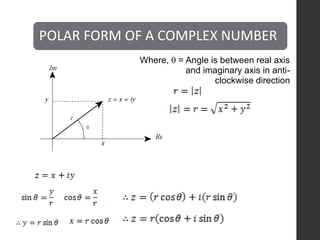
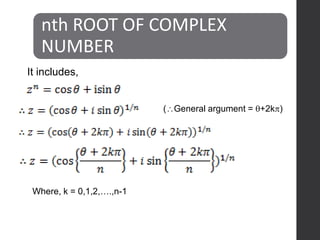
This document defines complex numbers and outlines their algebra. A complex number z is defined as an ordered pair (x,y) where x is the real part and y is the imaginary part. The four basic operations on complex numbers are defined: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Complex numbers can also be represented geometrically on an Argand diagram, with the real part on the x-axis and imaginary part on the y-axis. Polar form represents a complex number in terms of magnitude and angle. De Moivre's theorem and nth roots of complex numbers are also discussed.