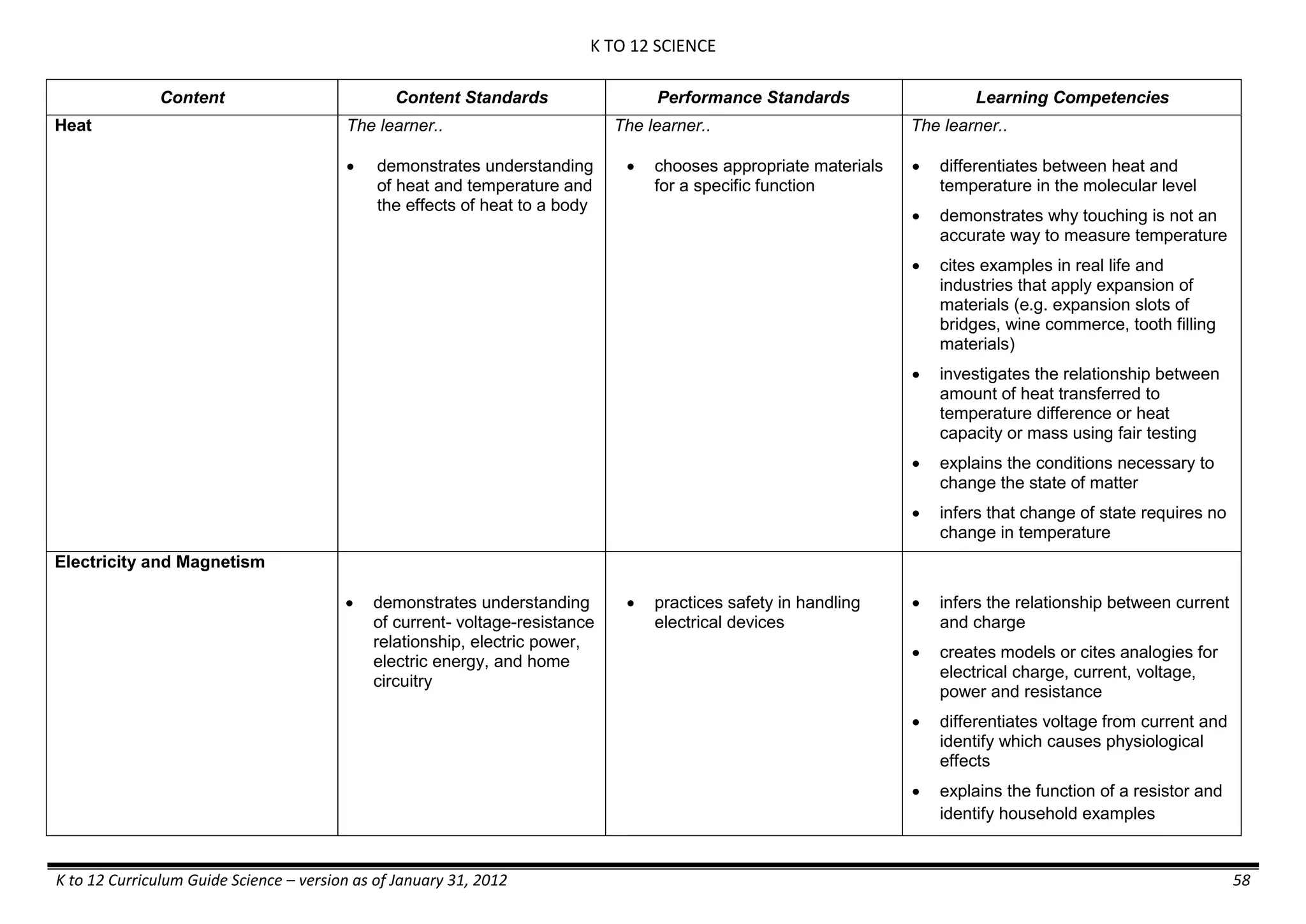
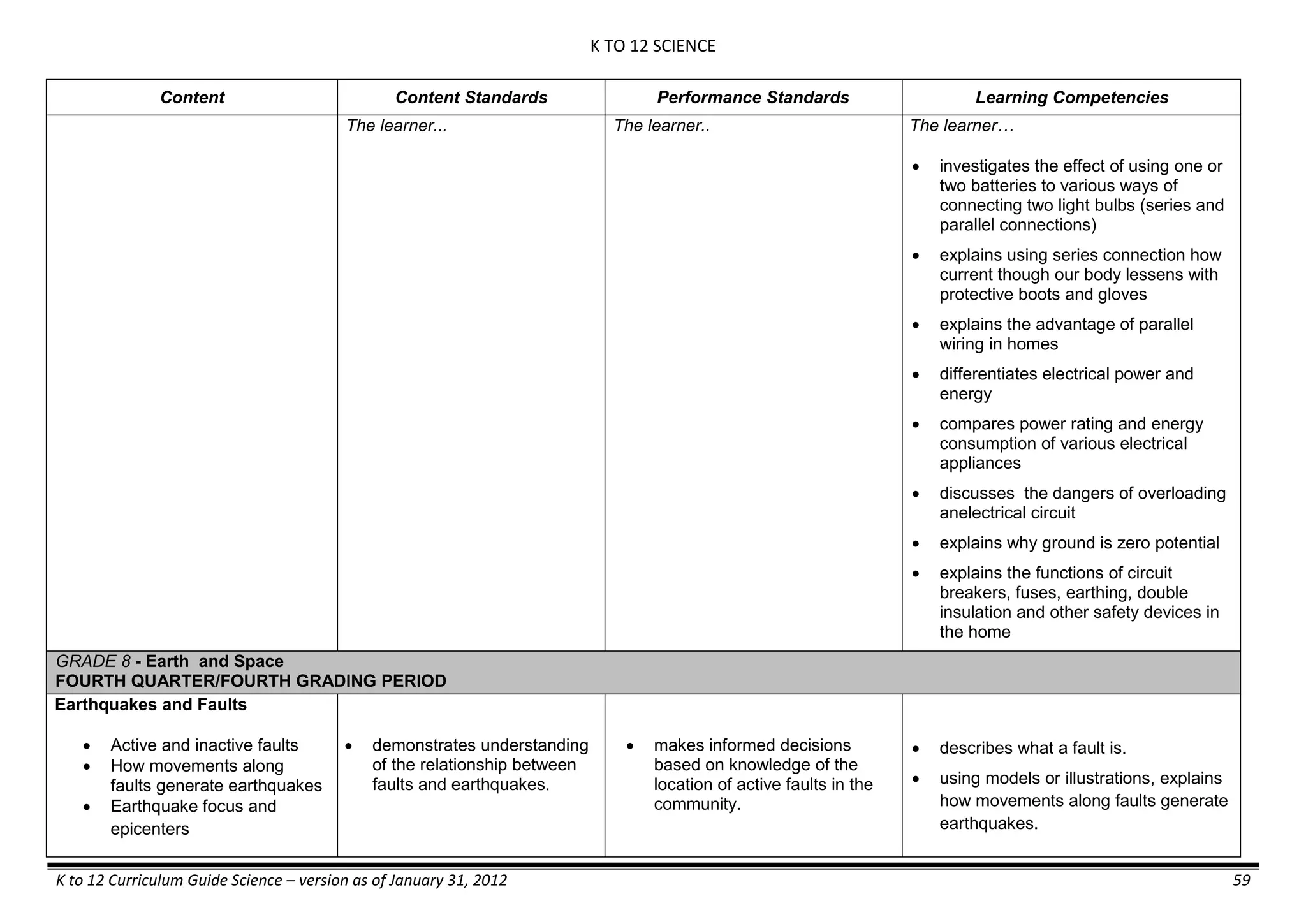
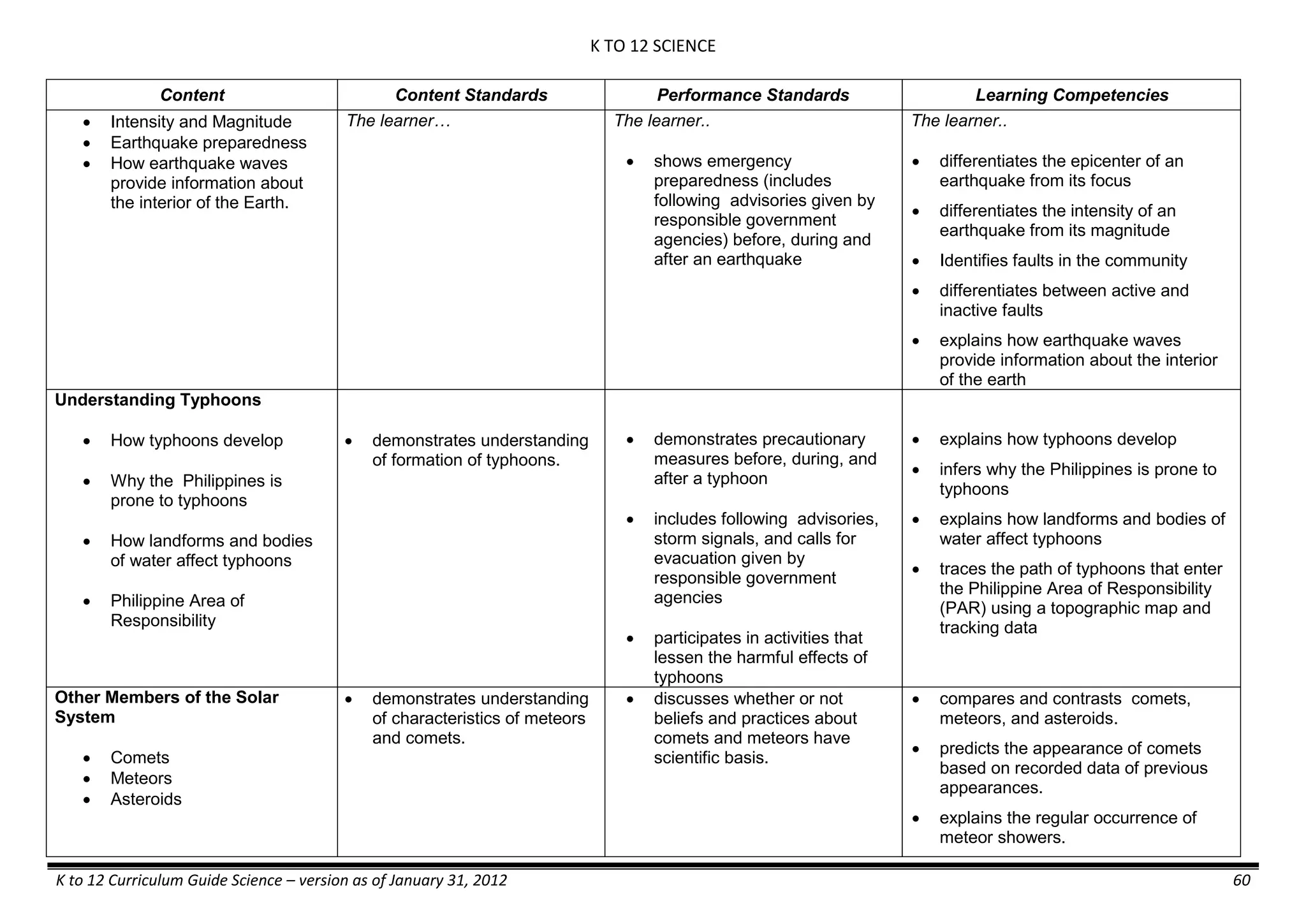
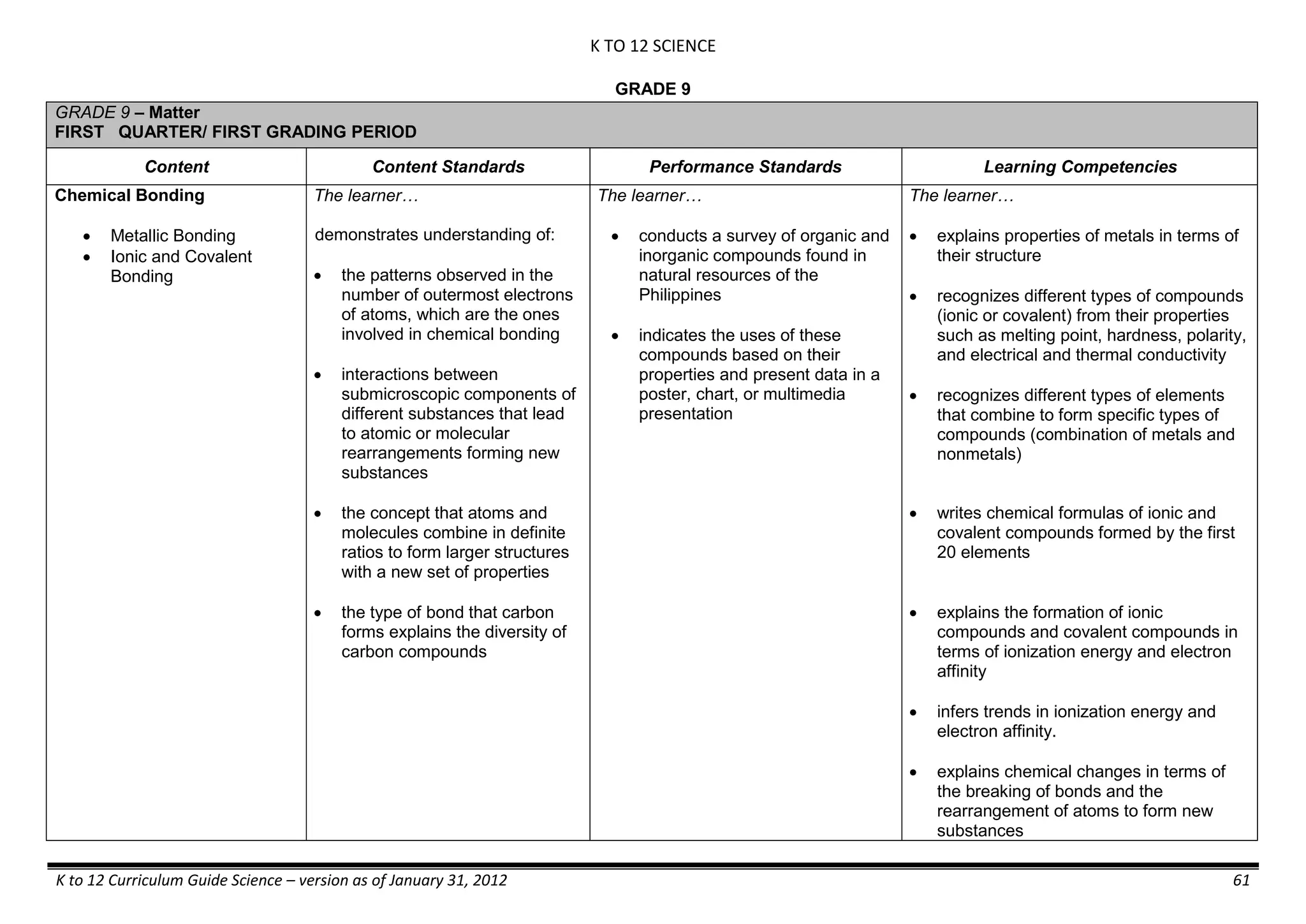
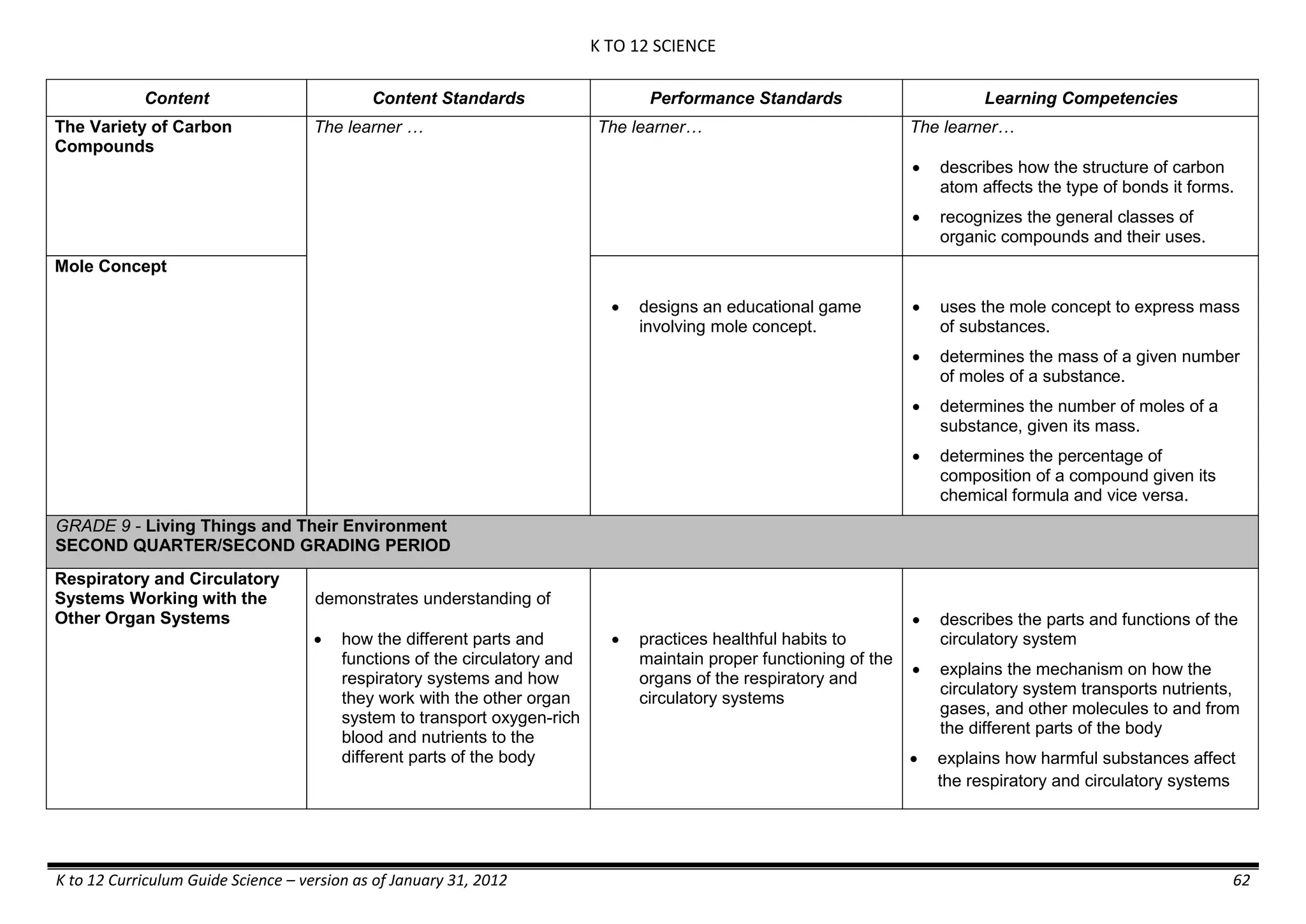
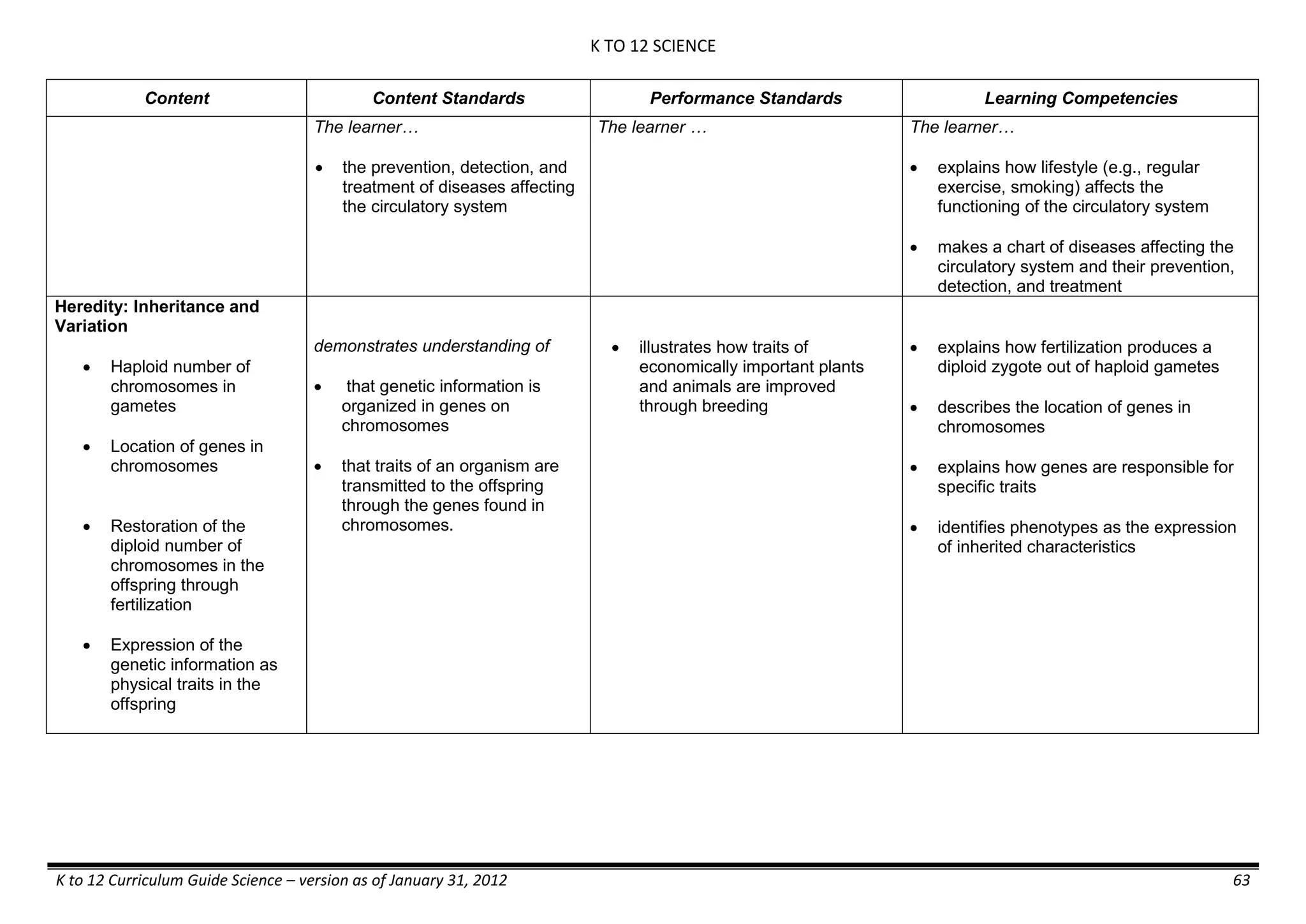
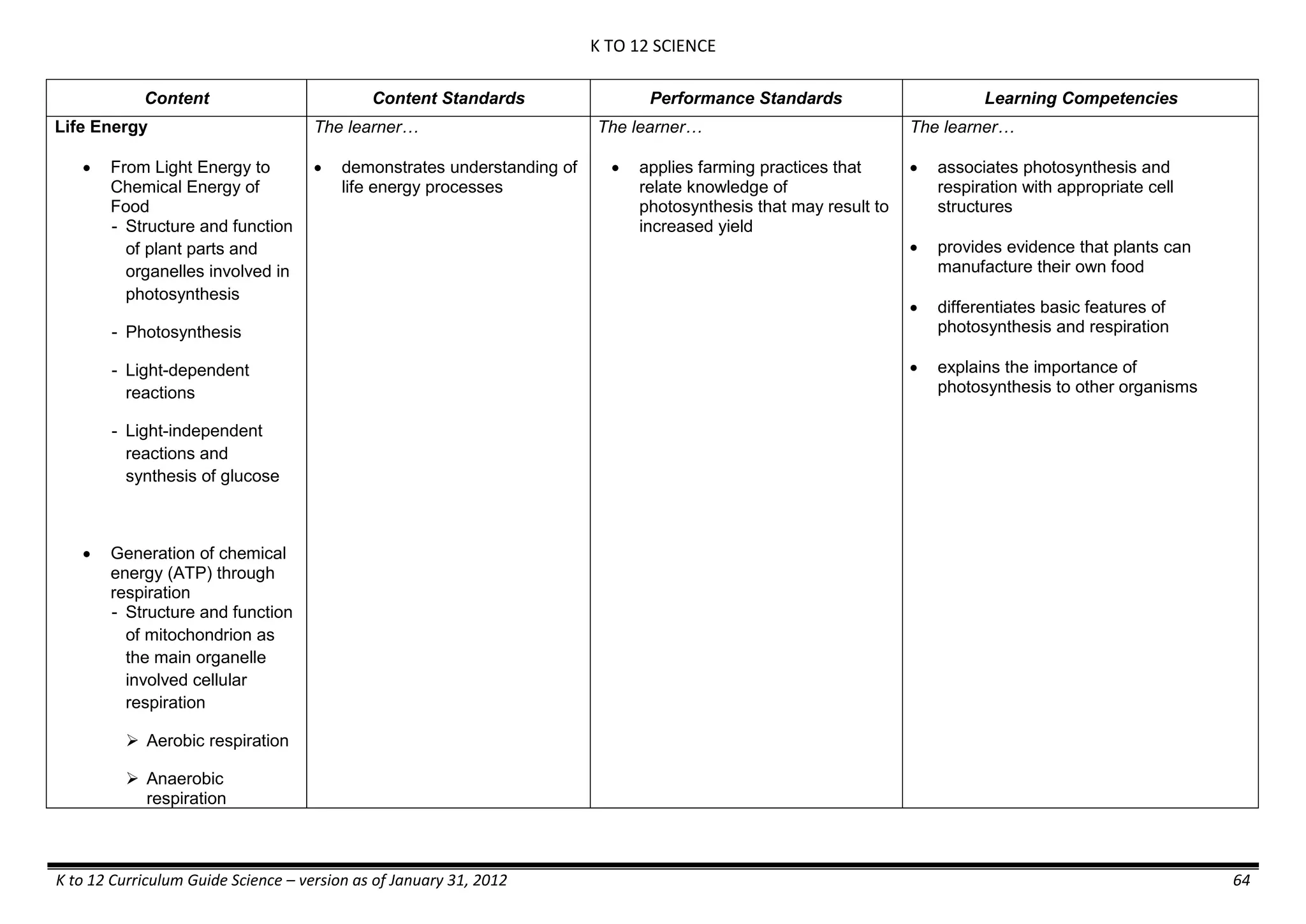
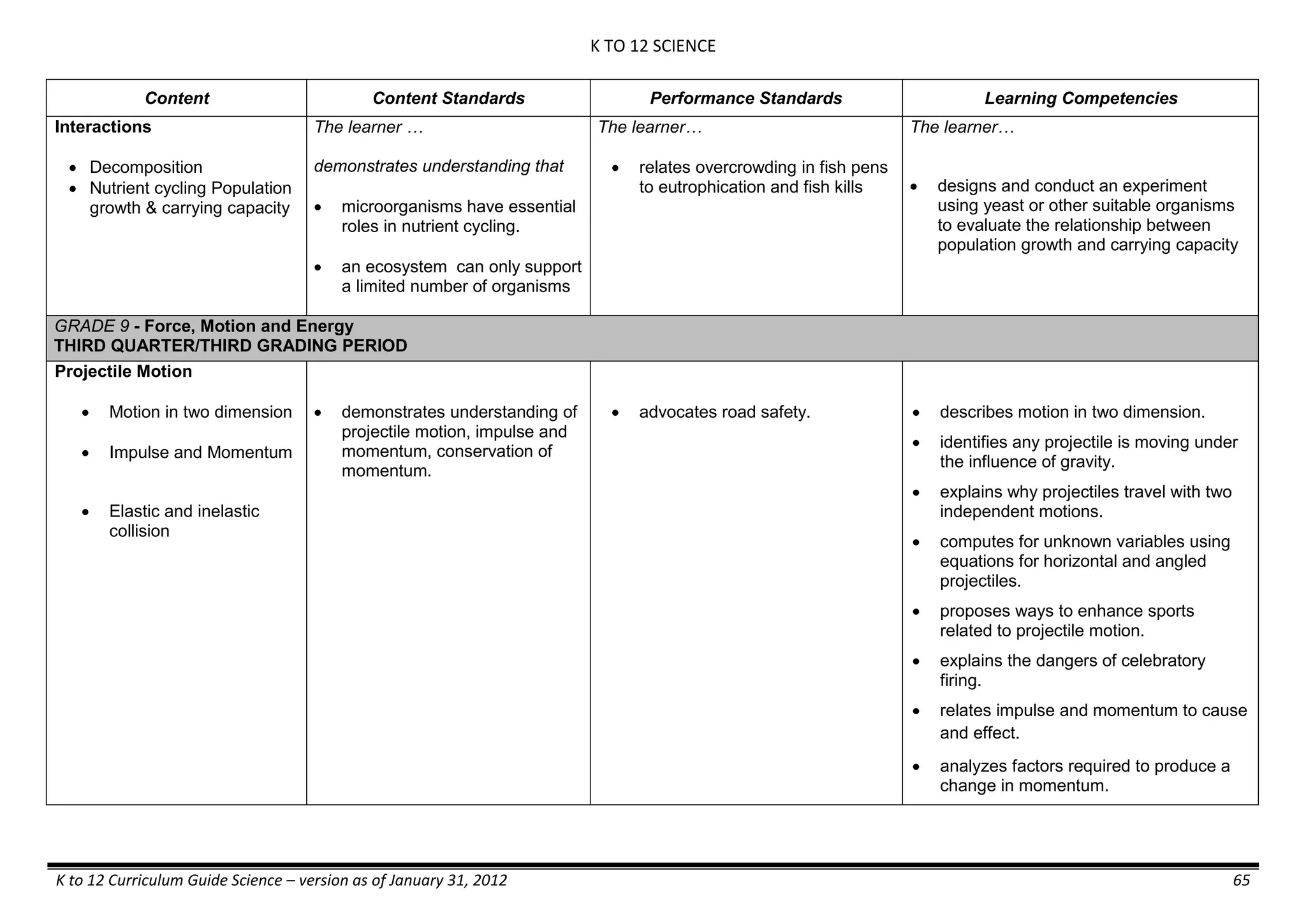
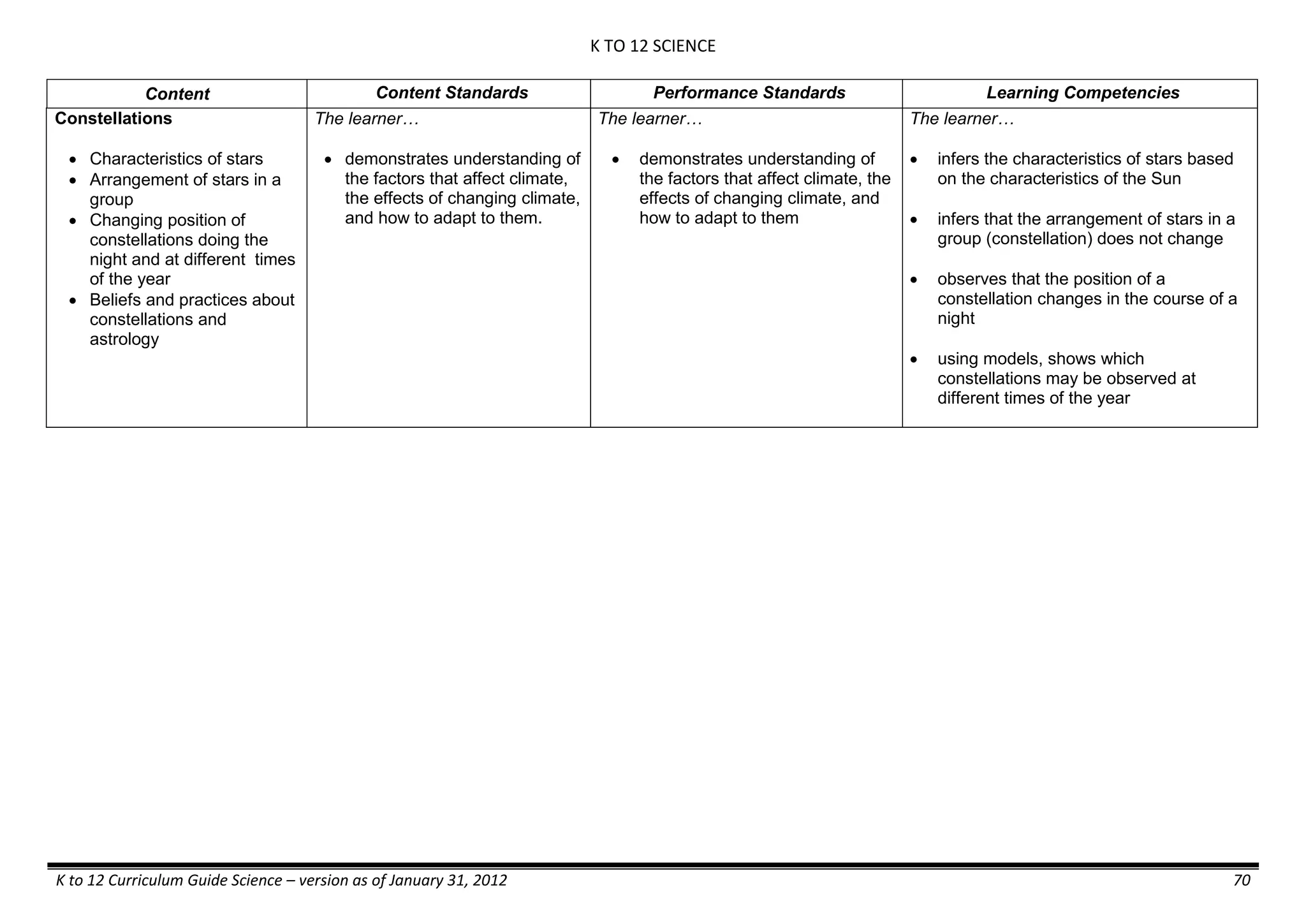
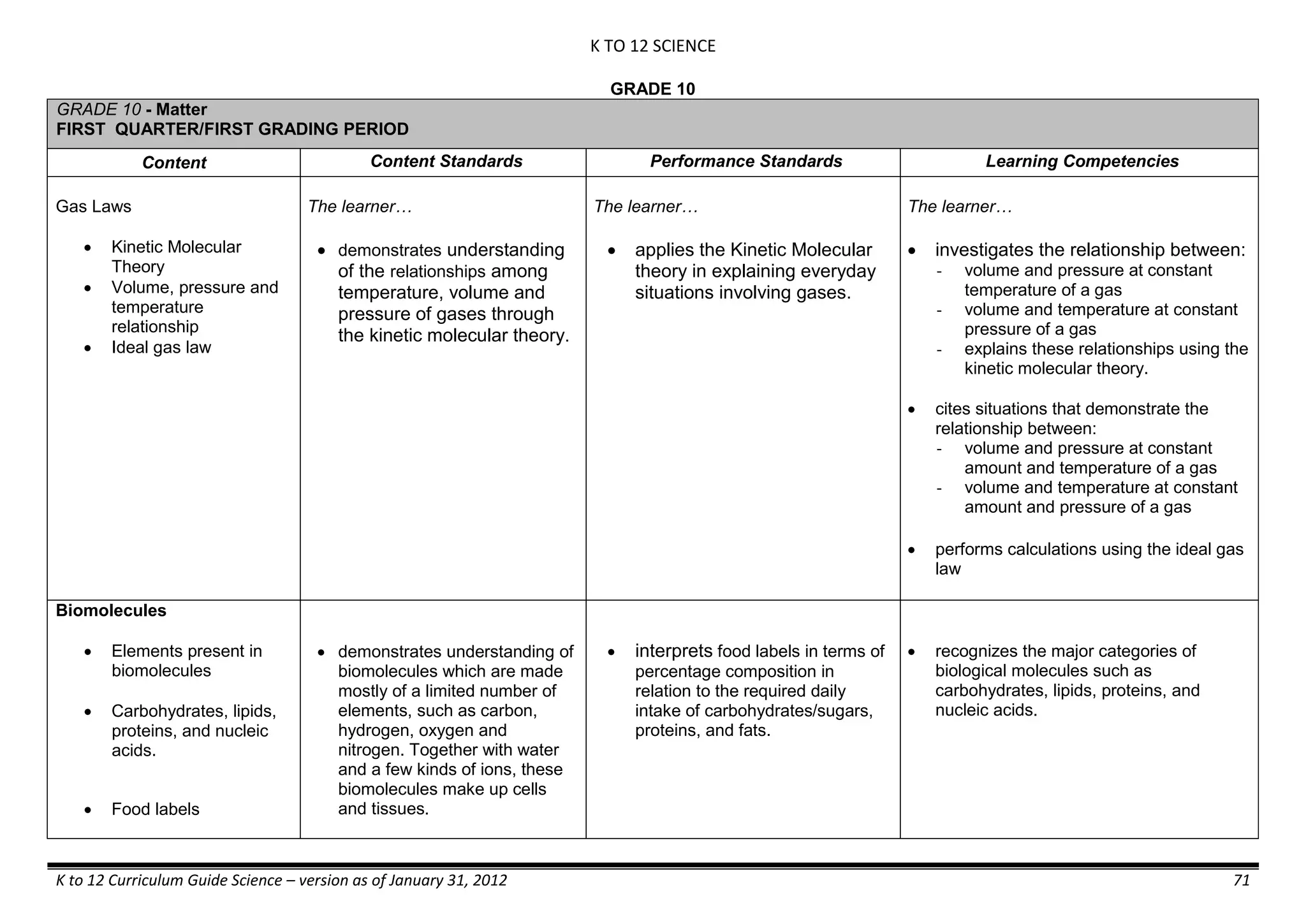
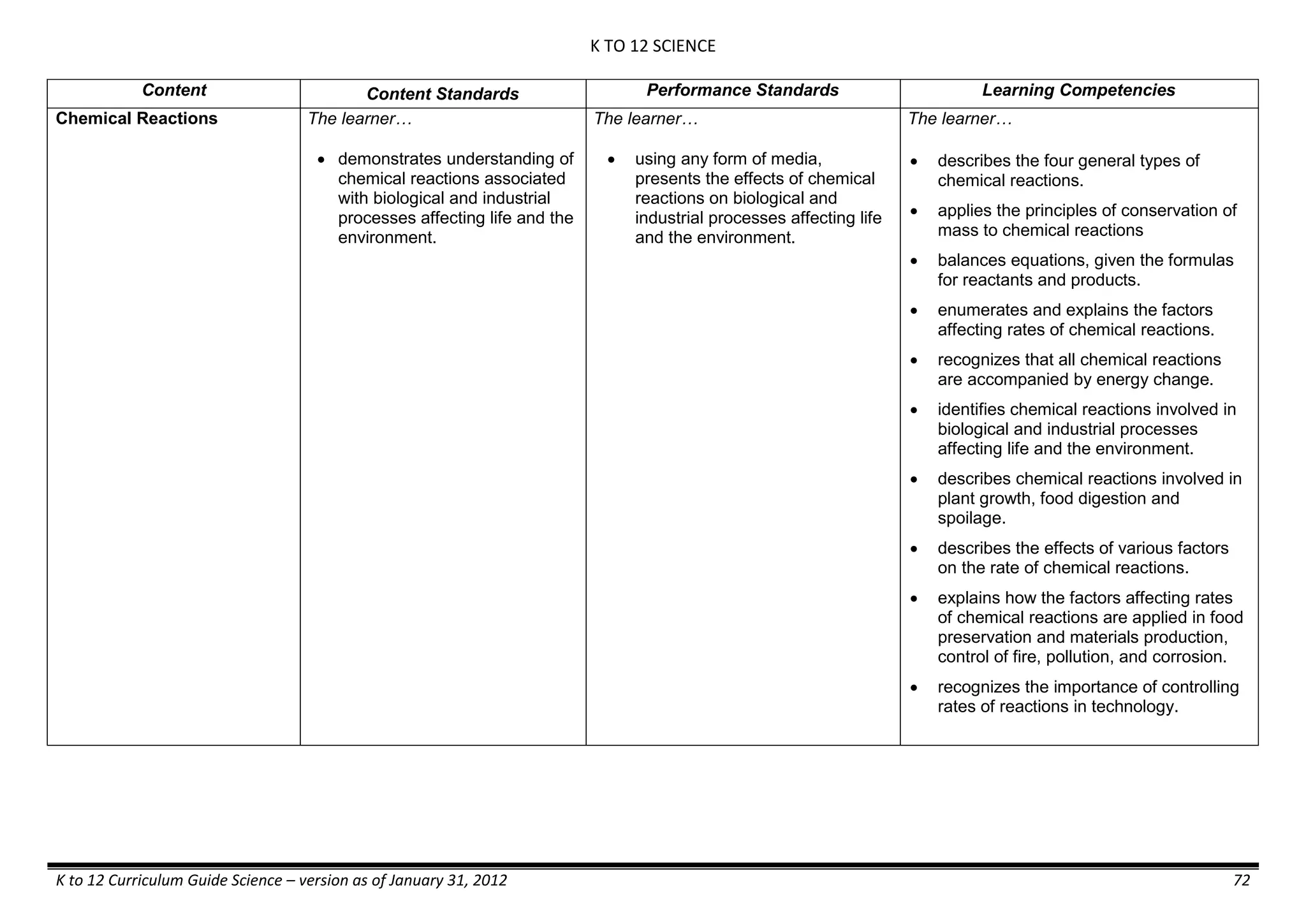
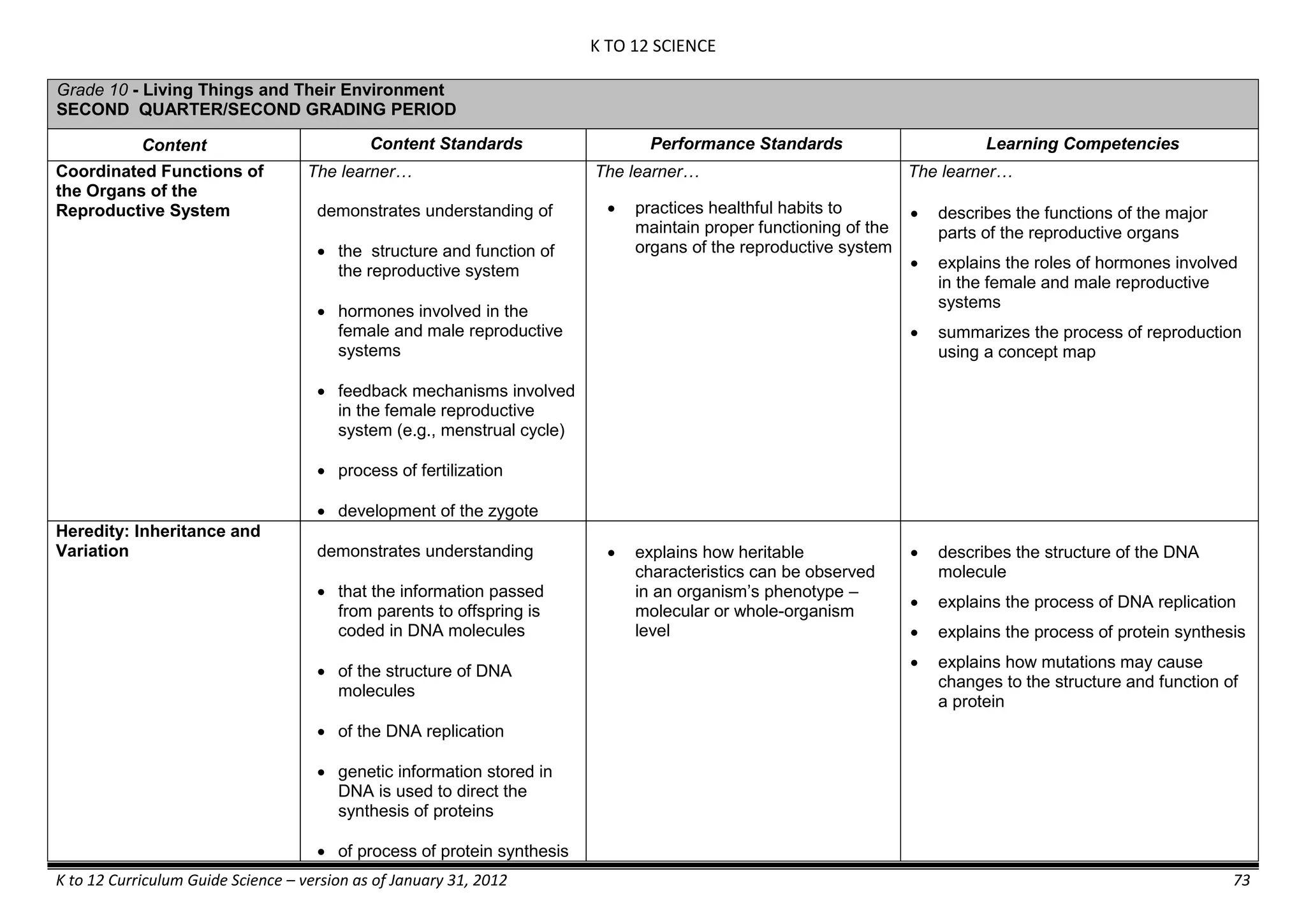
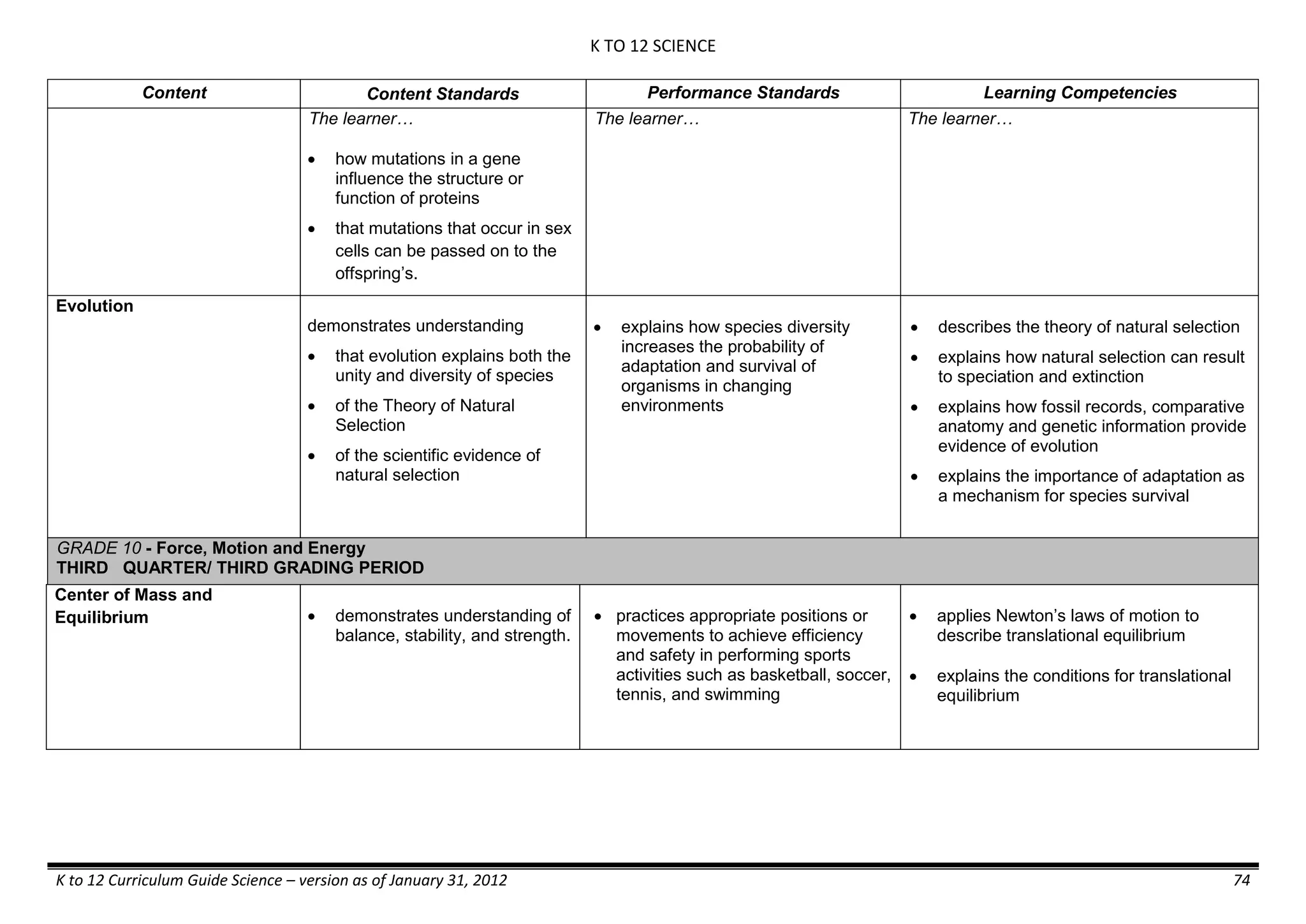
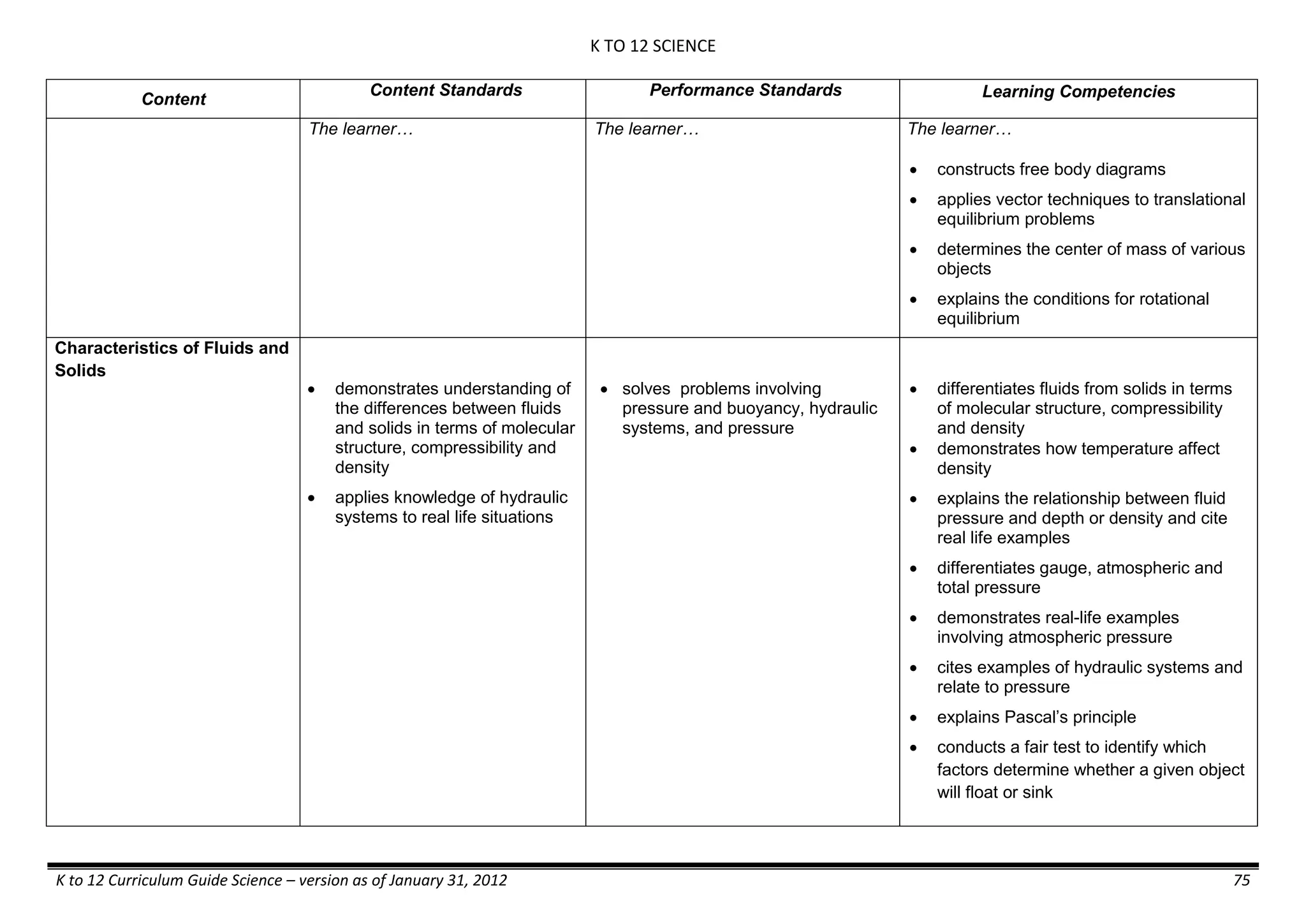
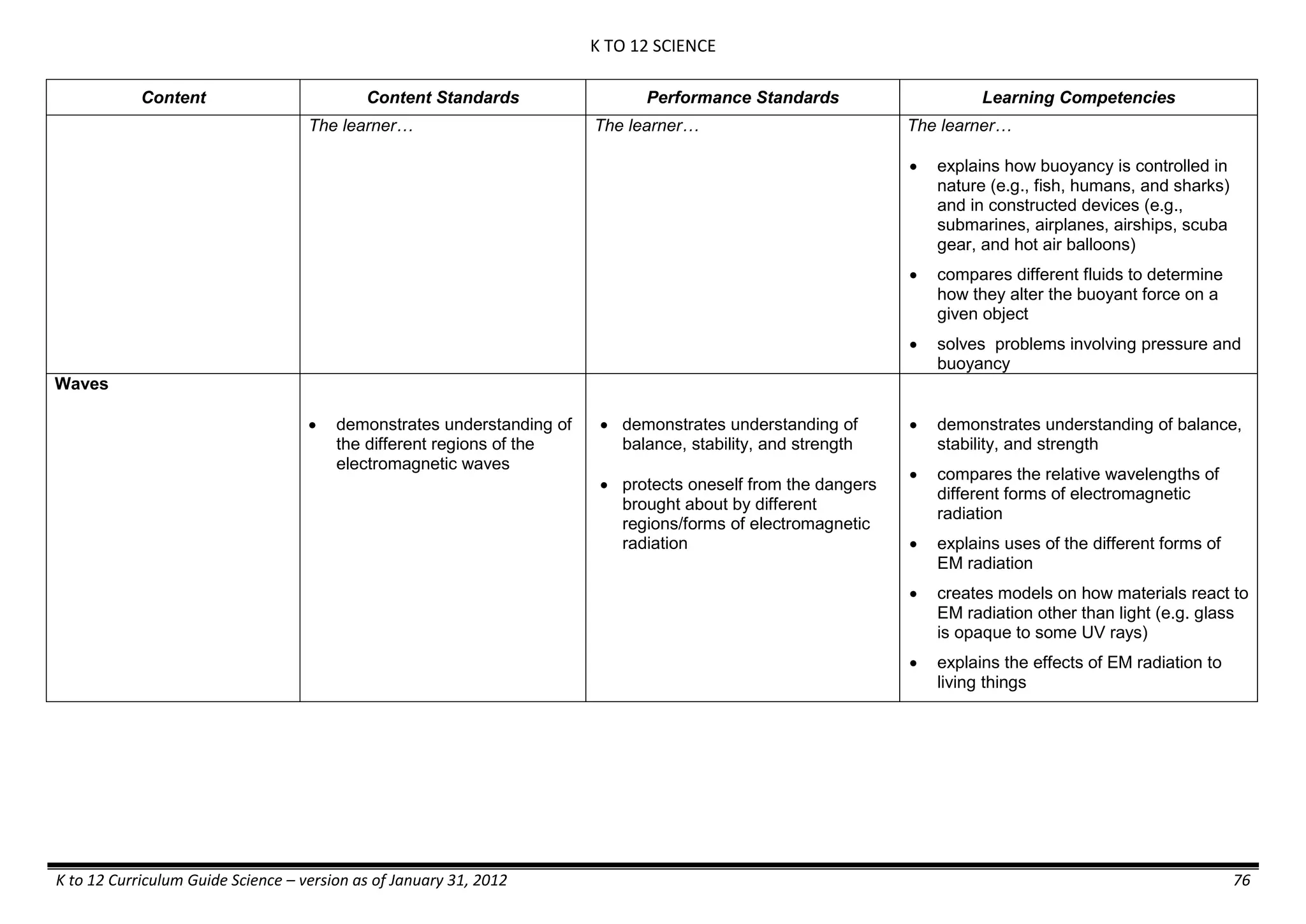
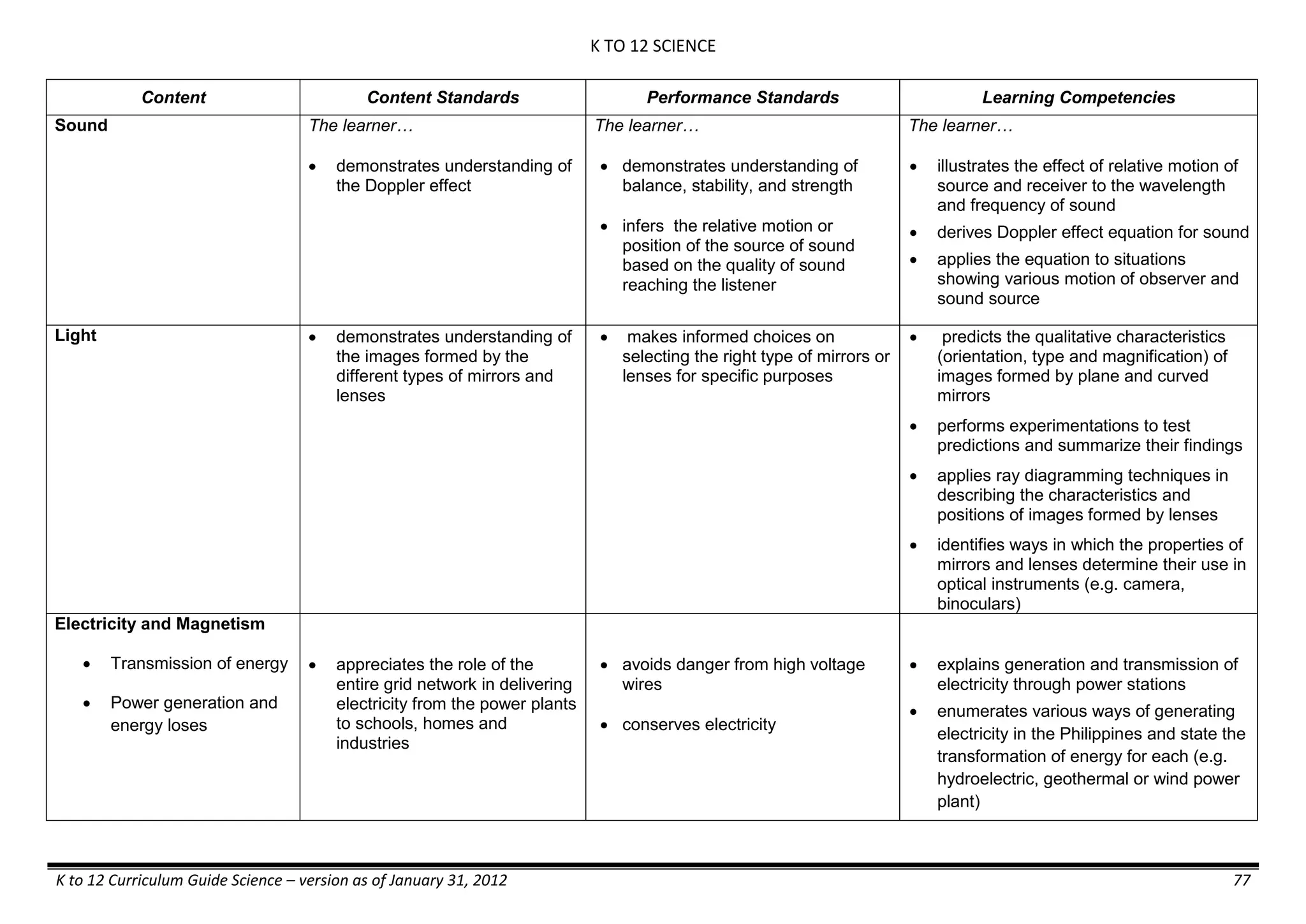
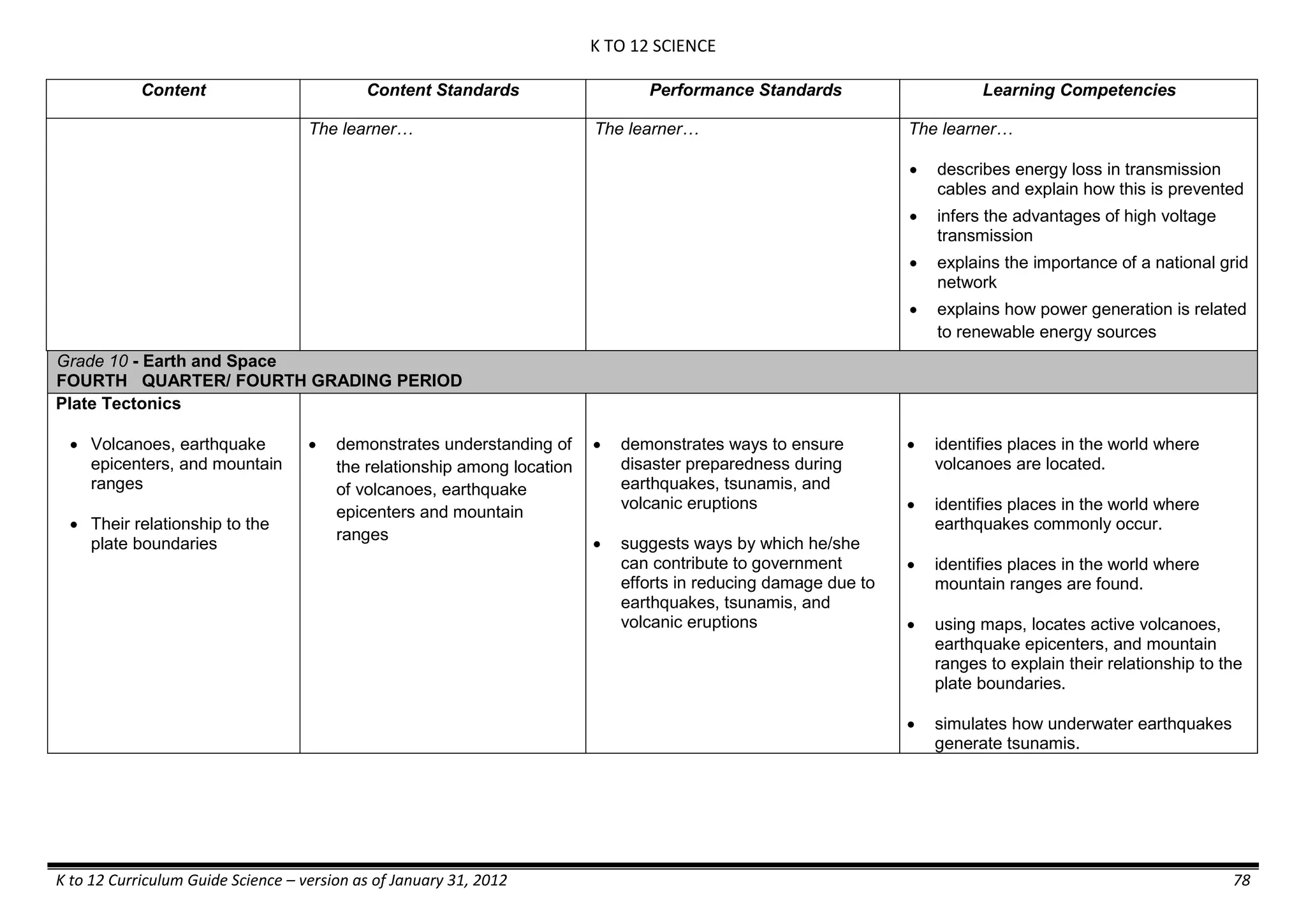
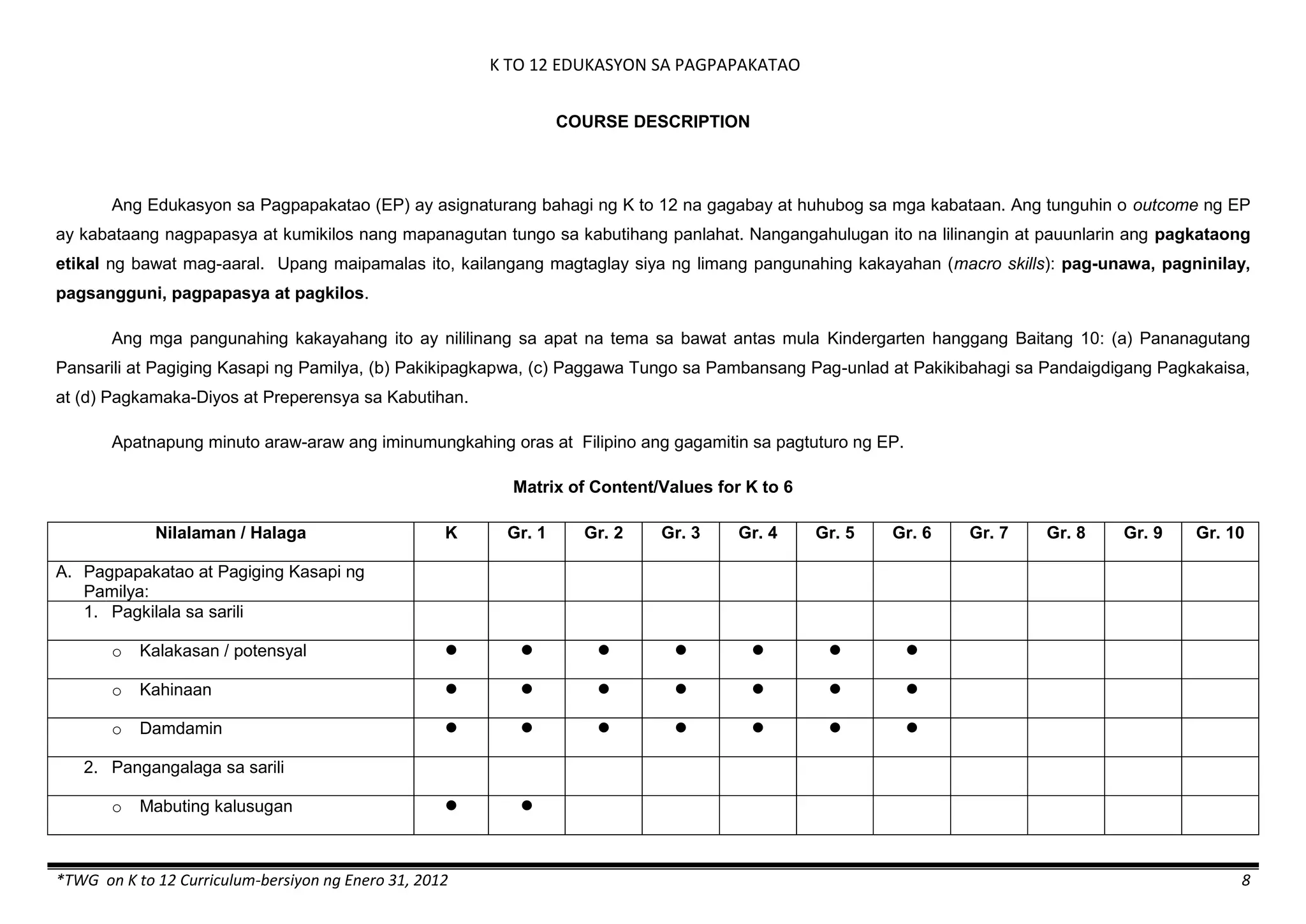
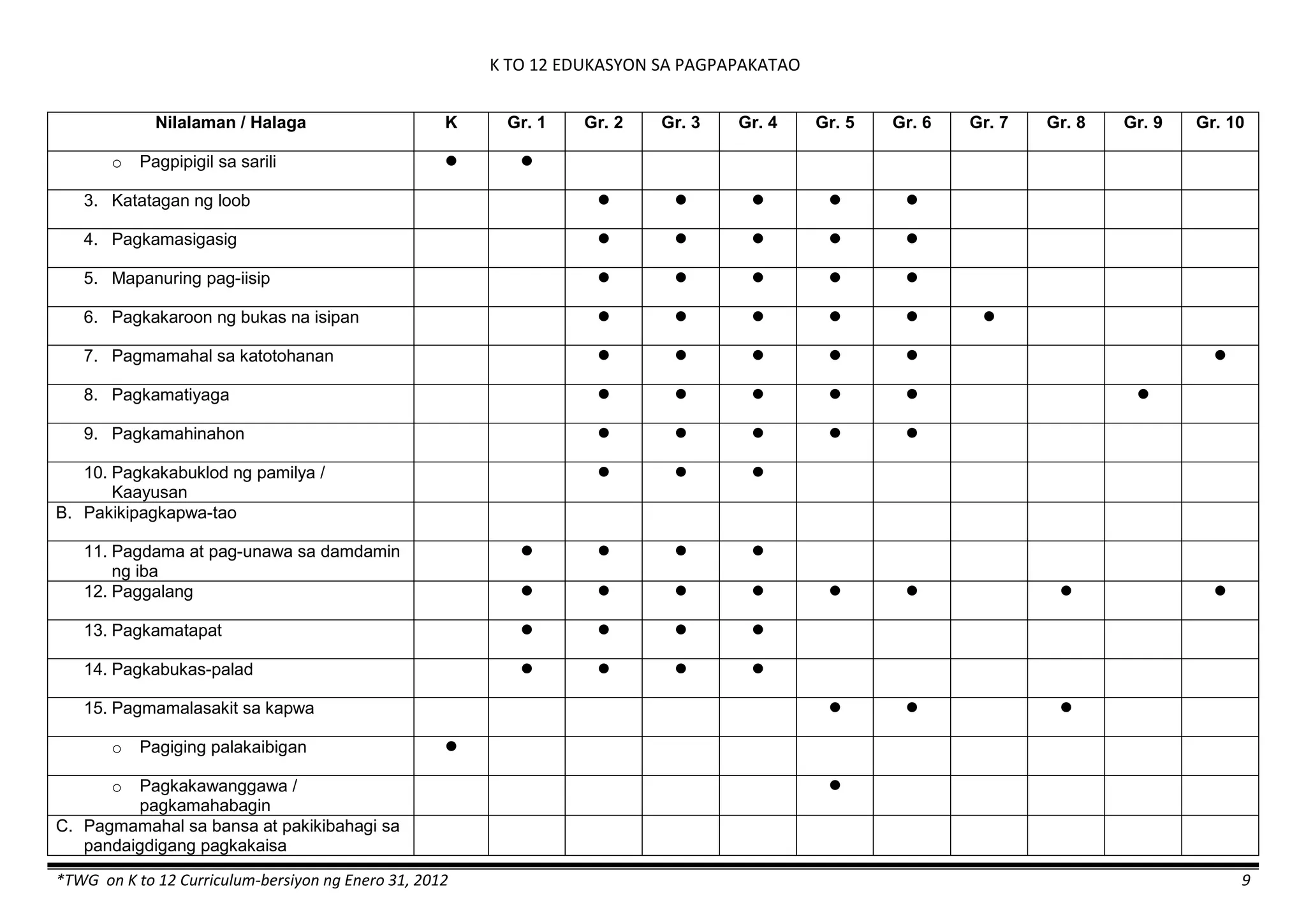
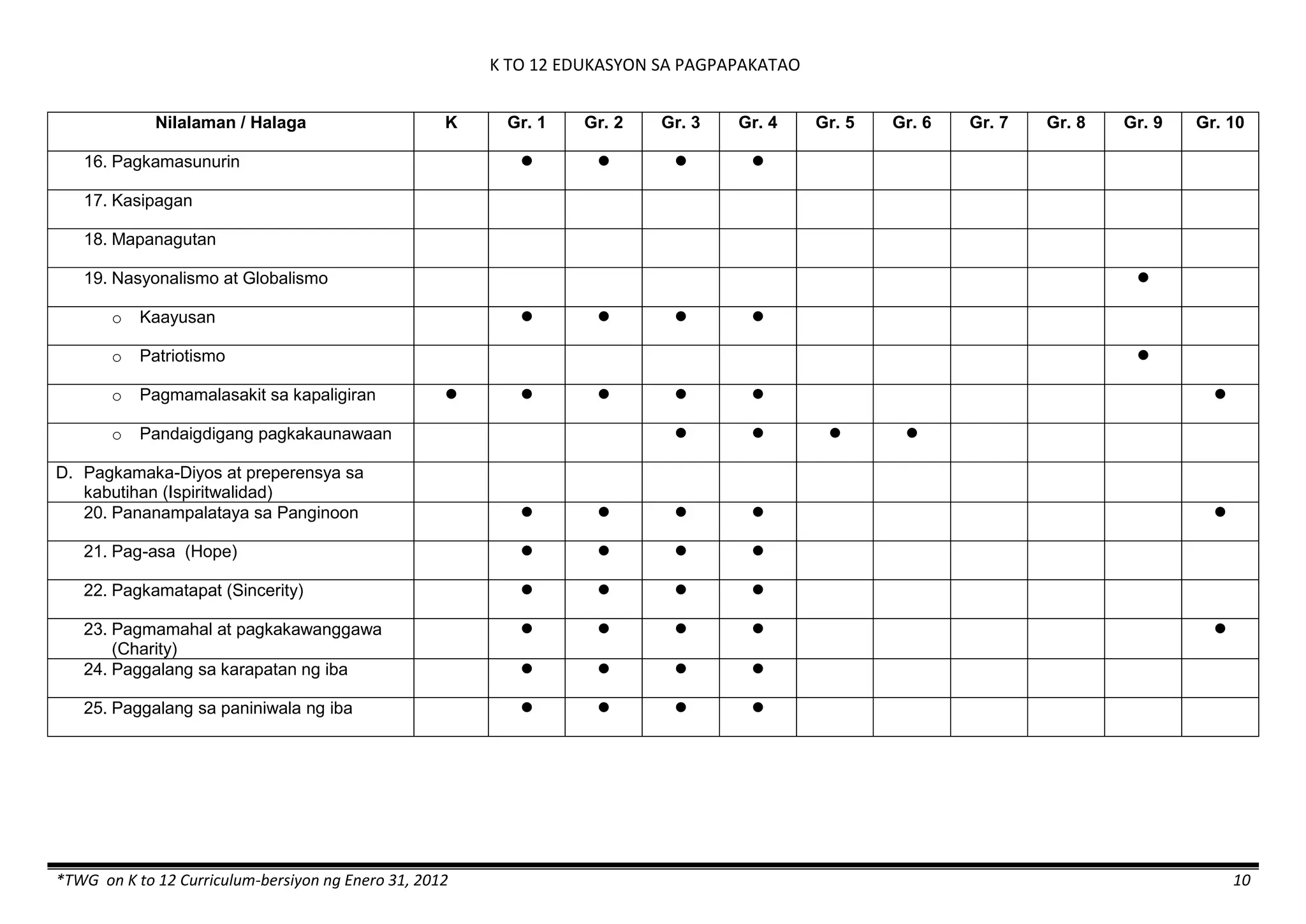
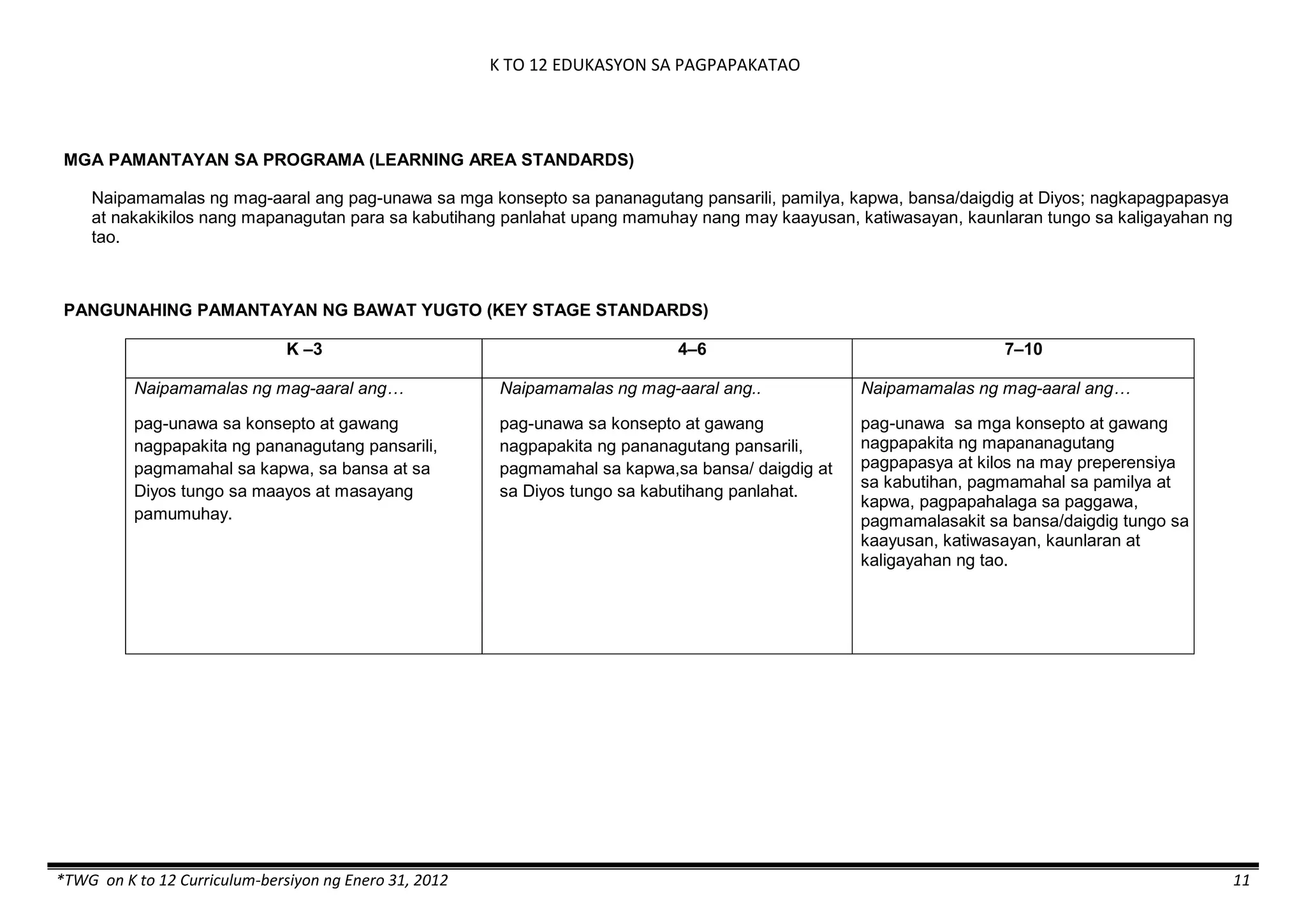
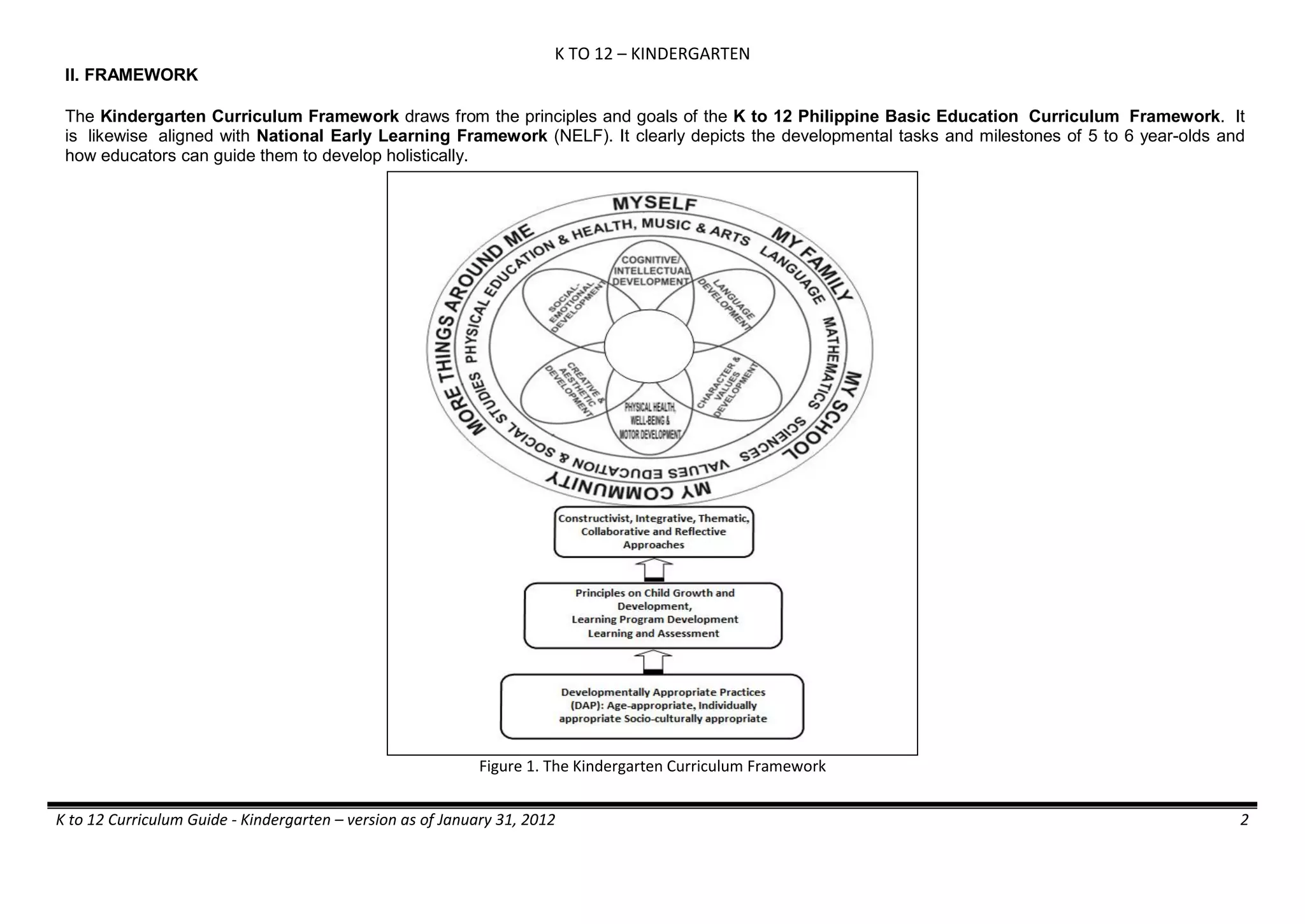
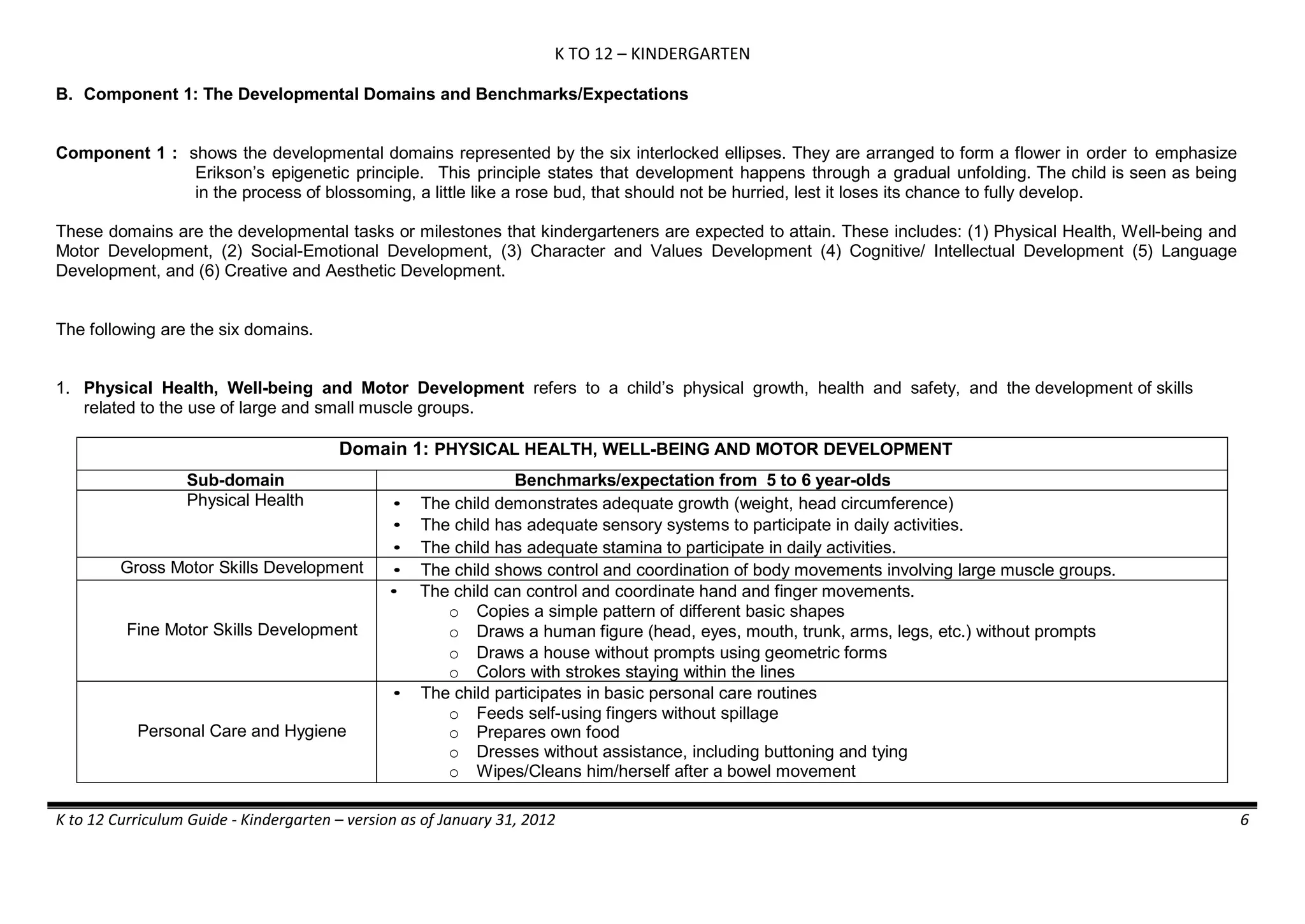
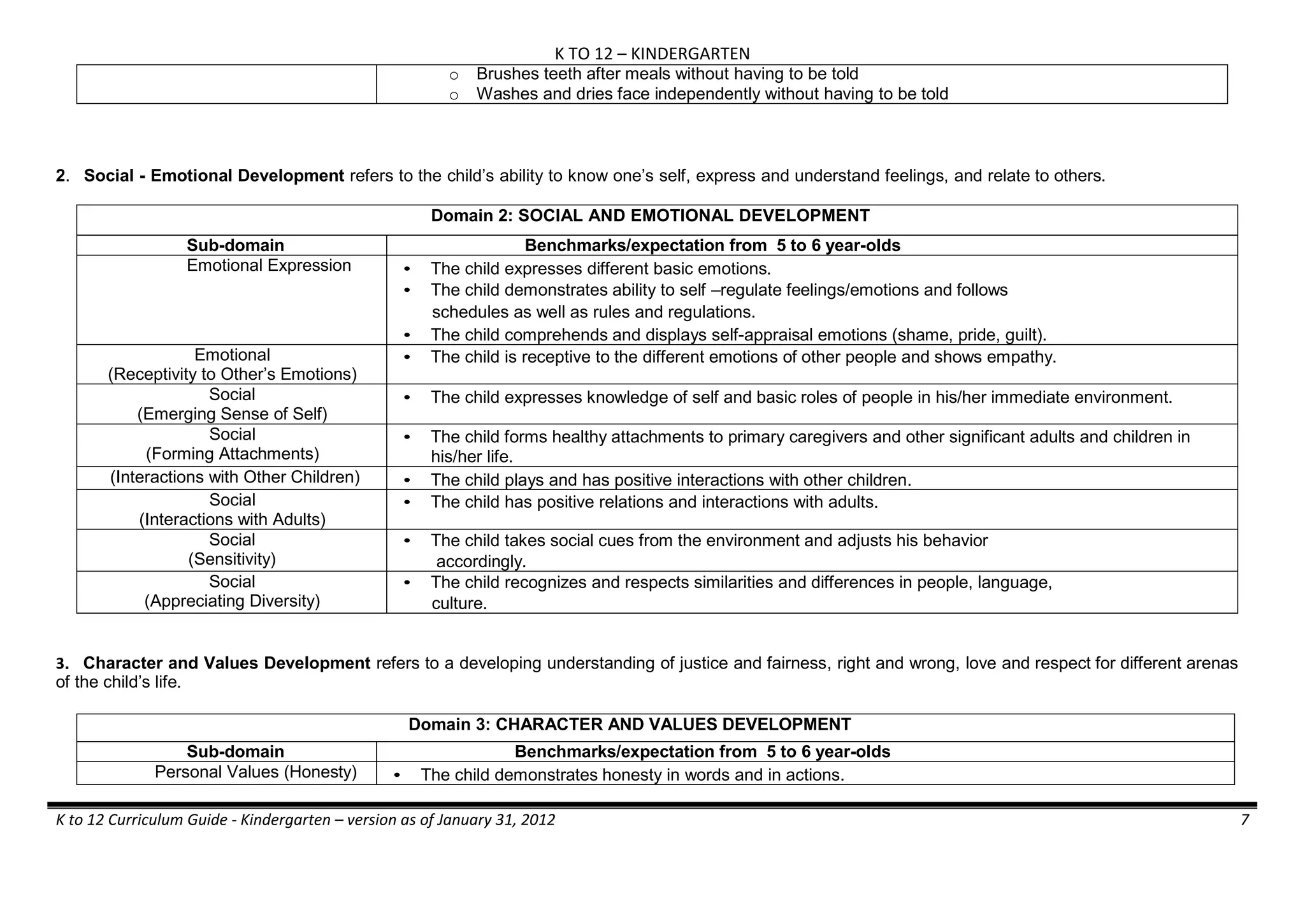
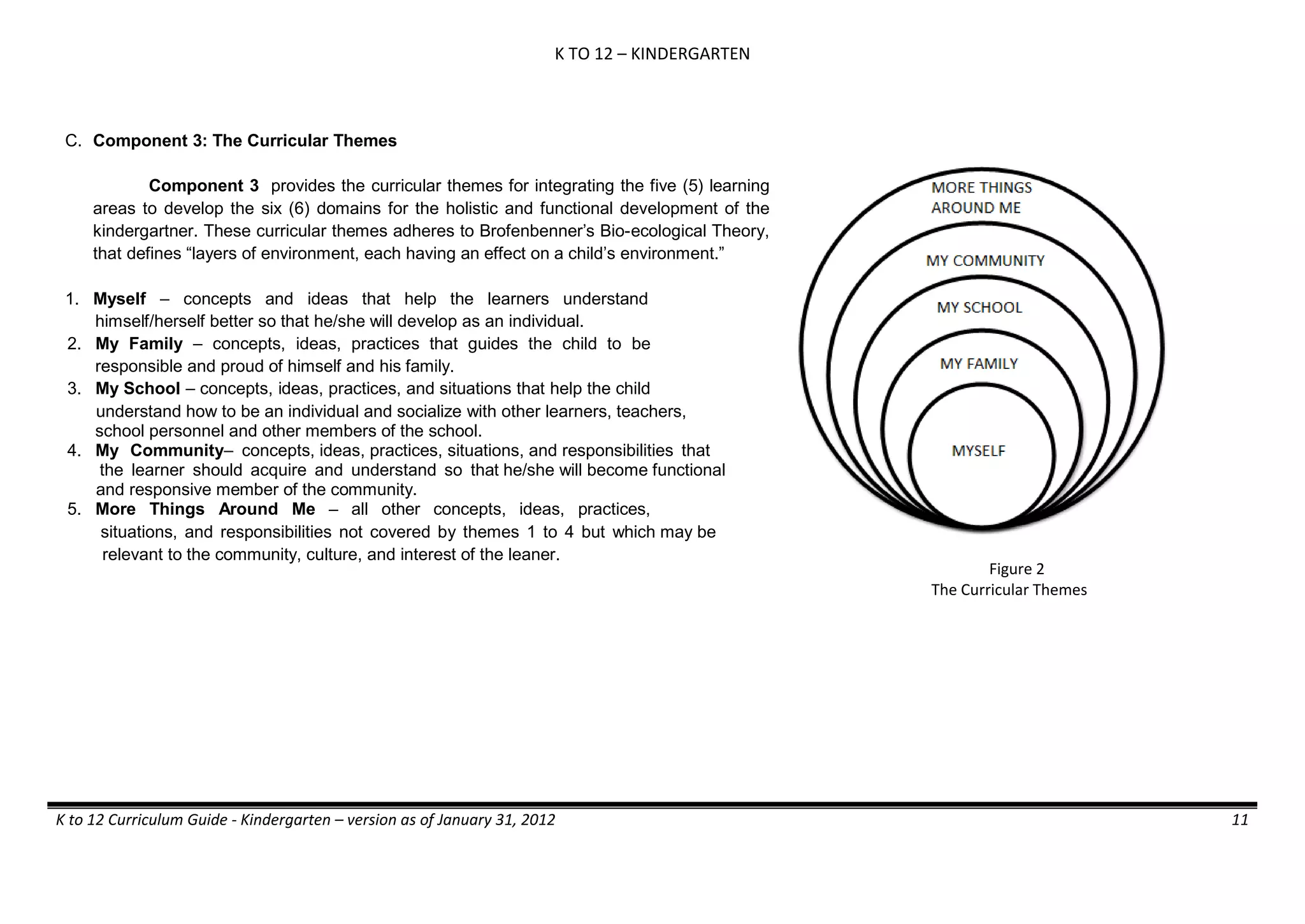
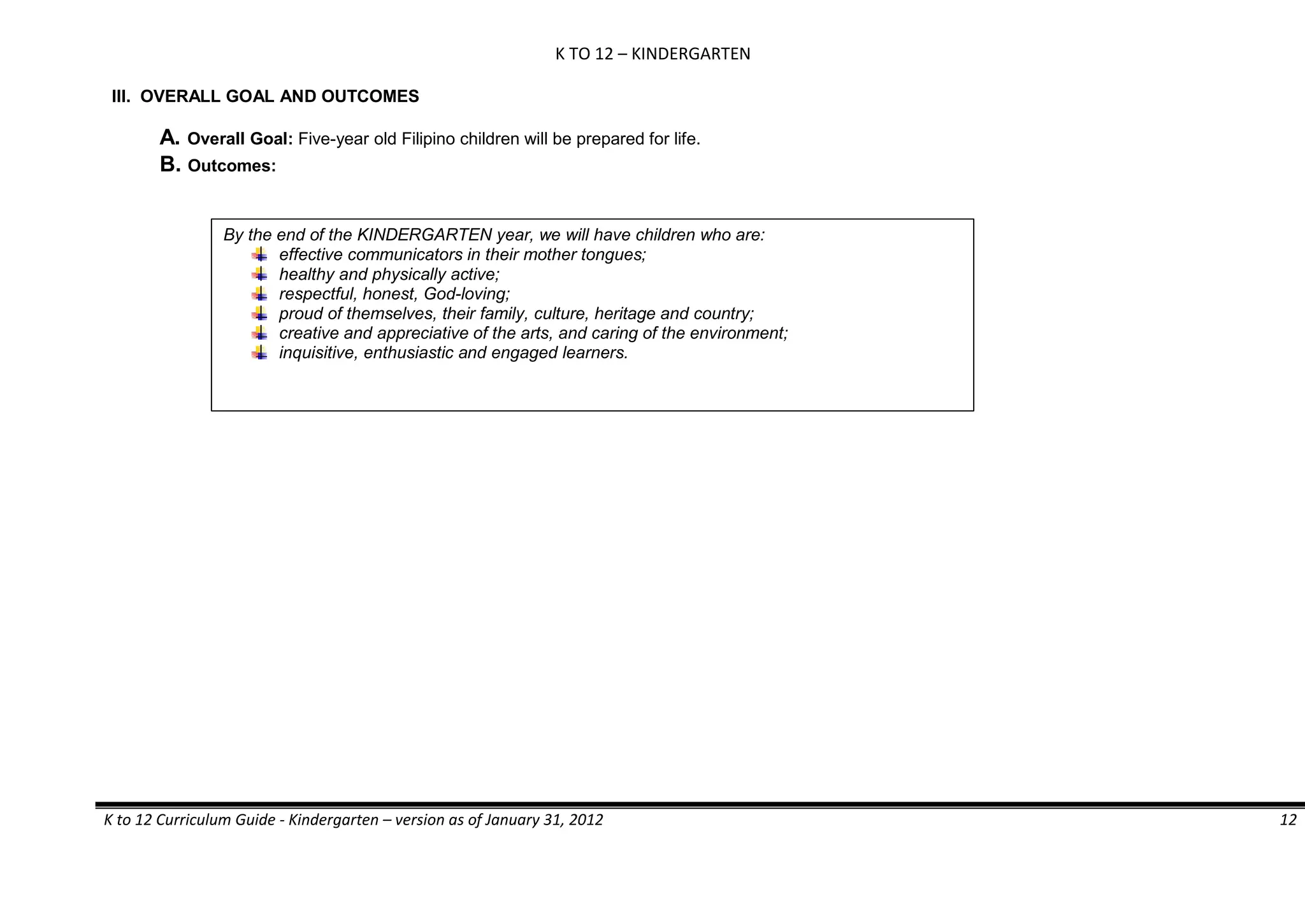
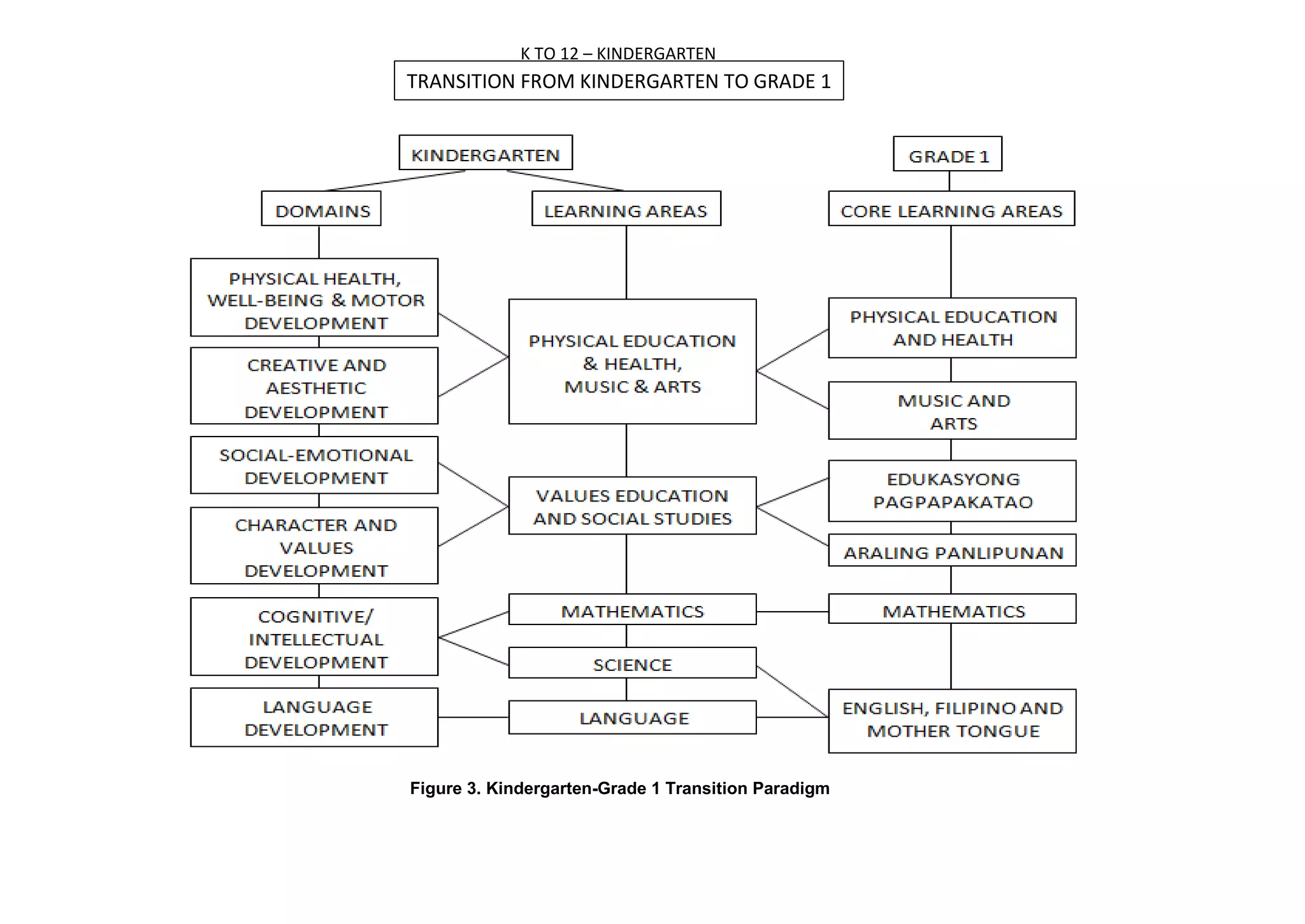
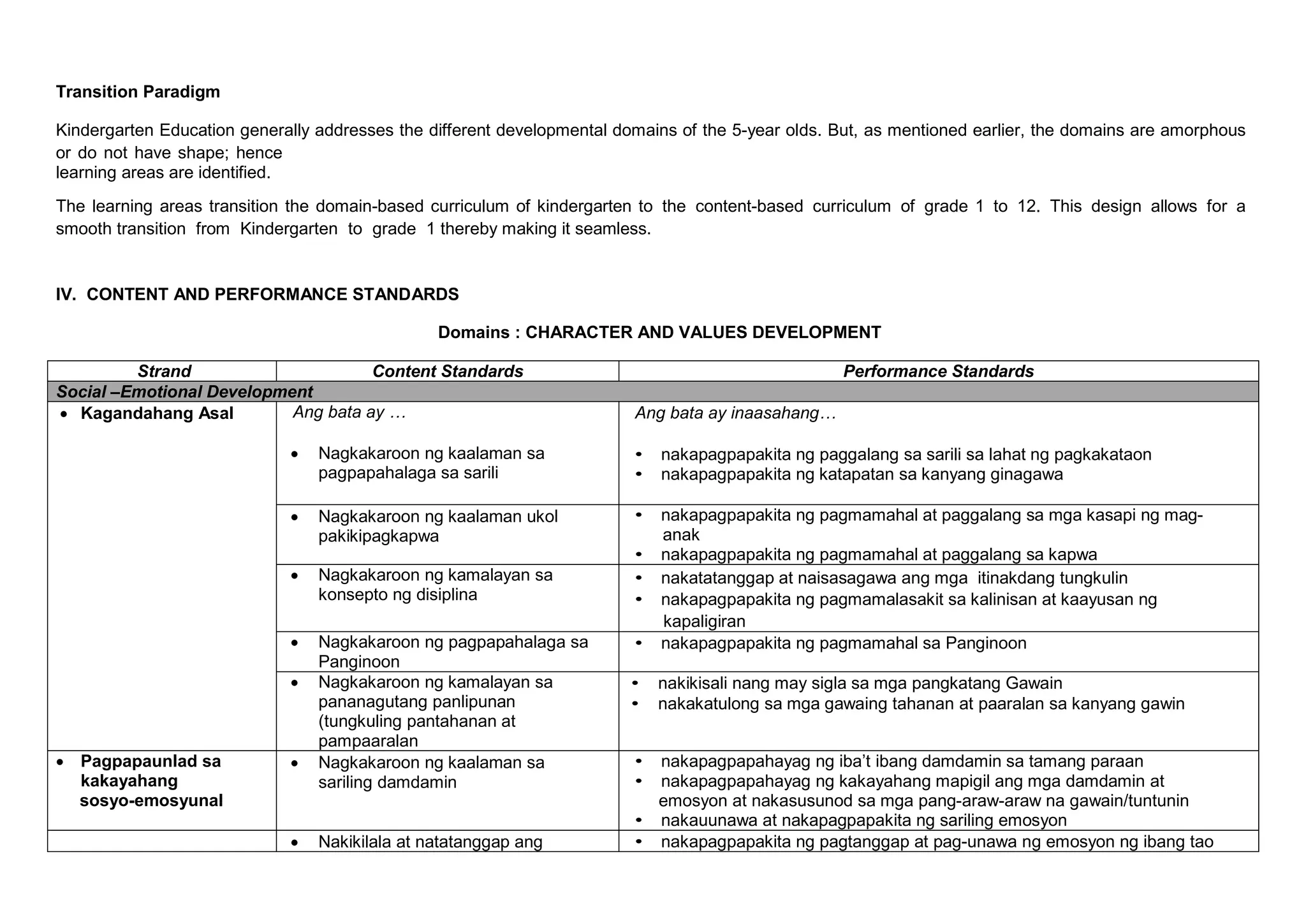
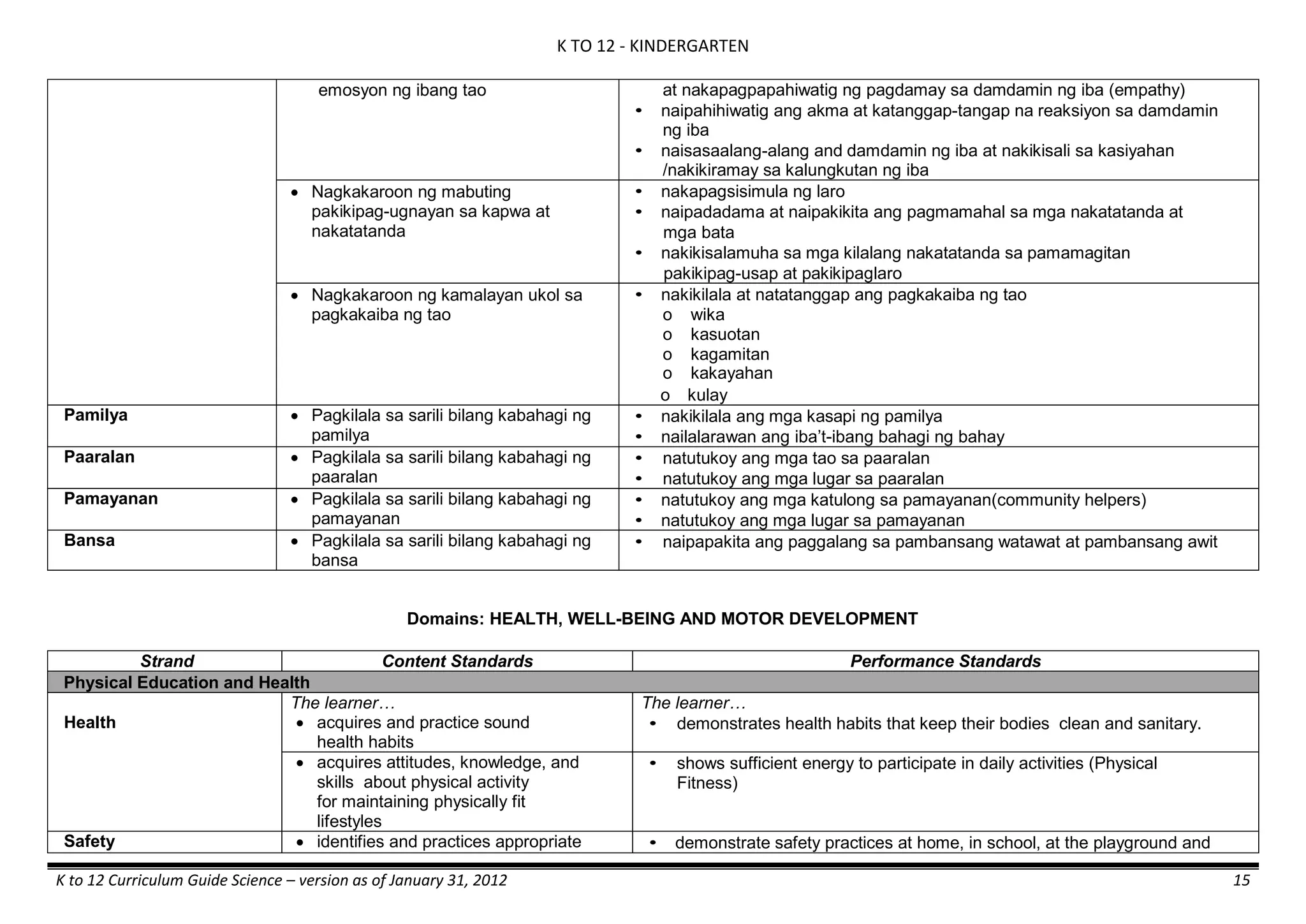
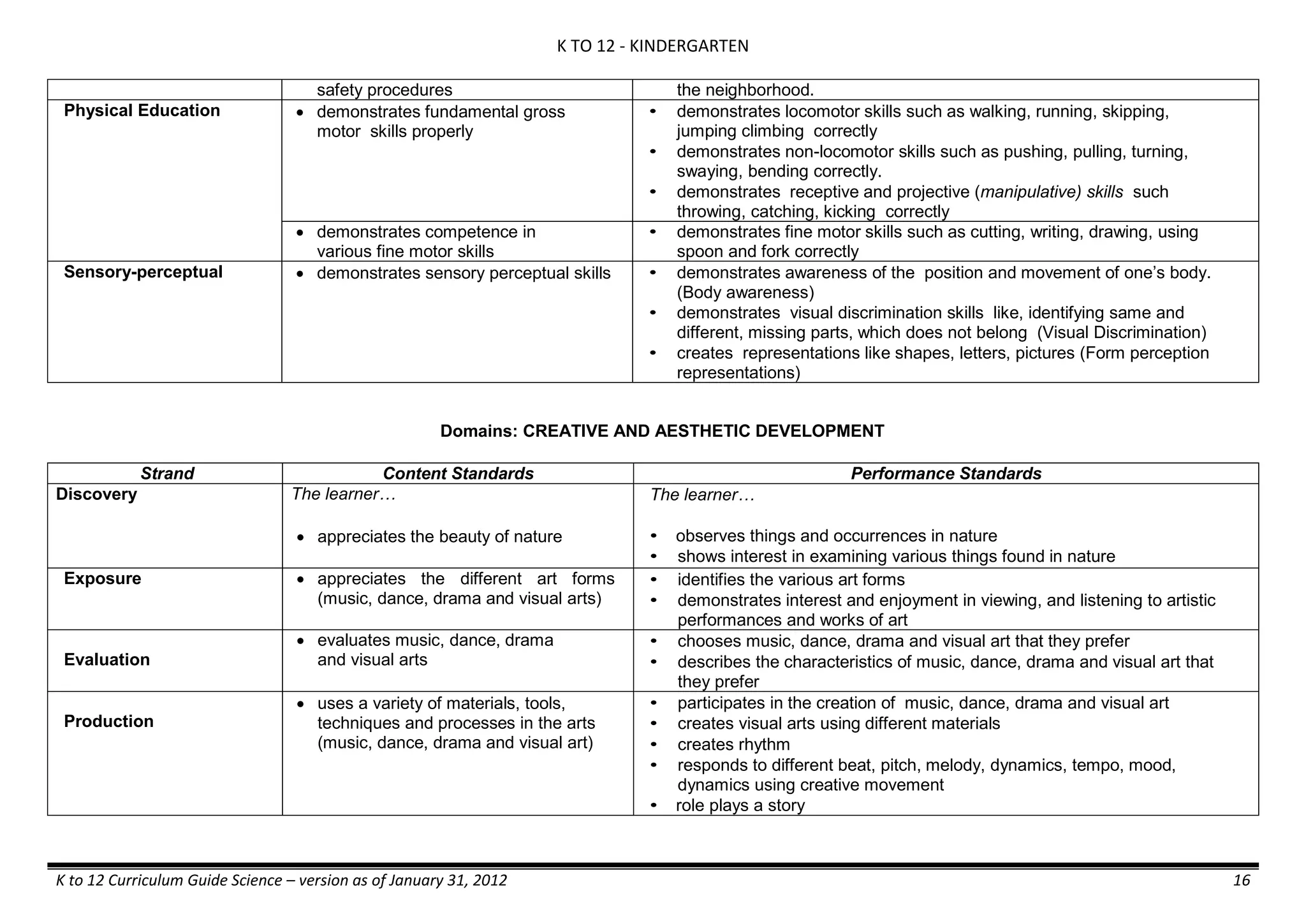
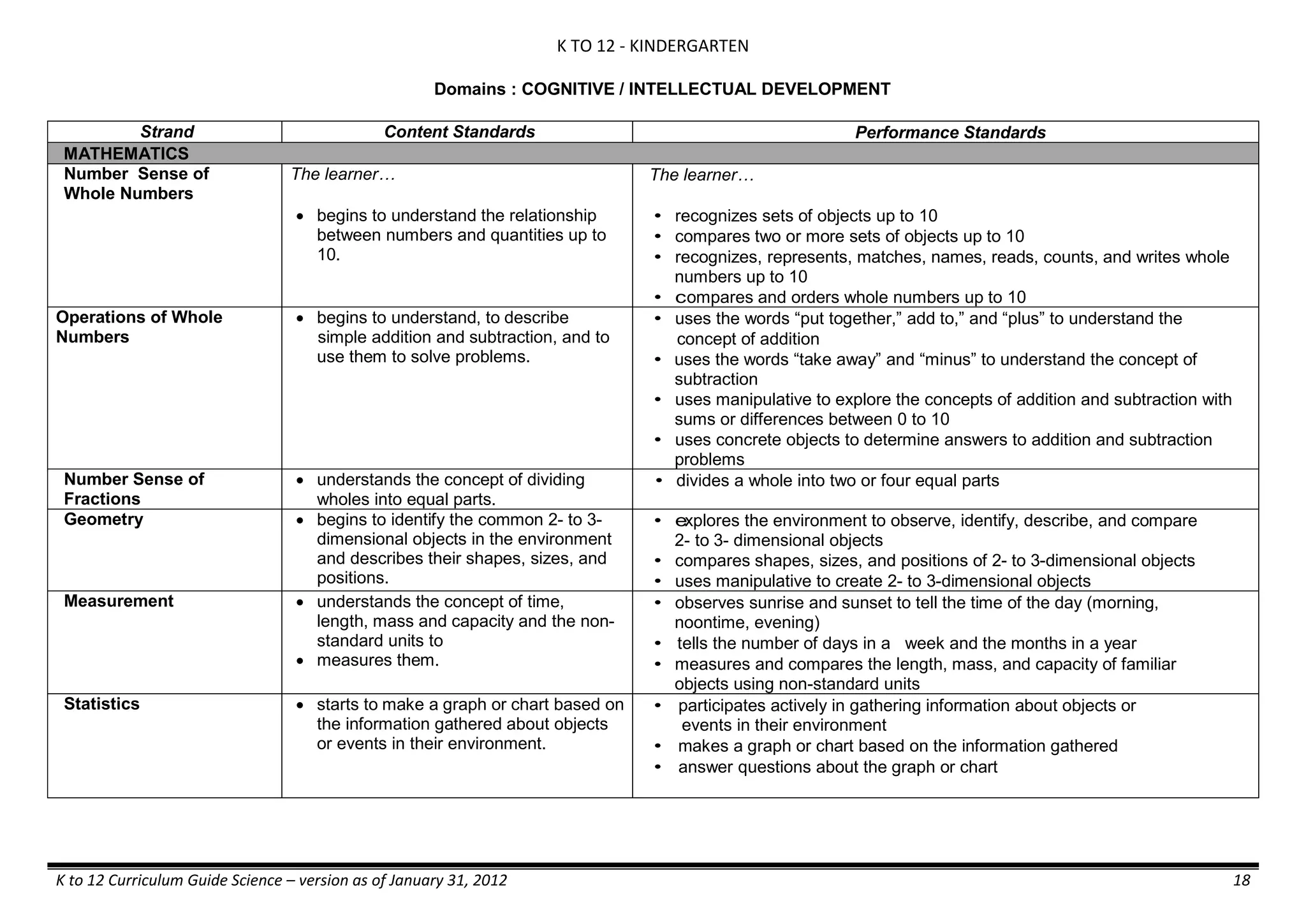
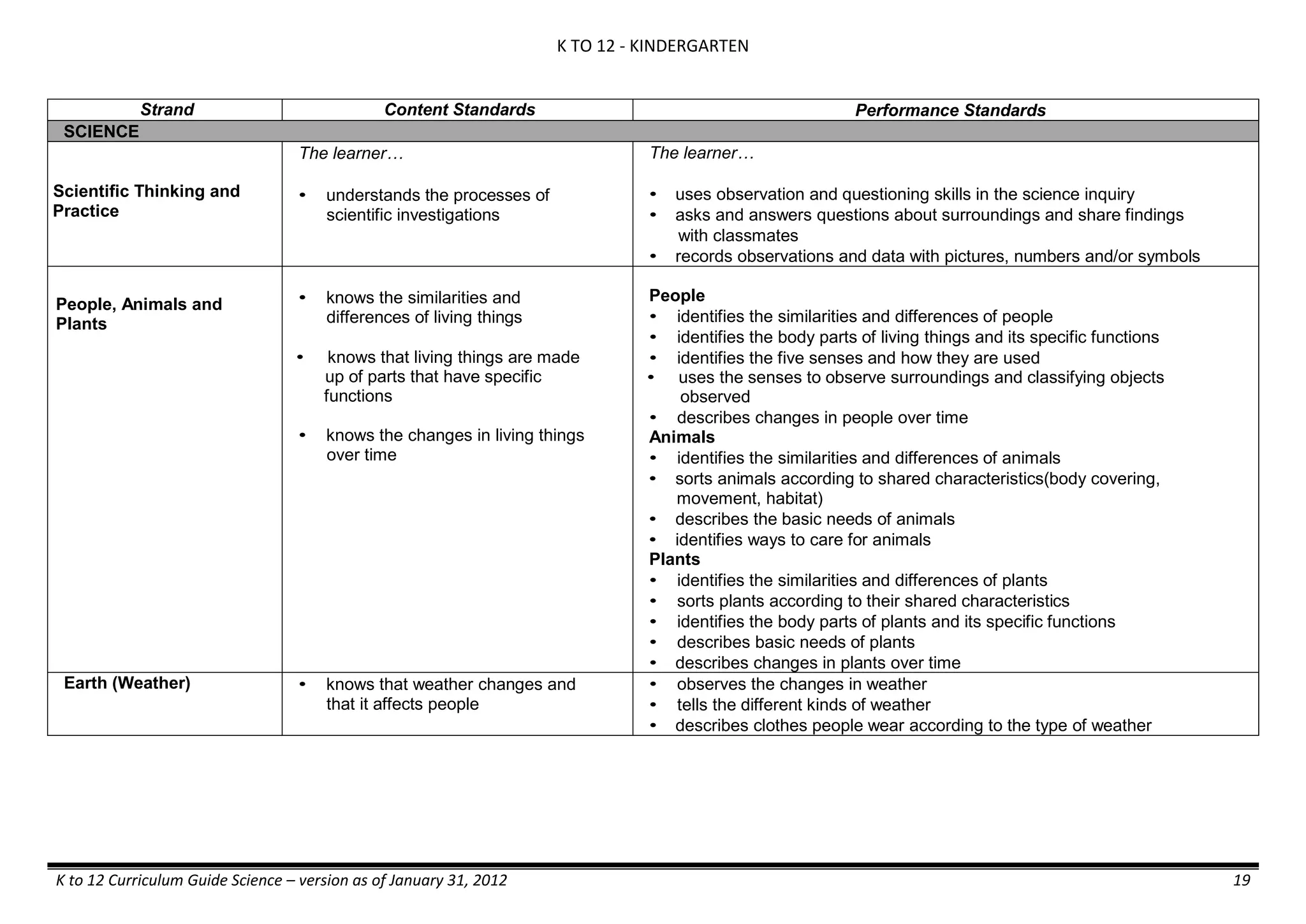
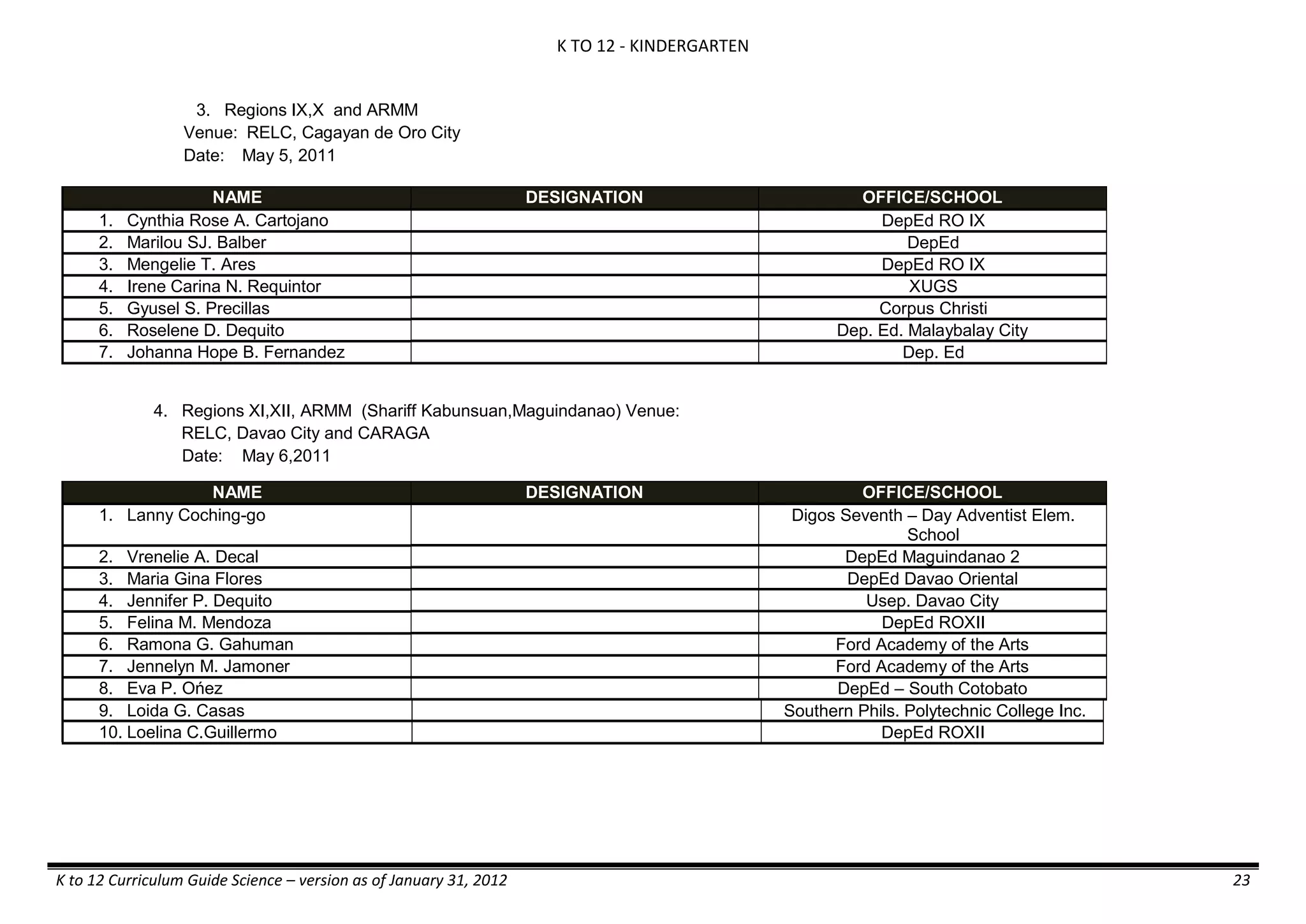
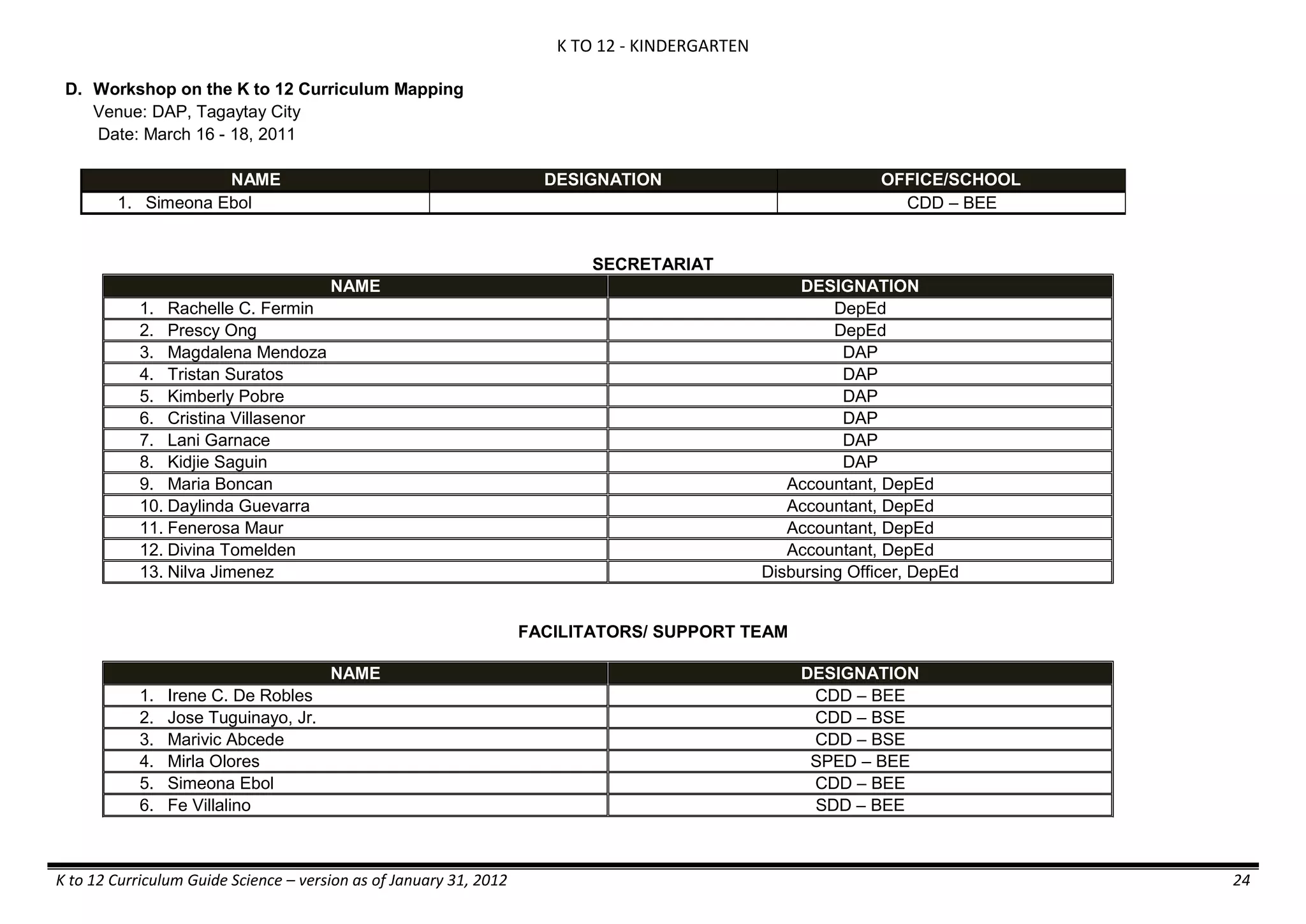
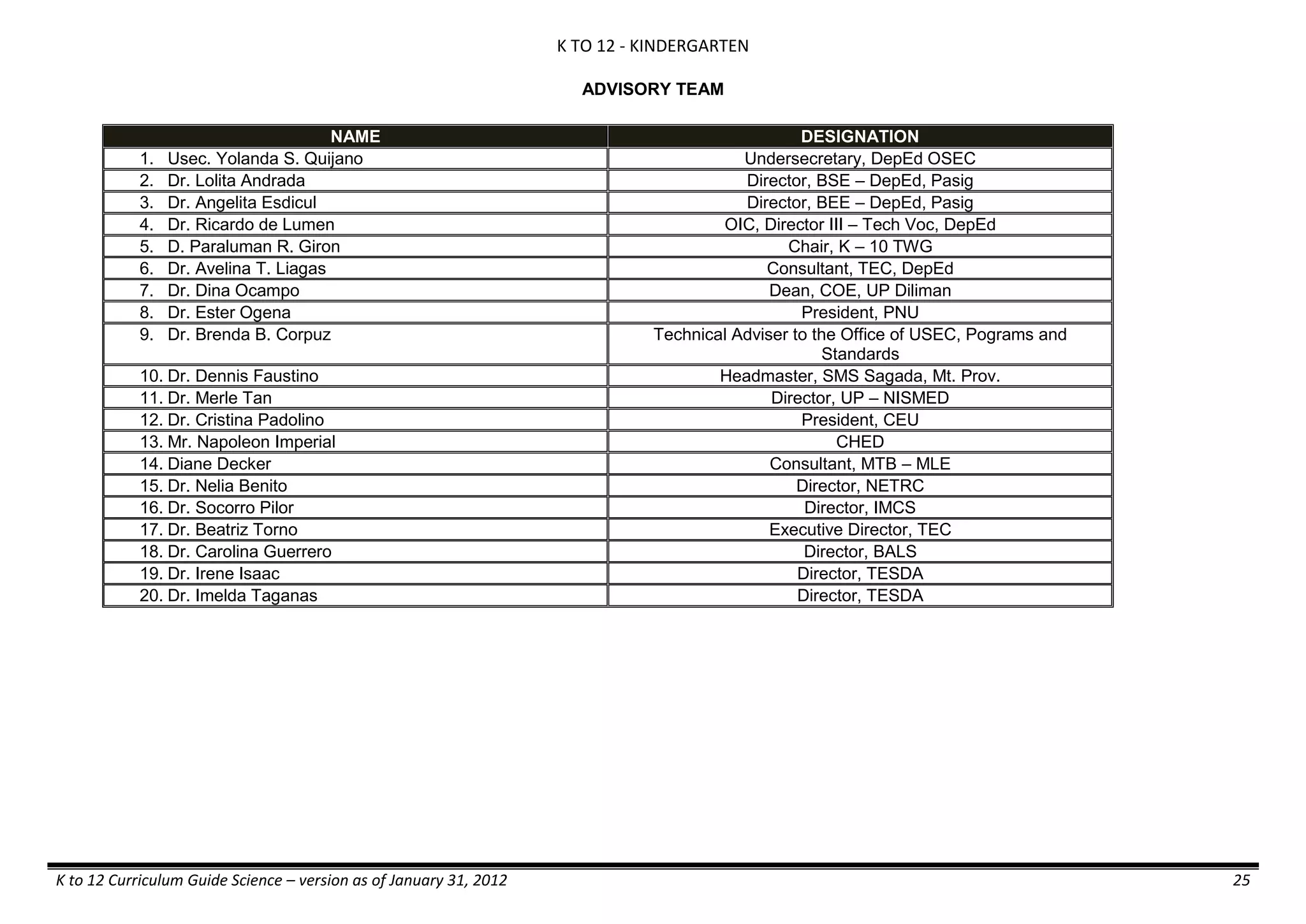
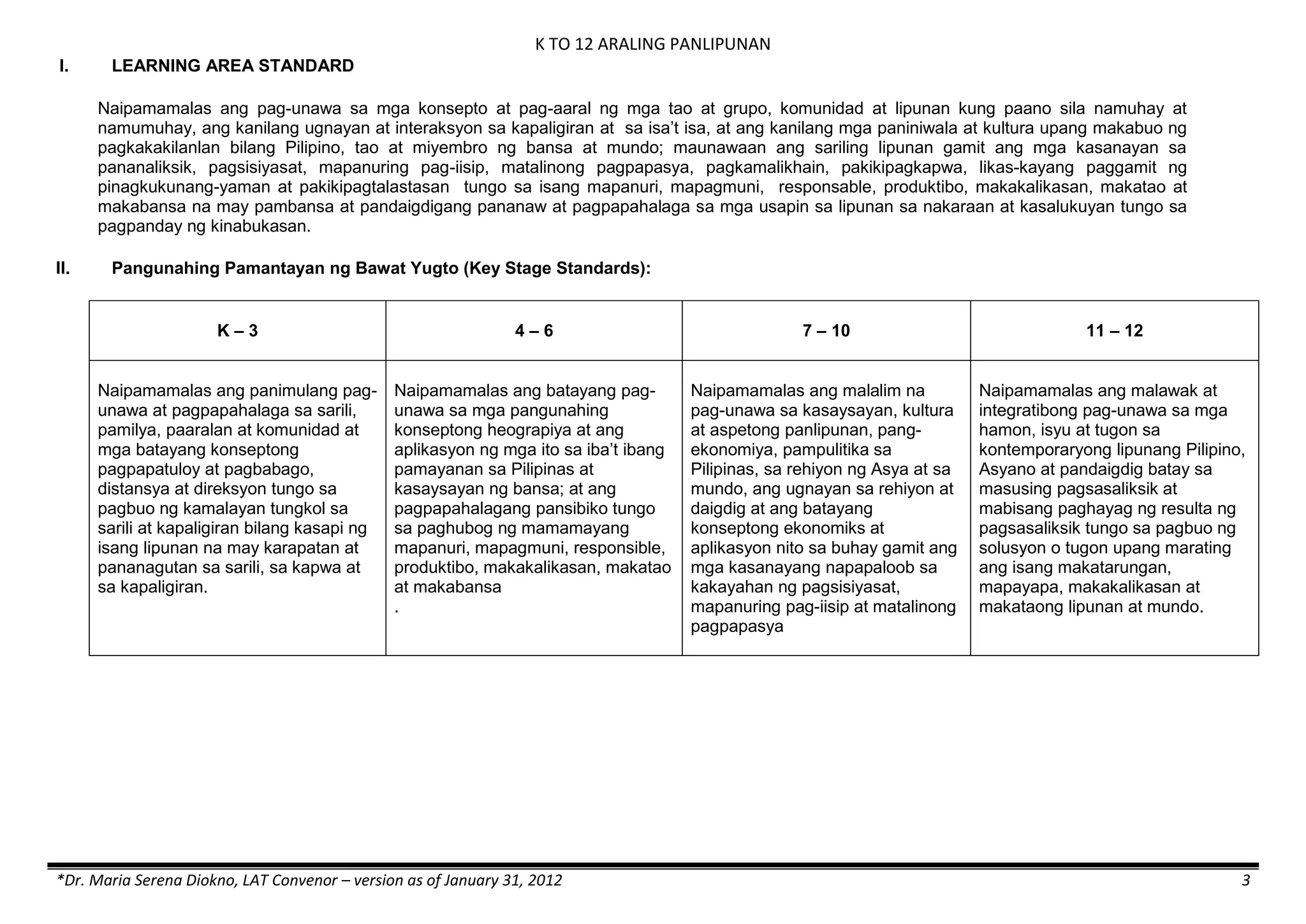
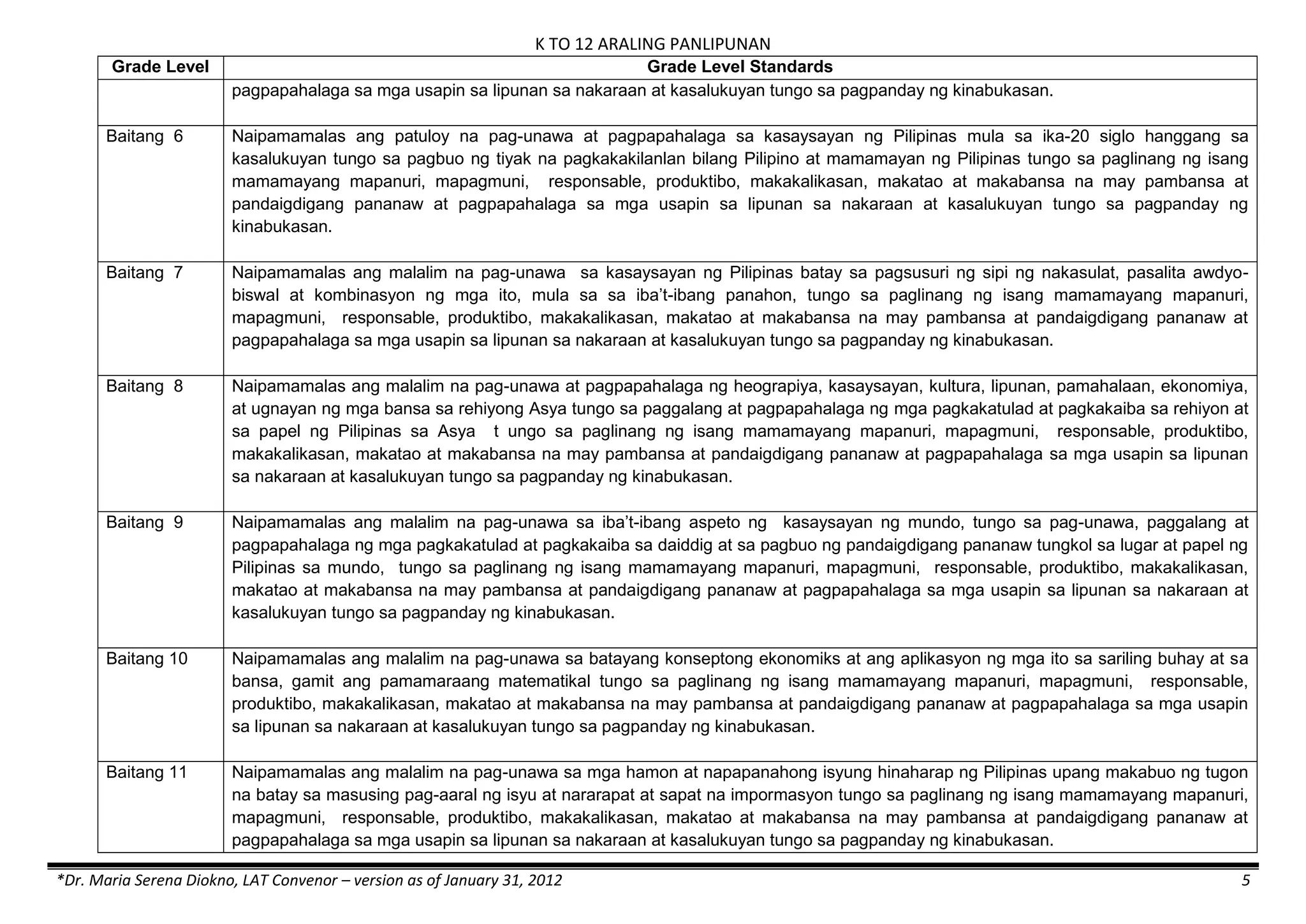
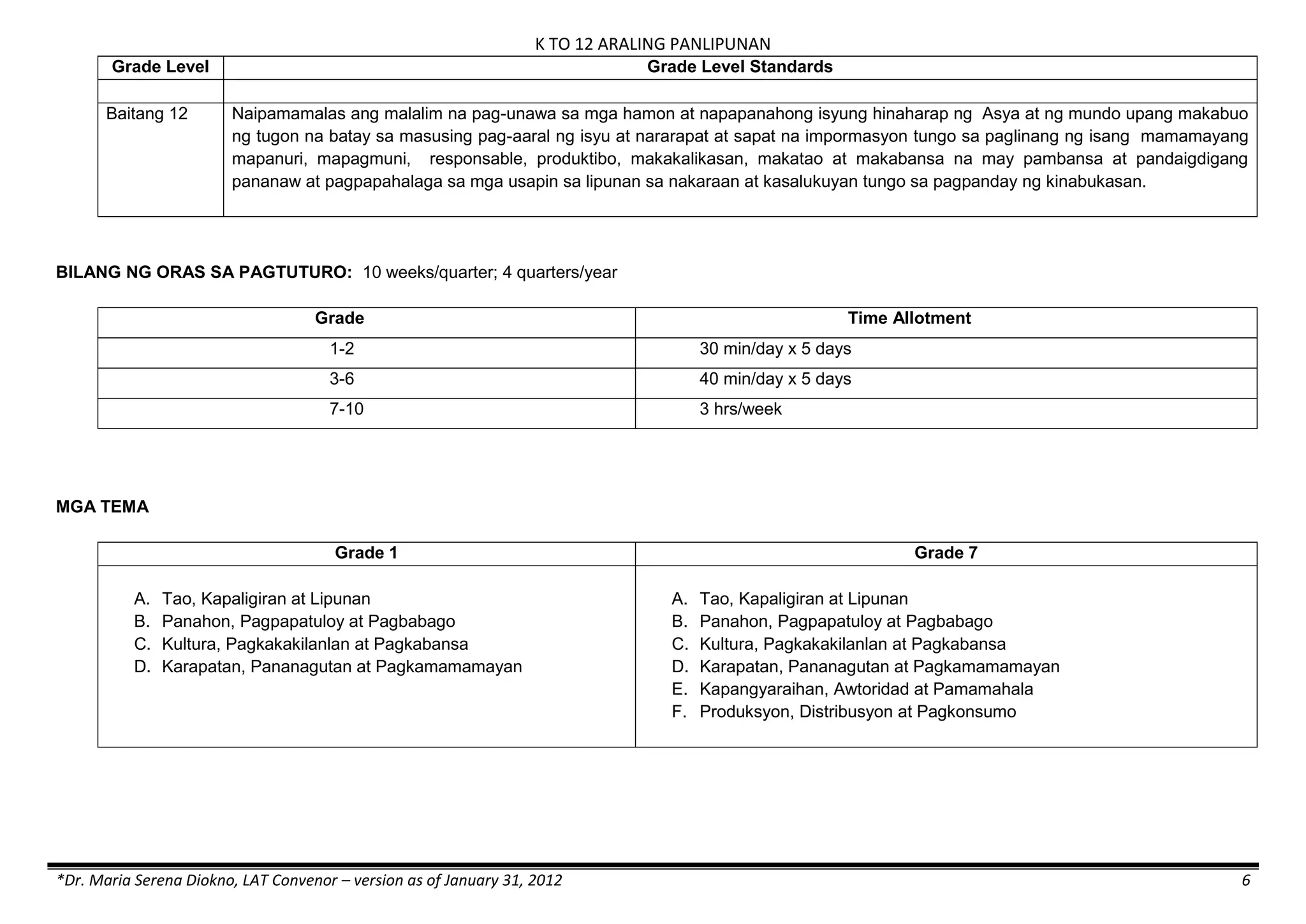
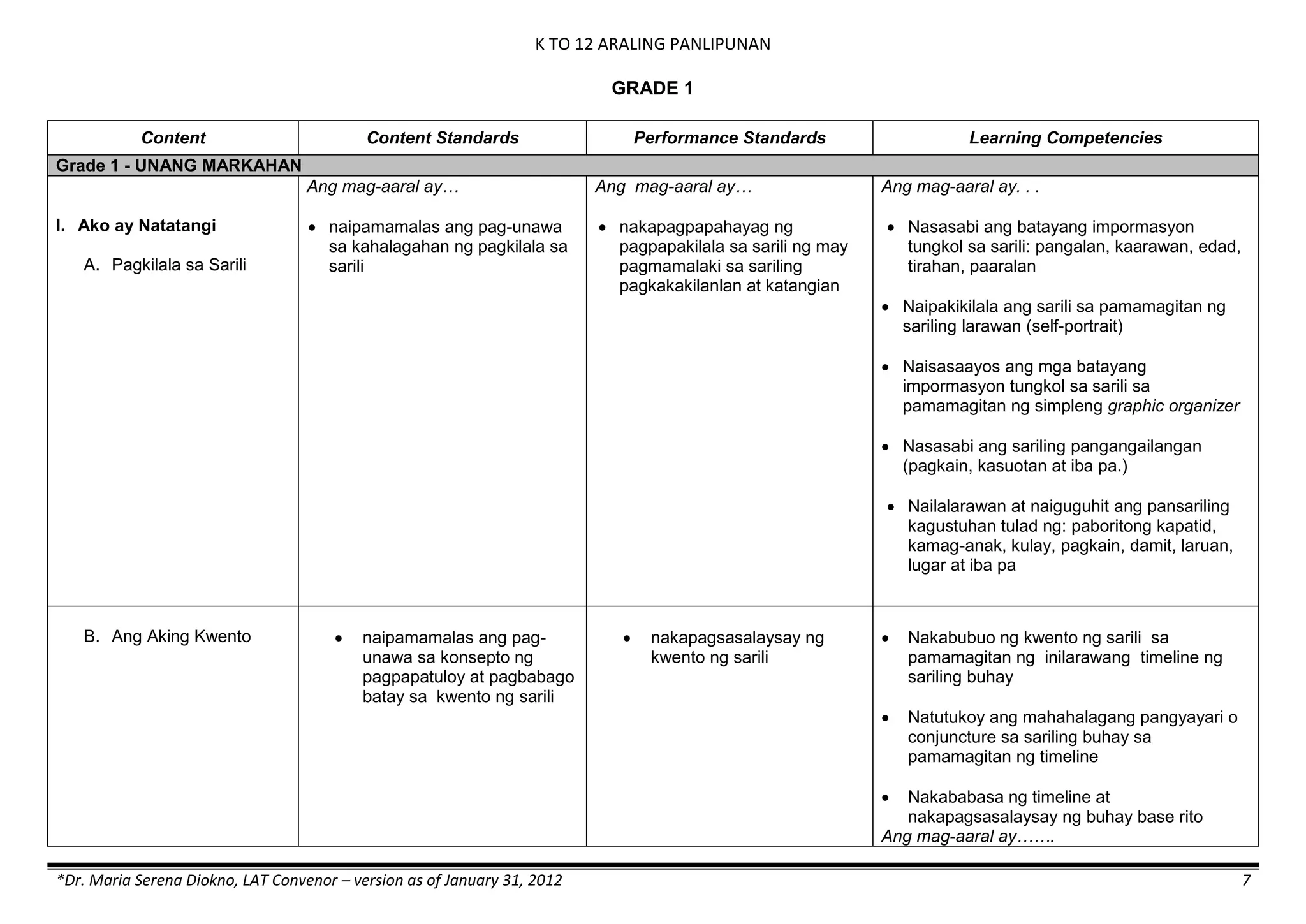
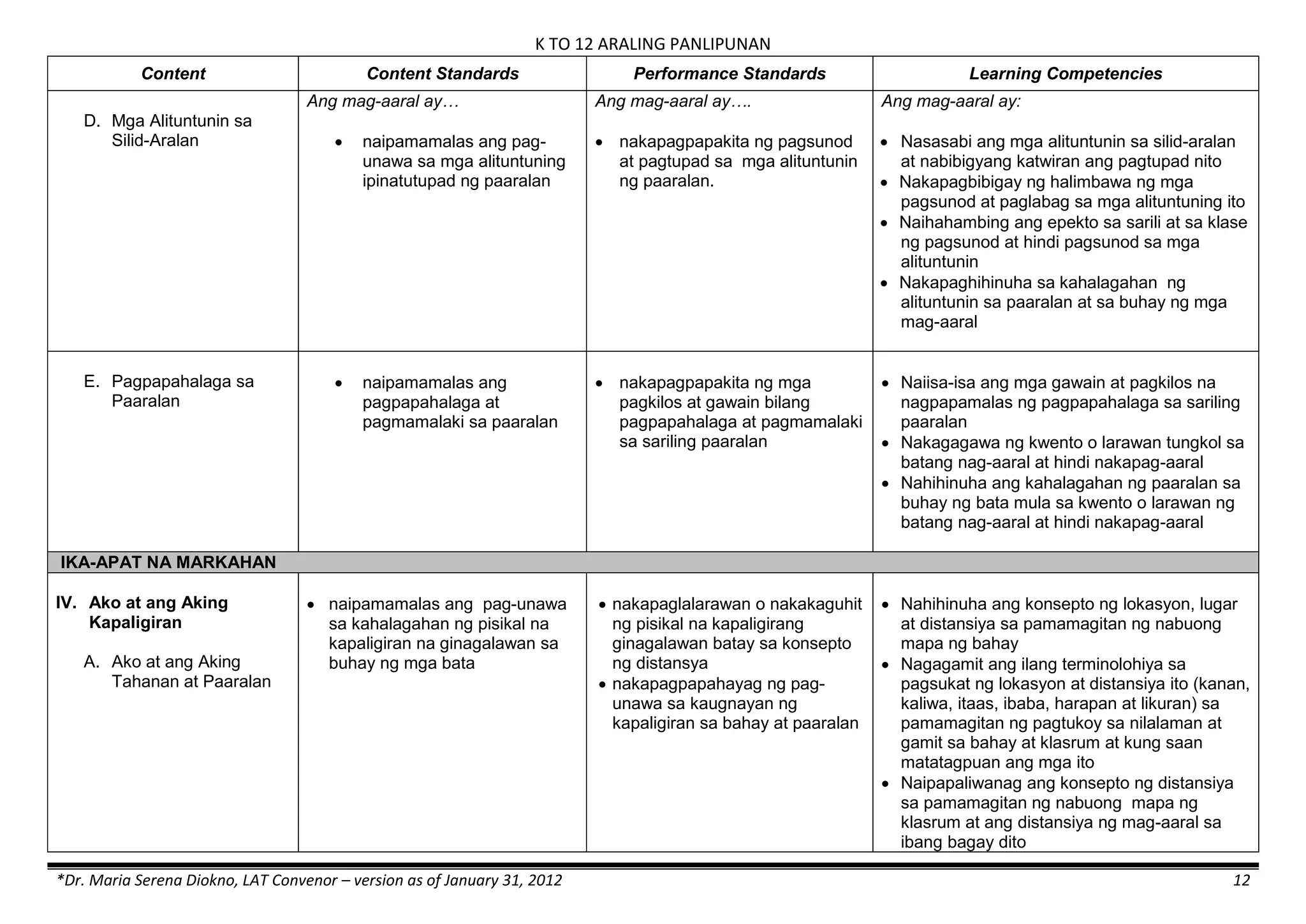
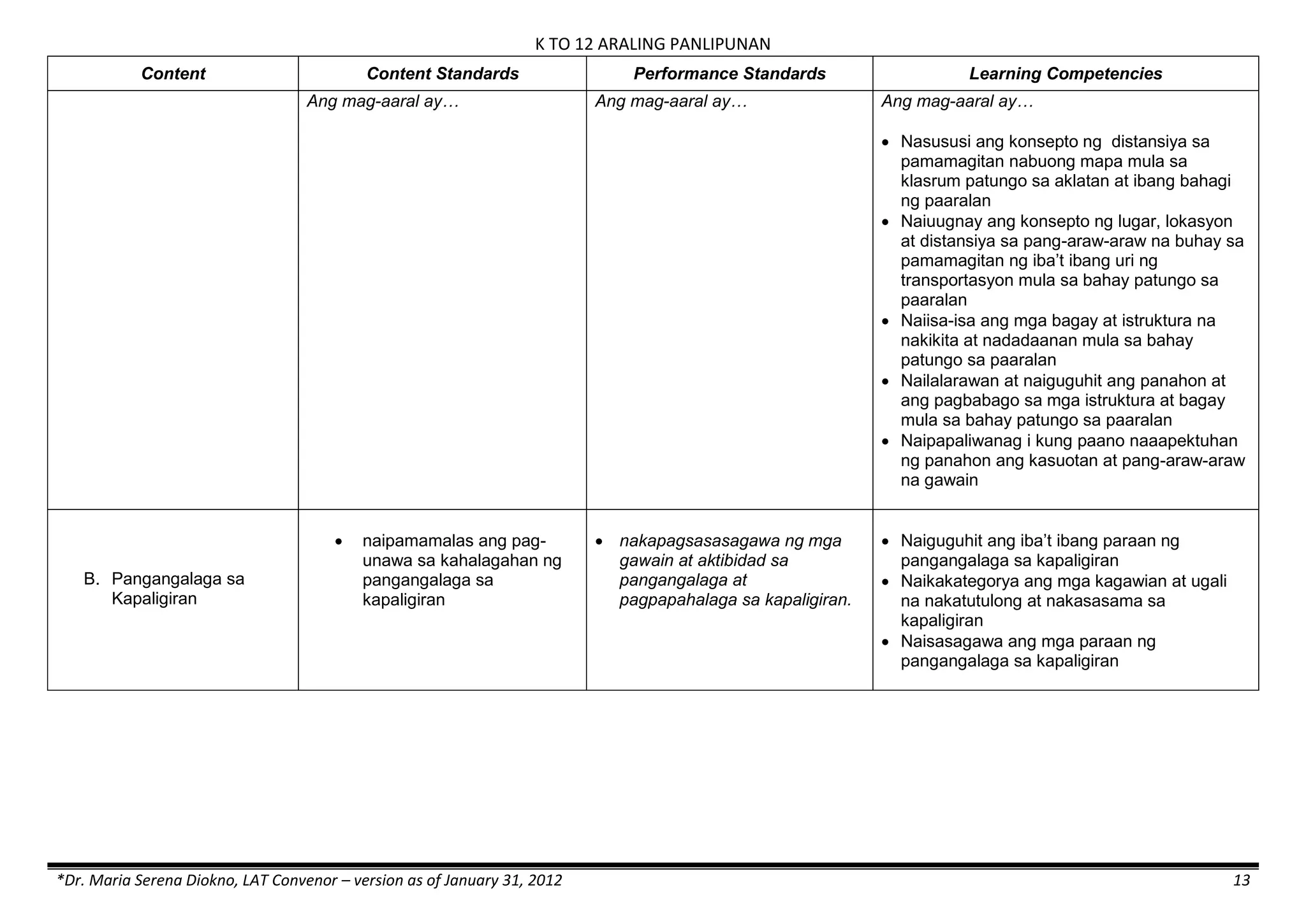
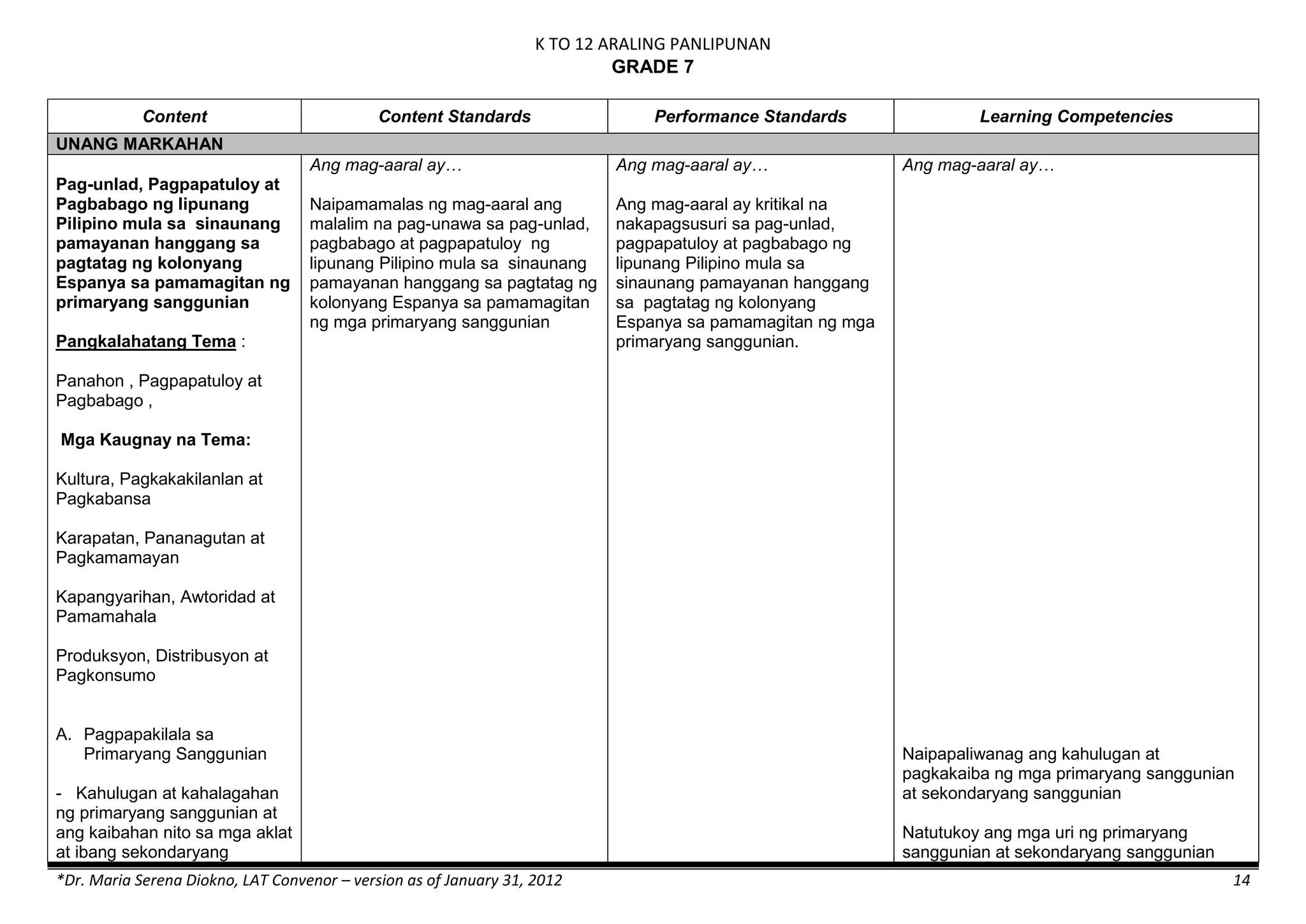
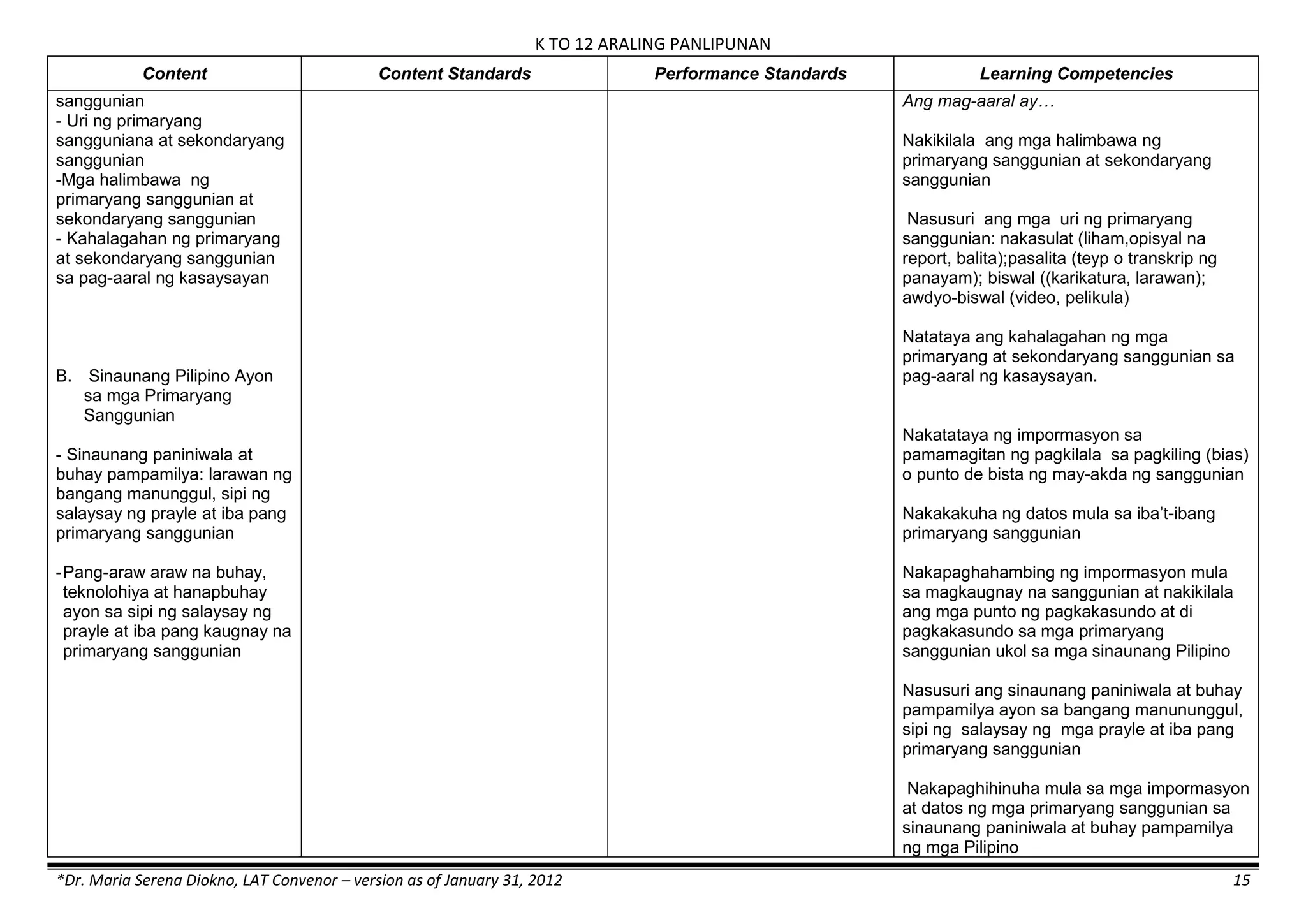
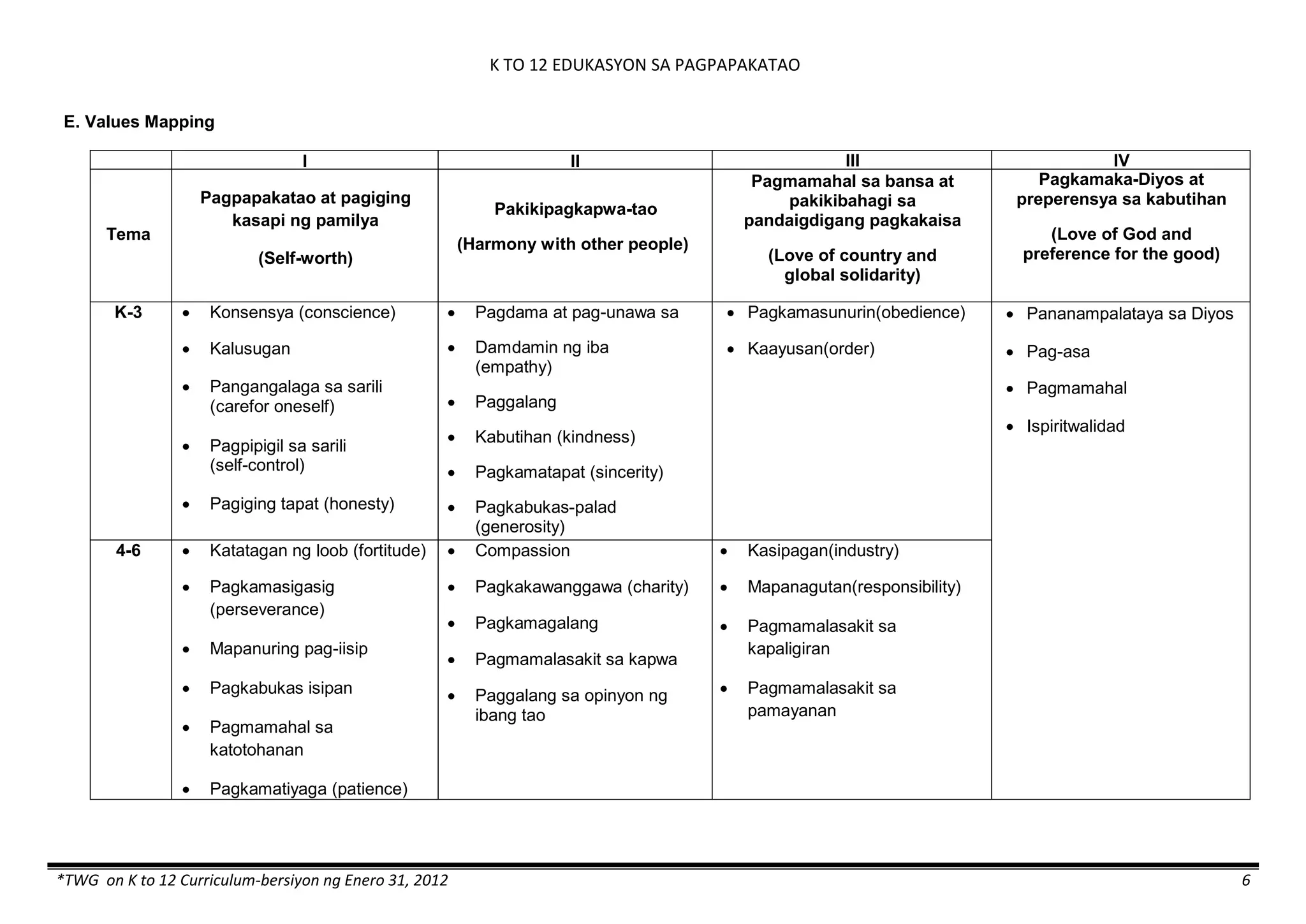
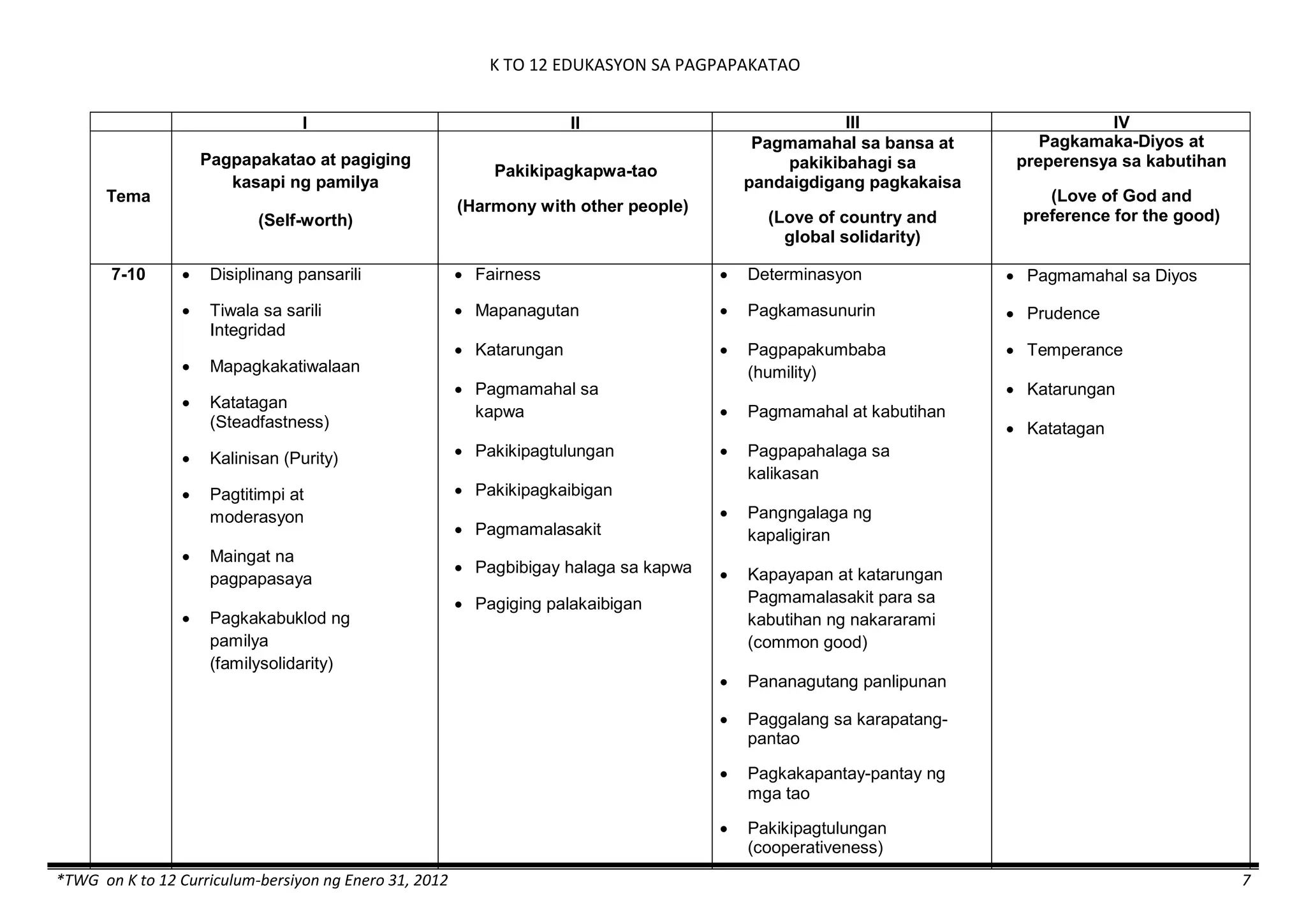
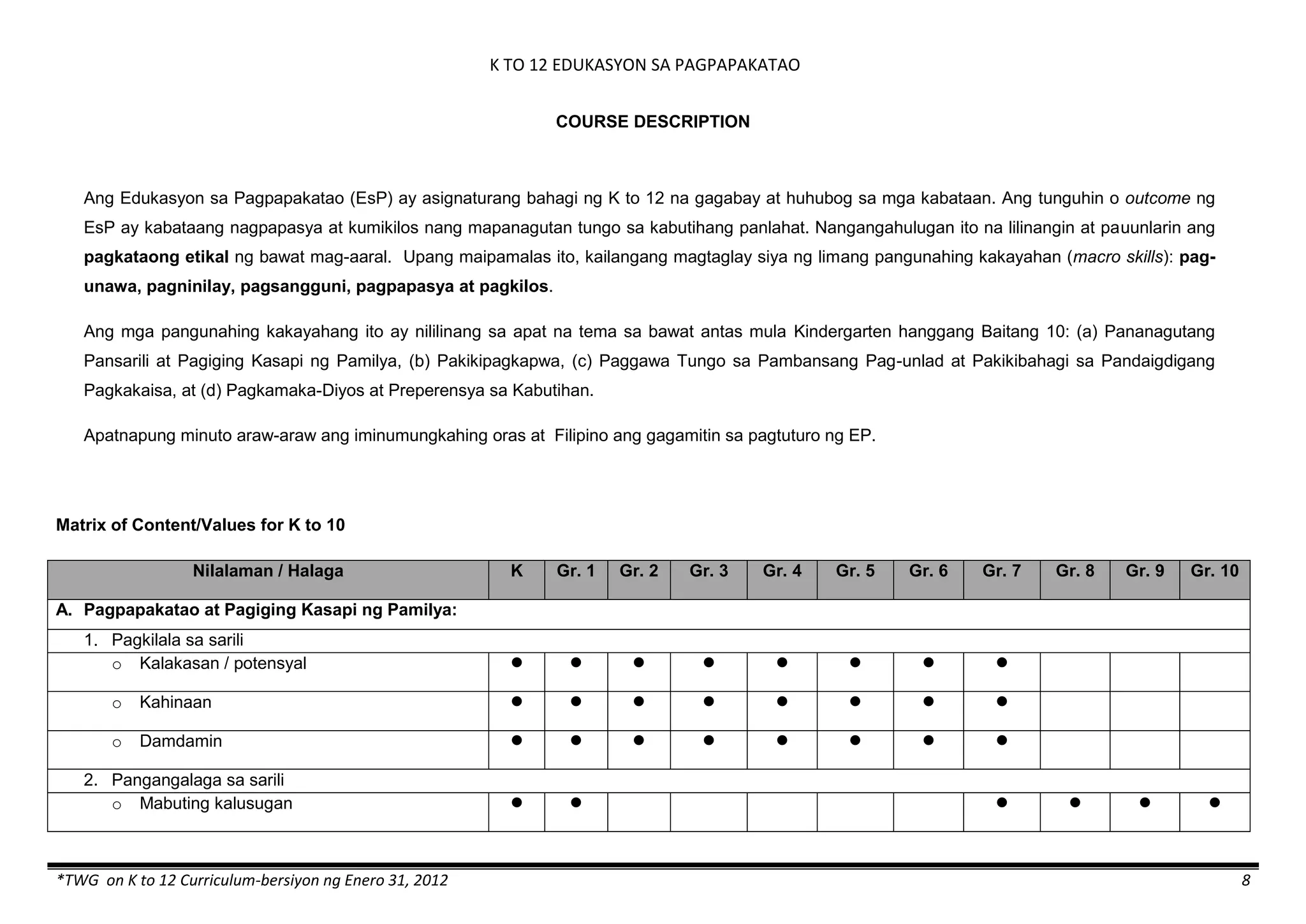
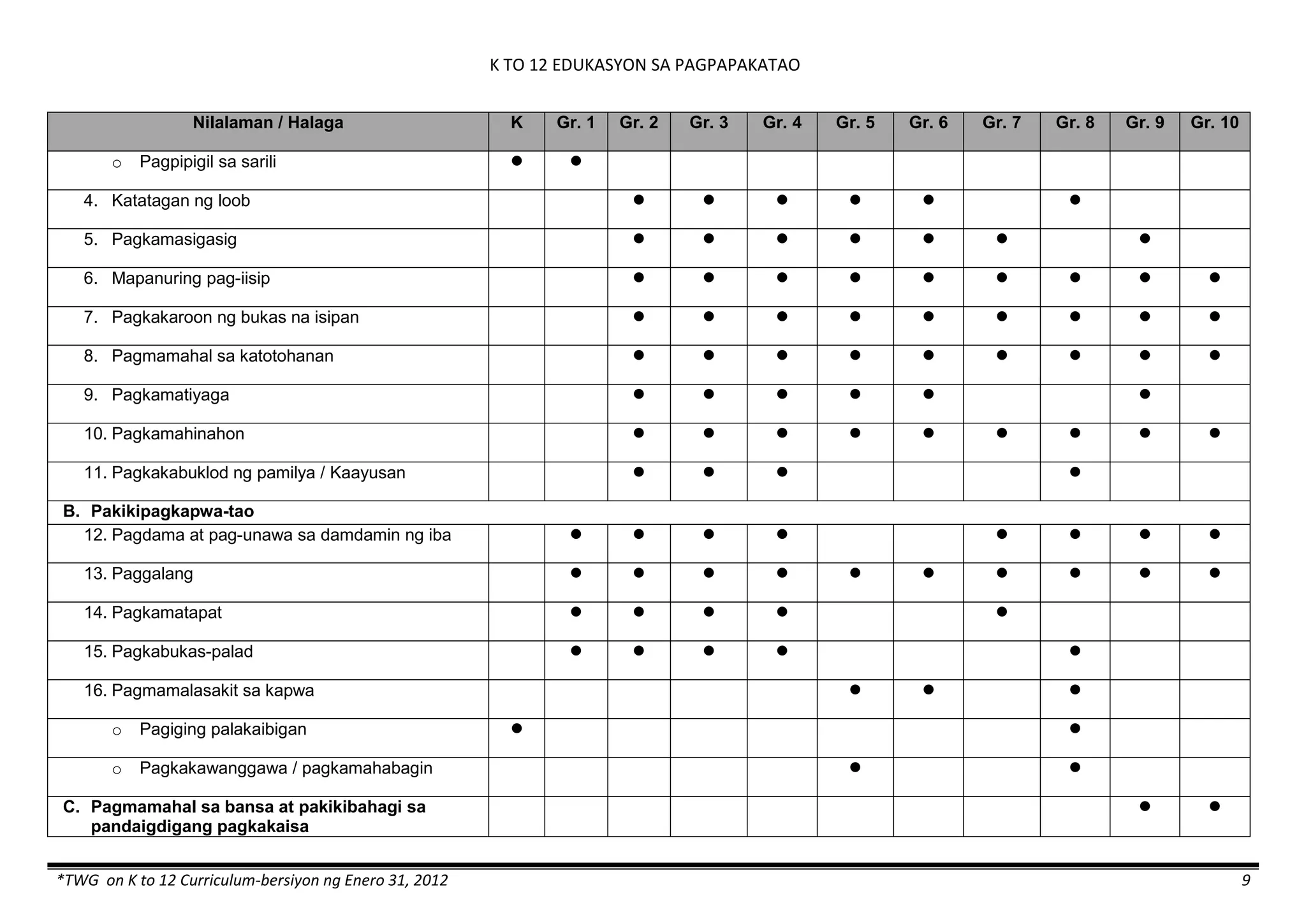
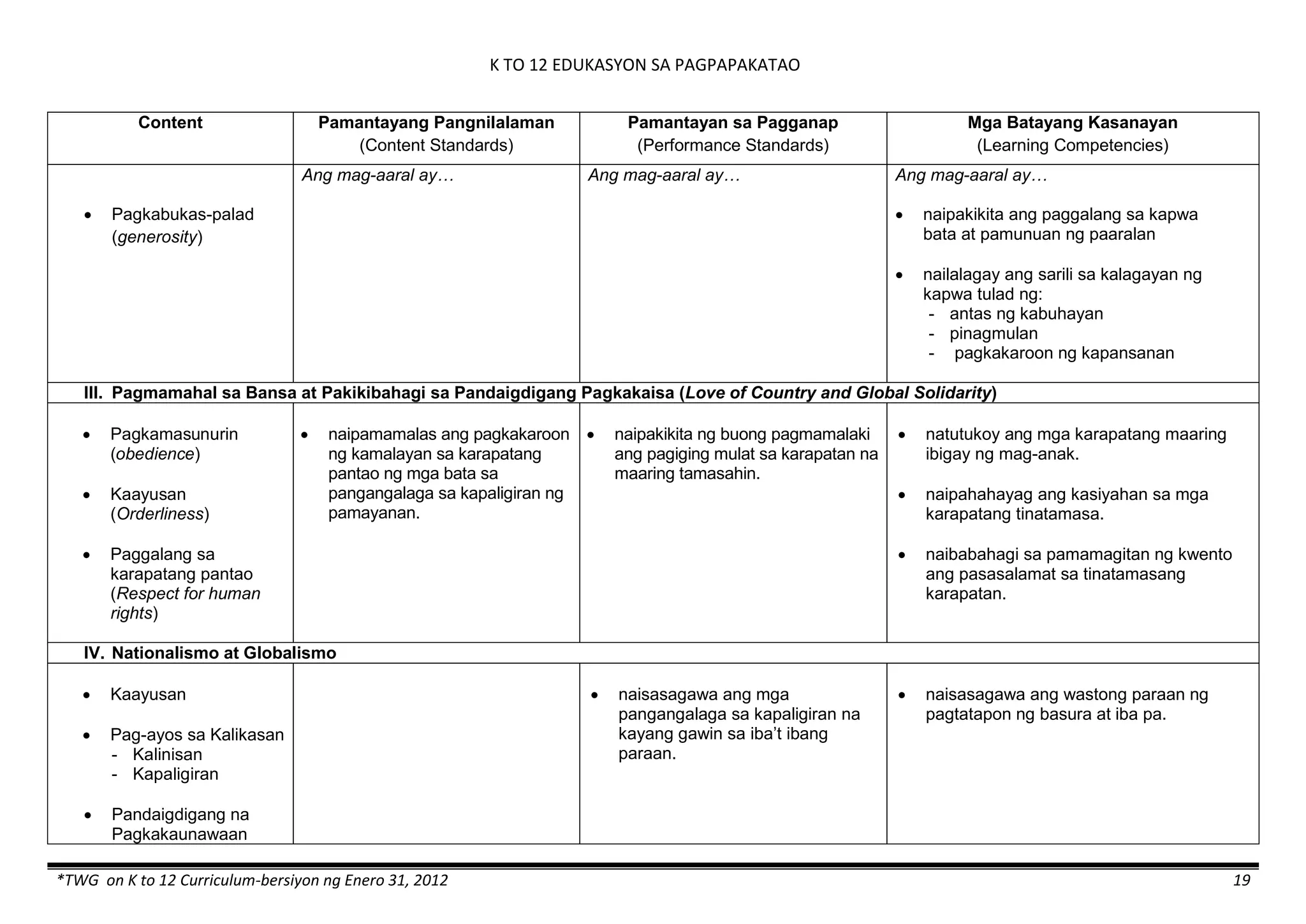
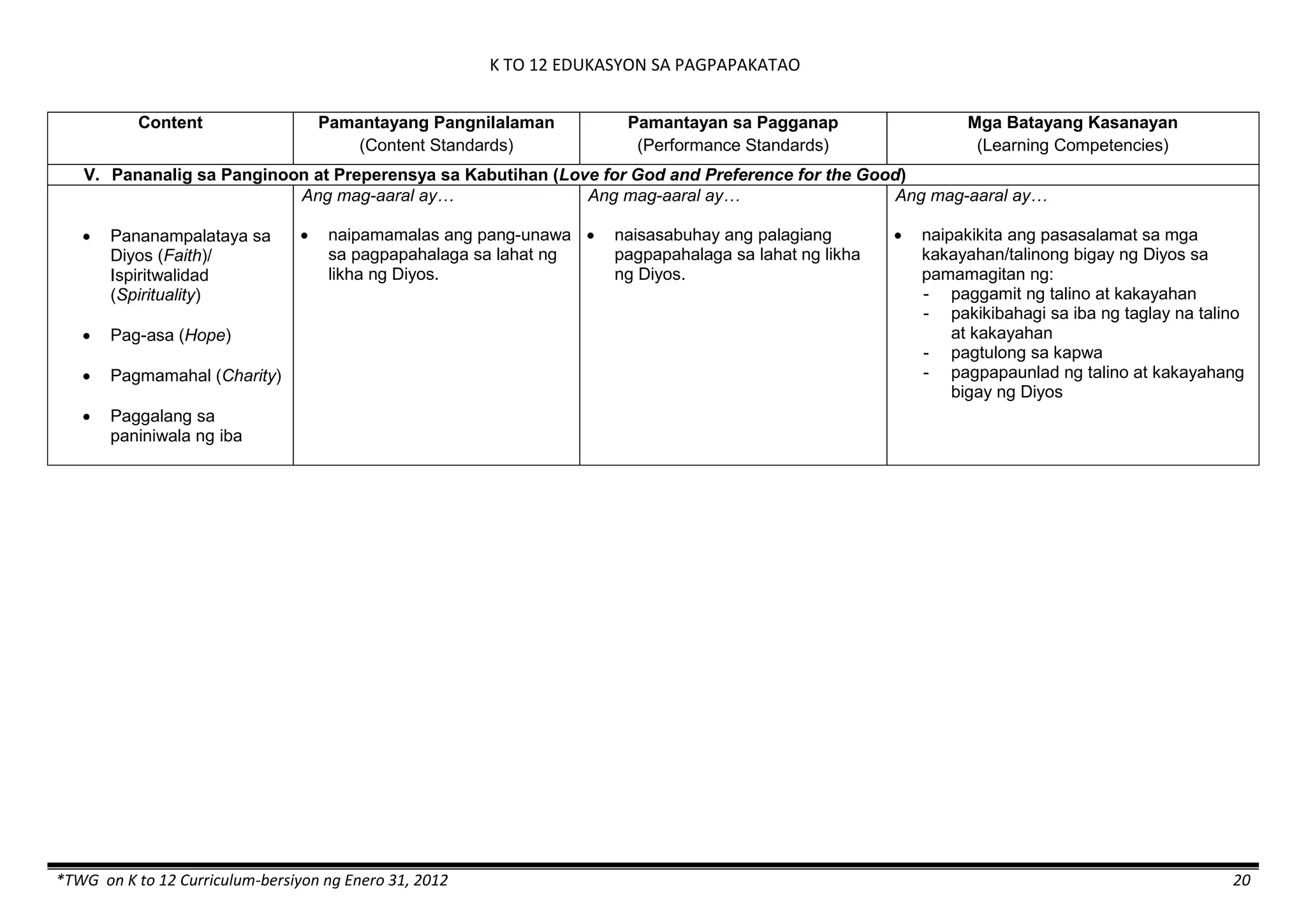
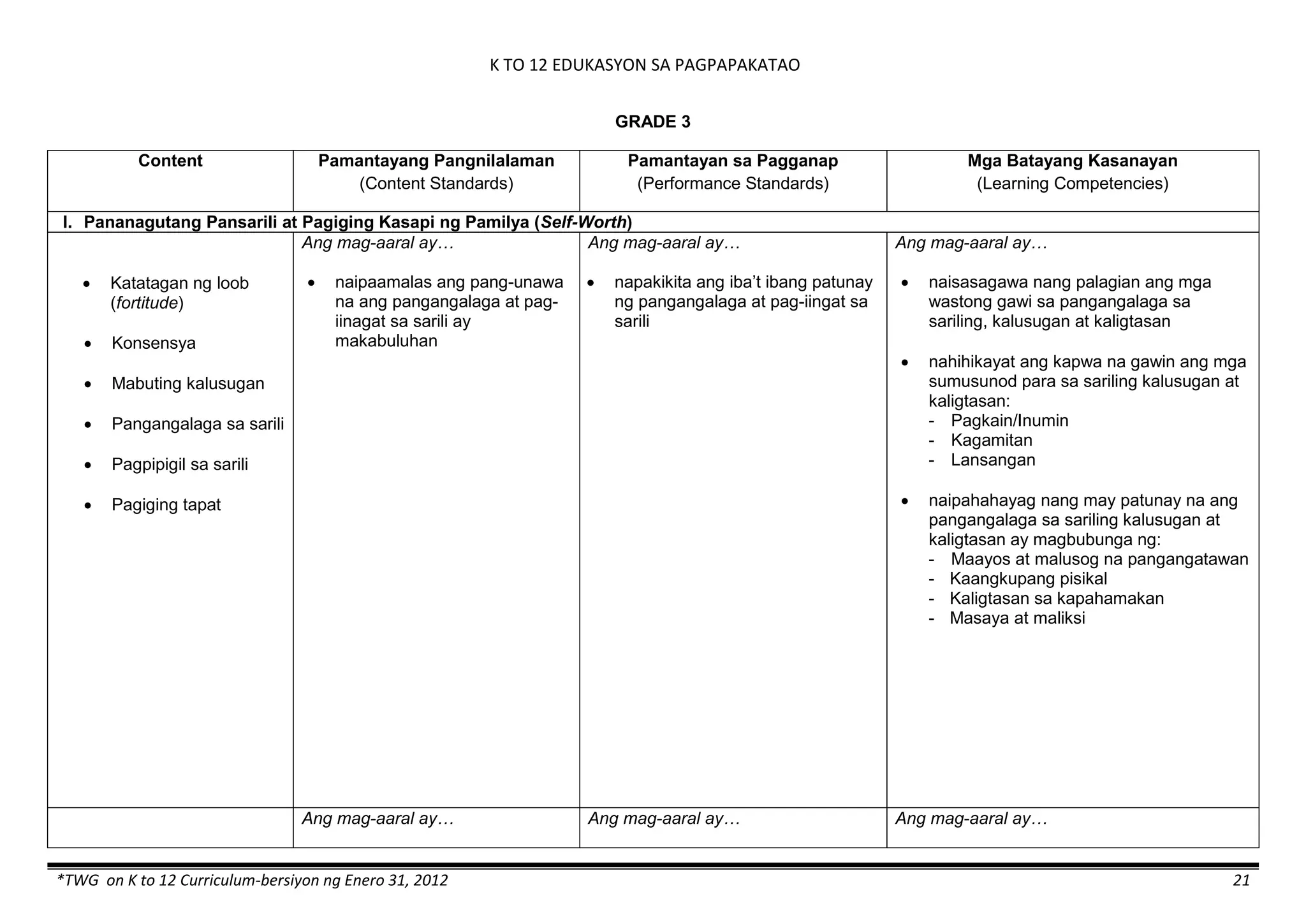
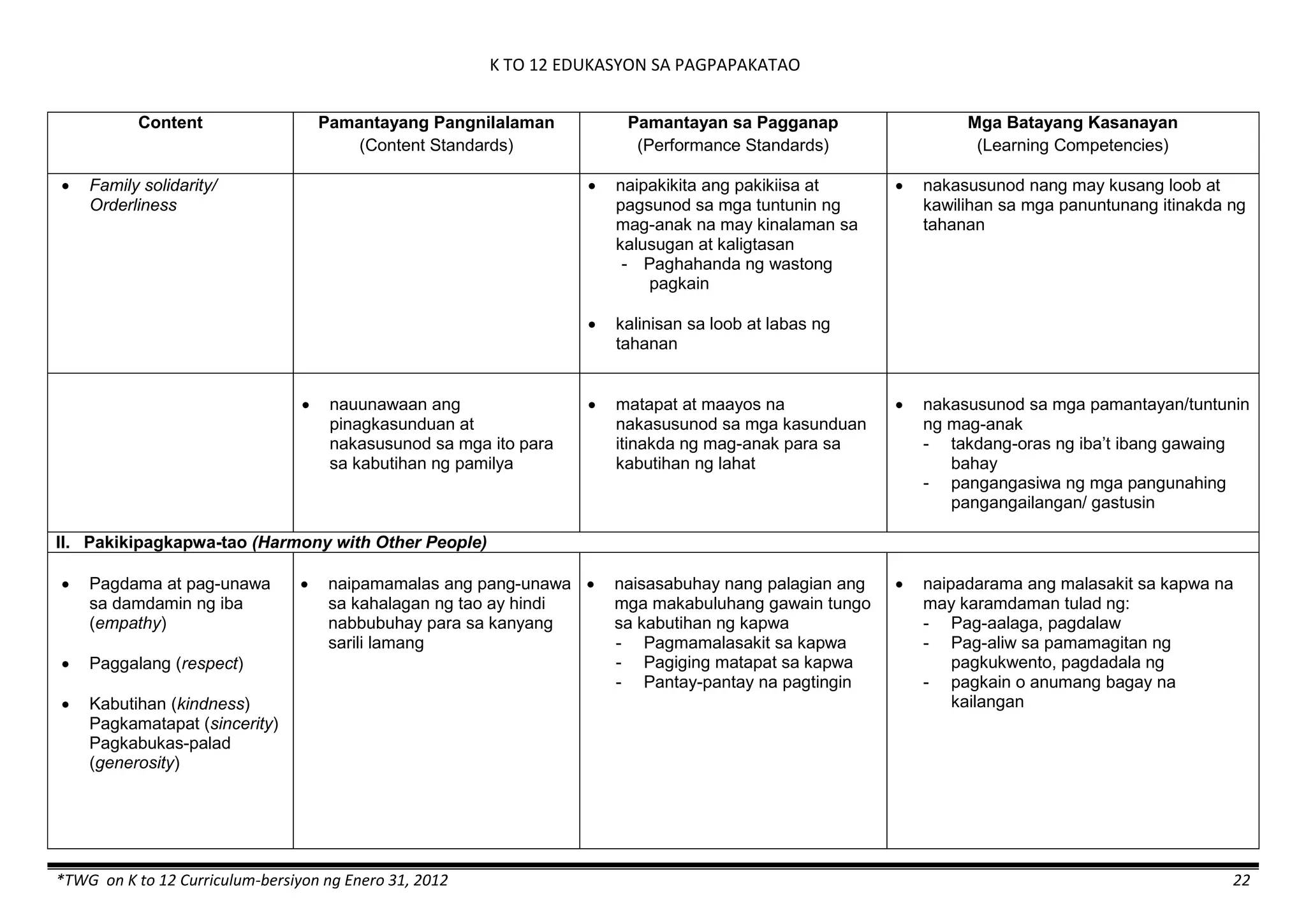
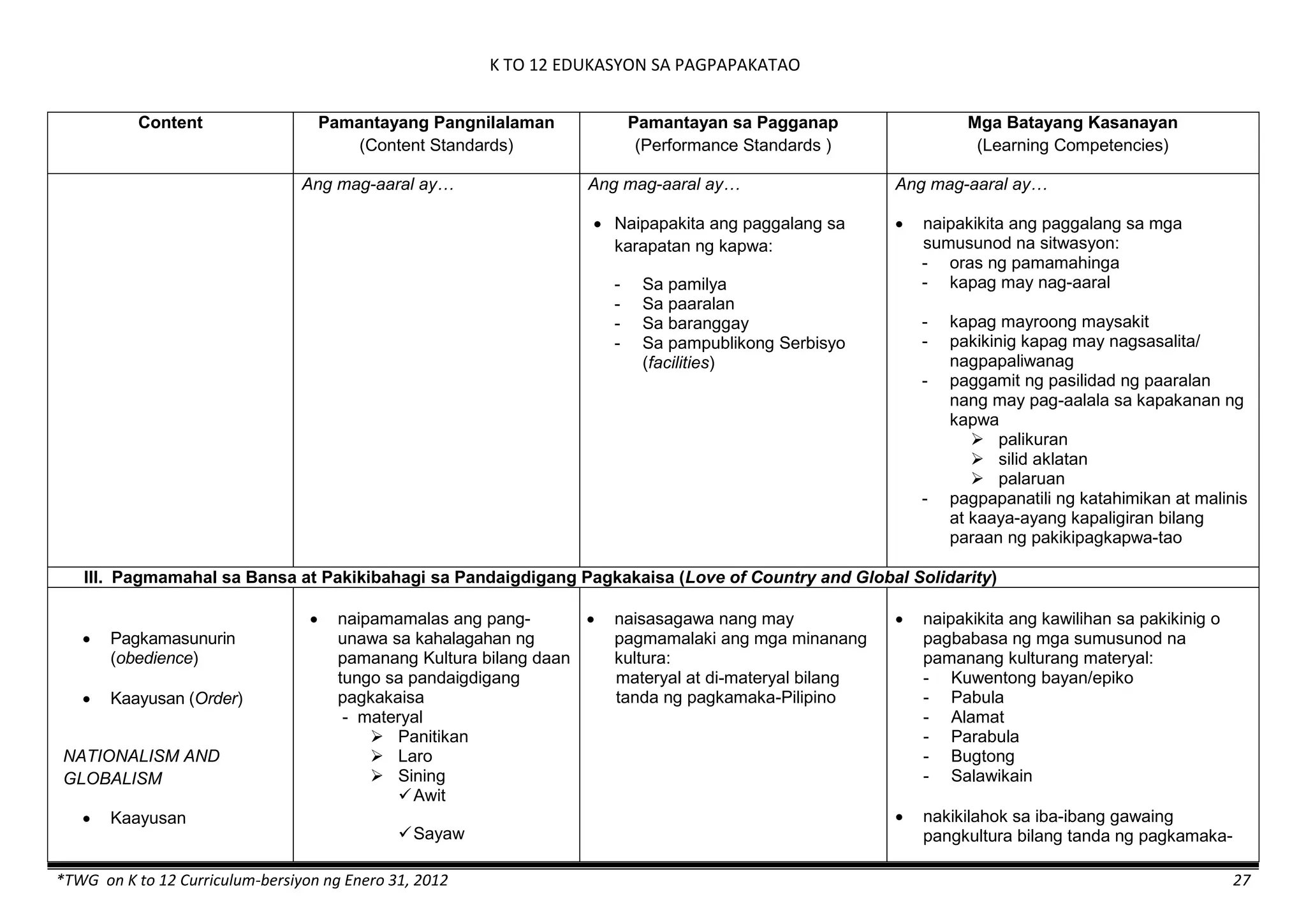
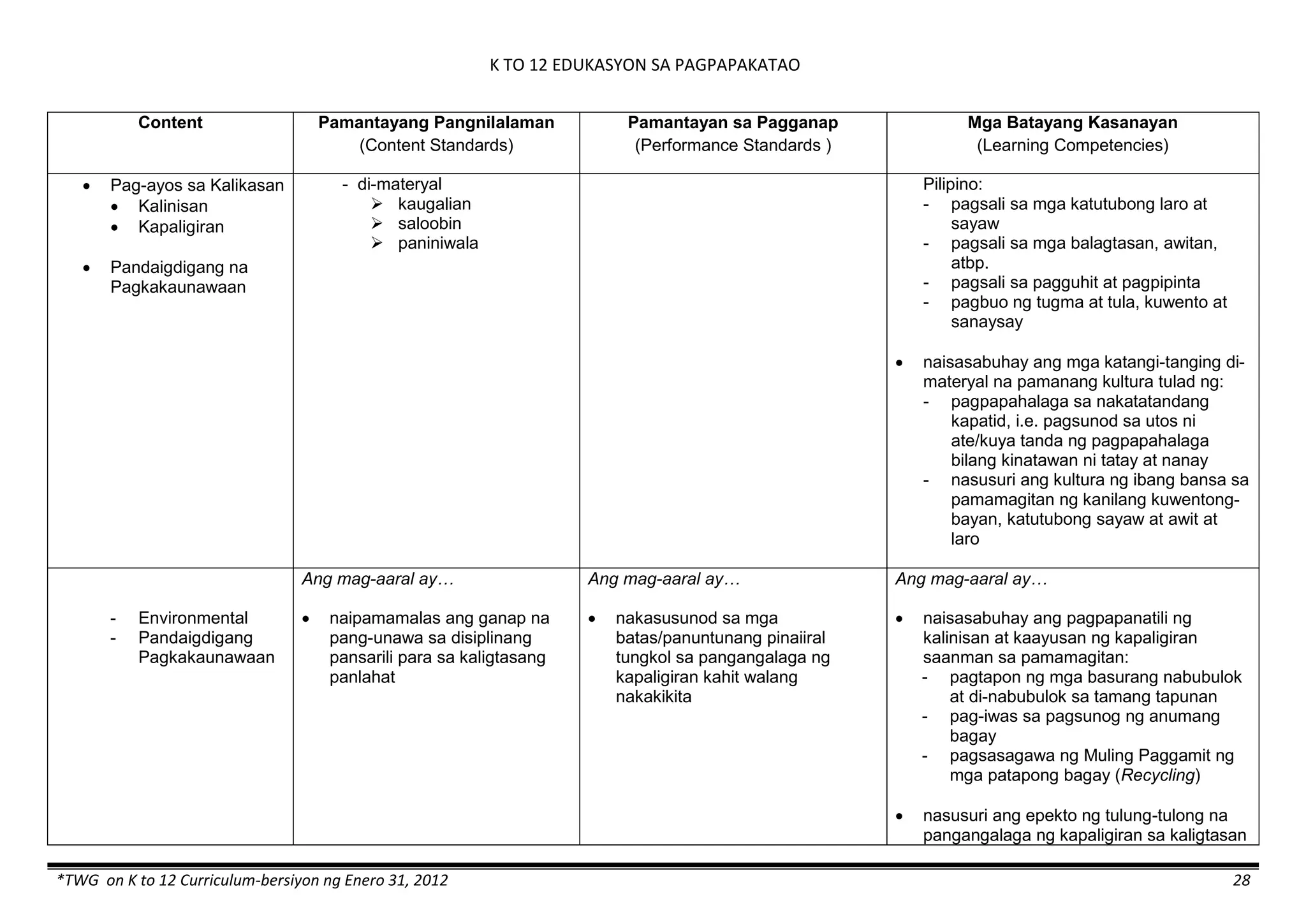
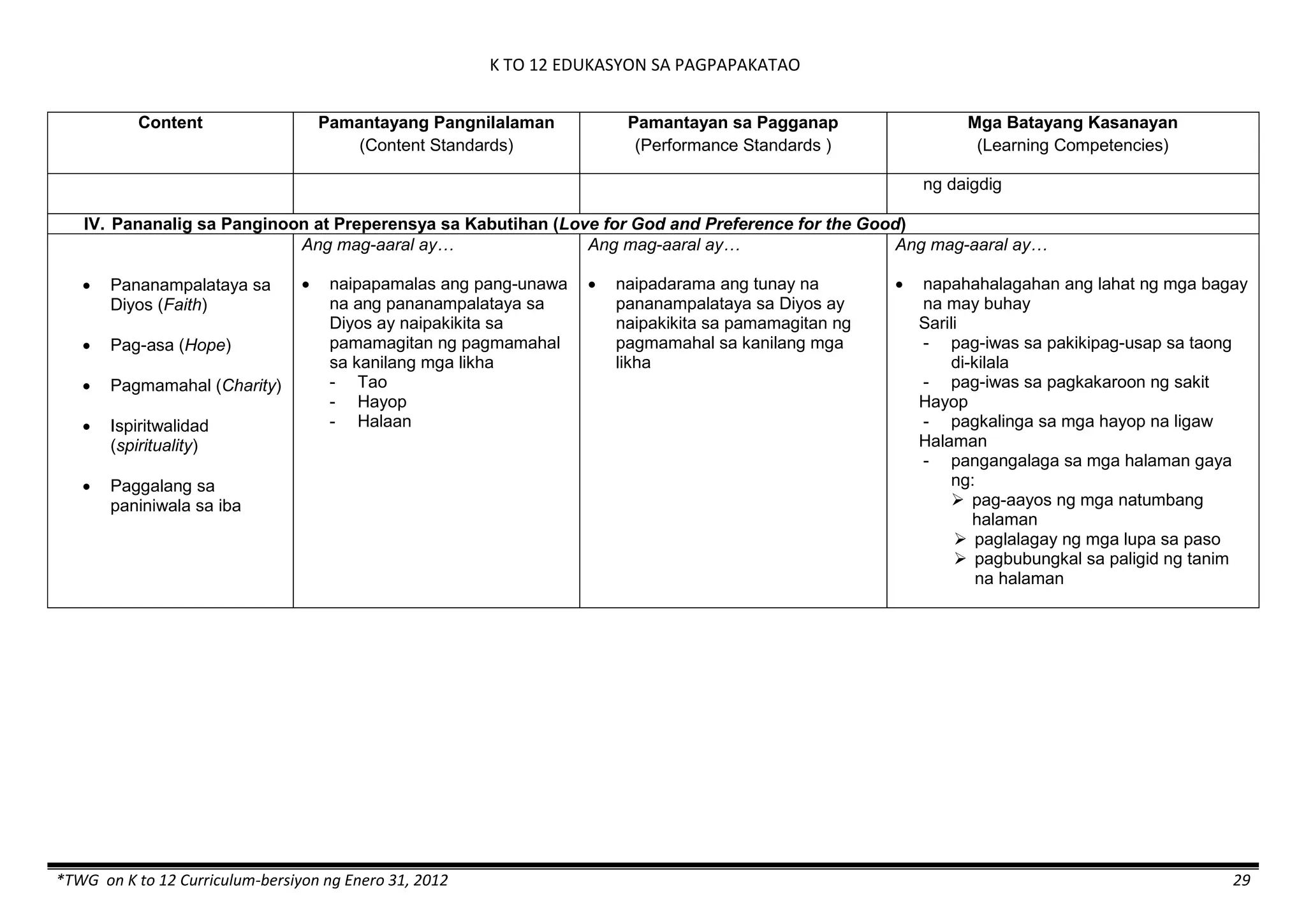
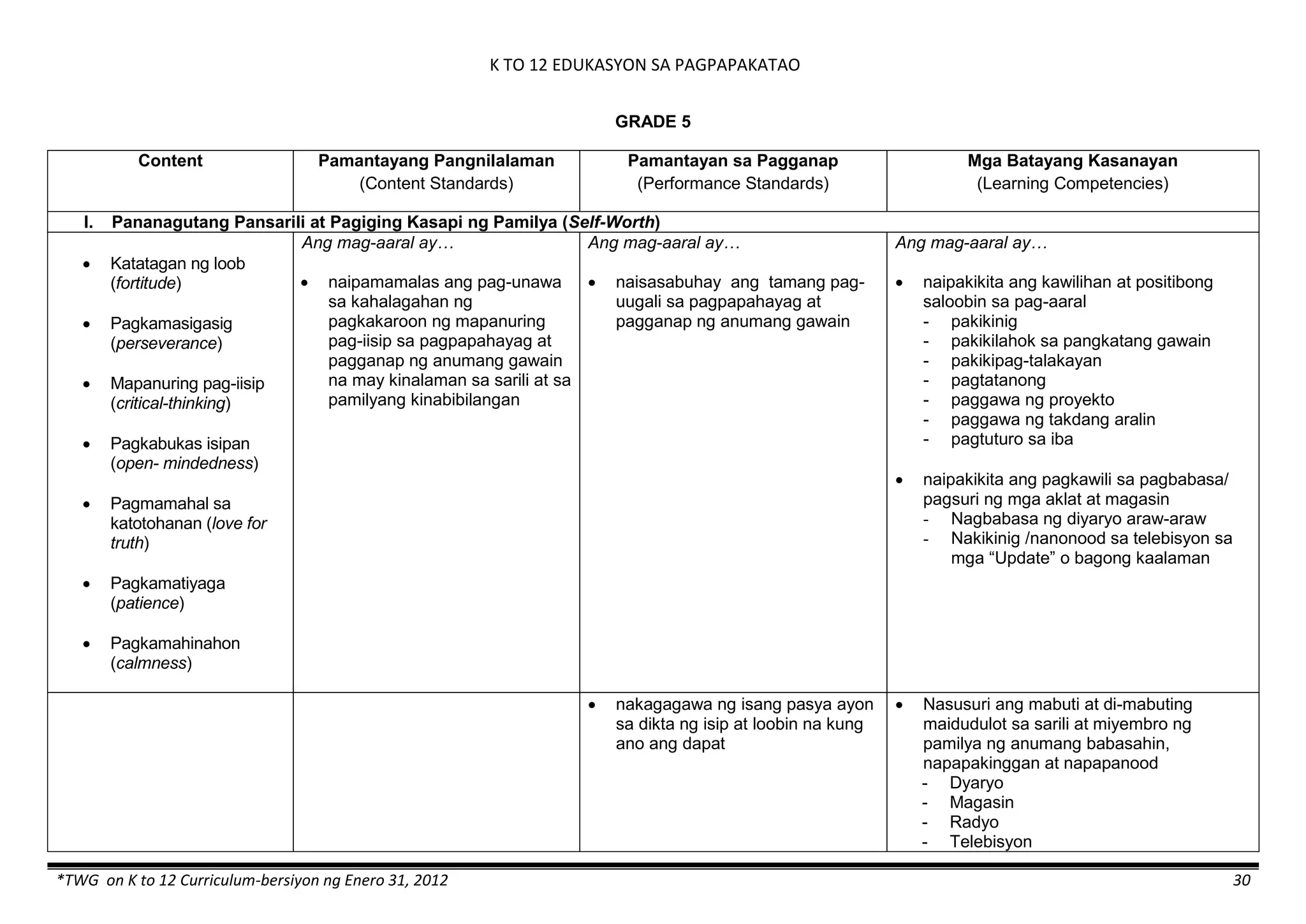
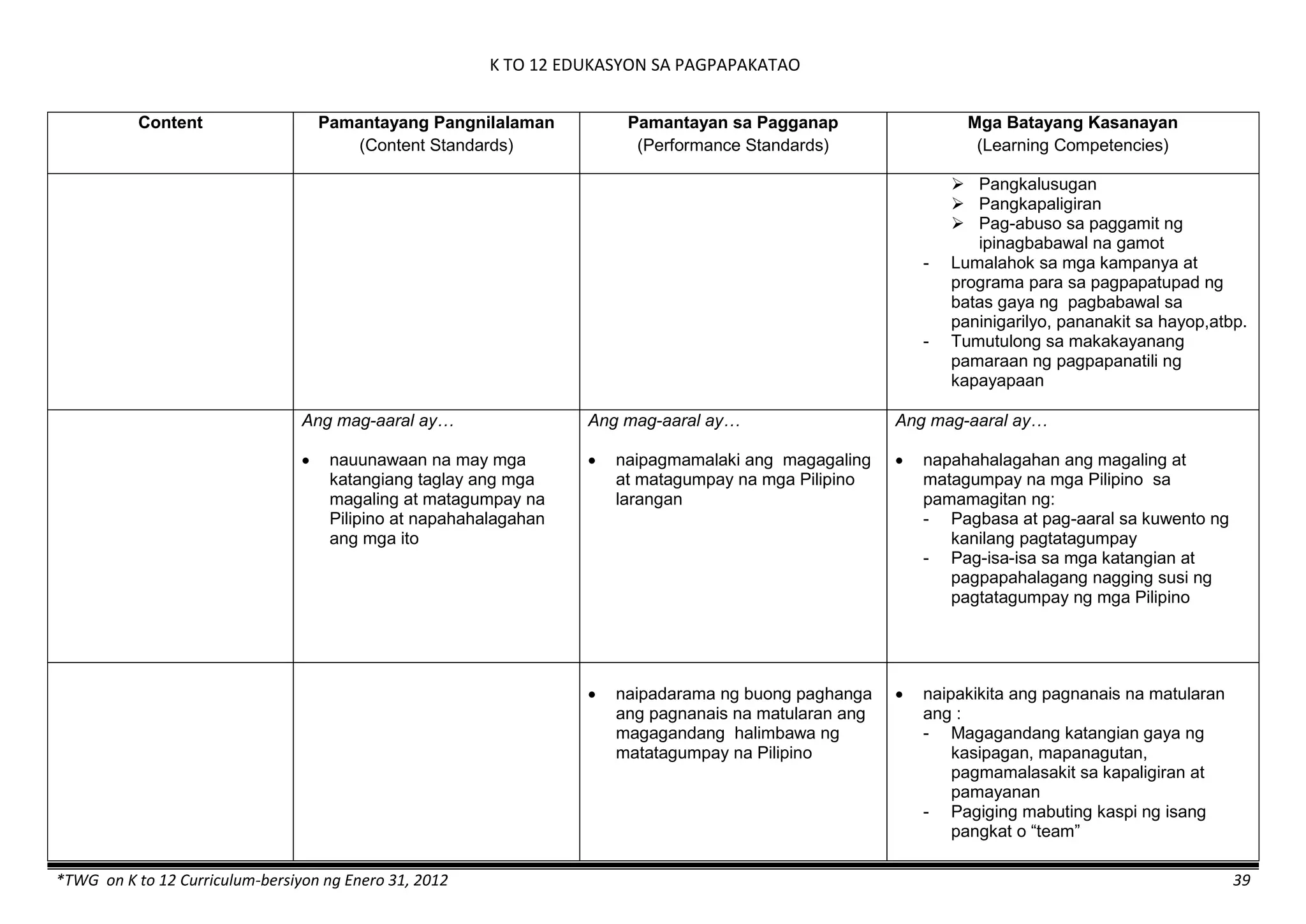
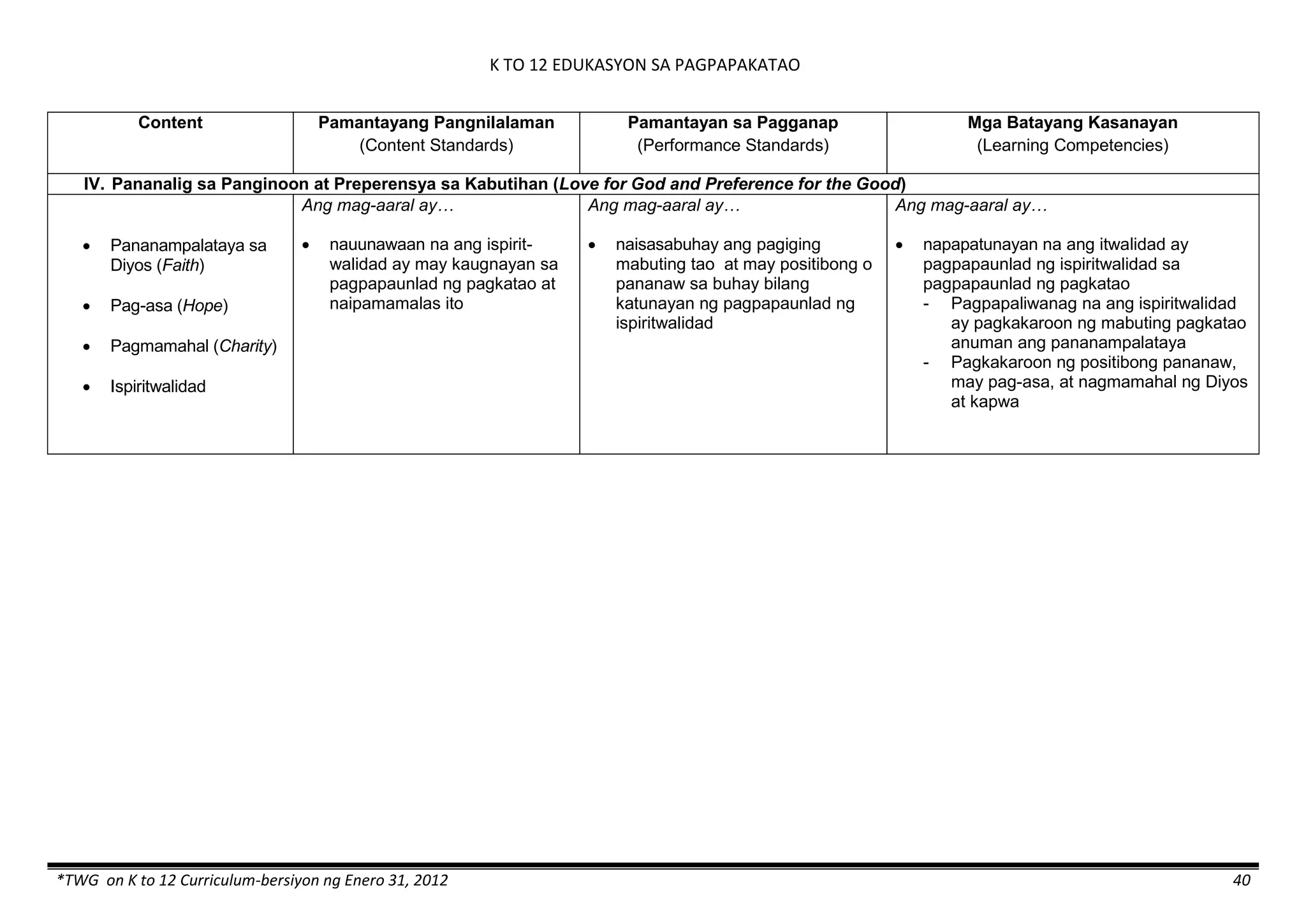
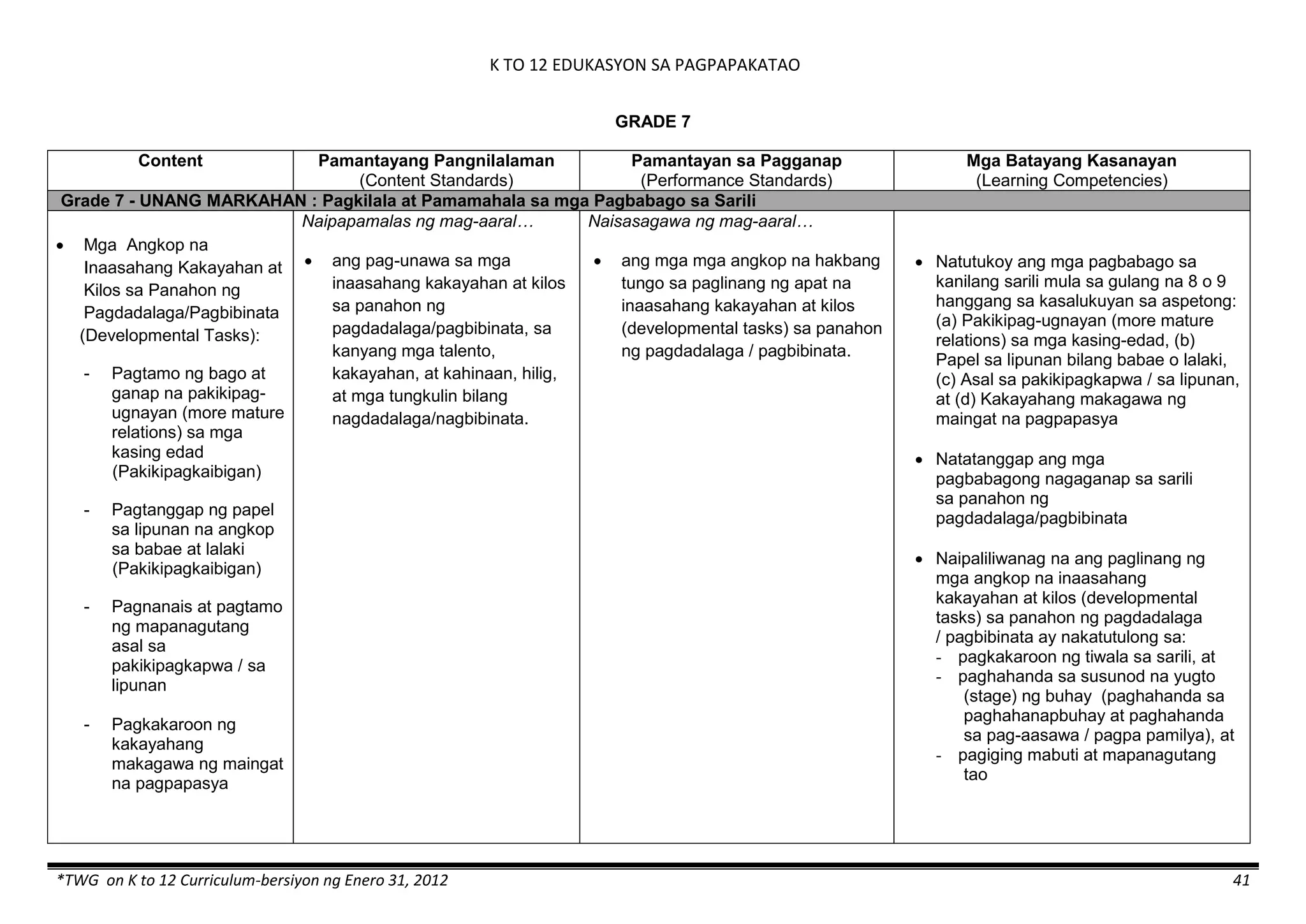
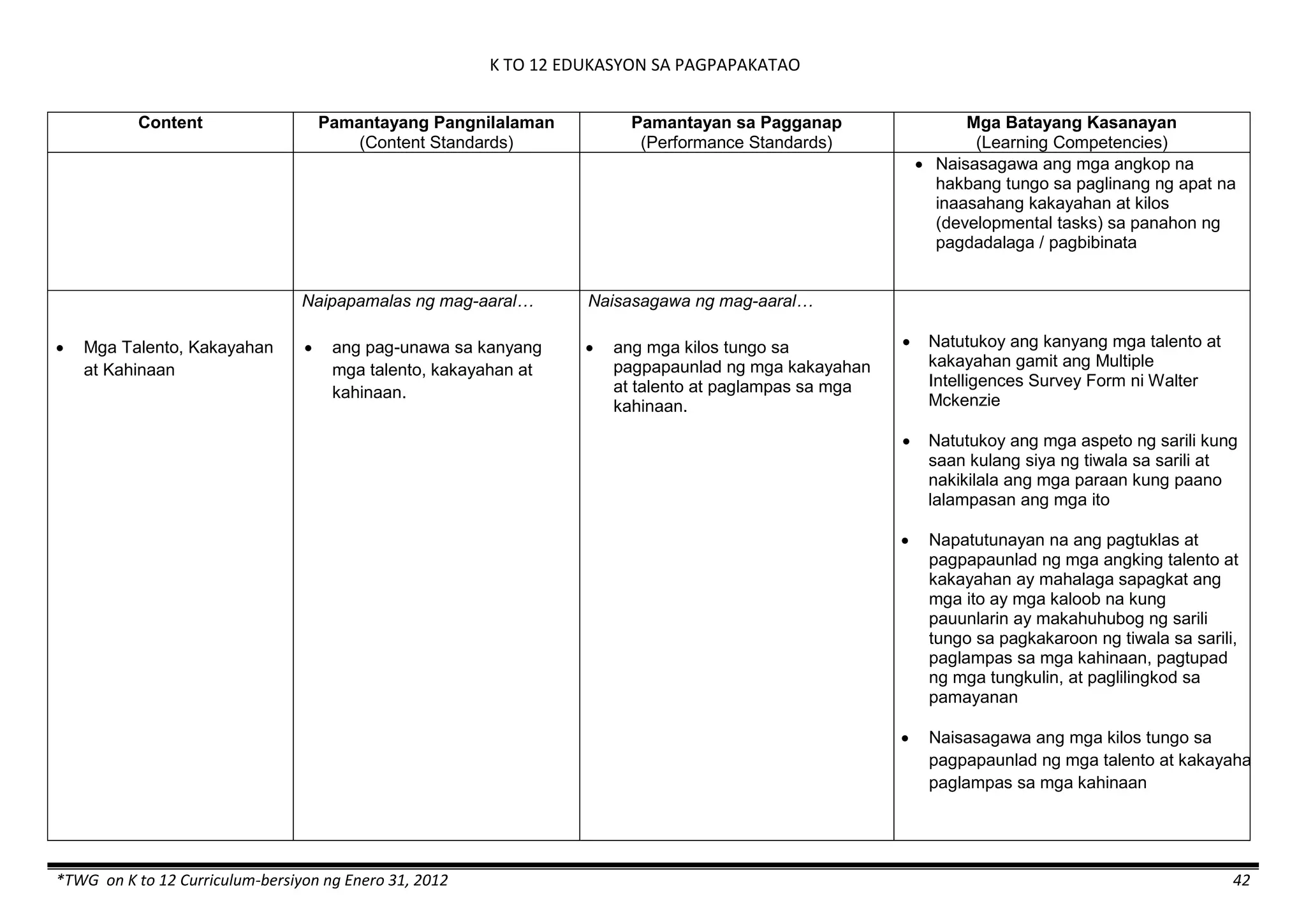
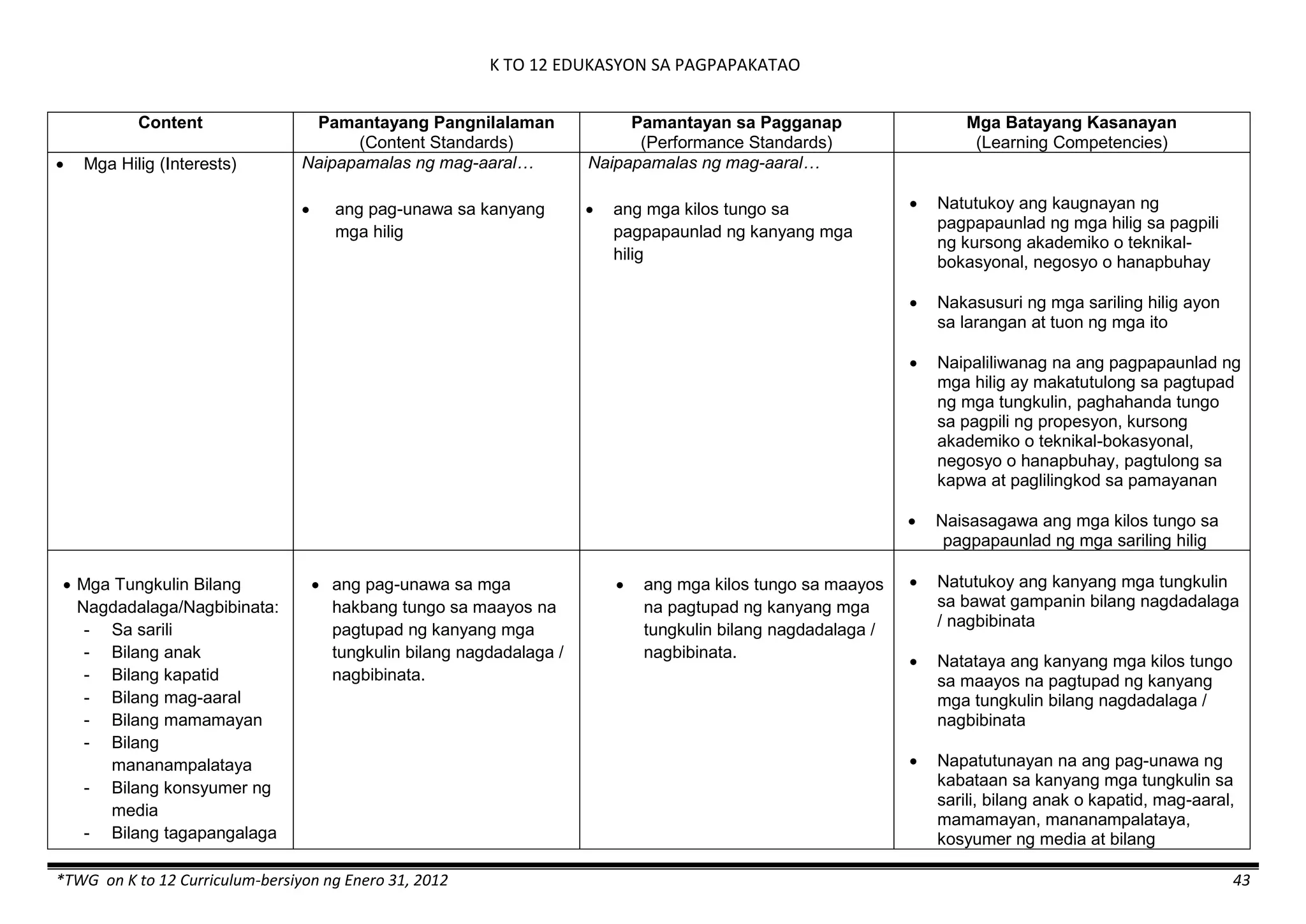
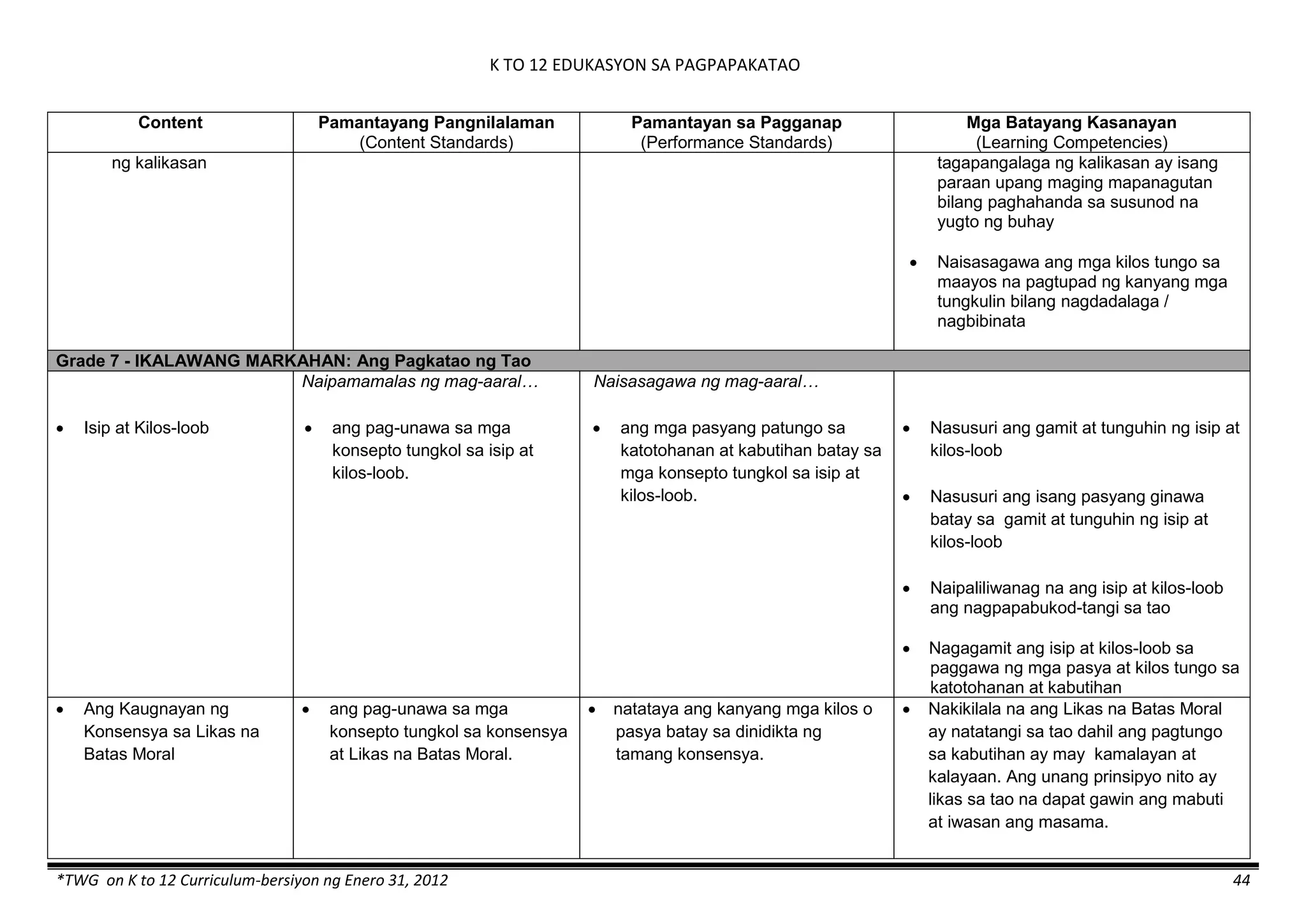
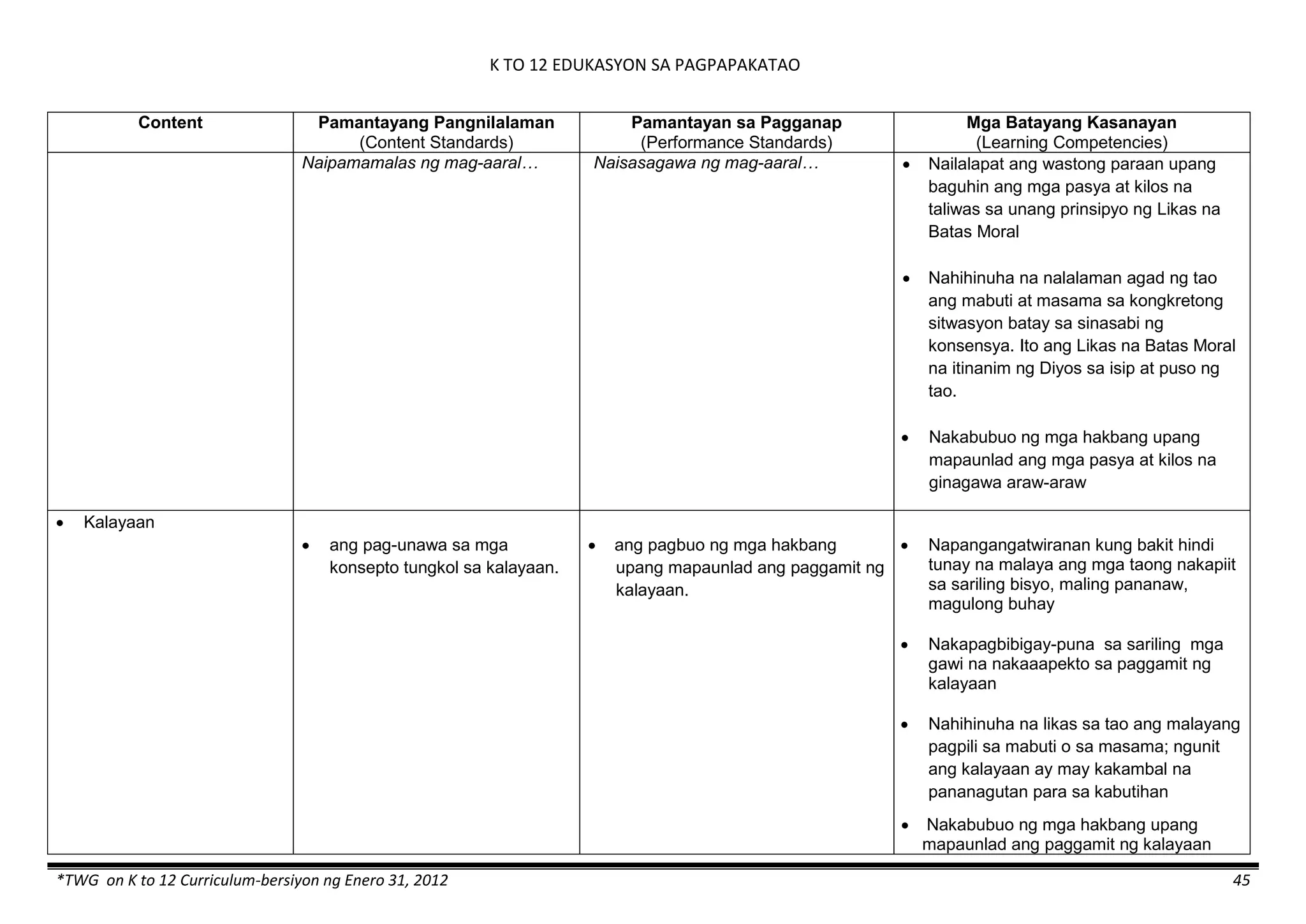
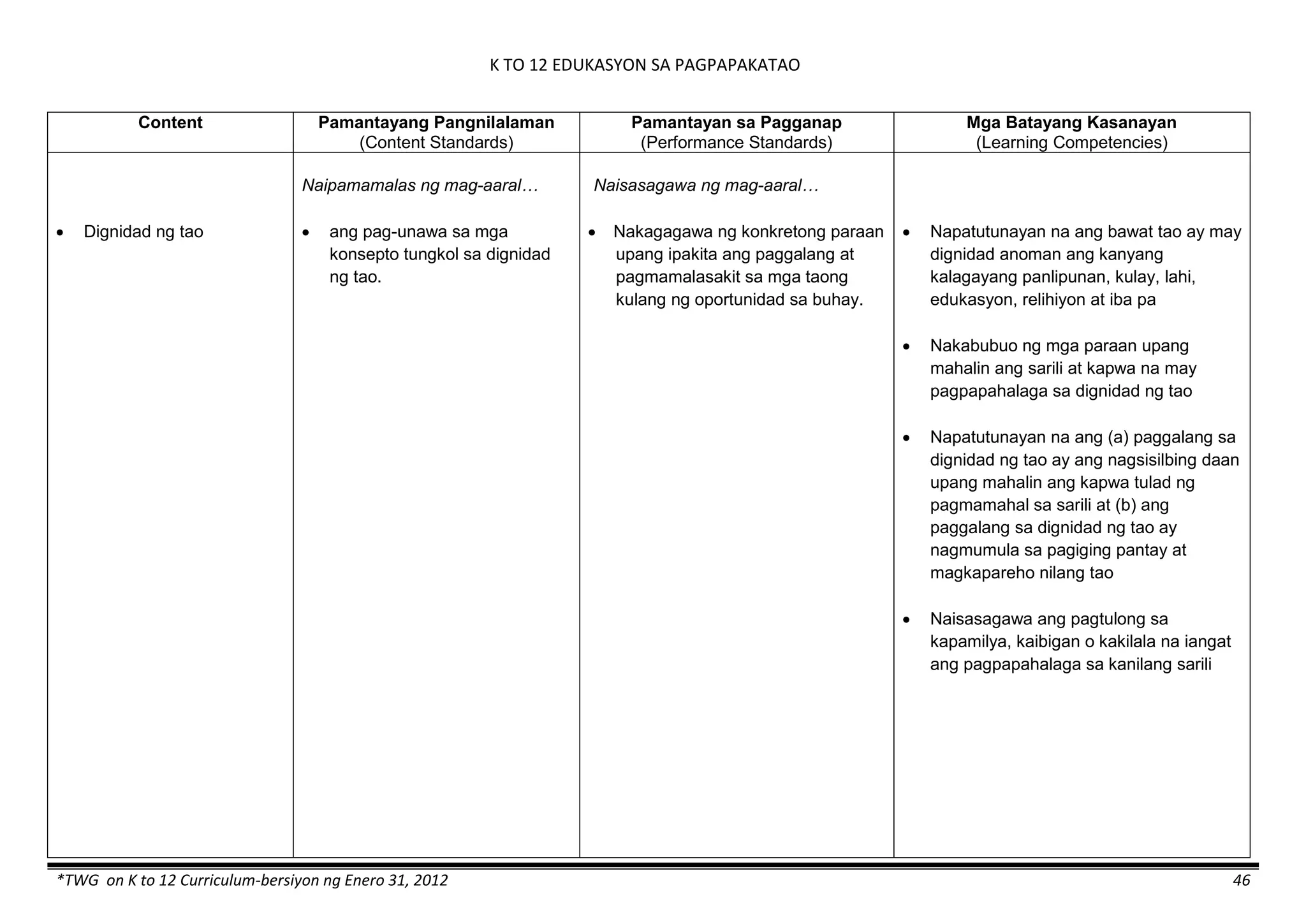
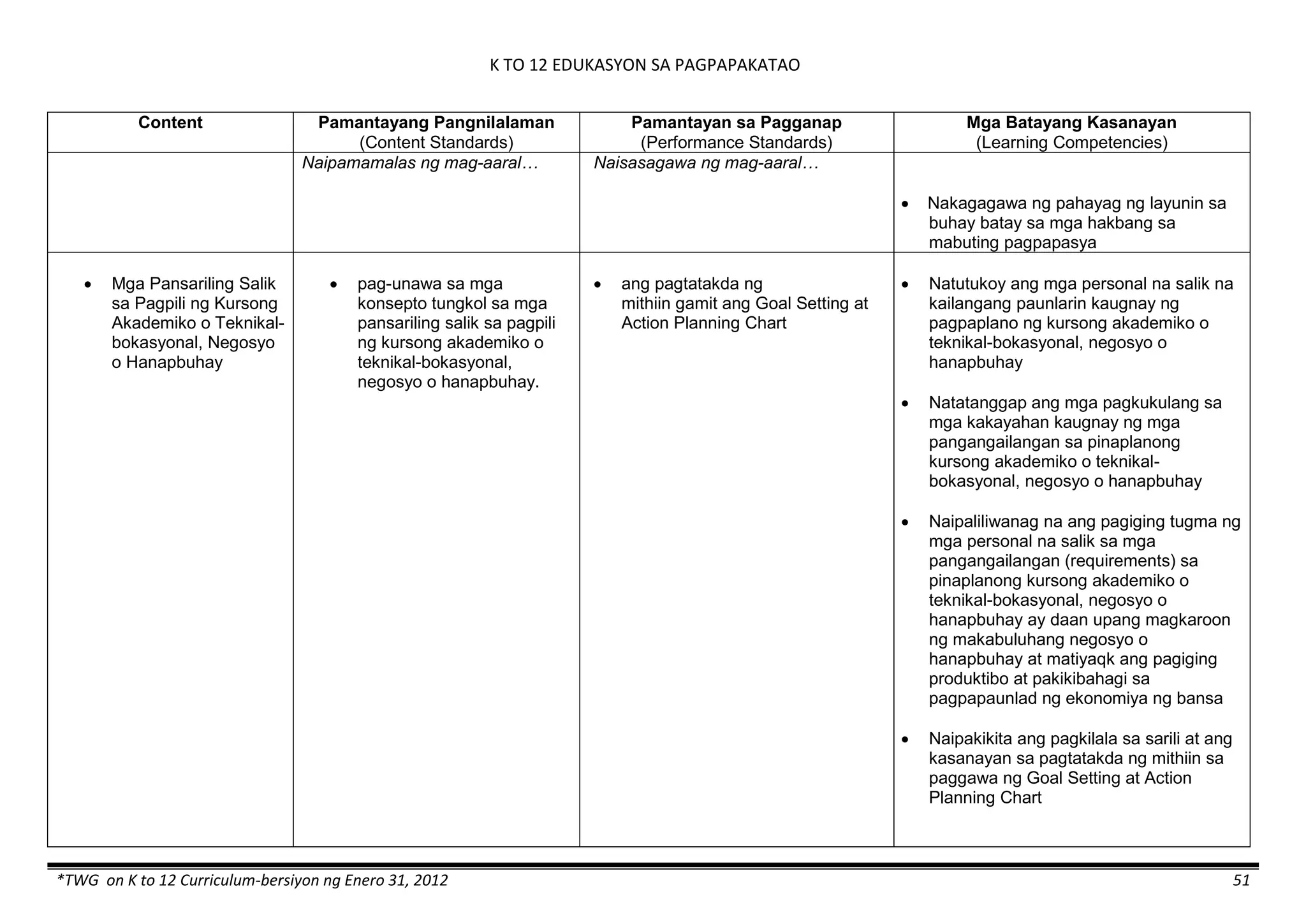
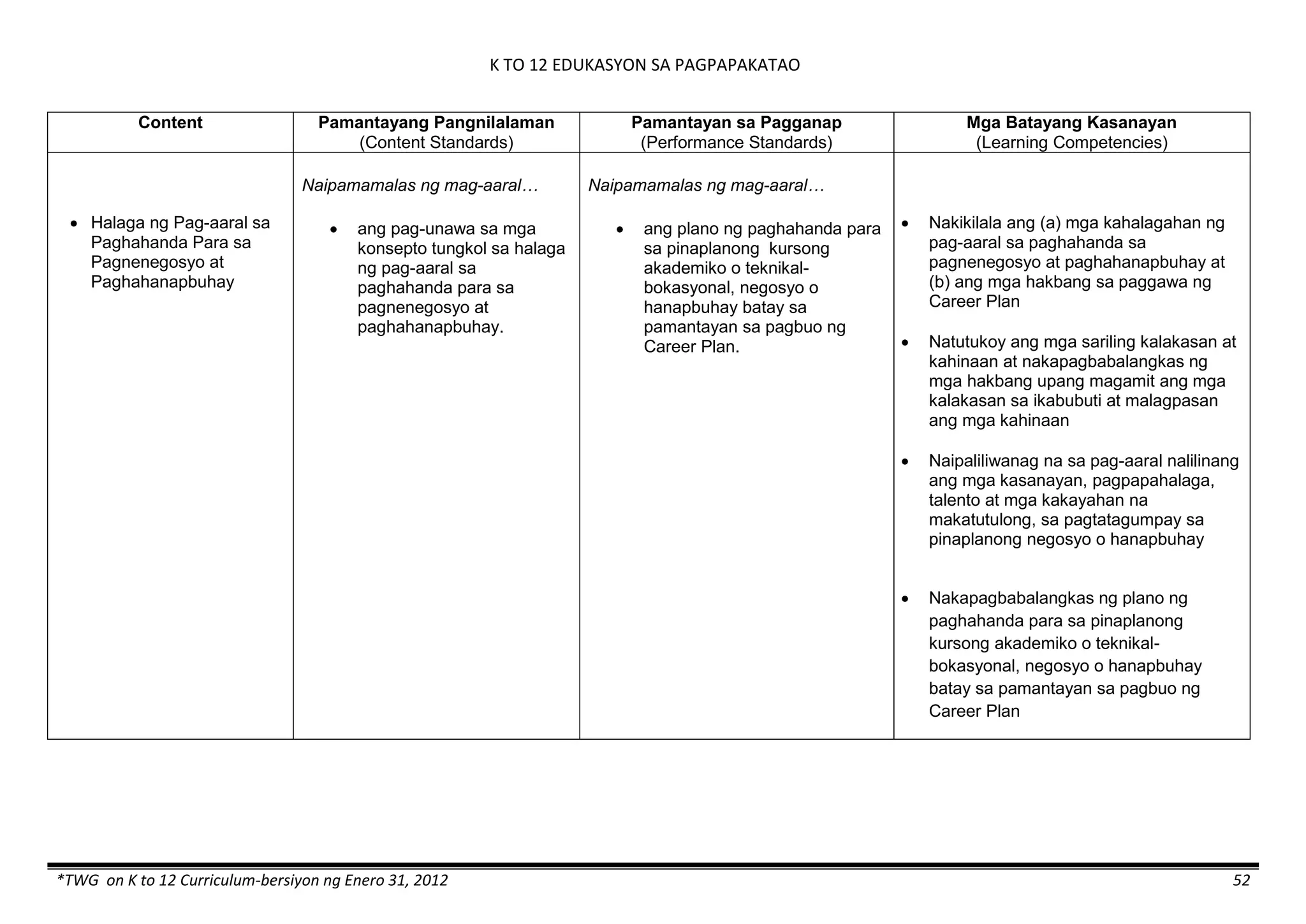
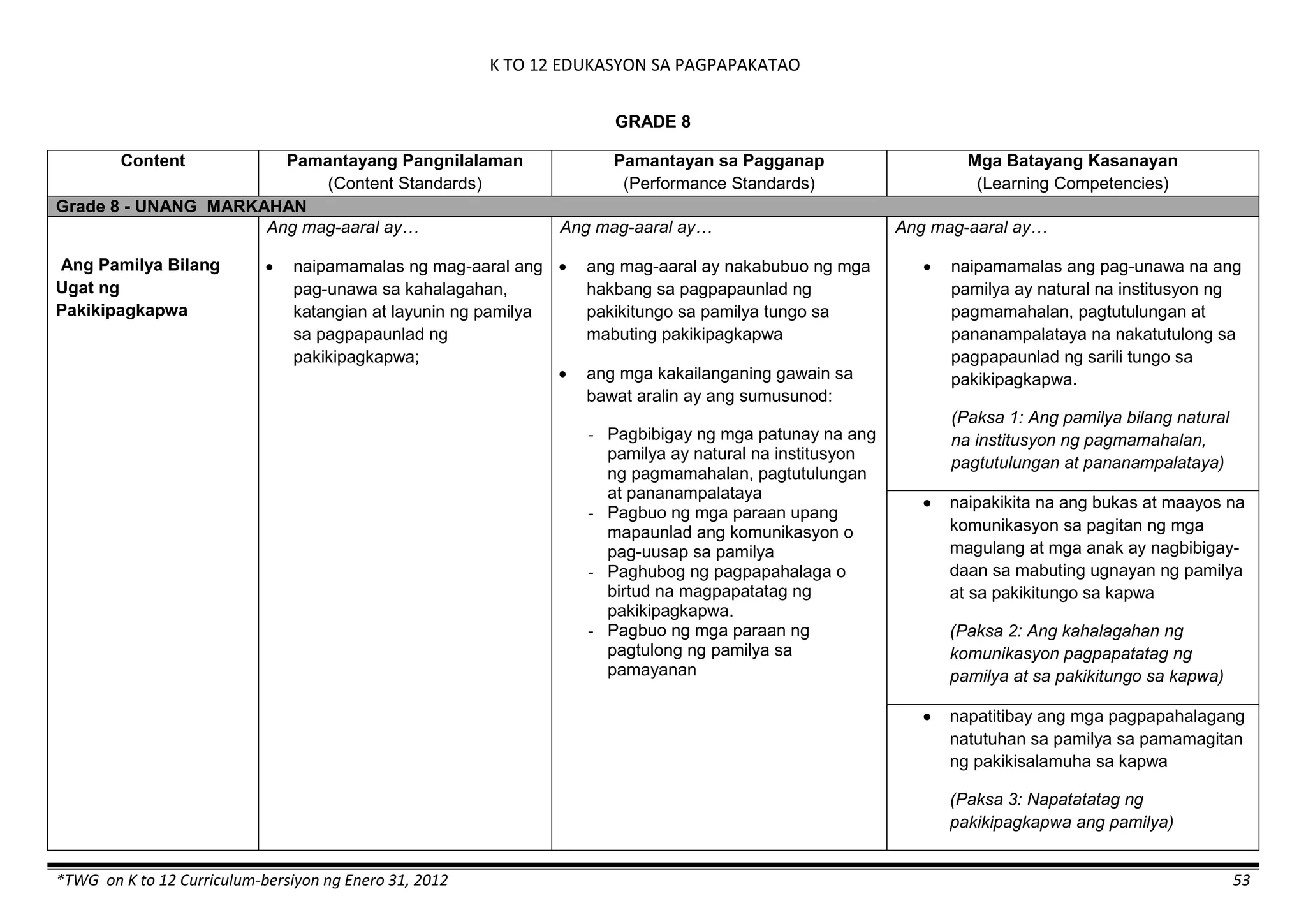
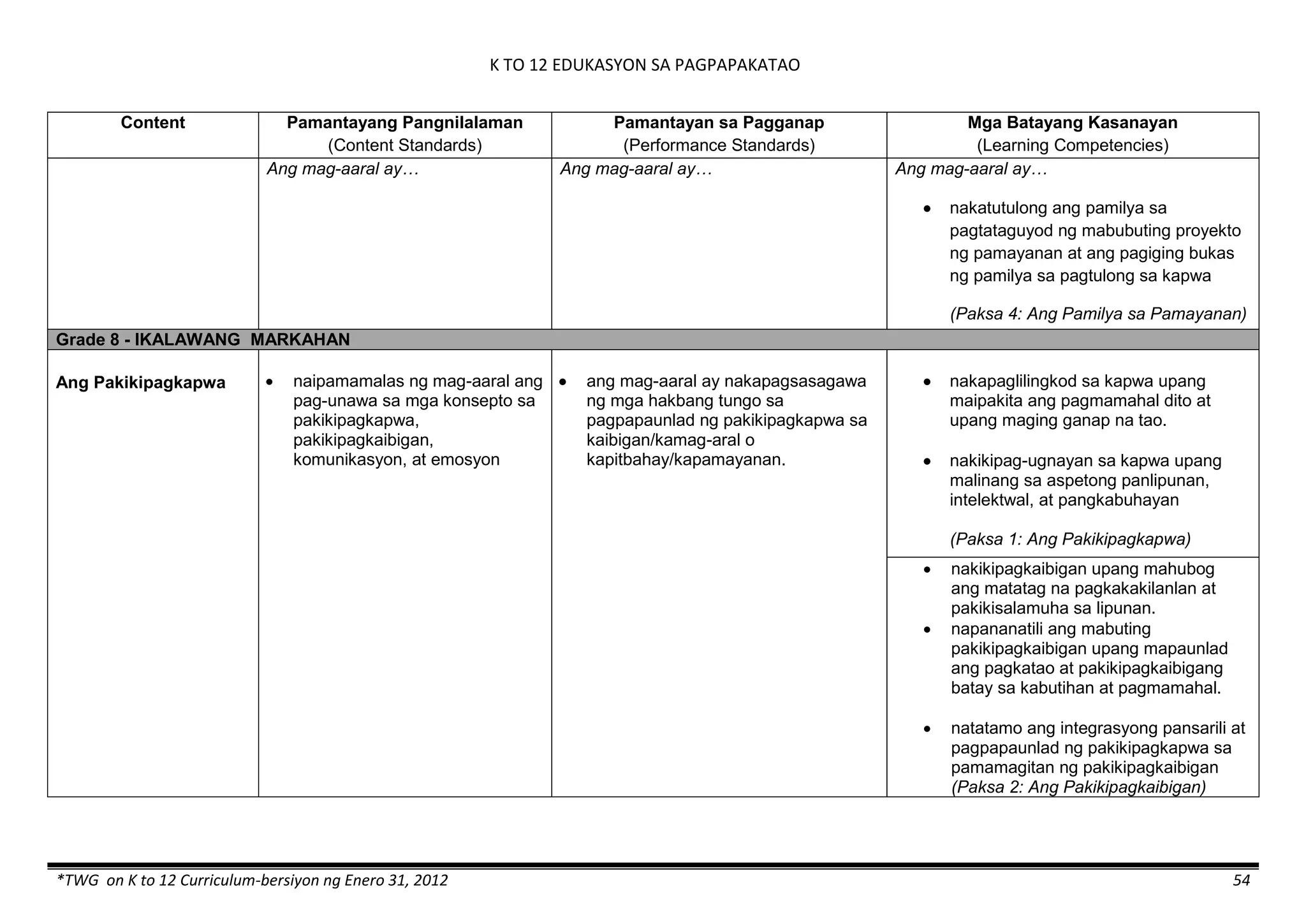
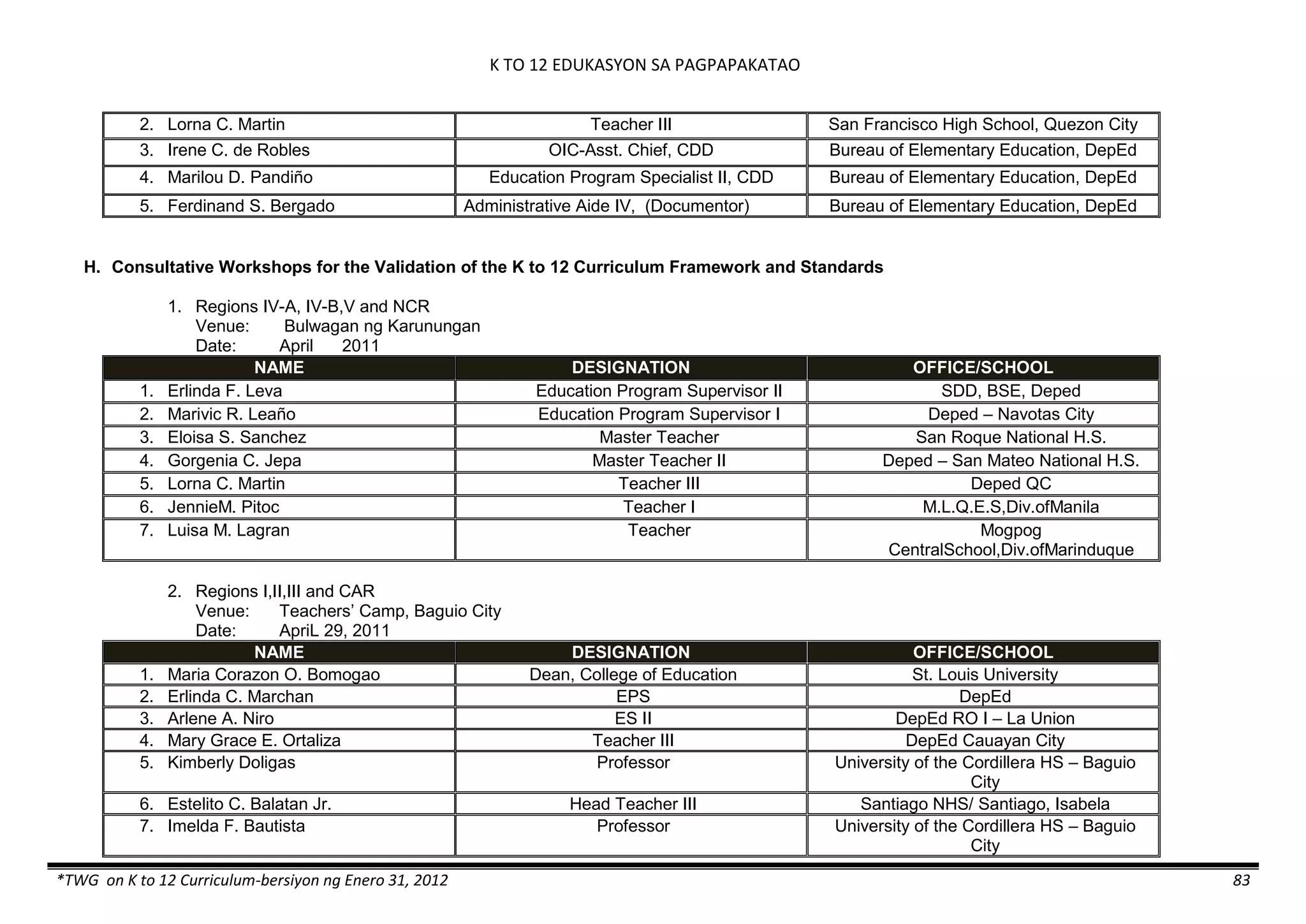
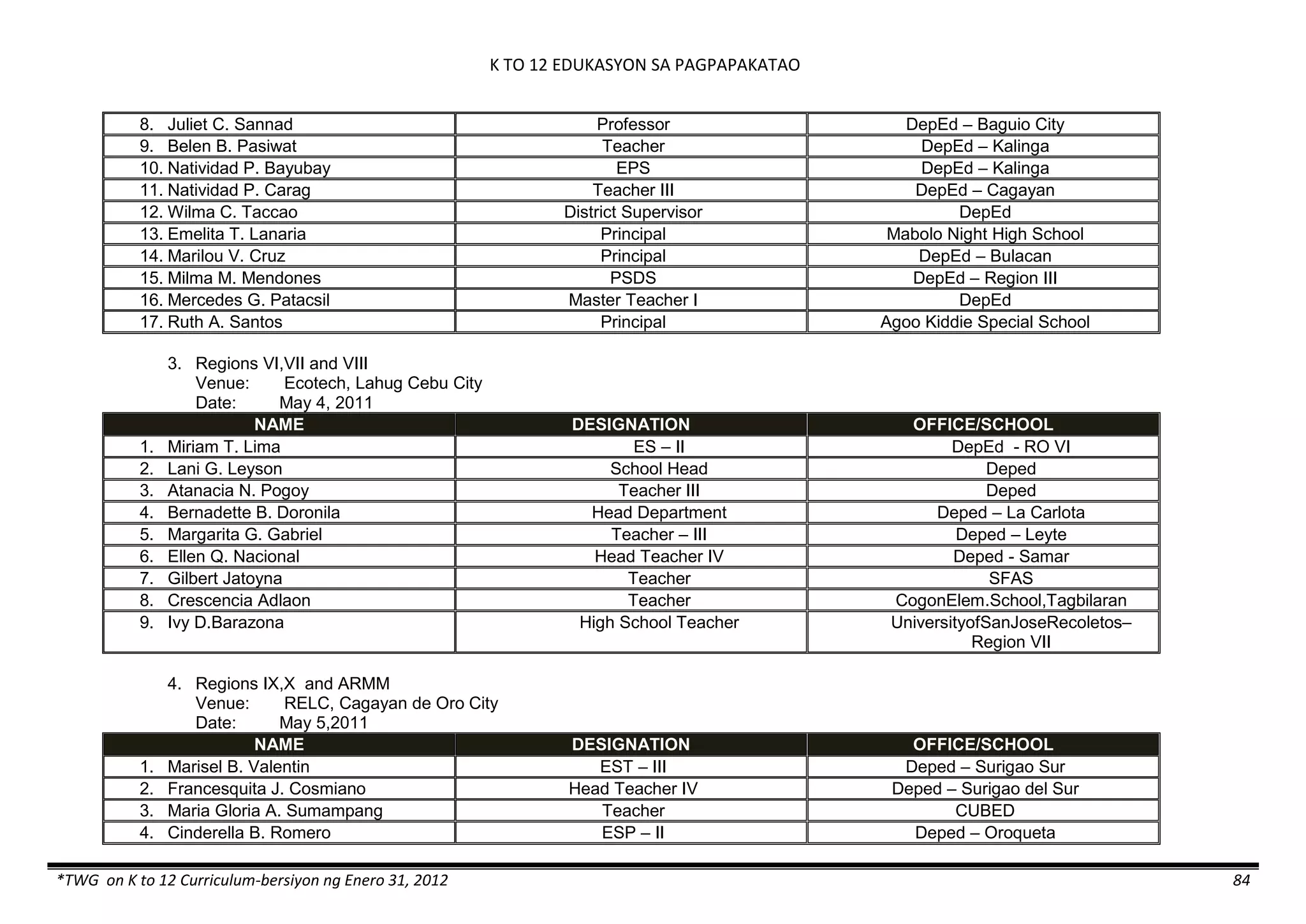
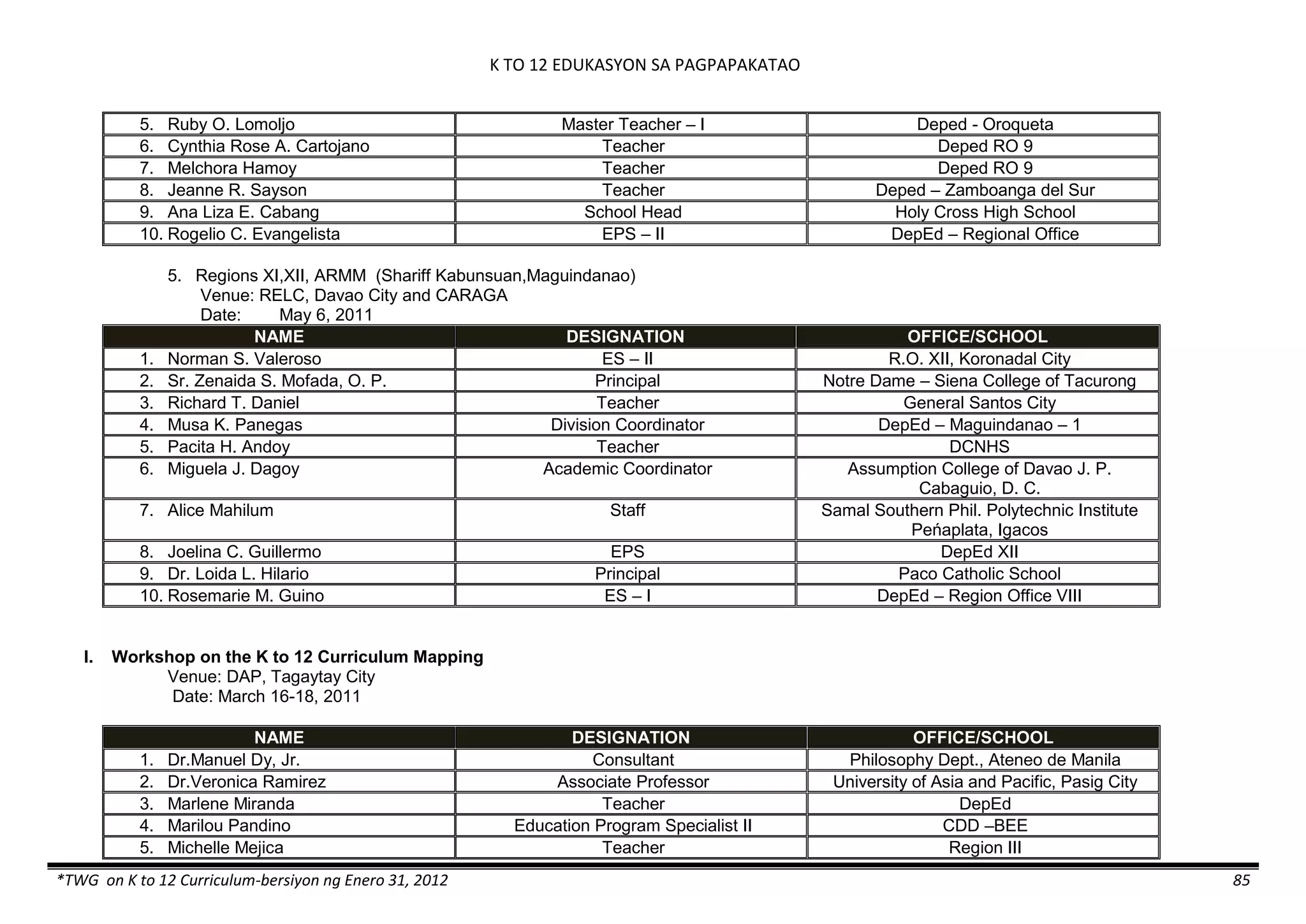
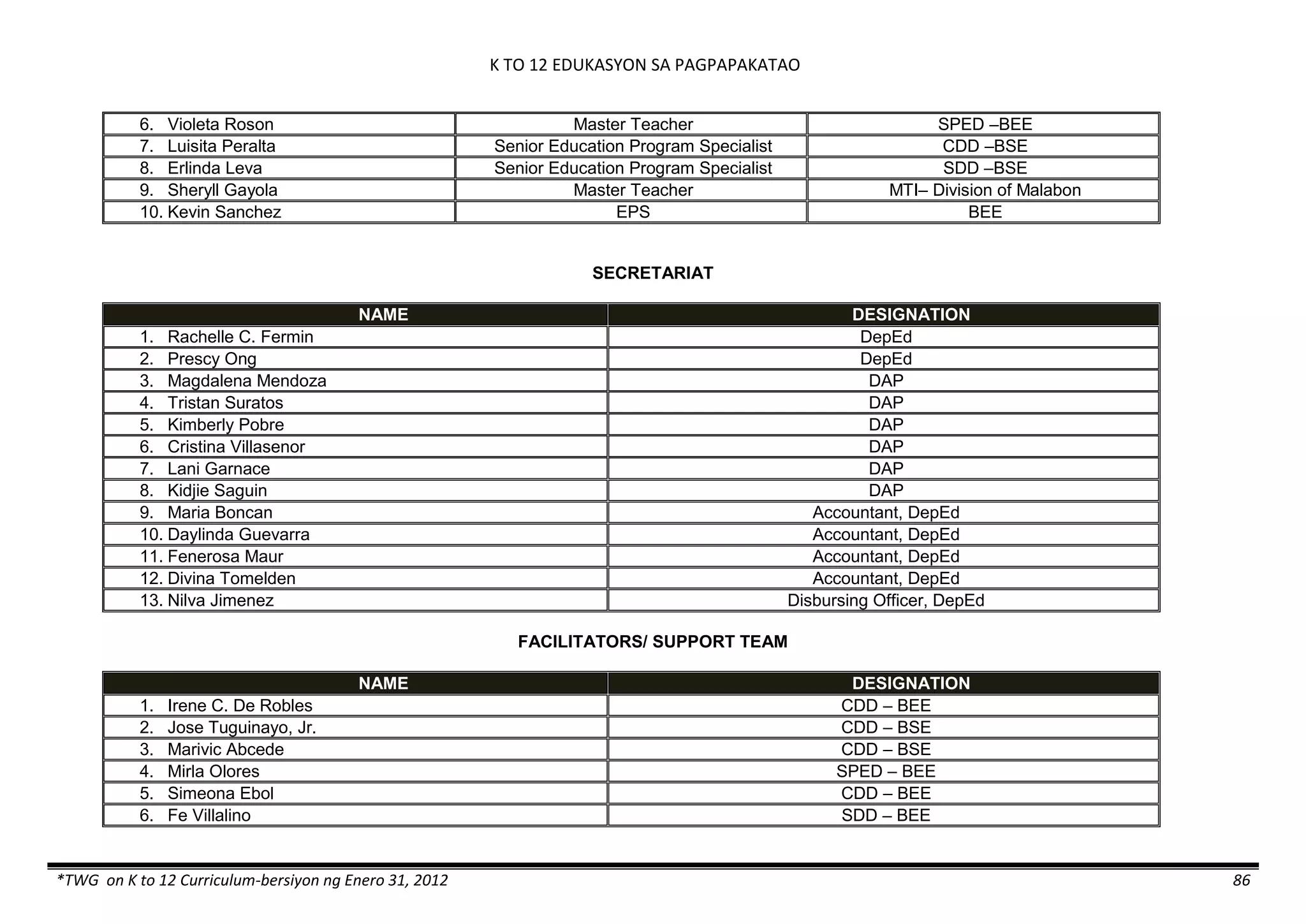
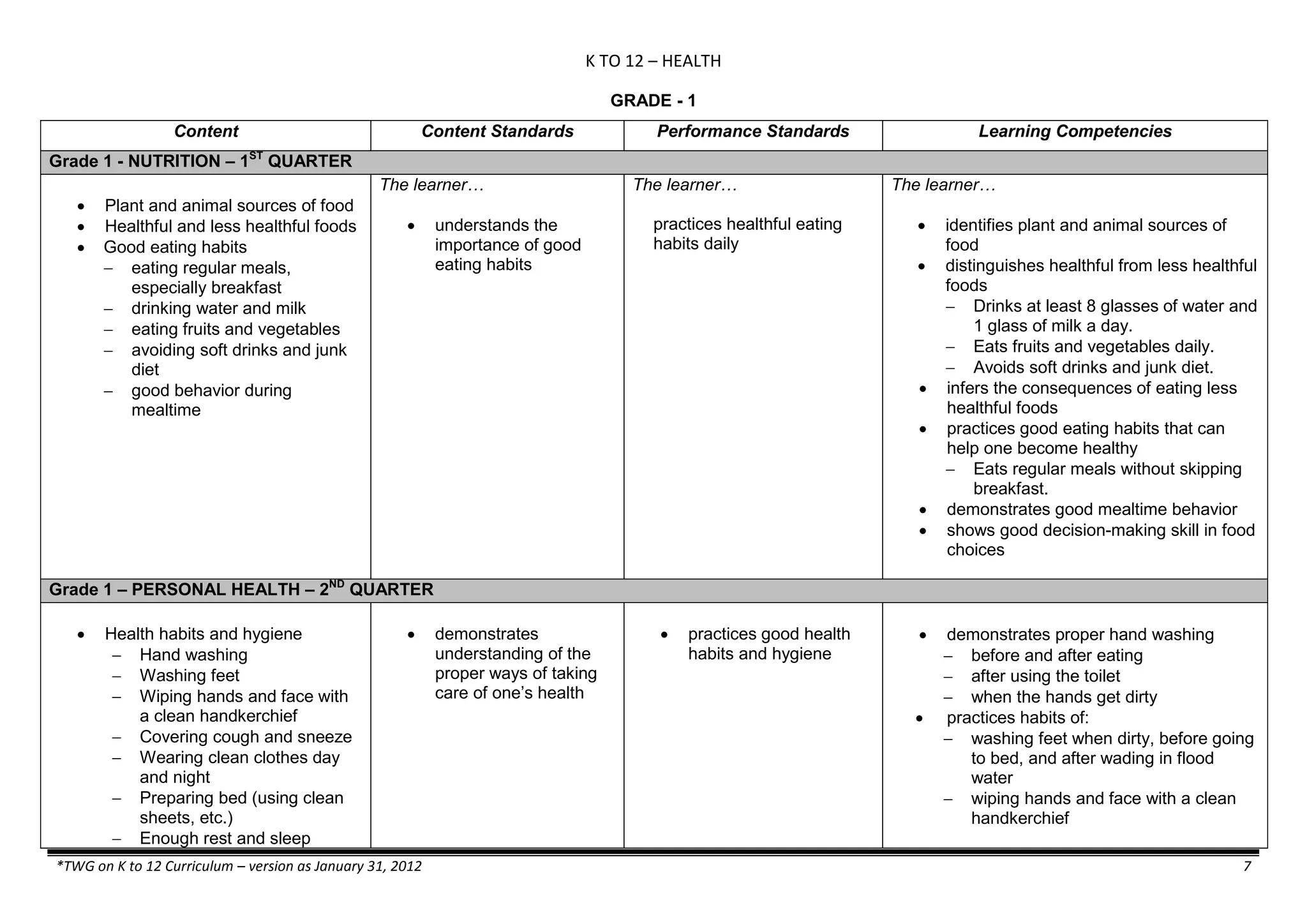
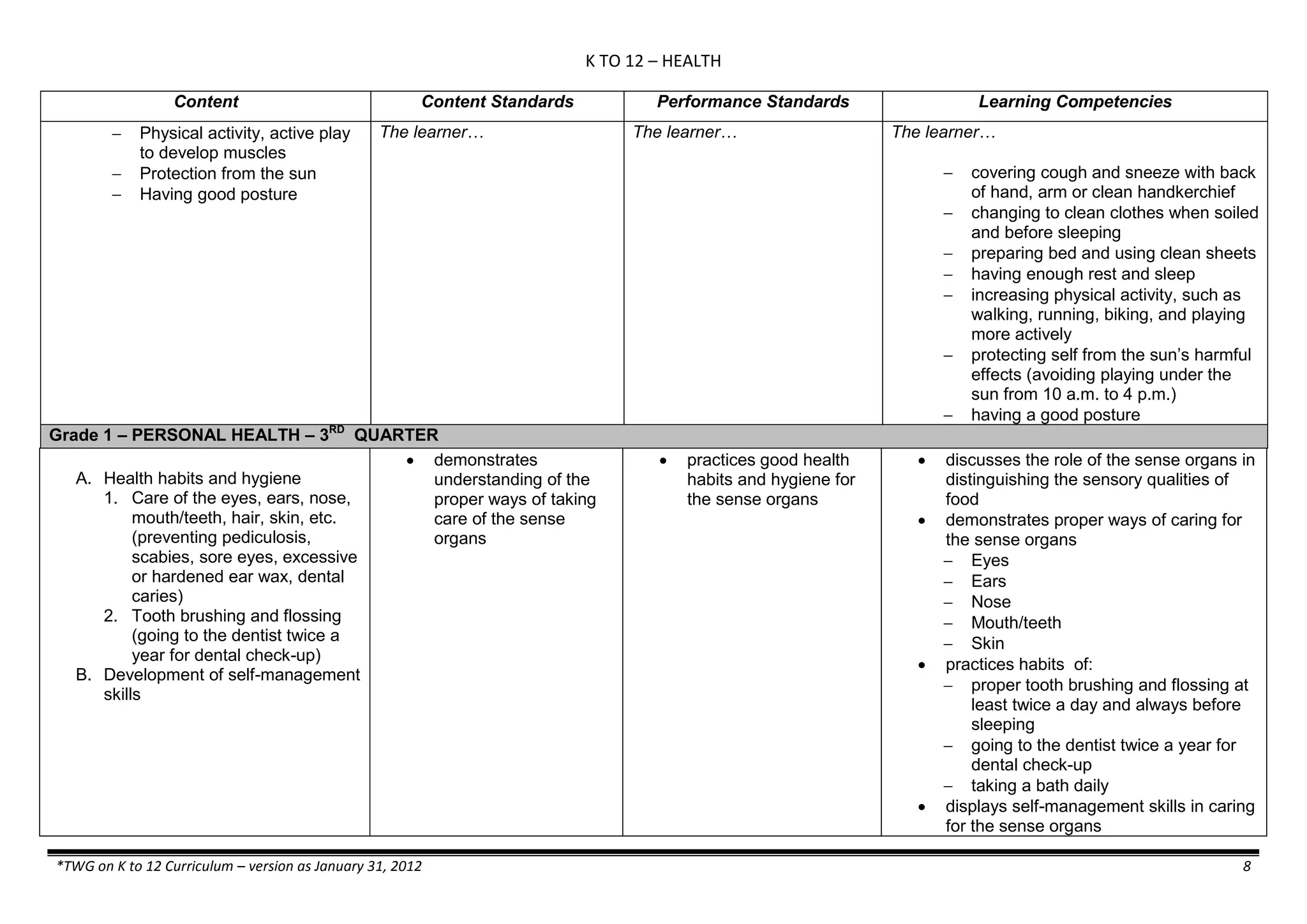
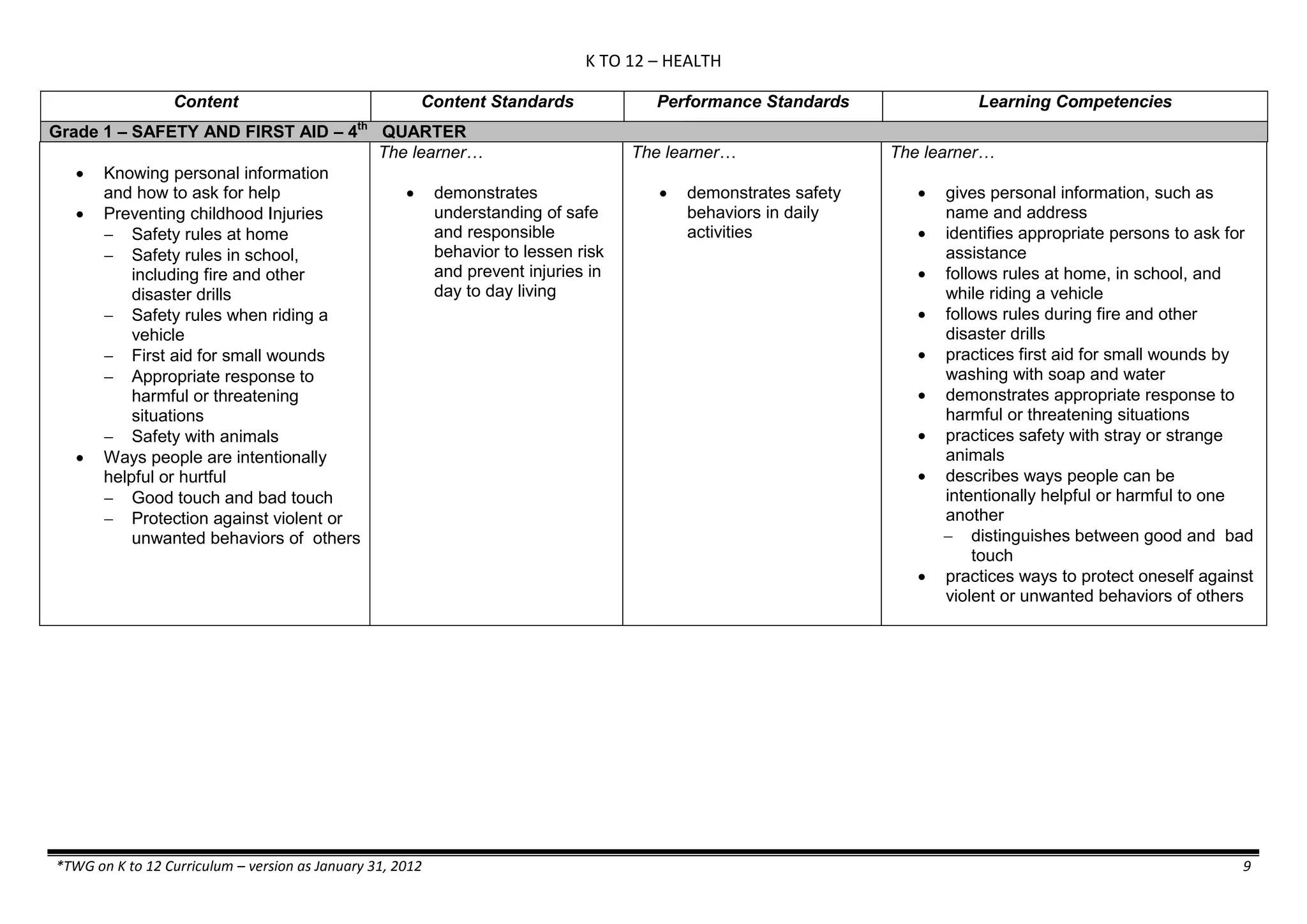
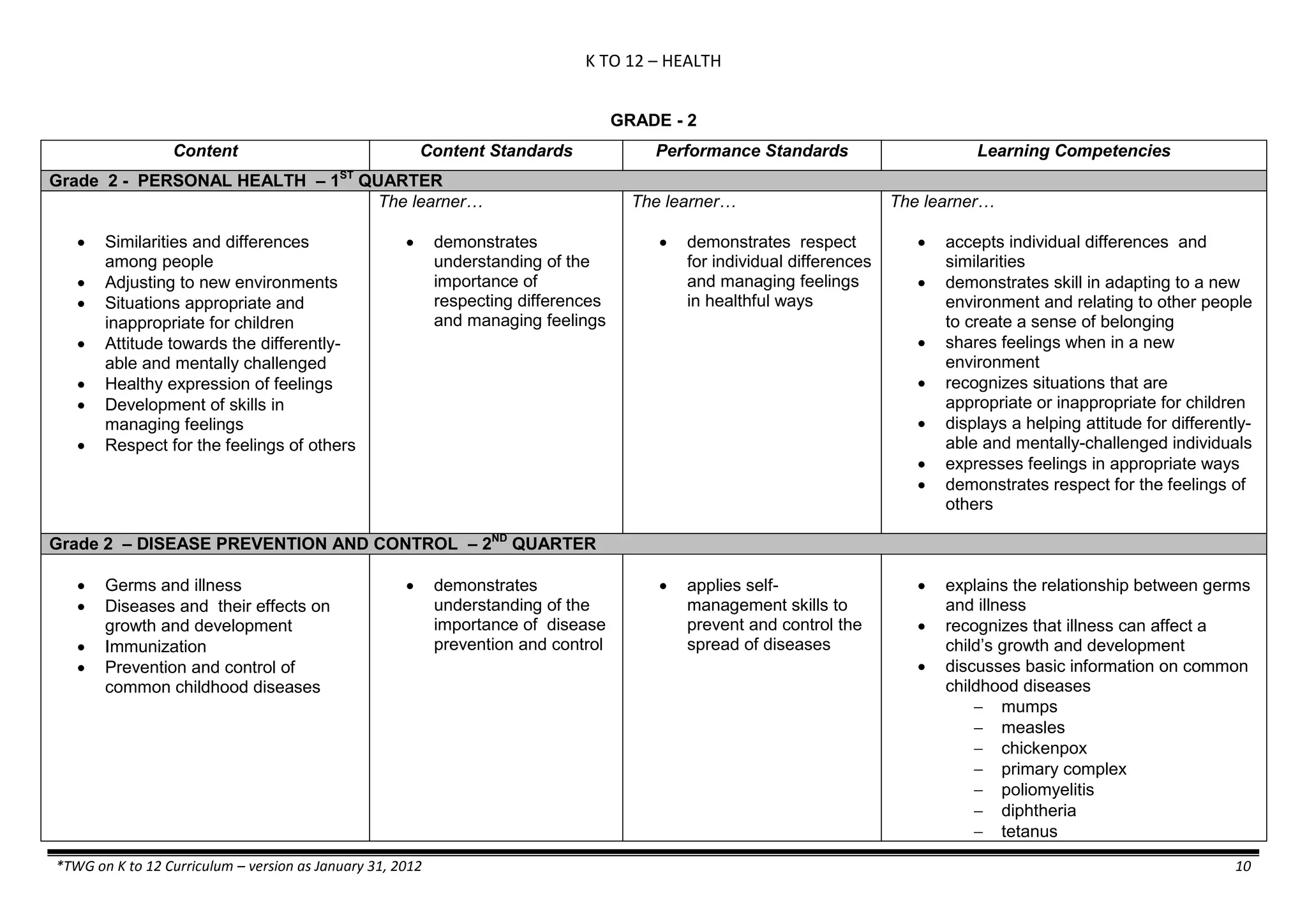
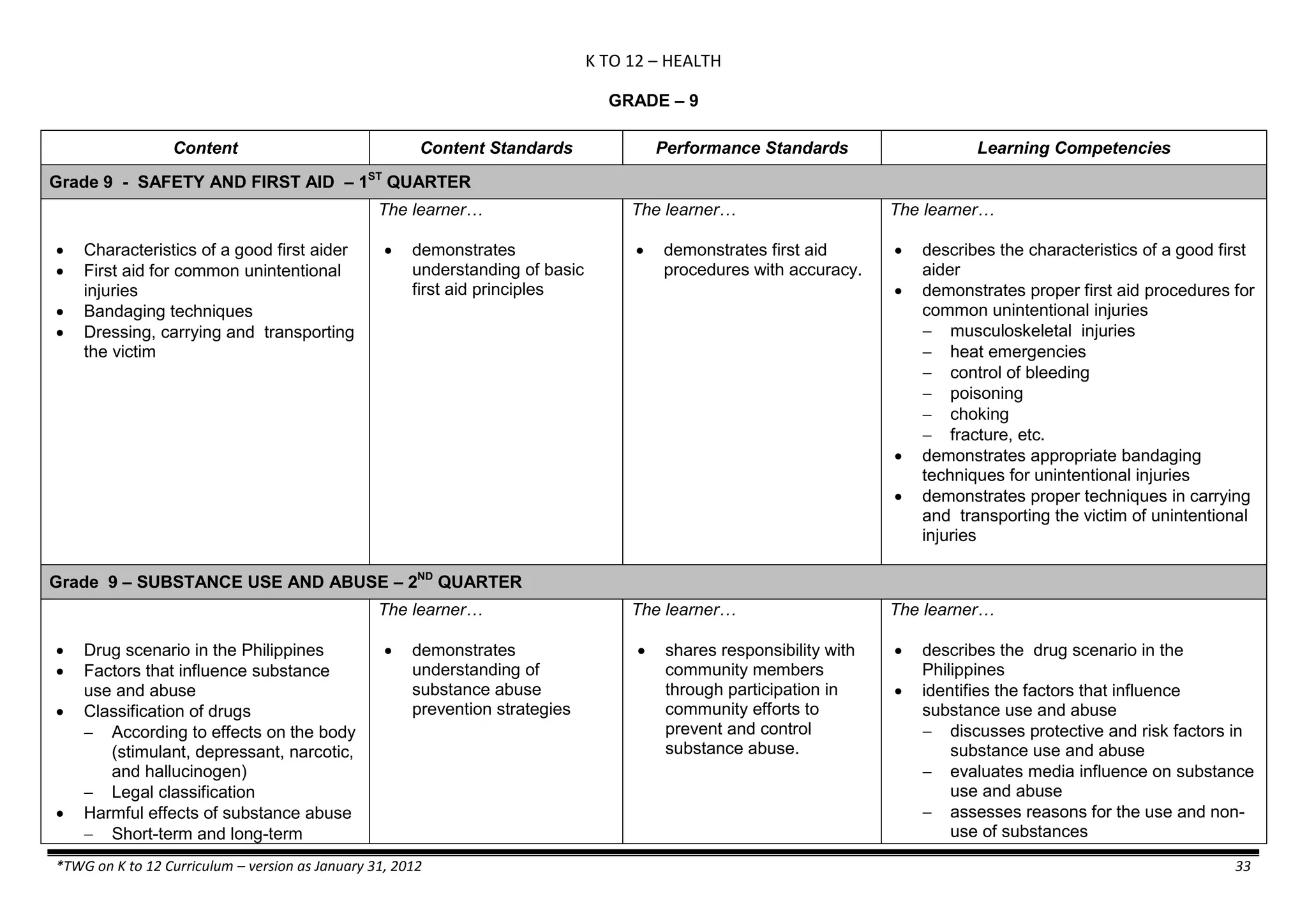
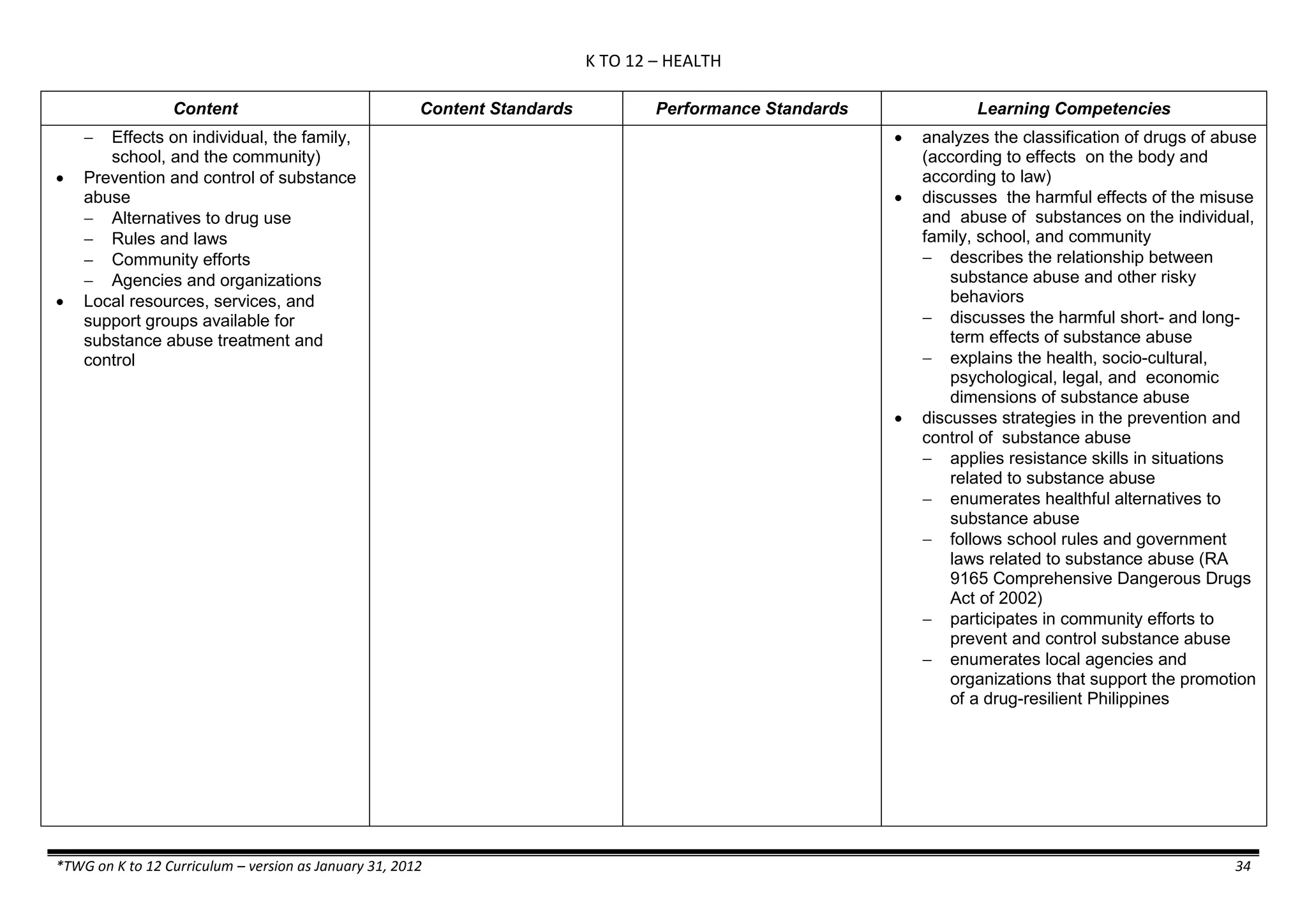
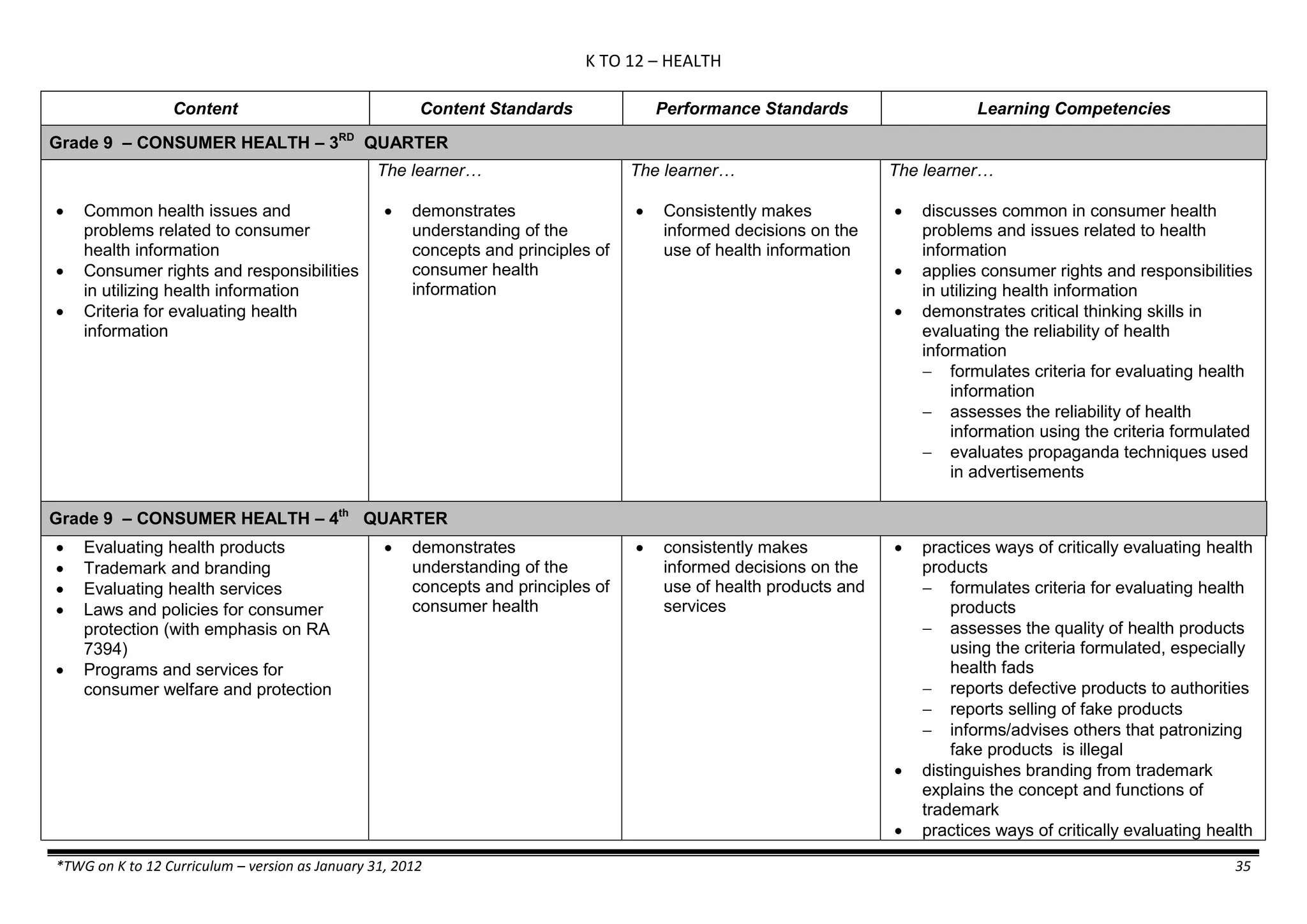
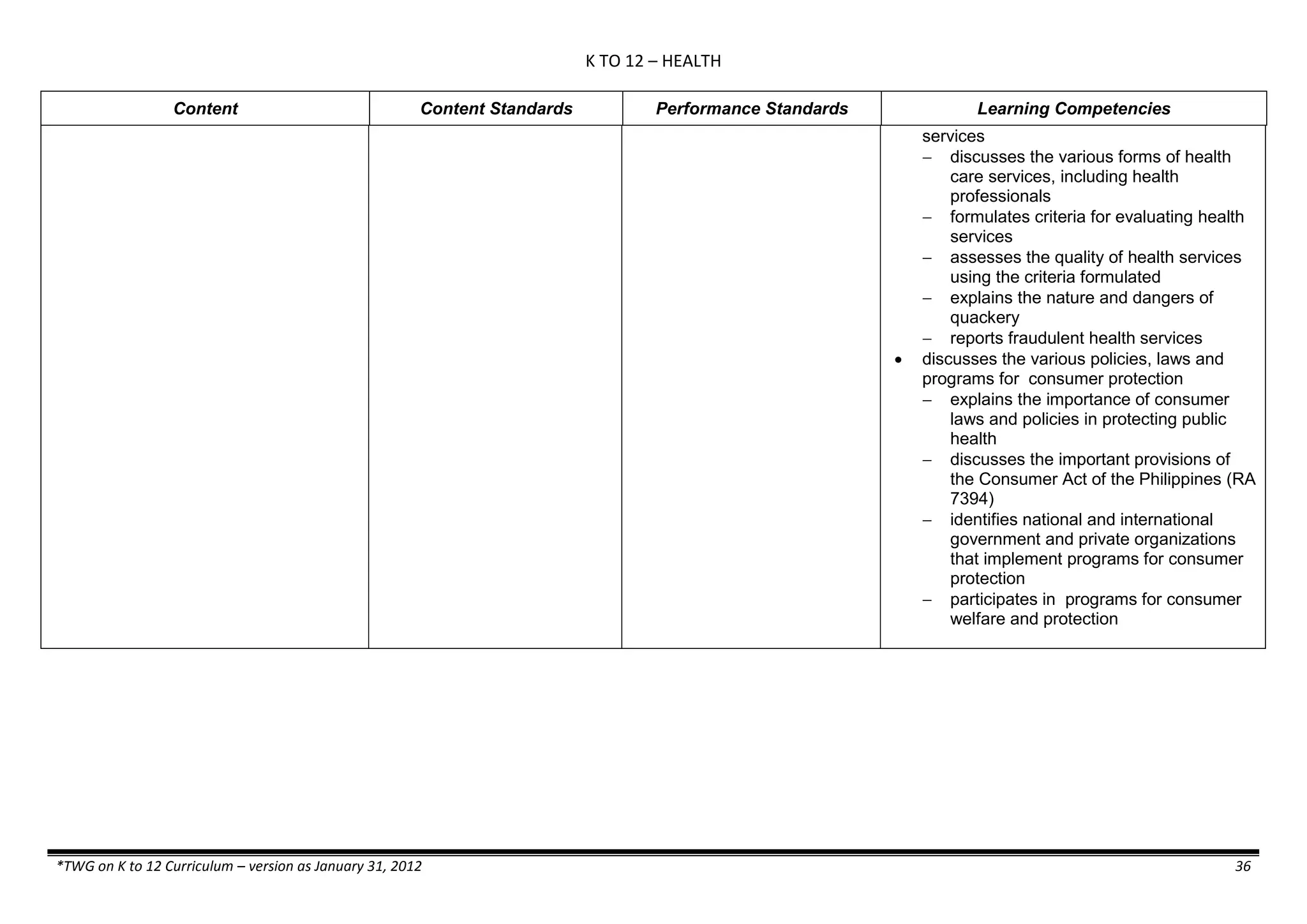
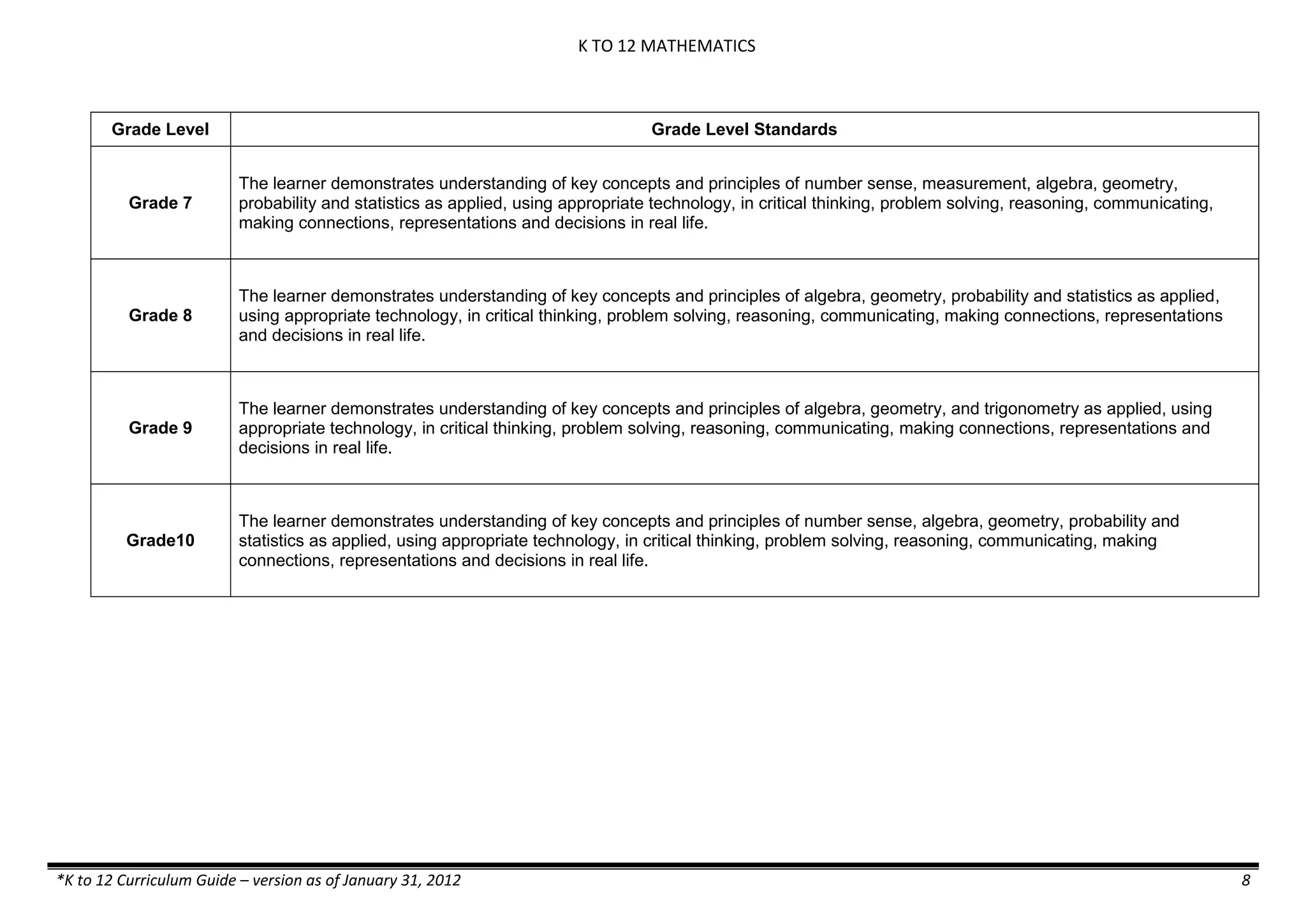
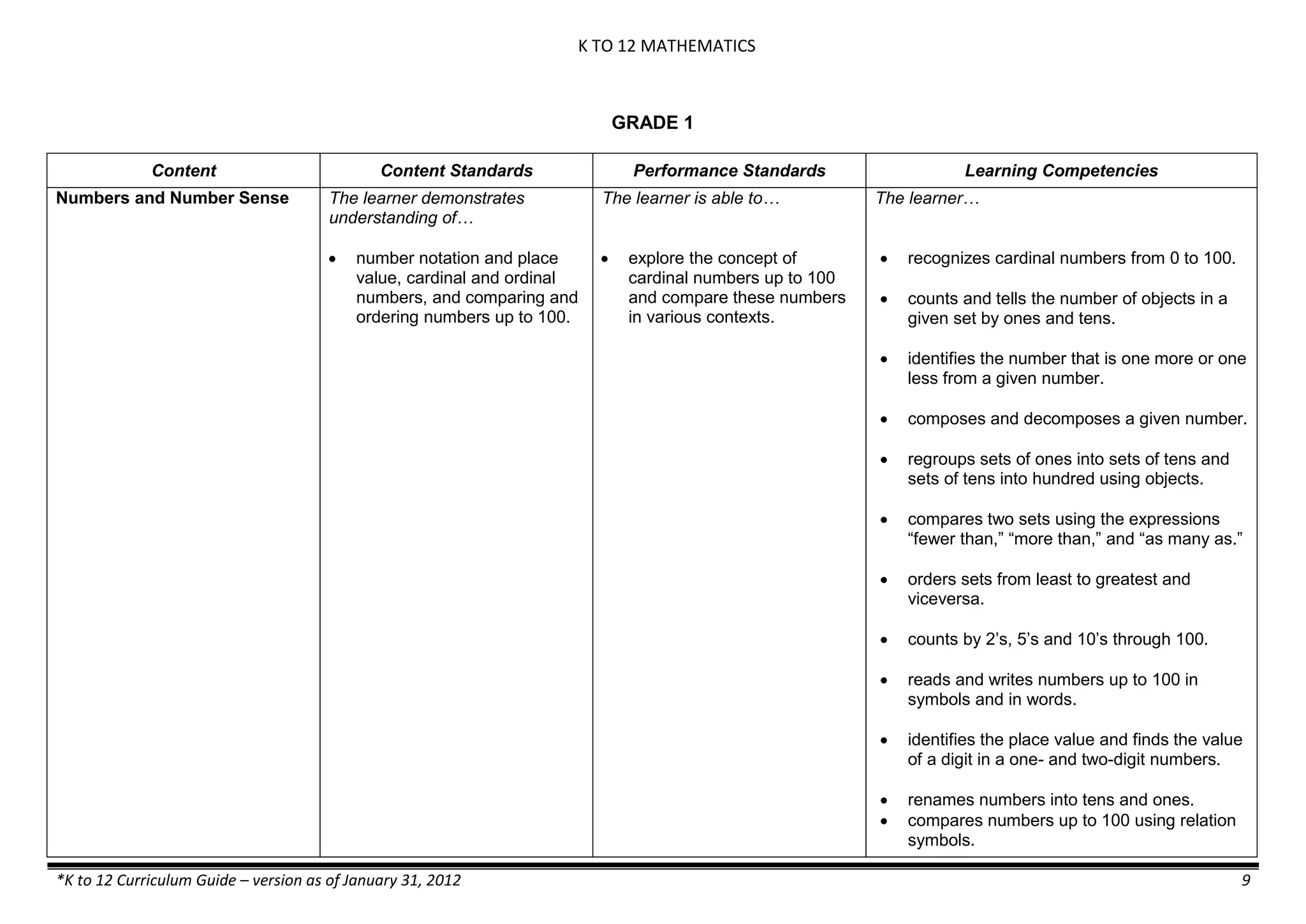
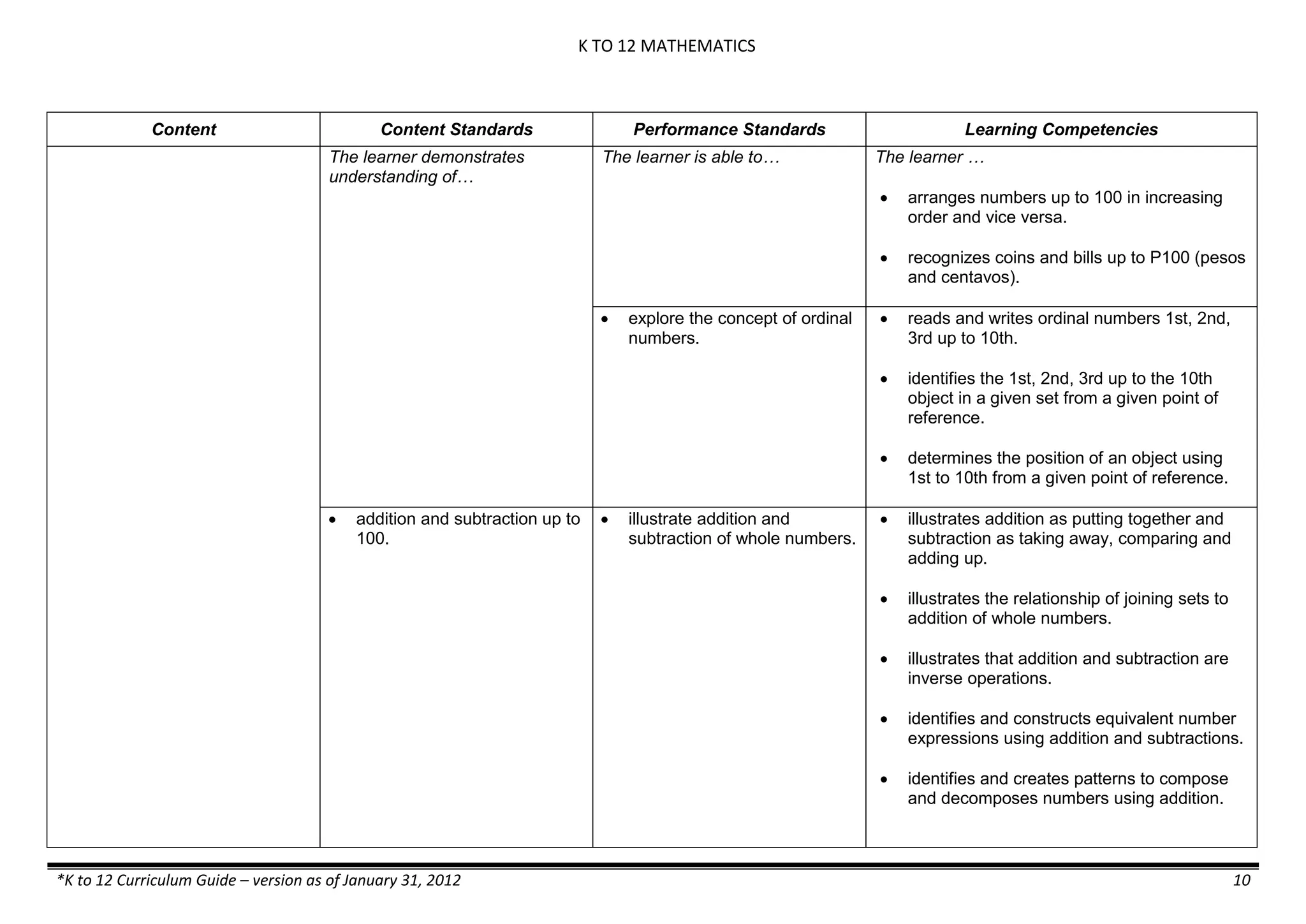
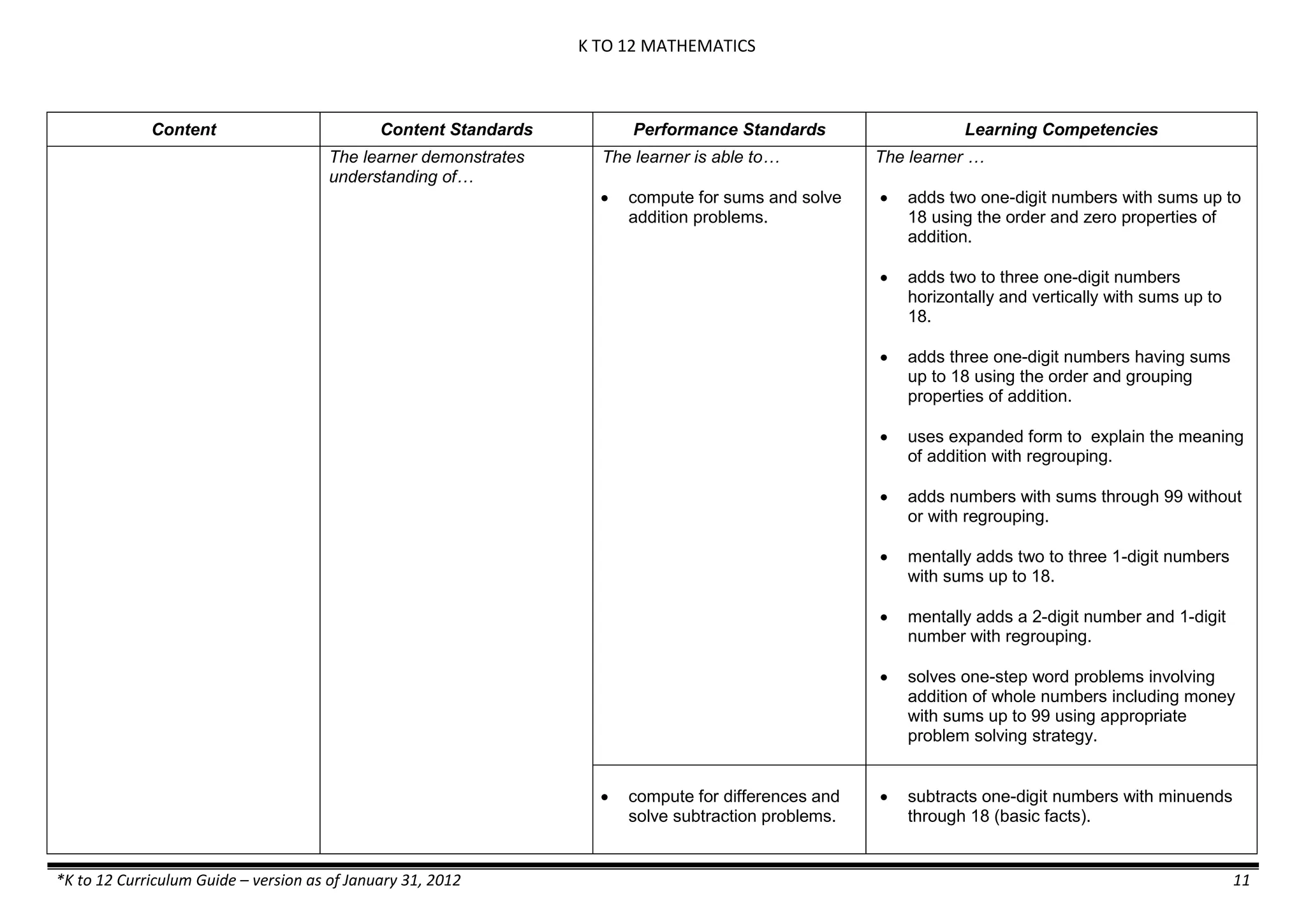
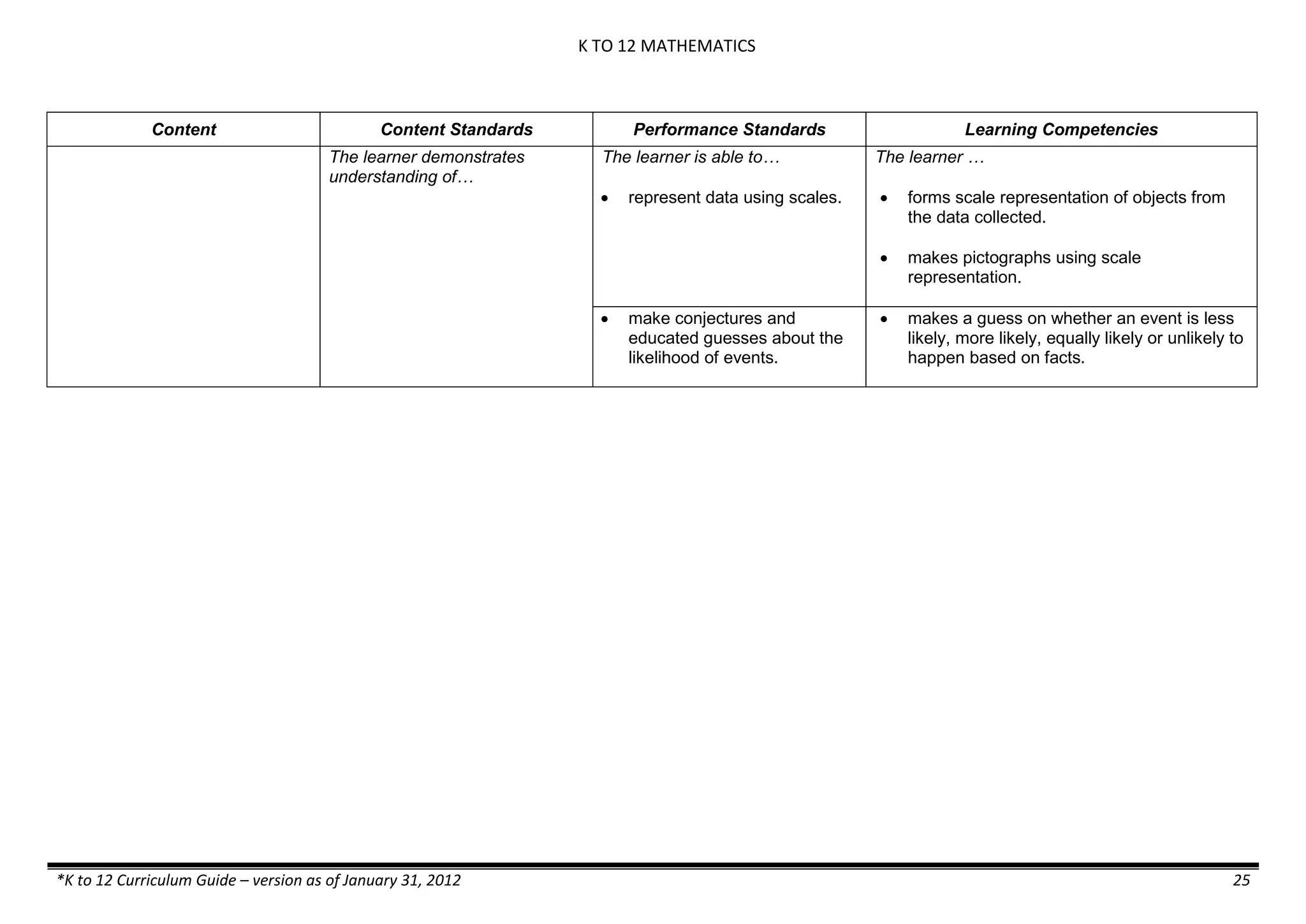
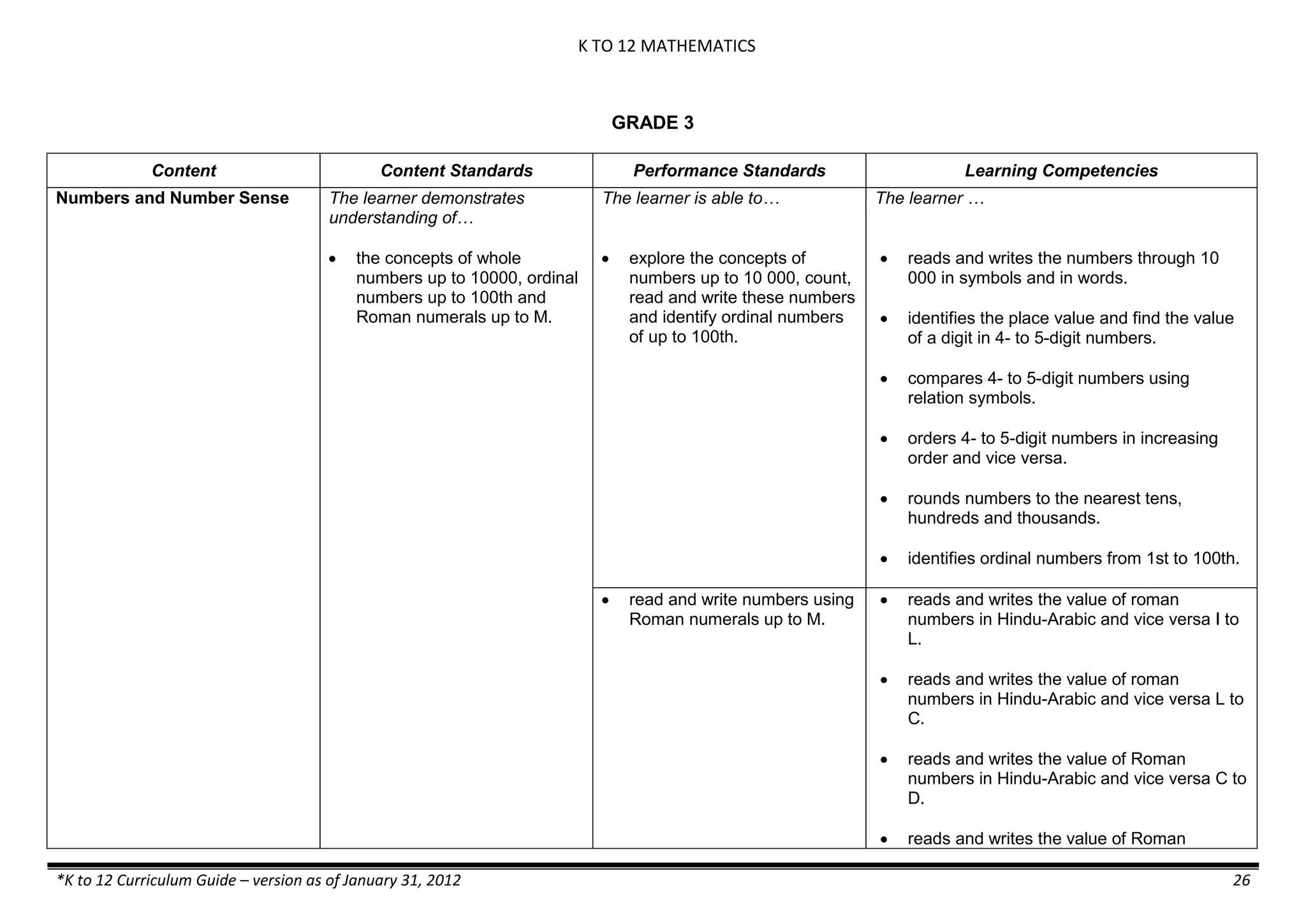
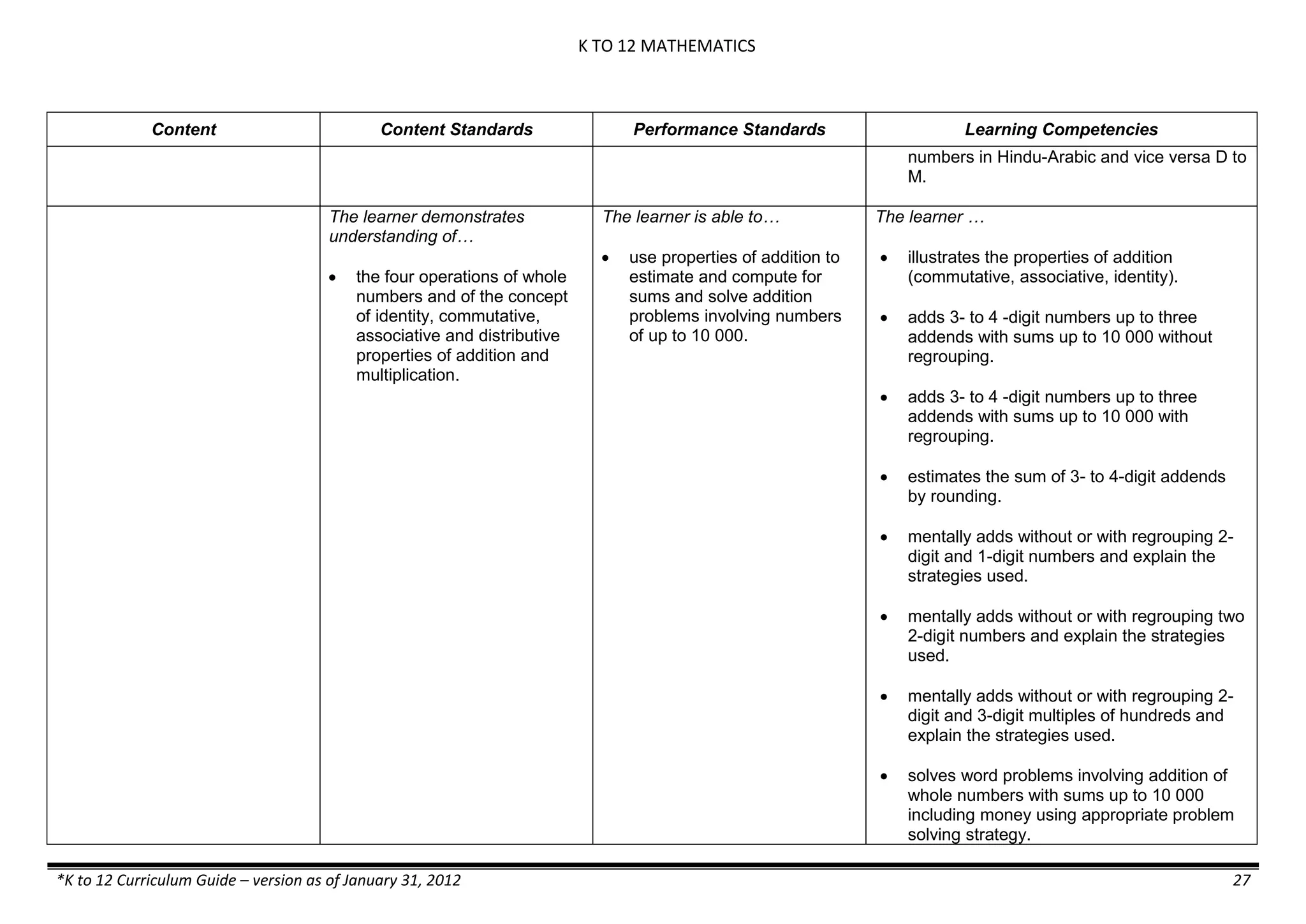
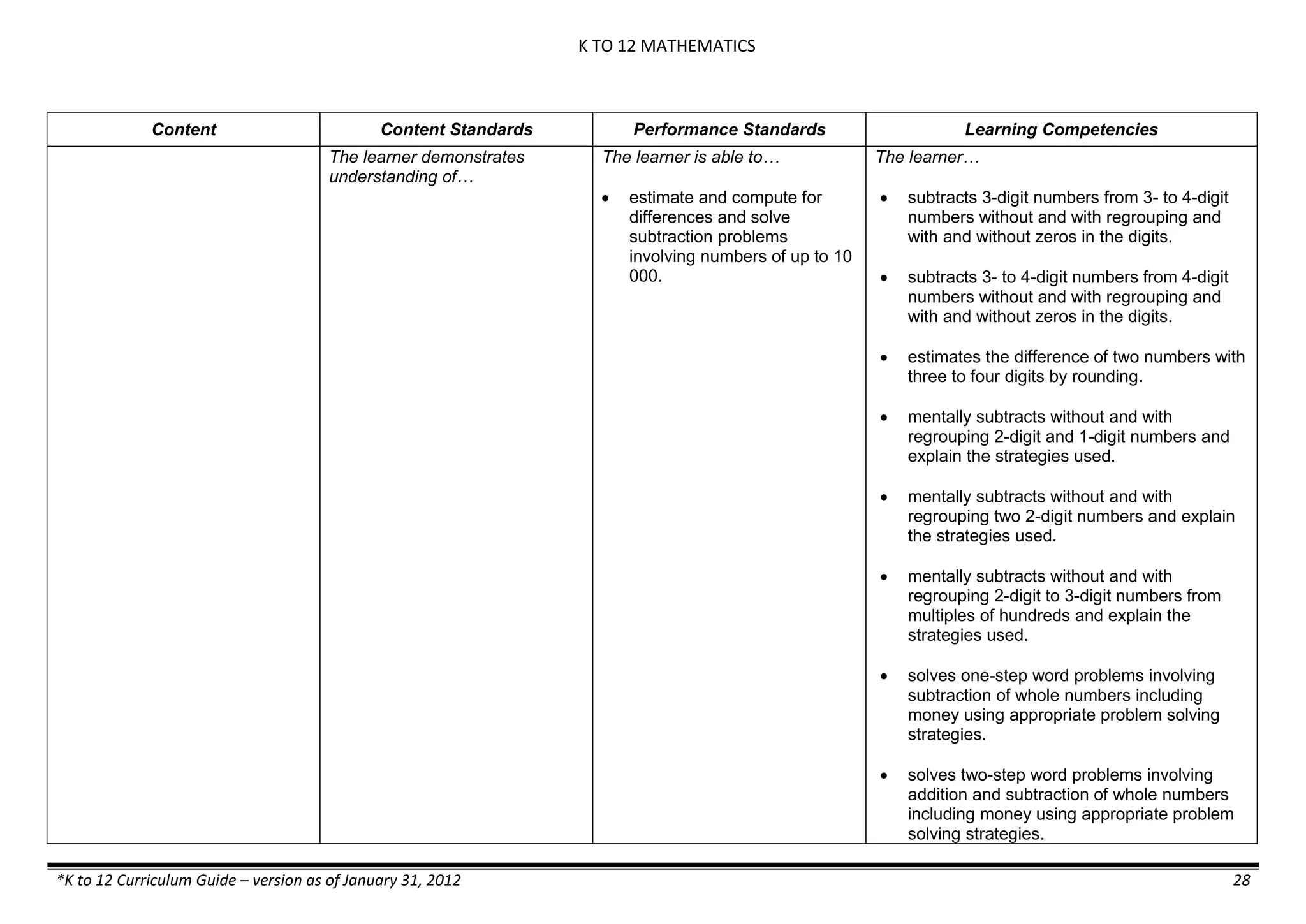
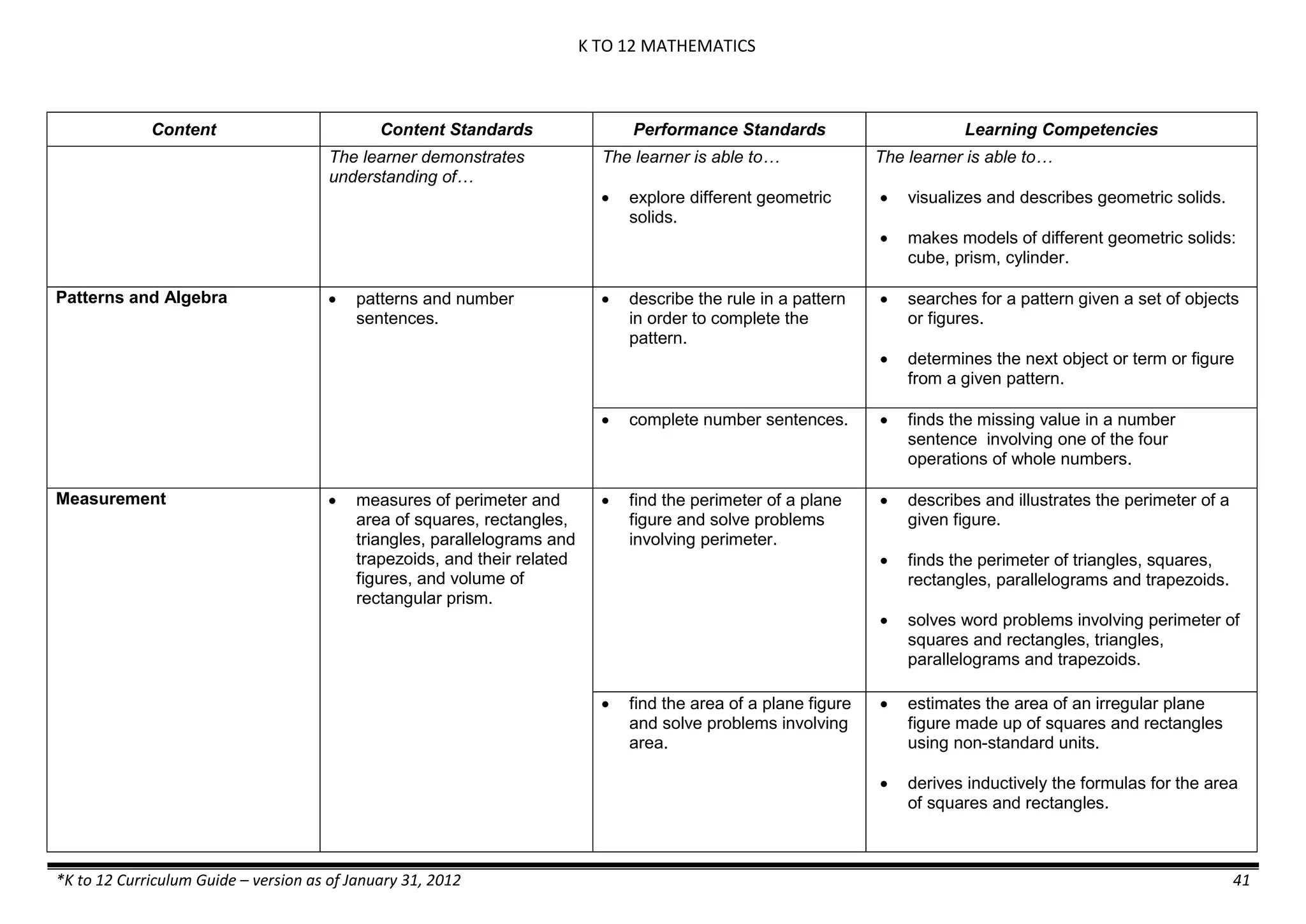
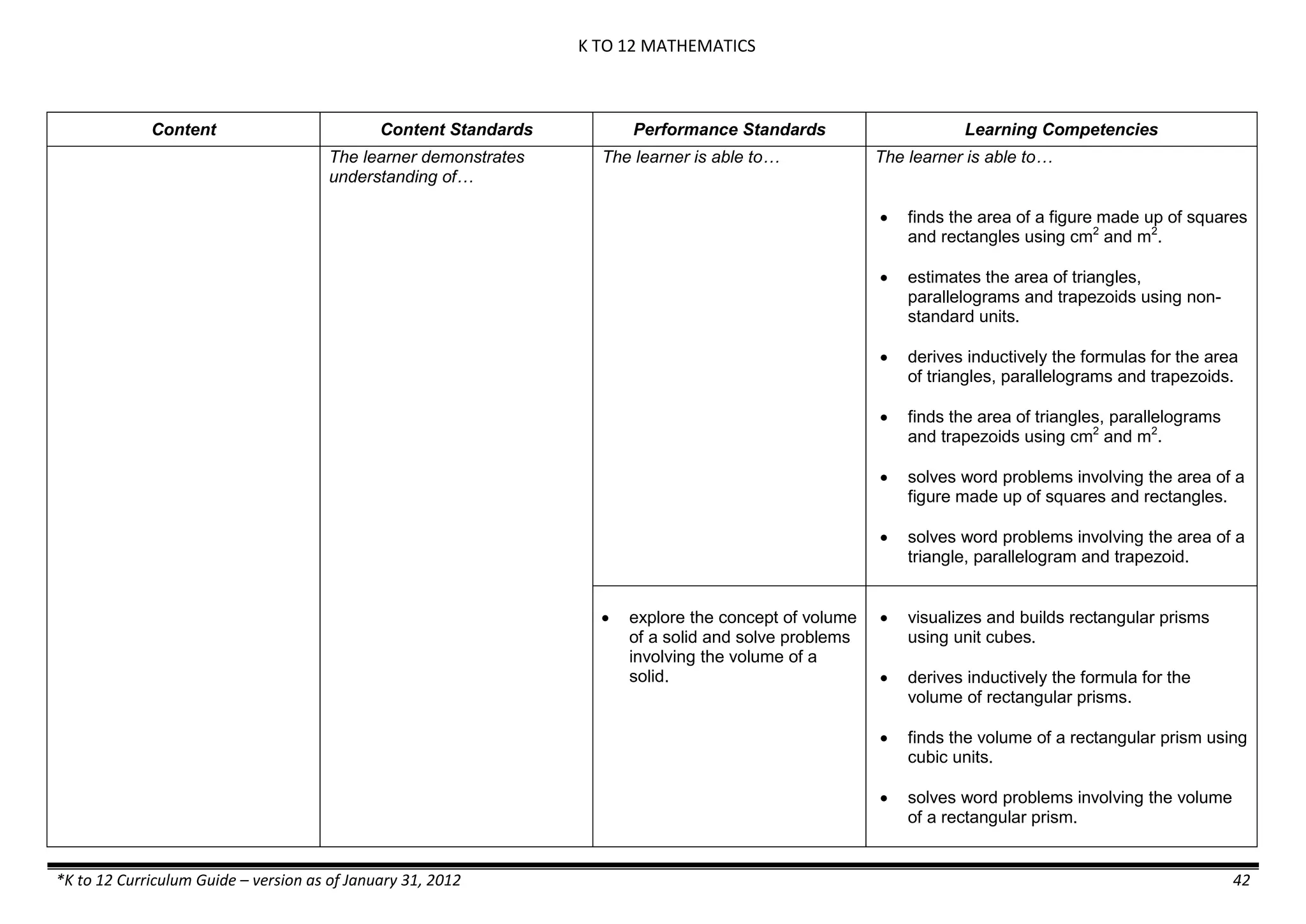
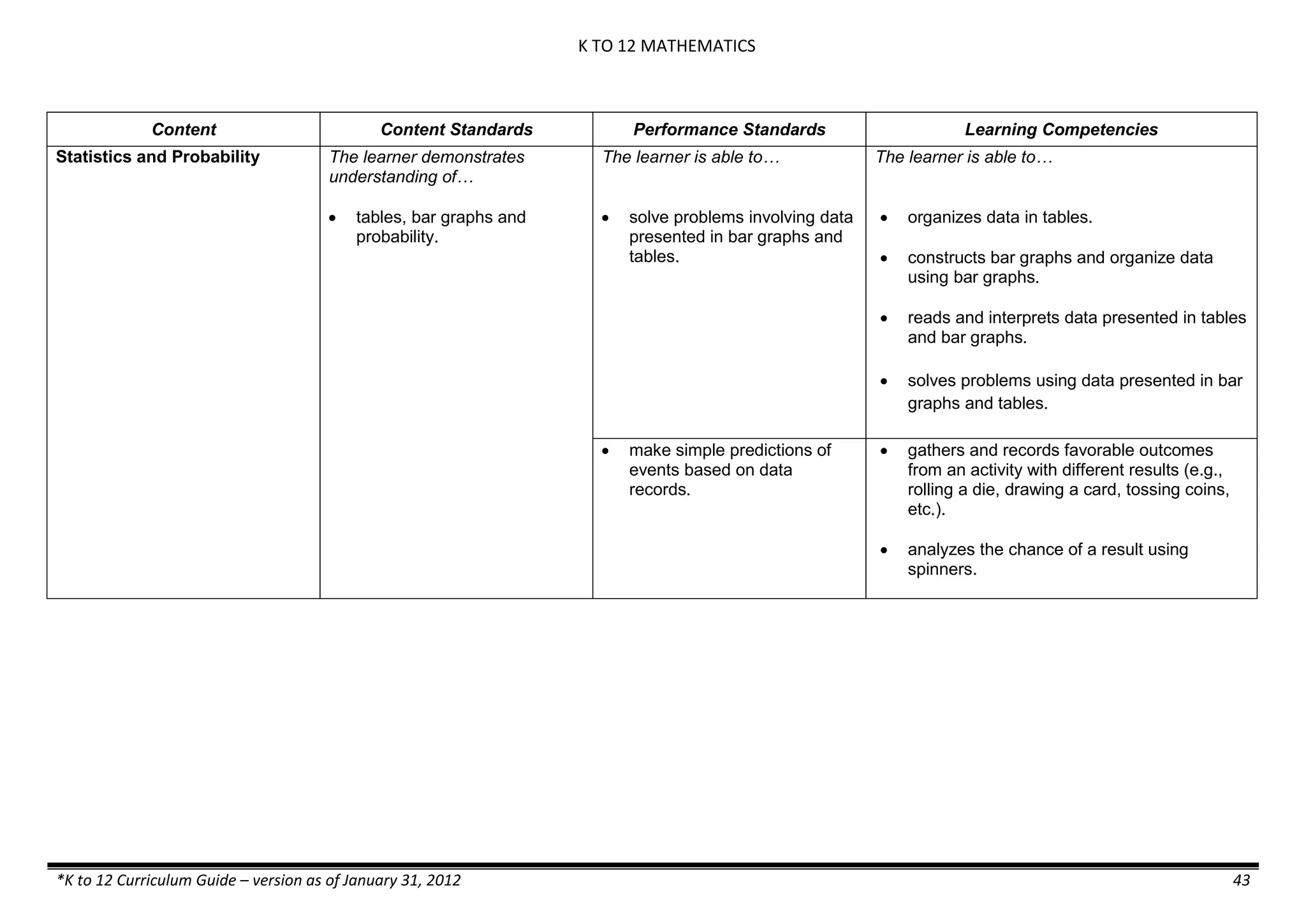
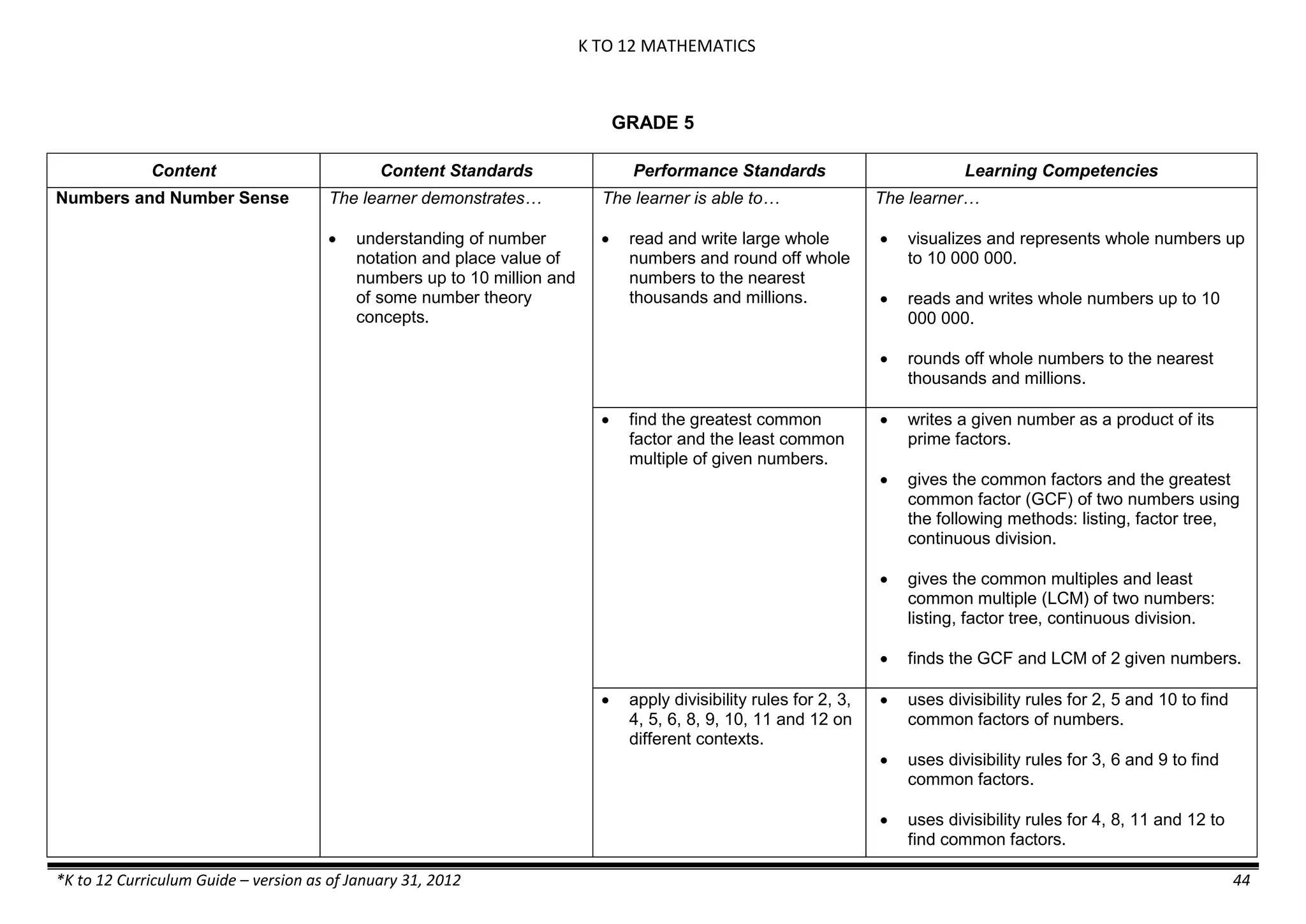
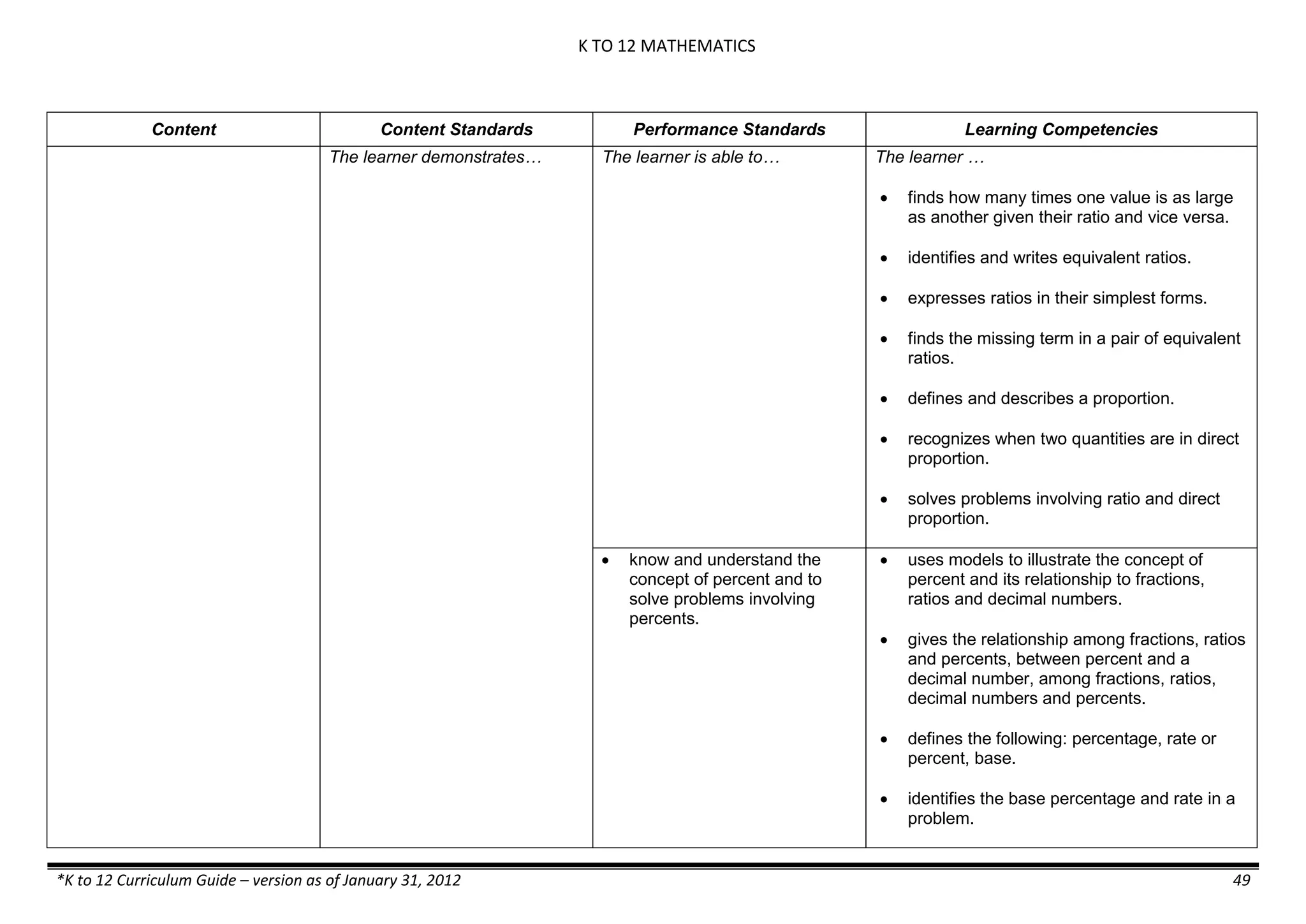
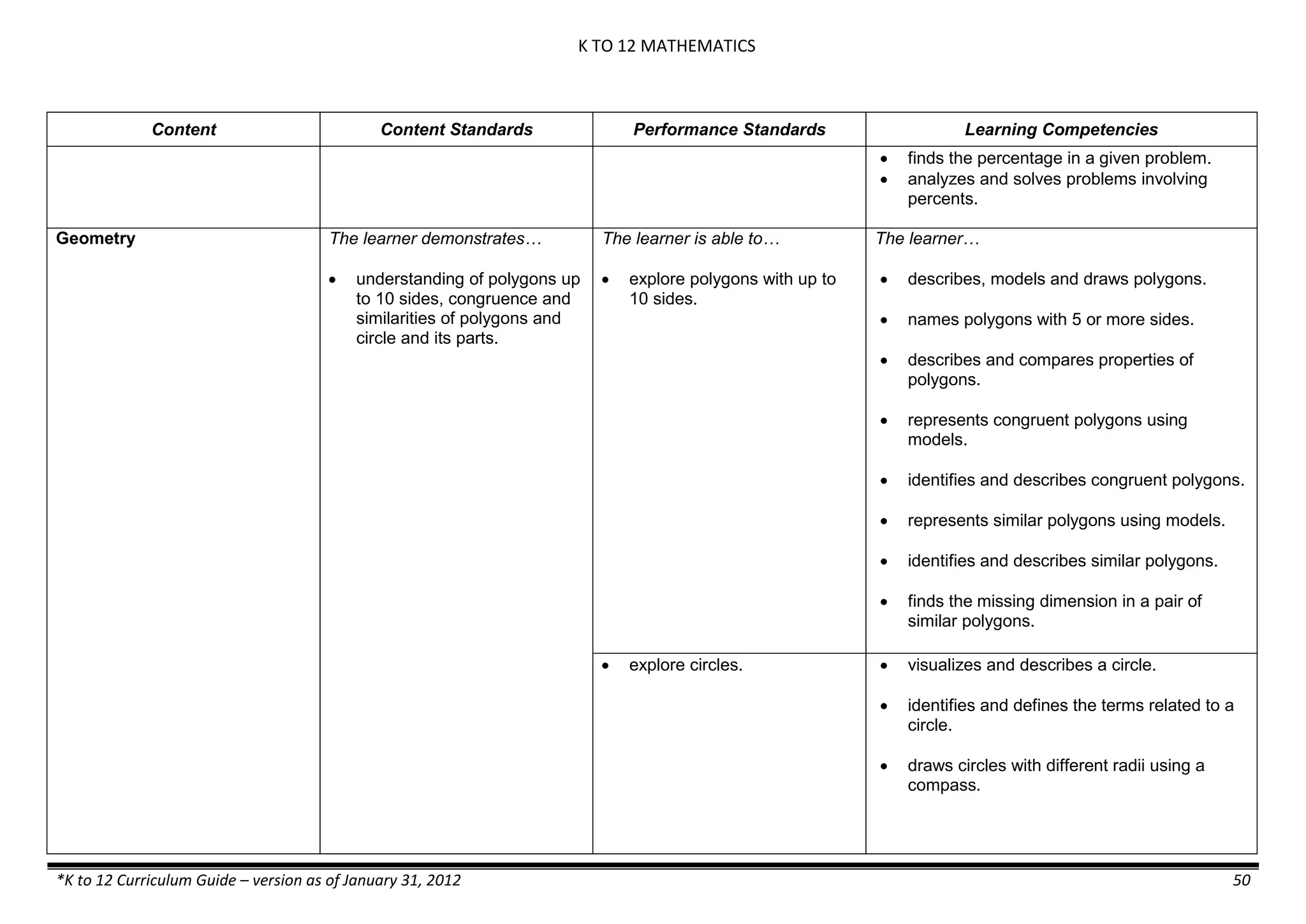
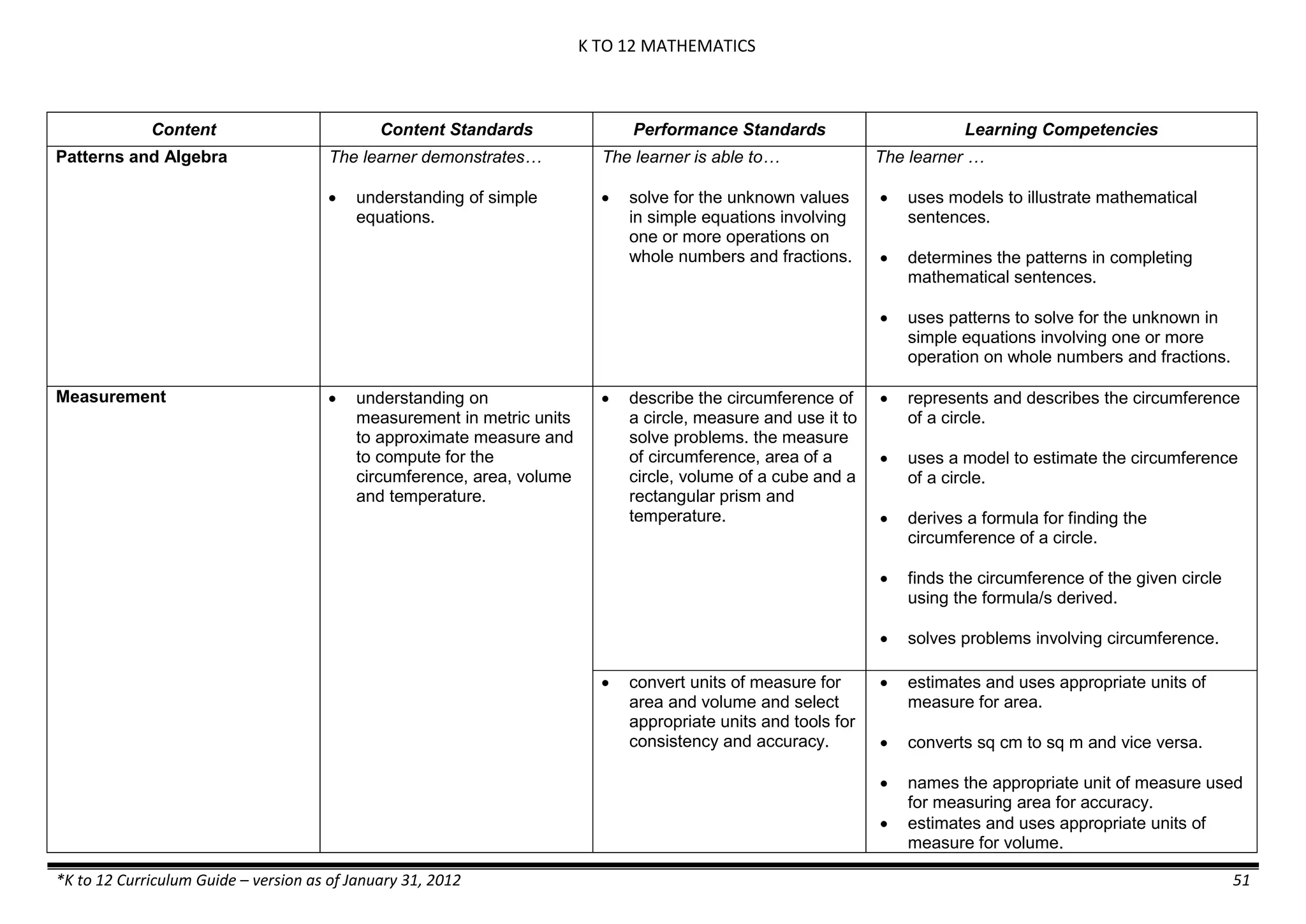
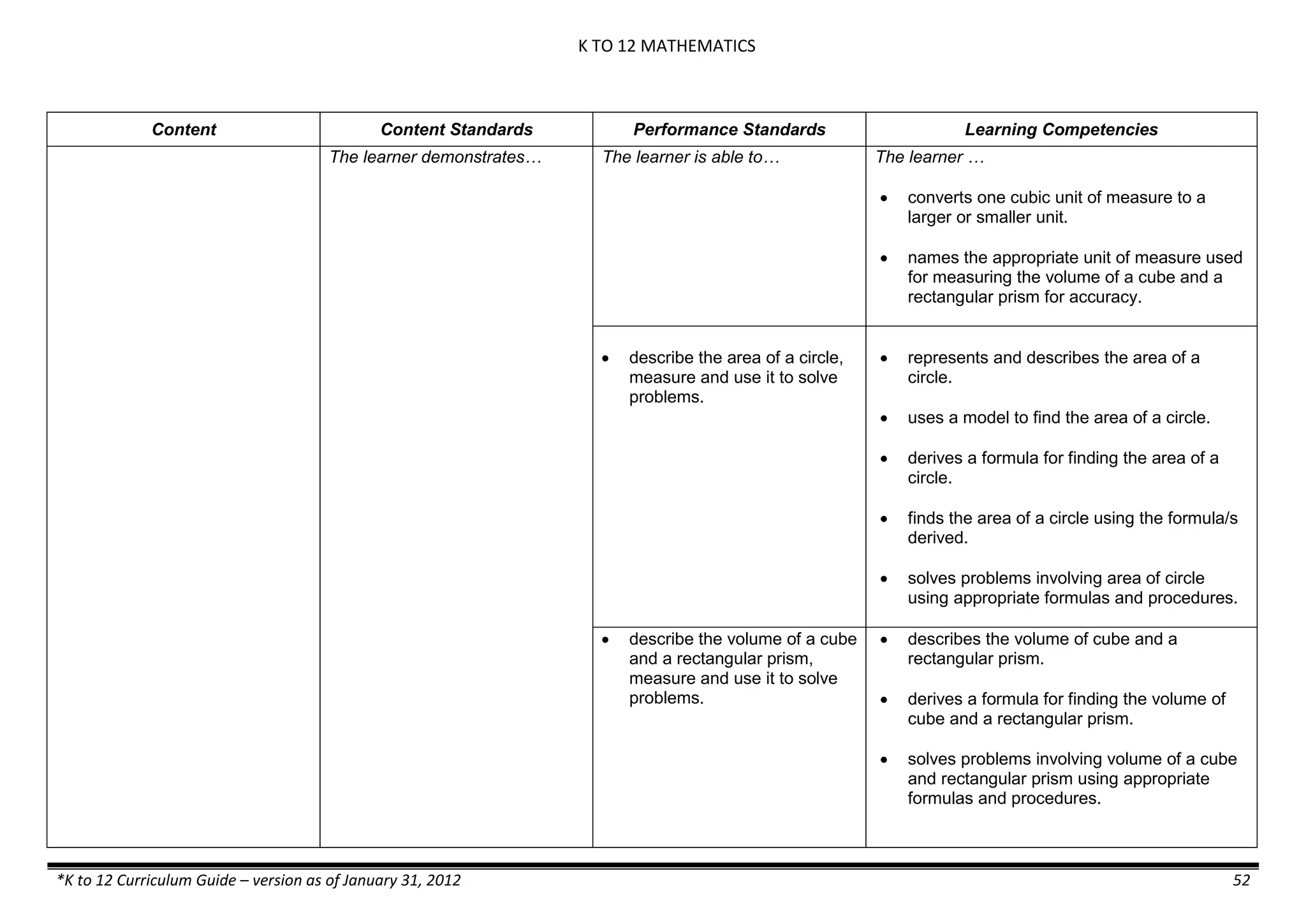
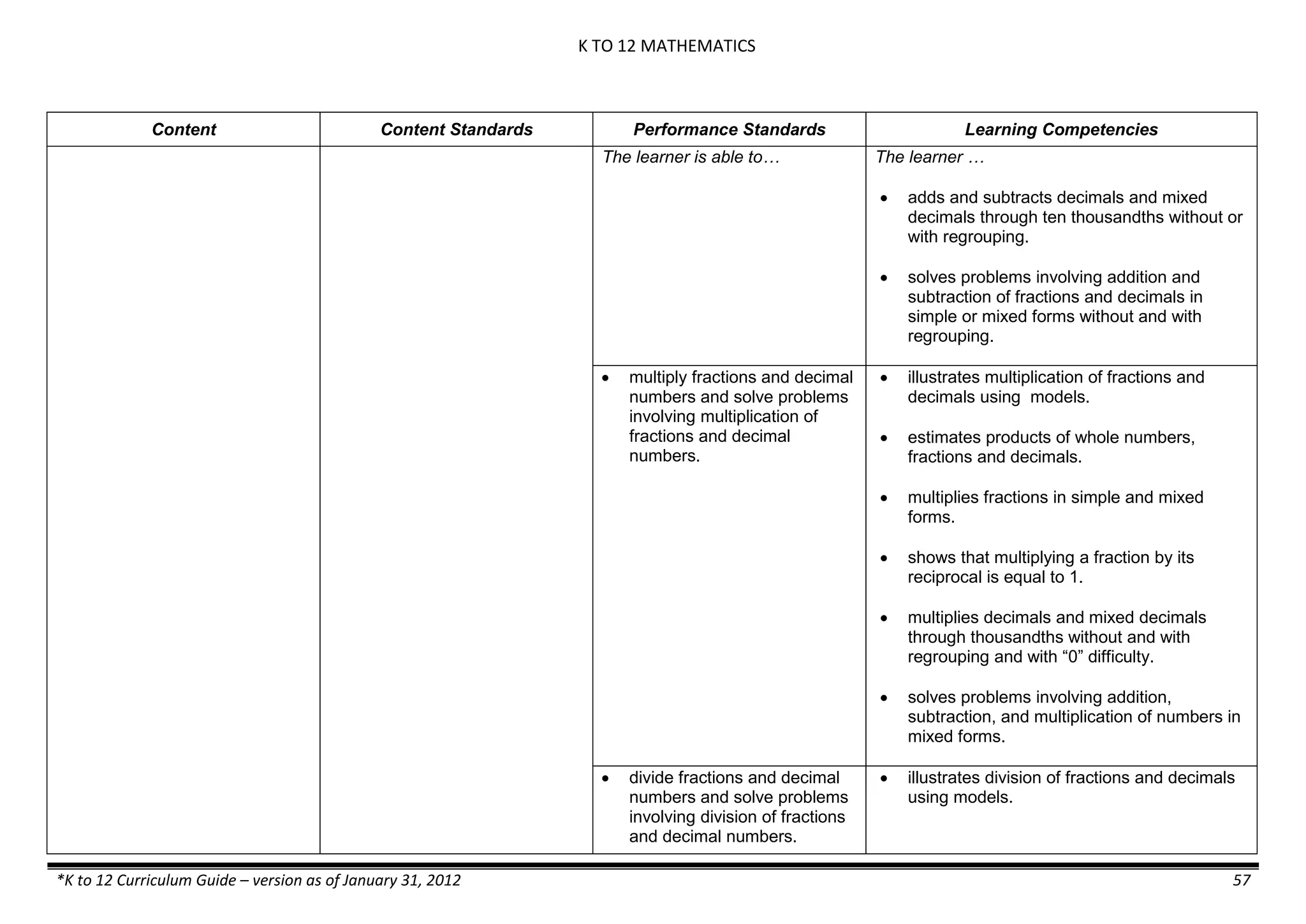
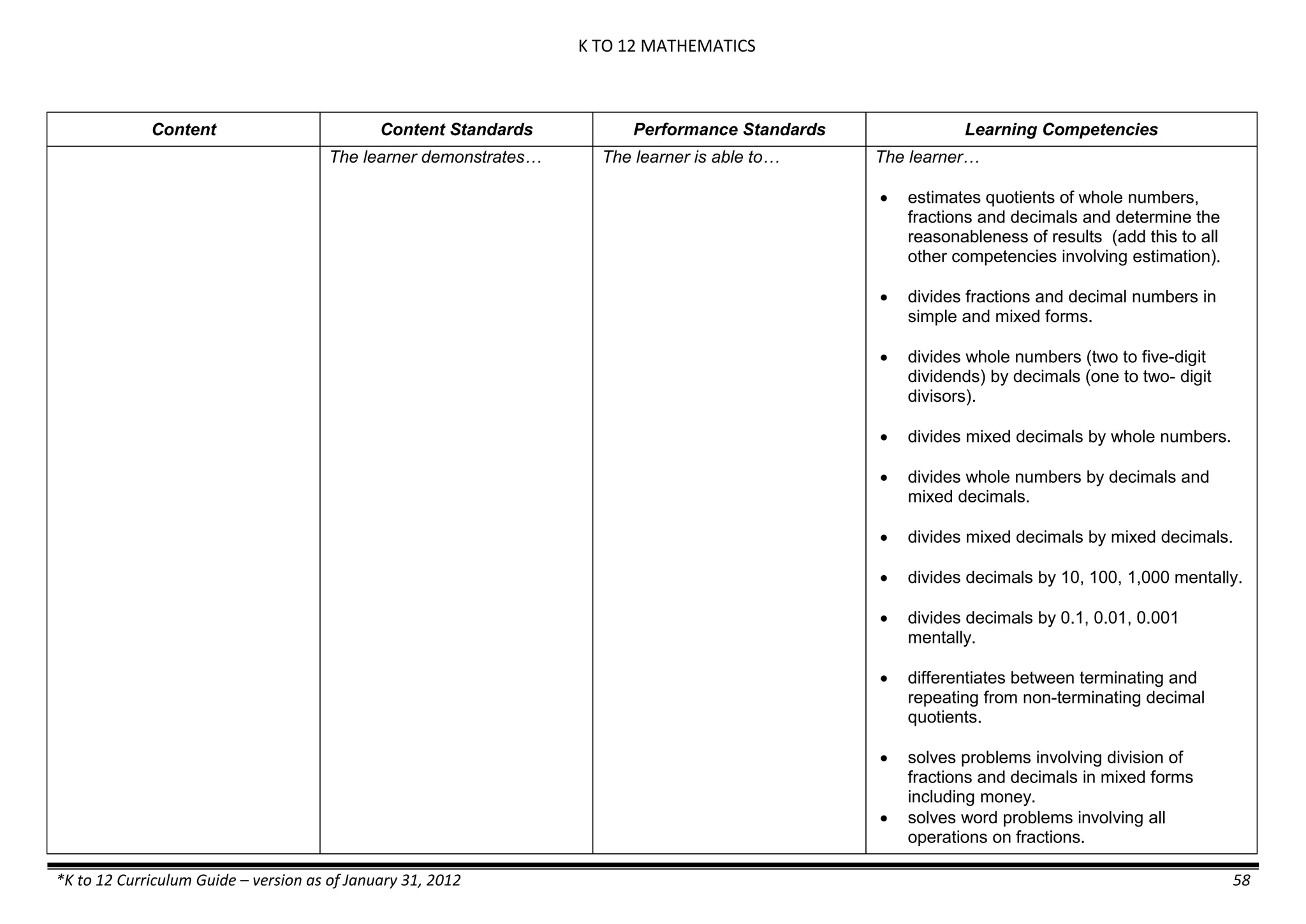
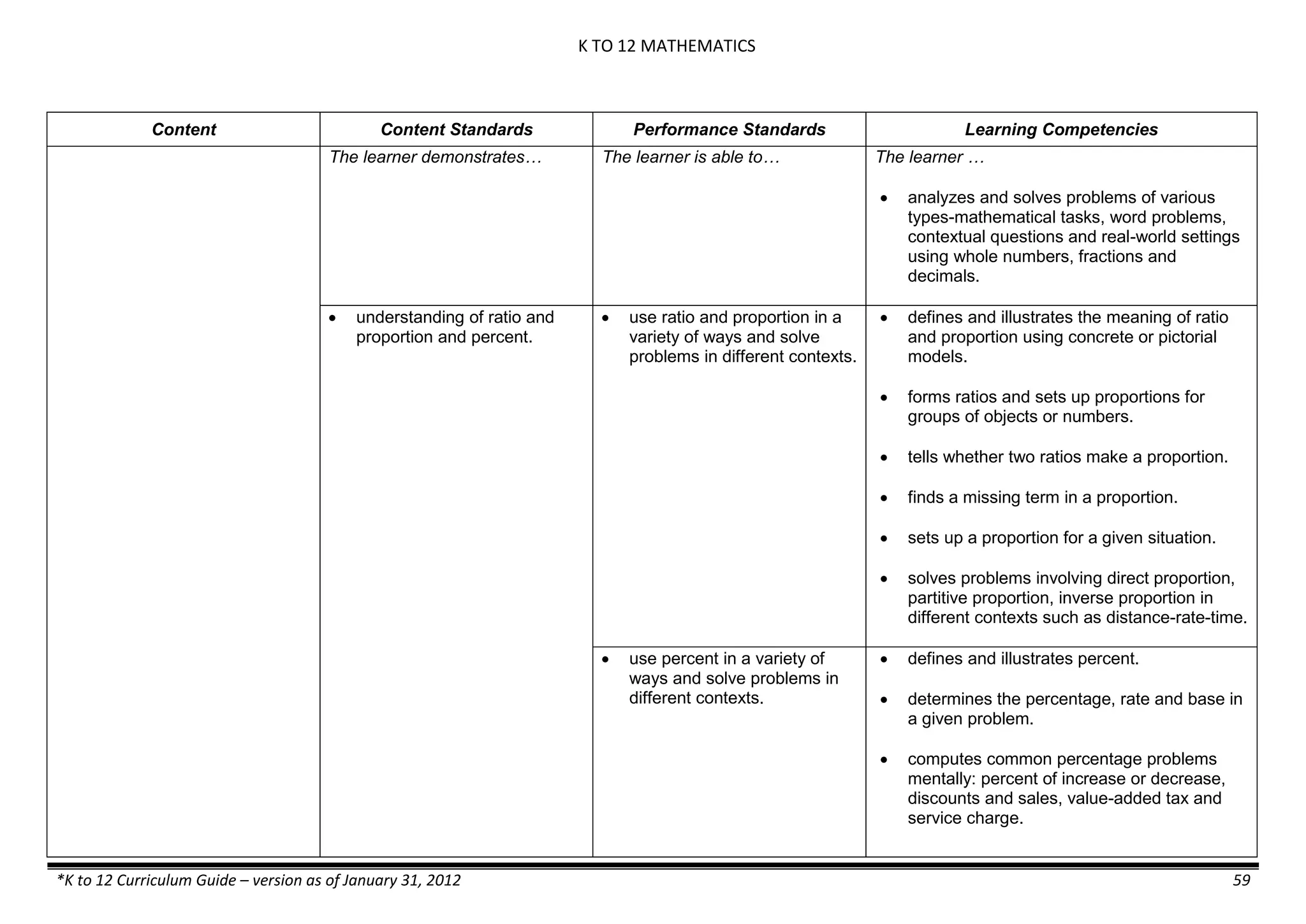
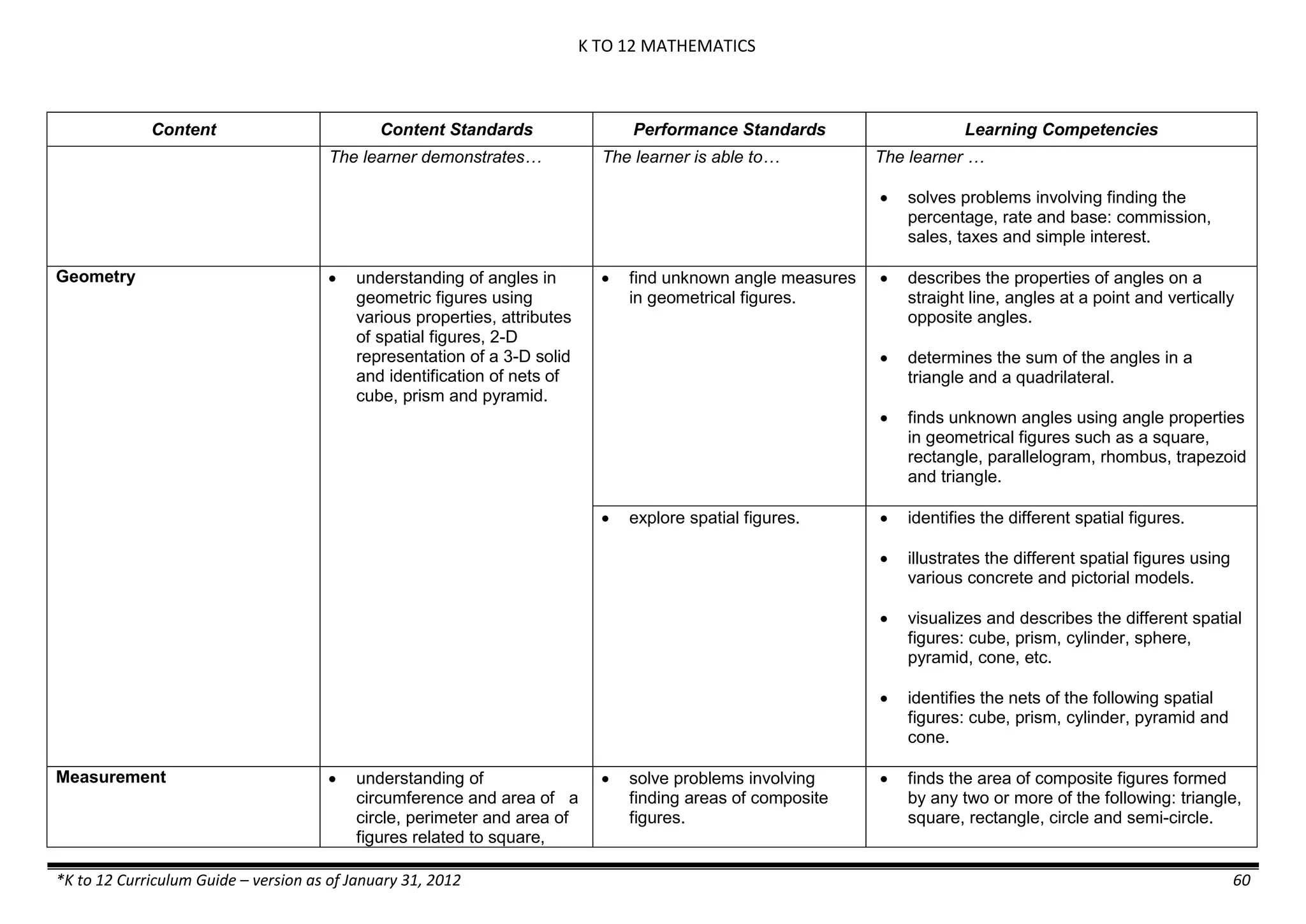
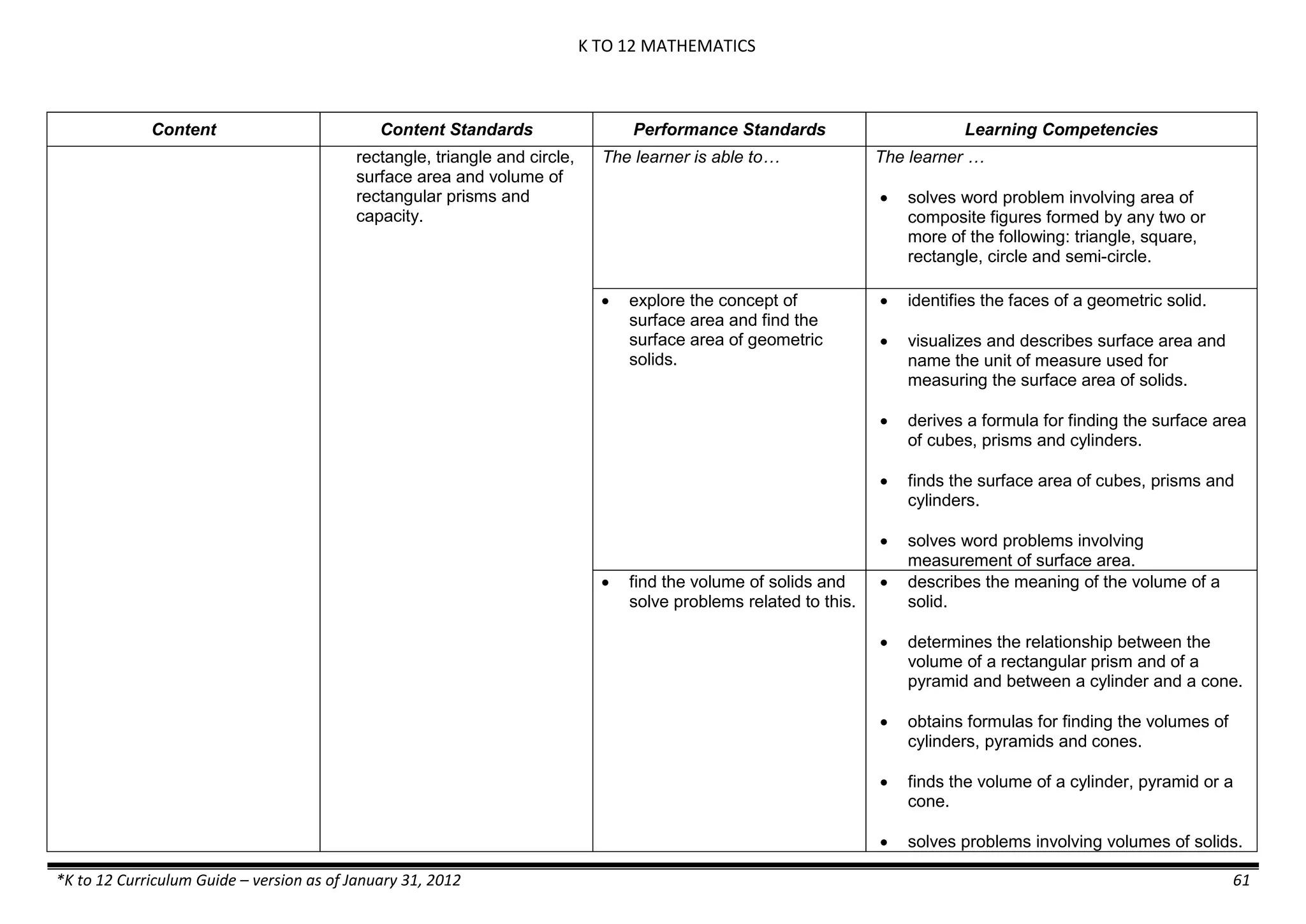
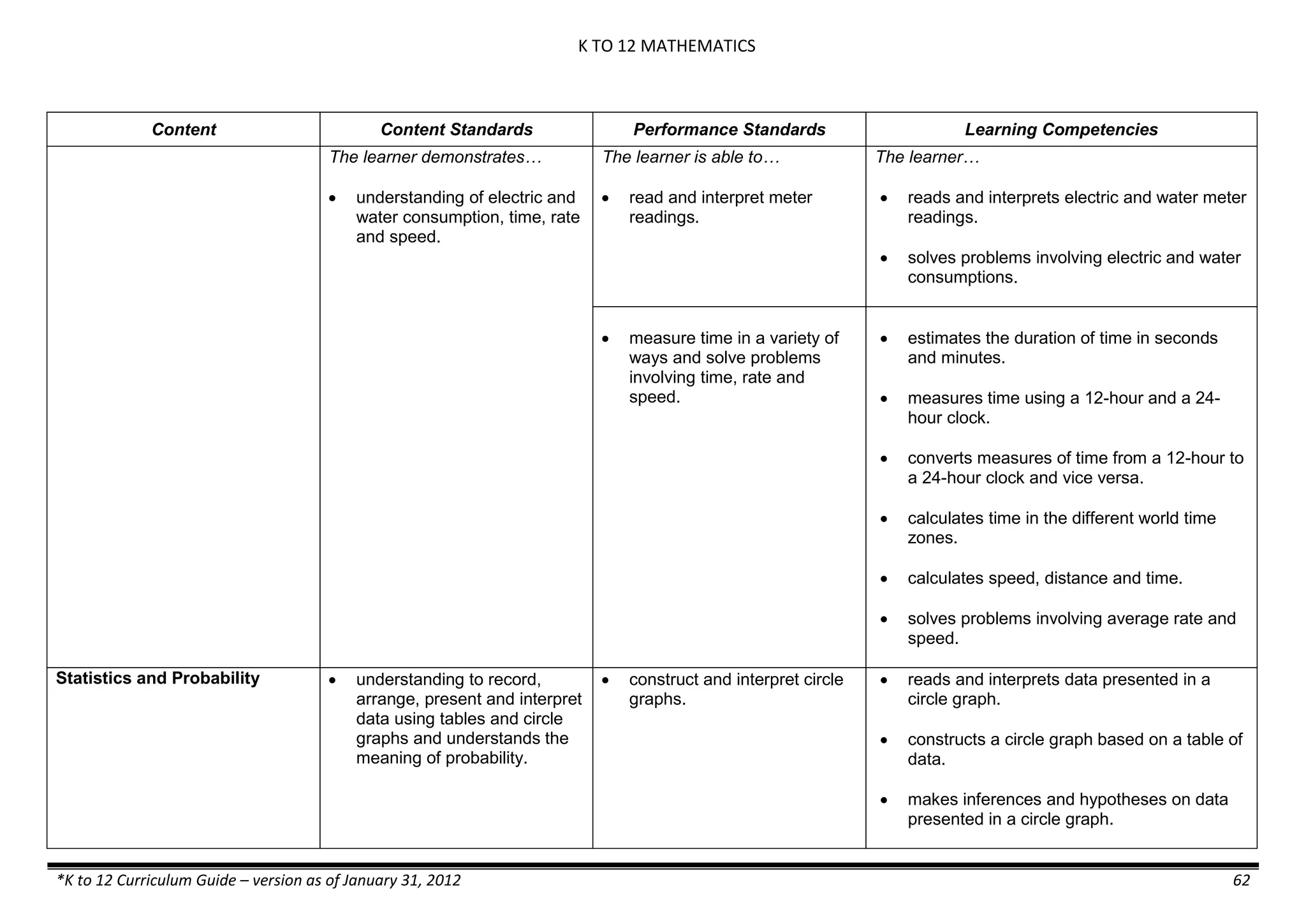
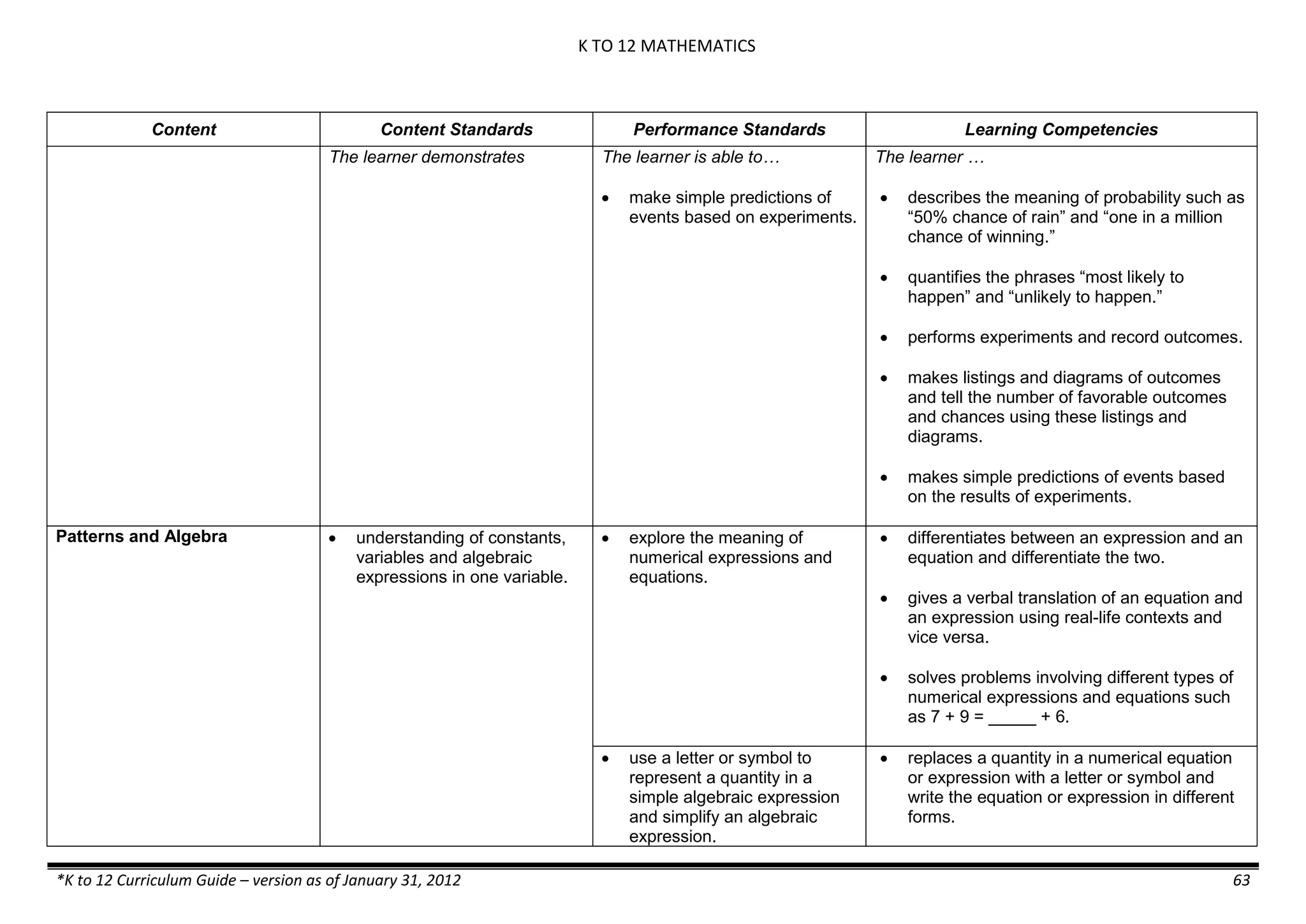
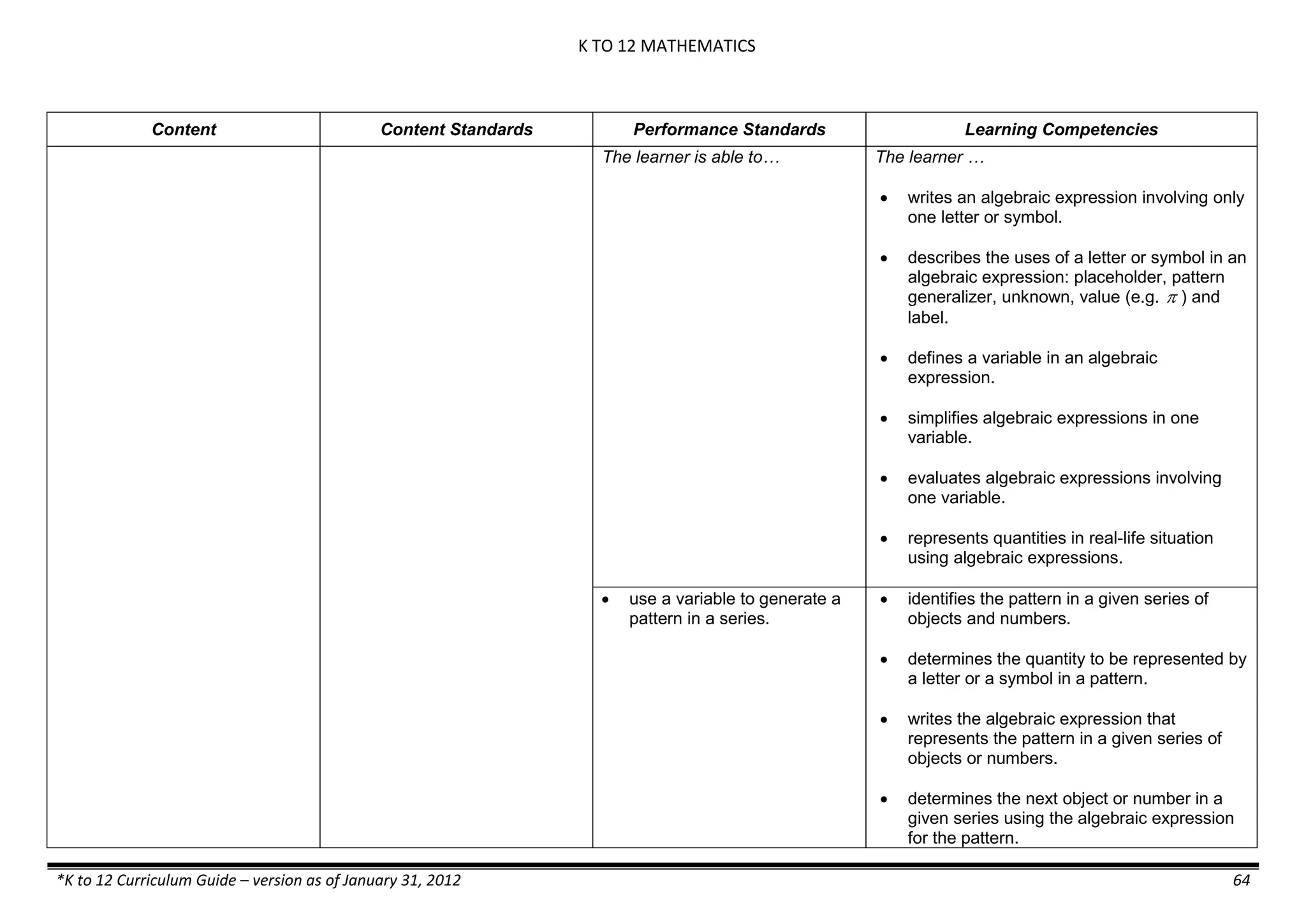
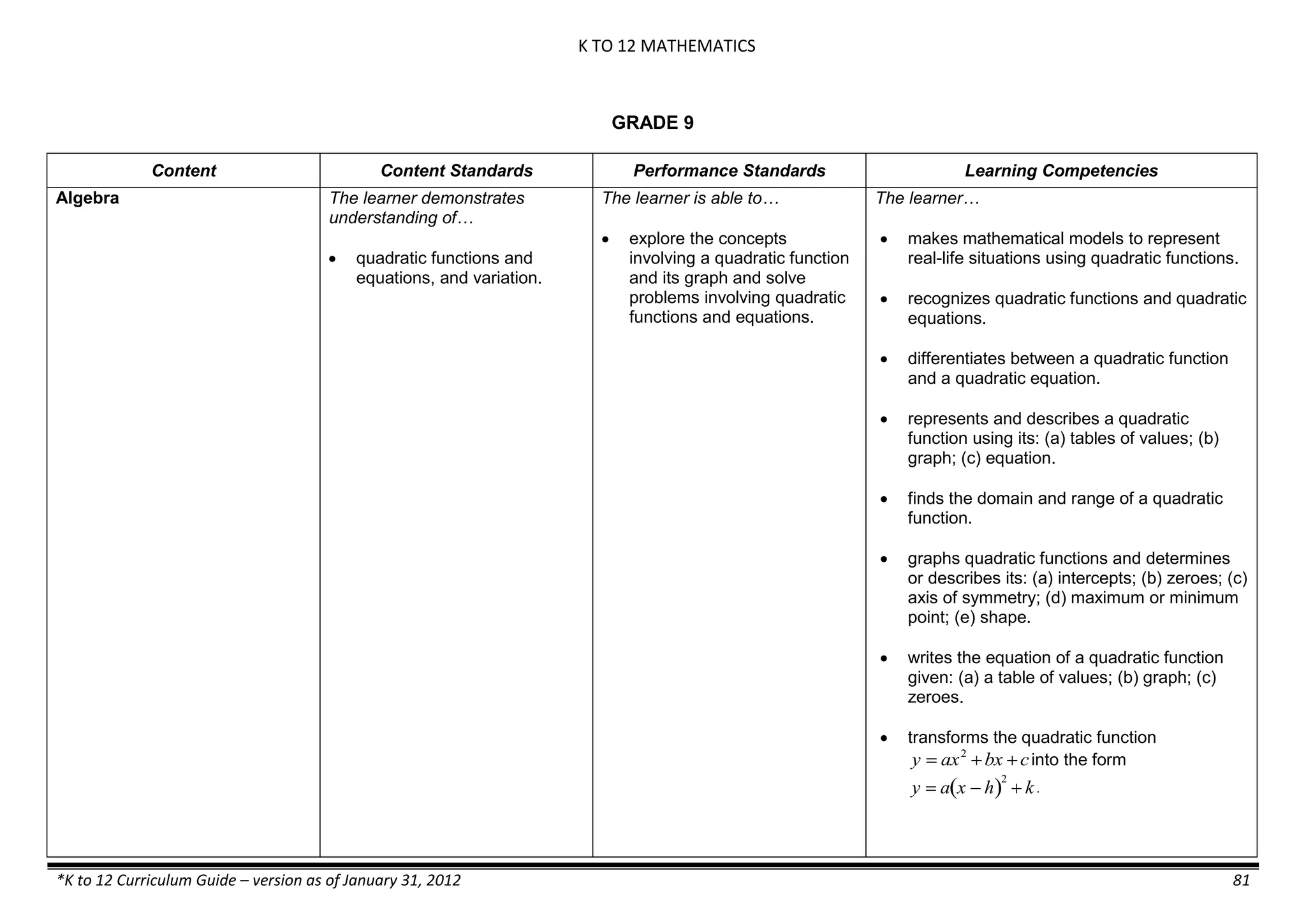
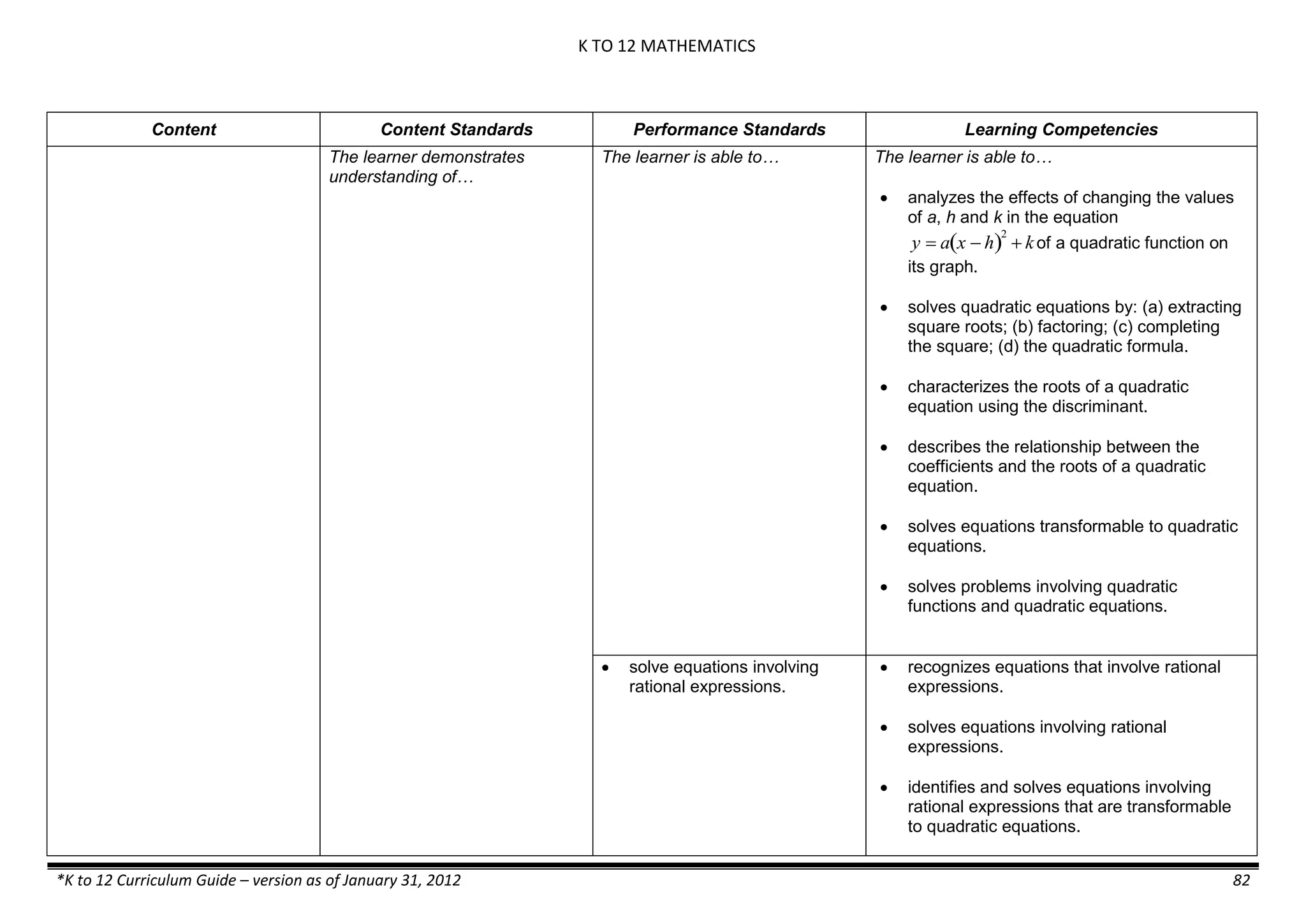
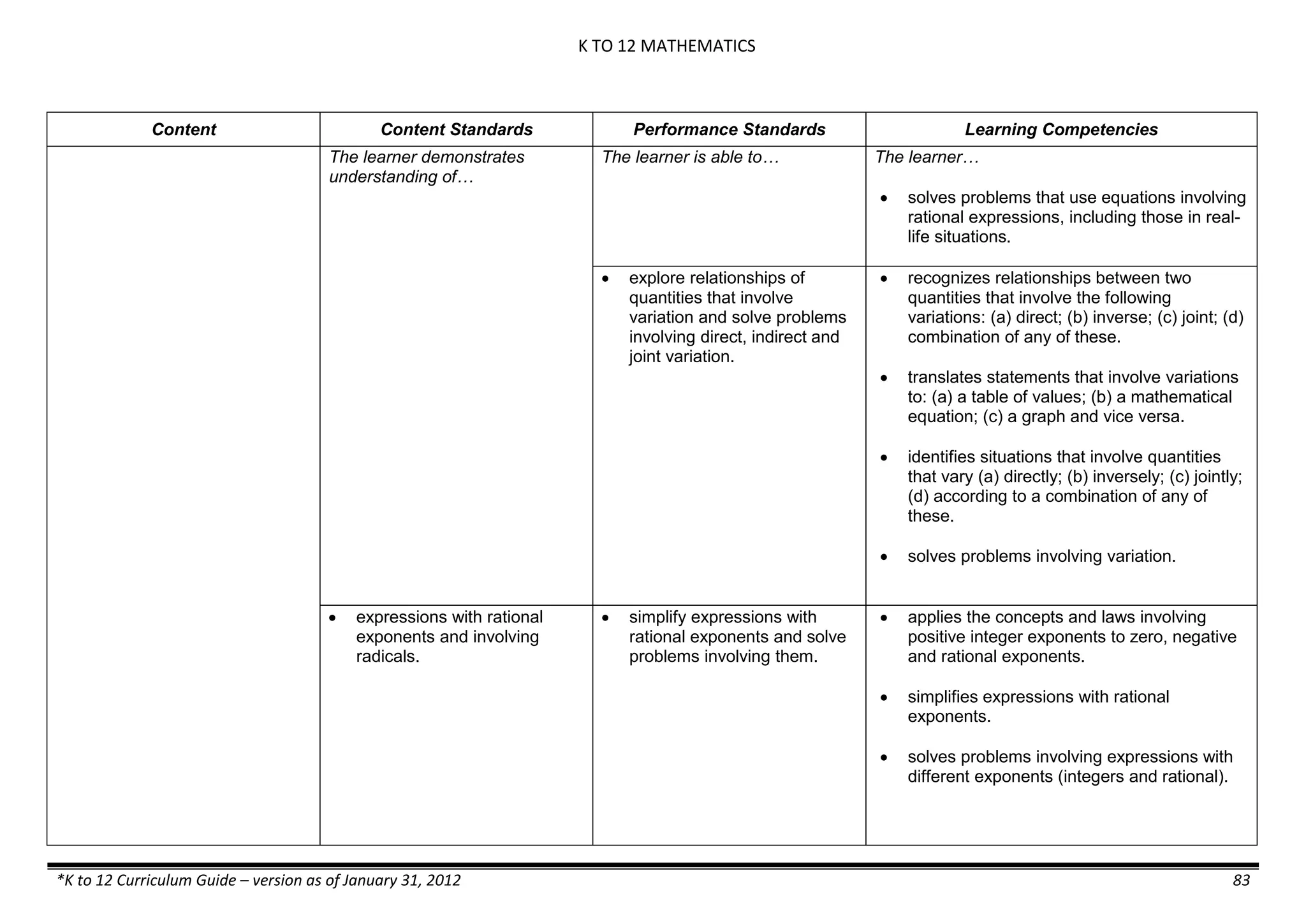
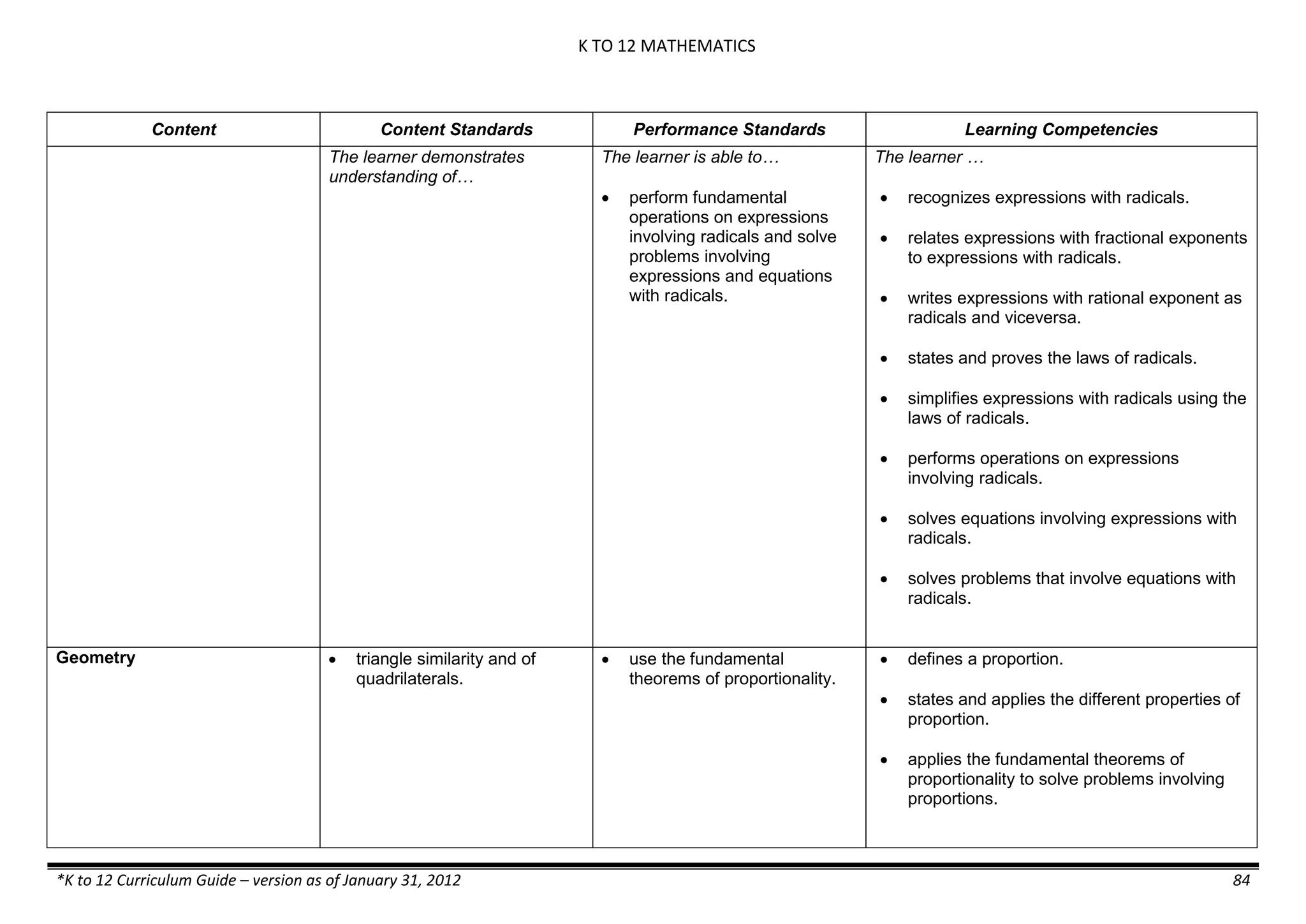
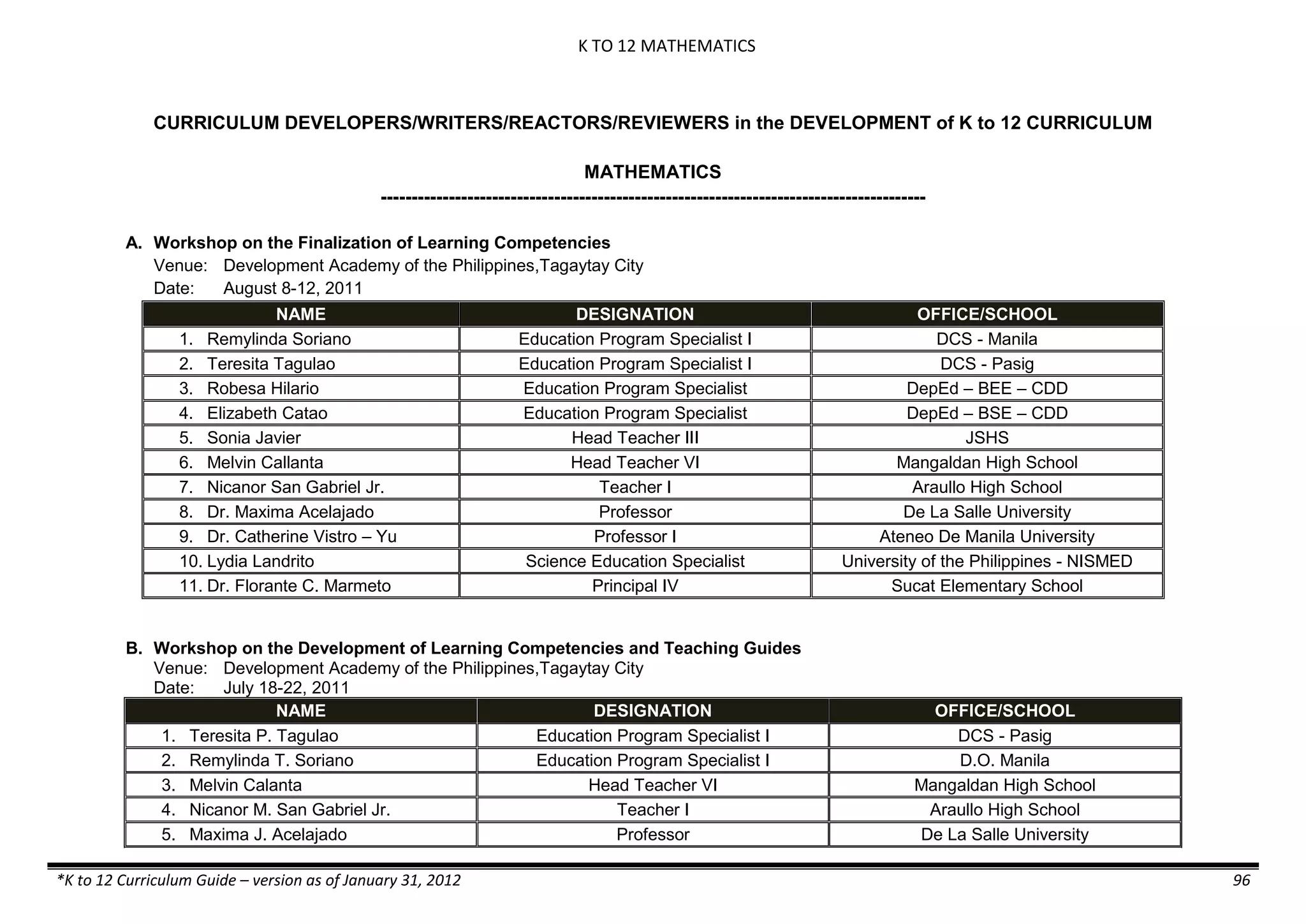
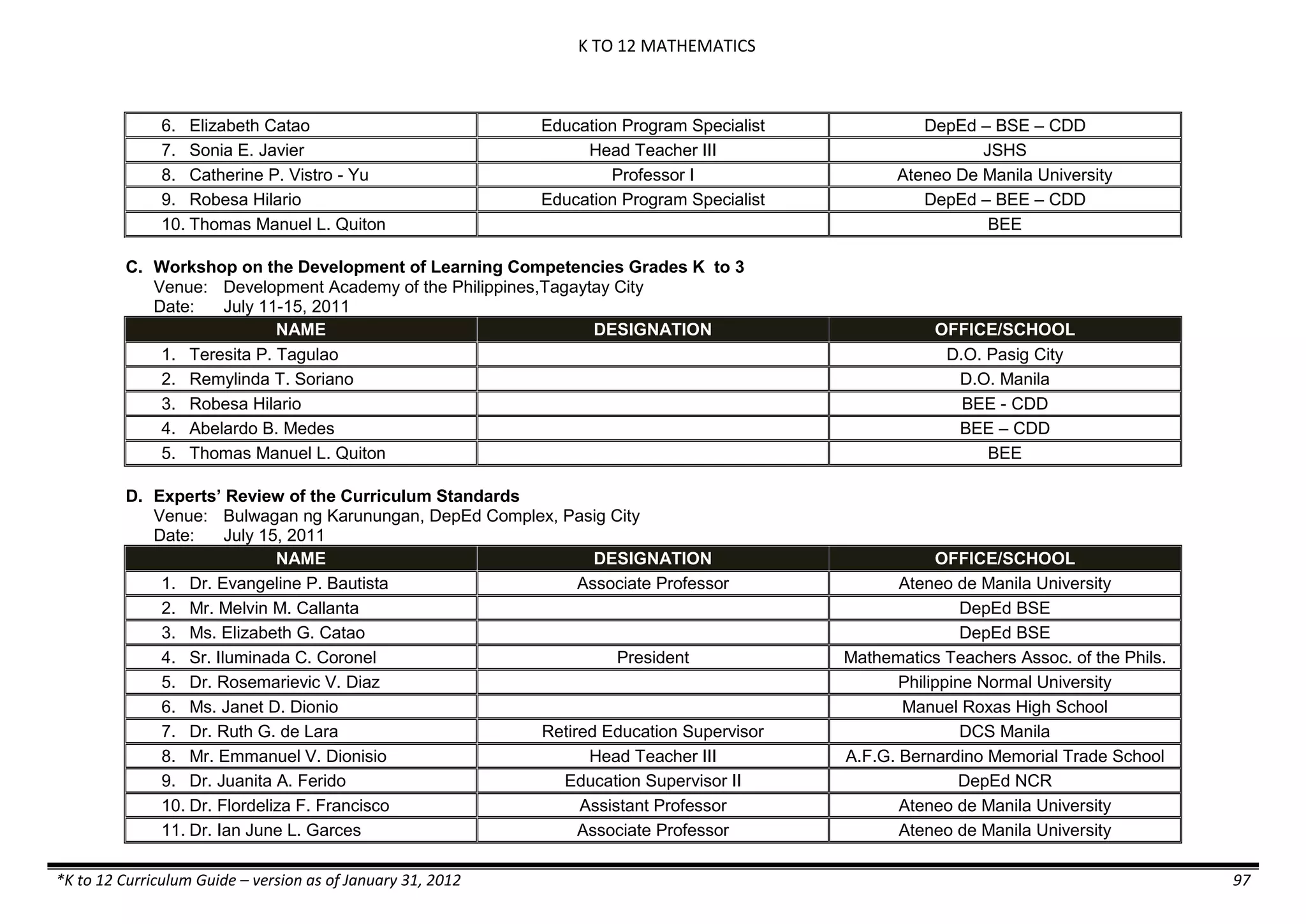
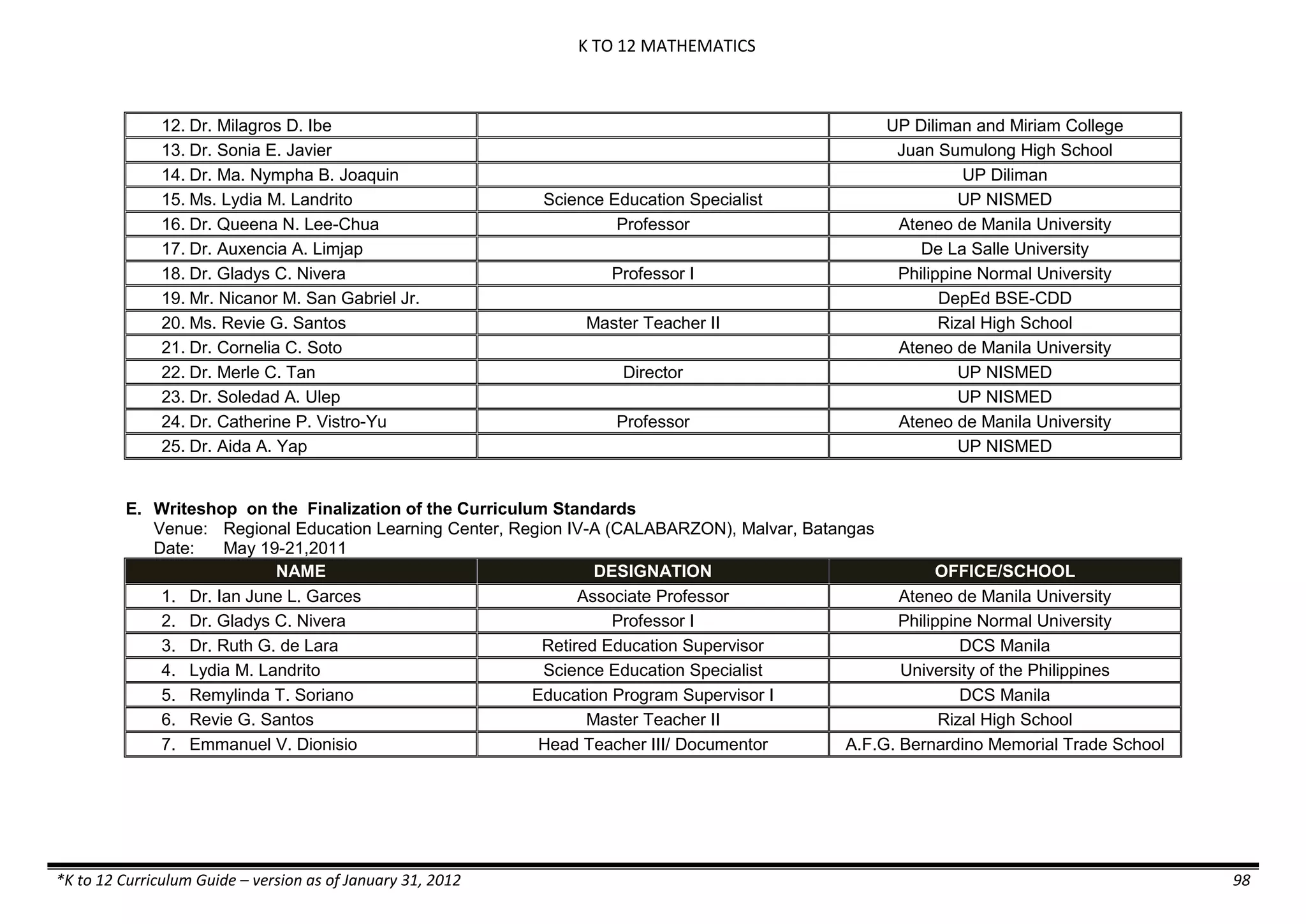
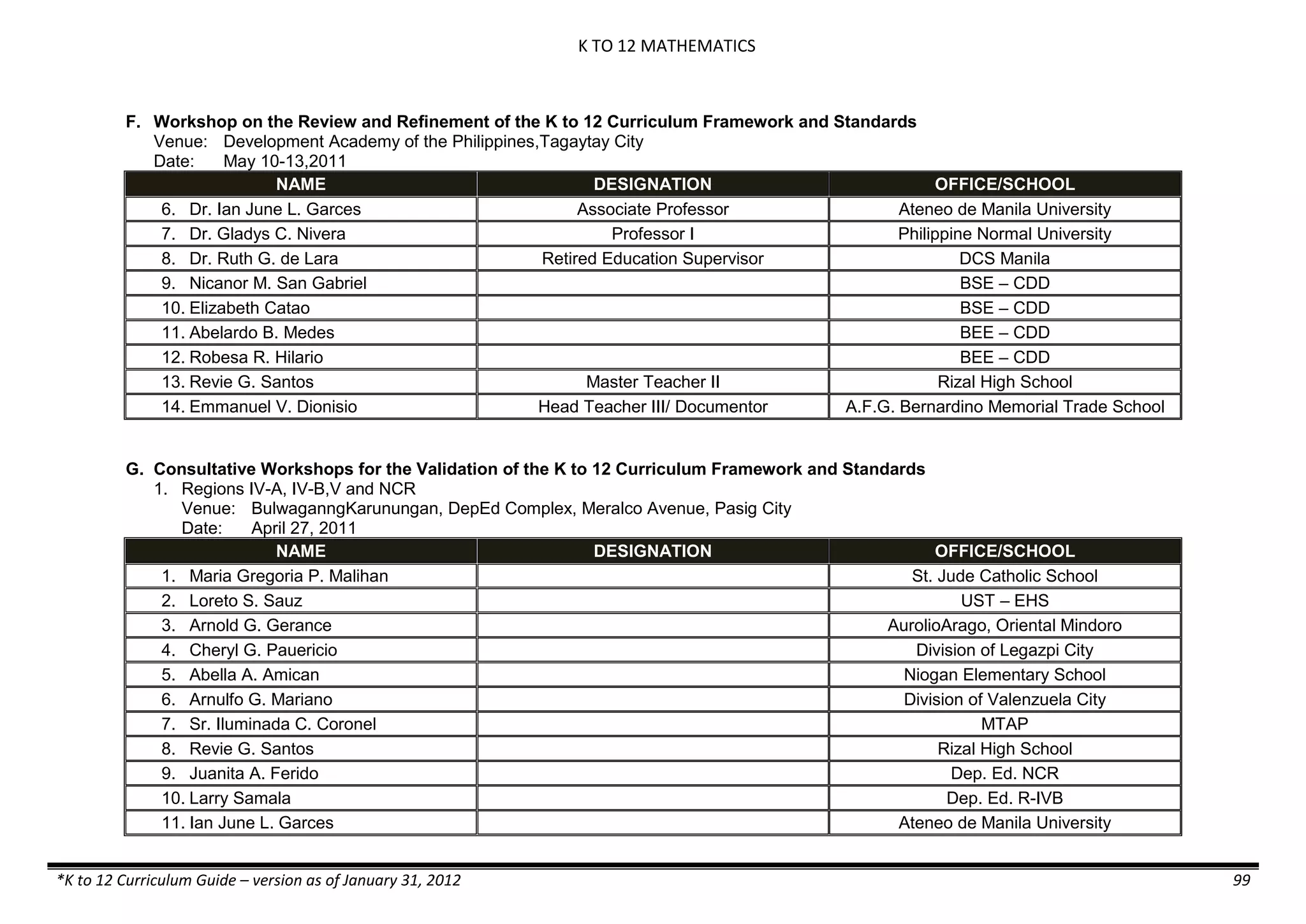
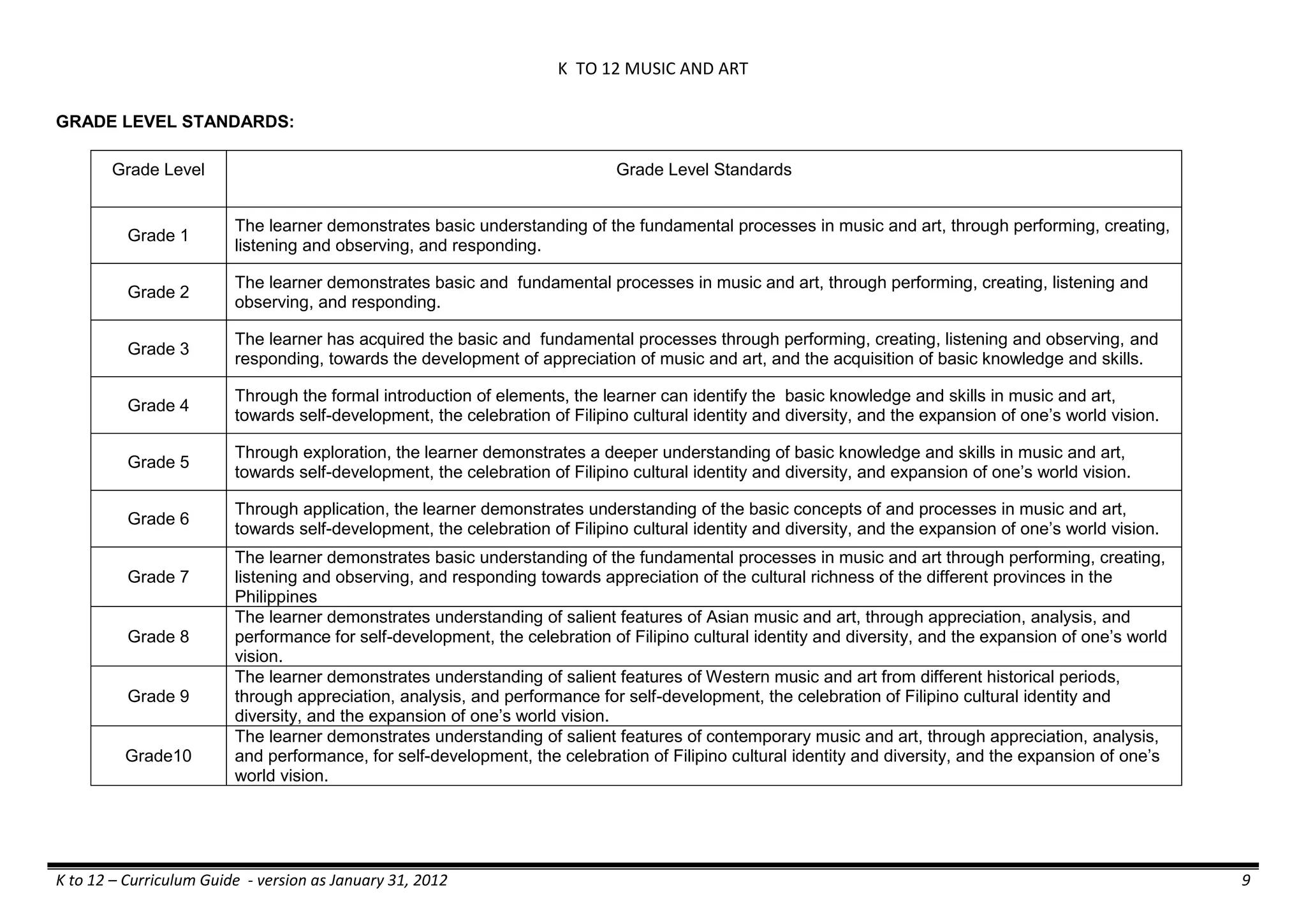
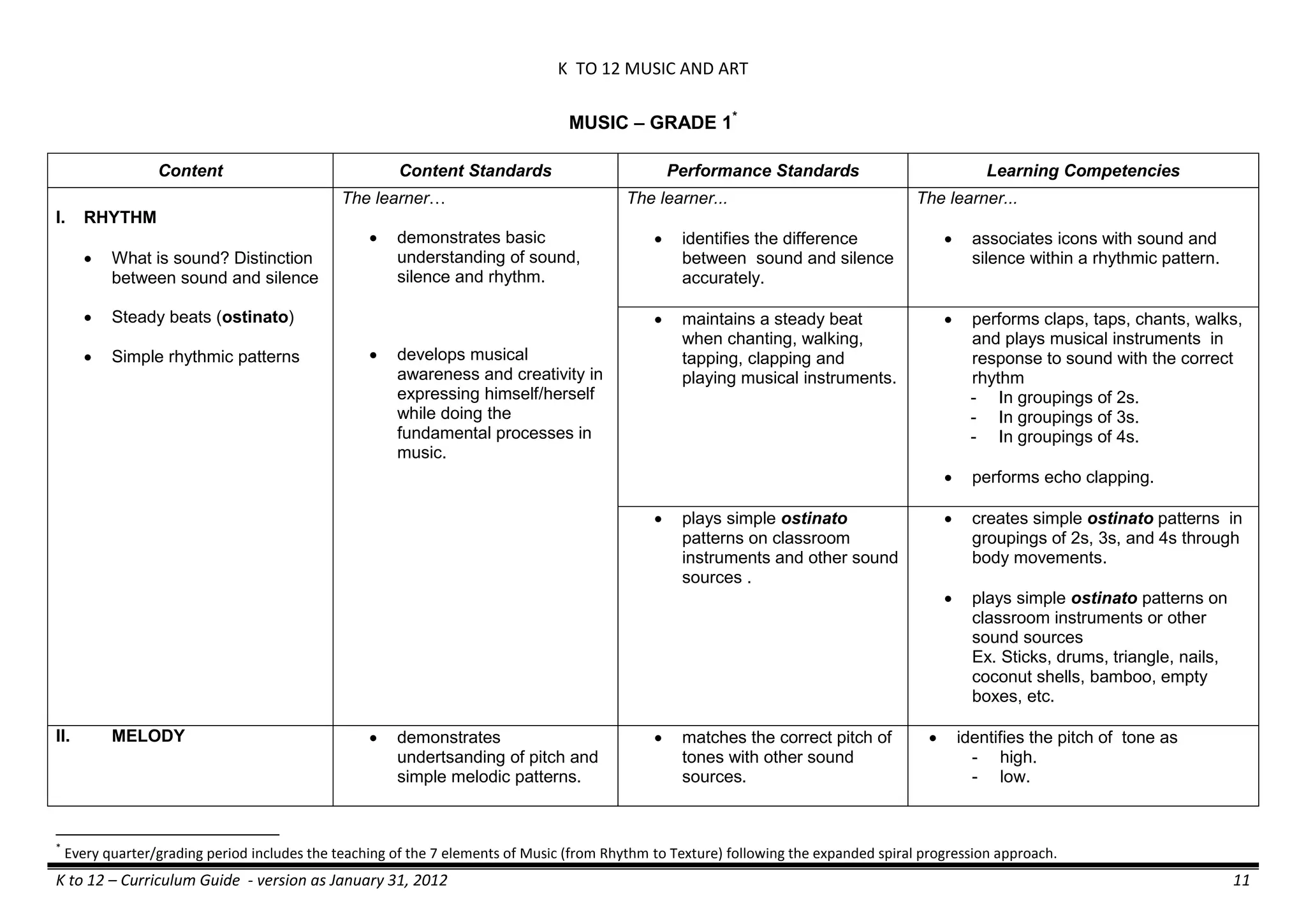
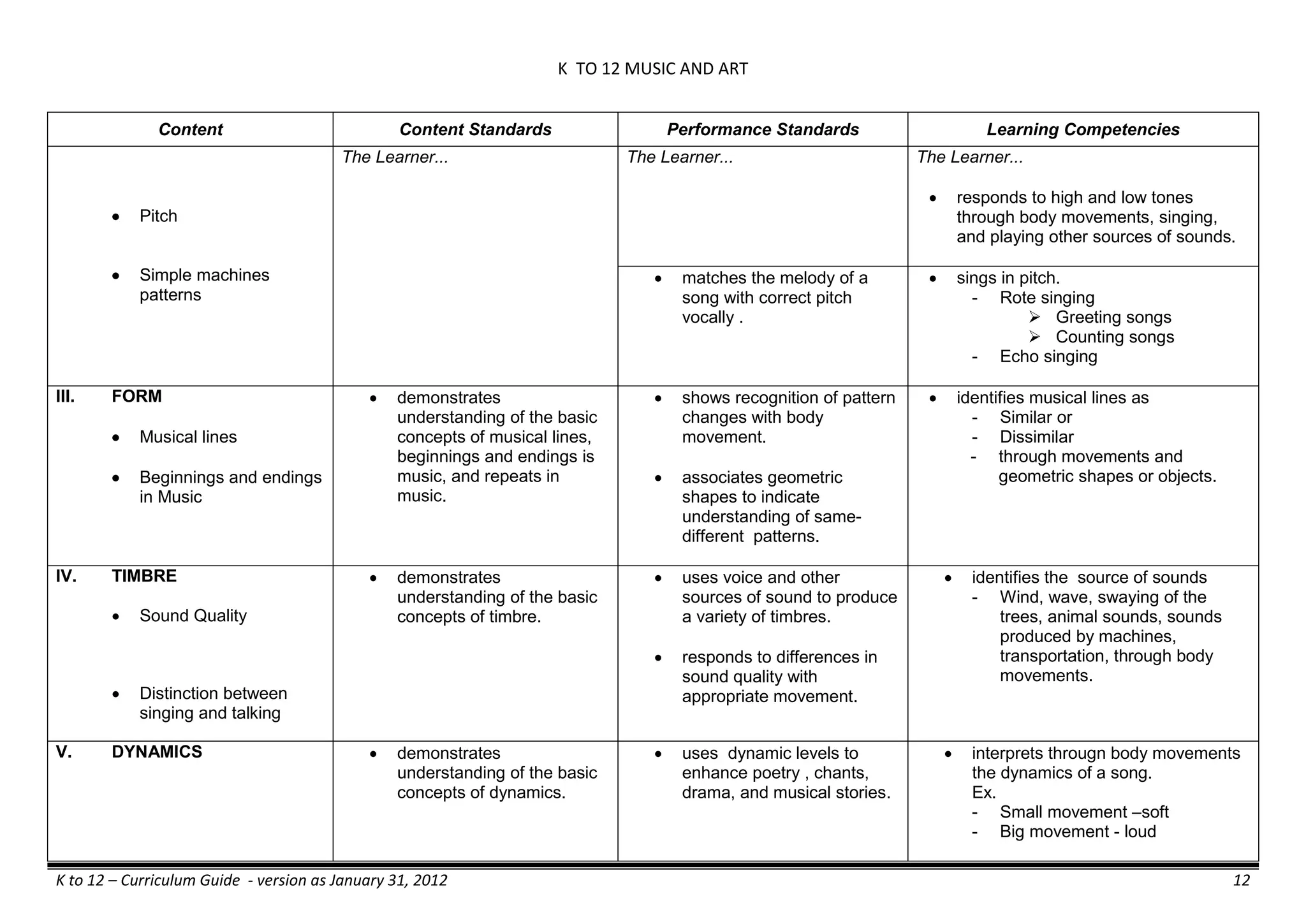
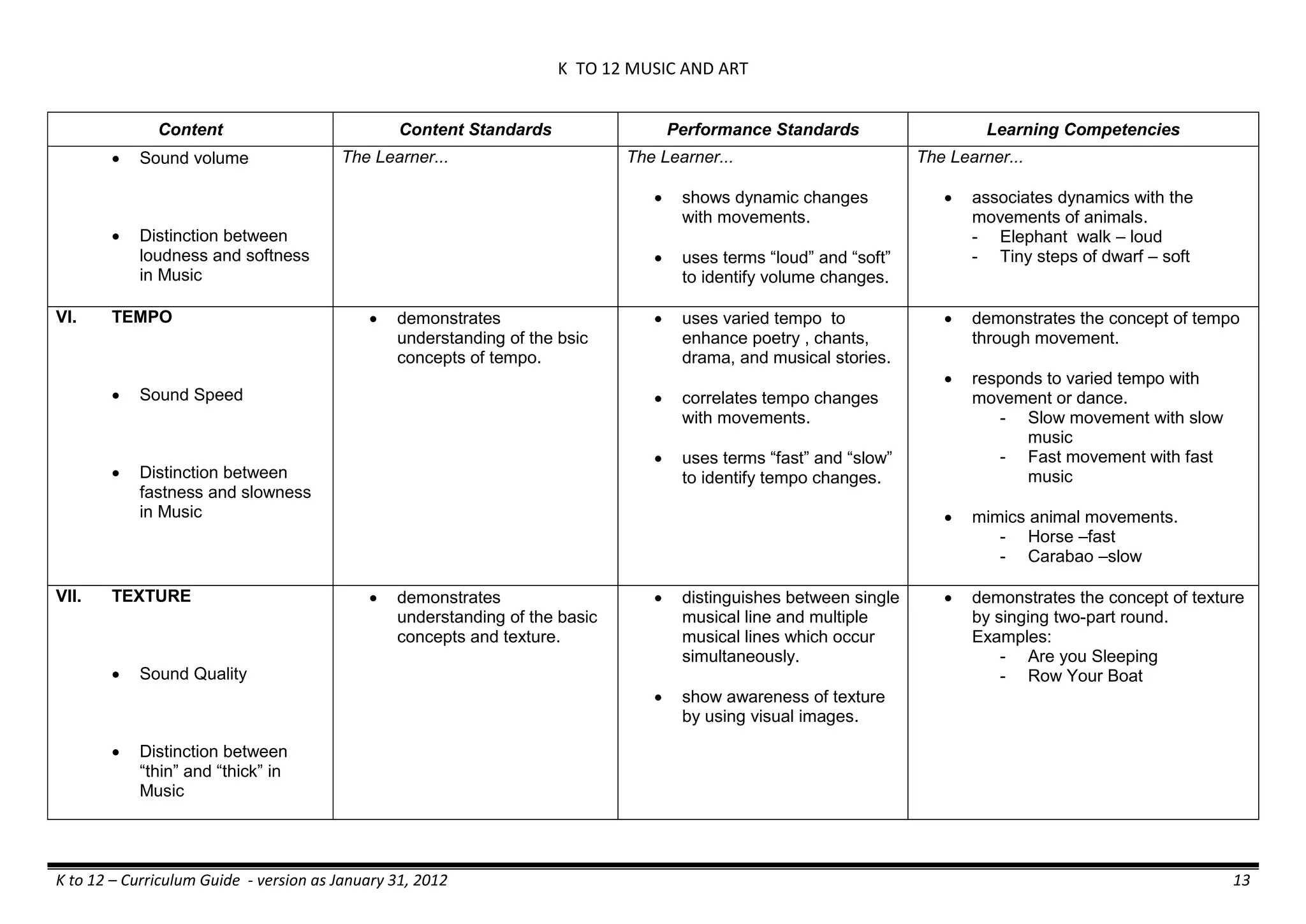
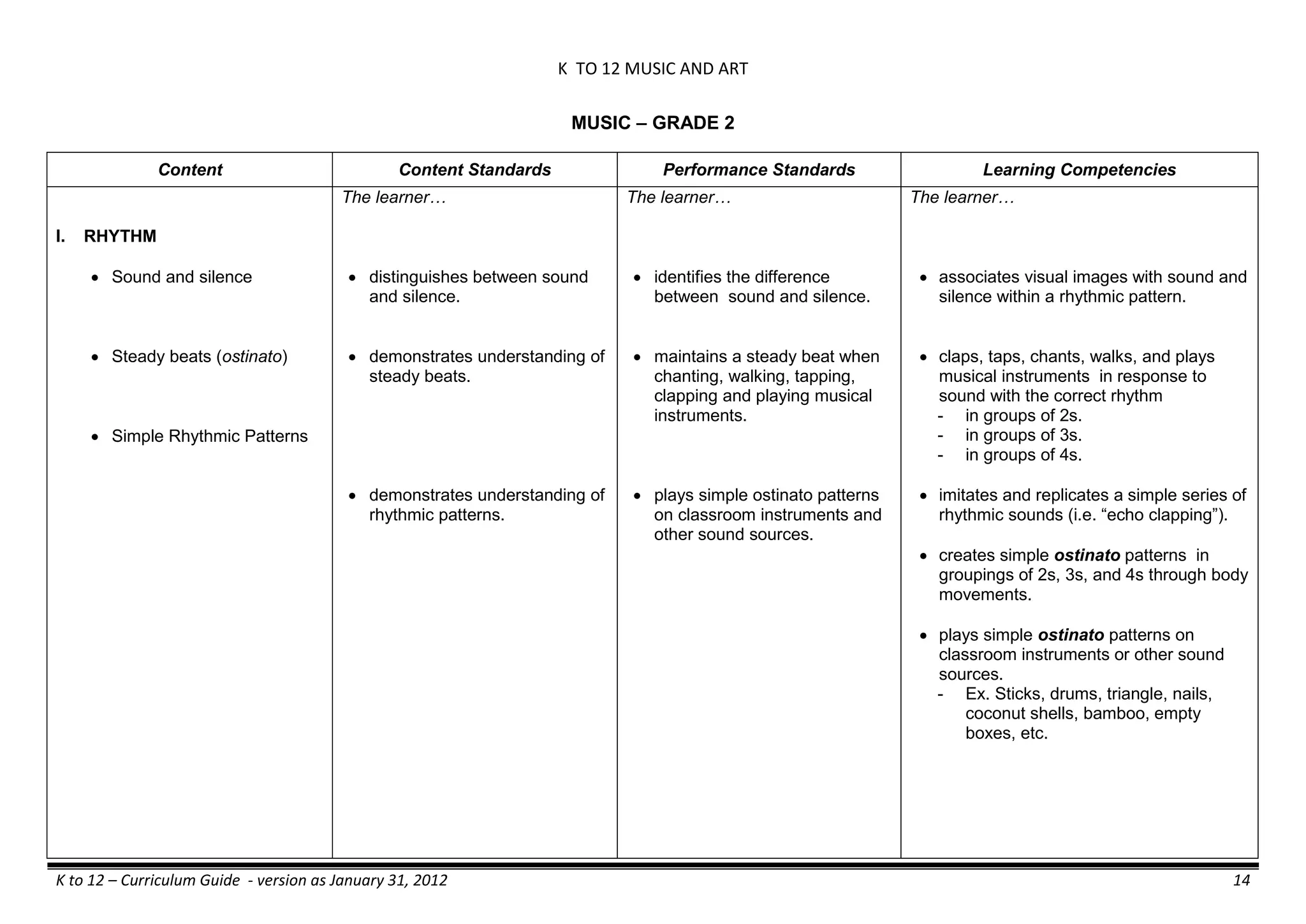
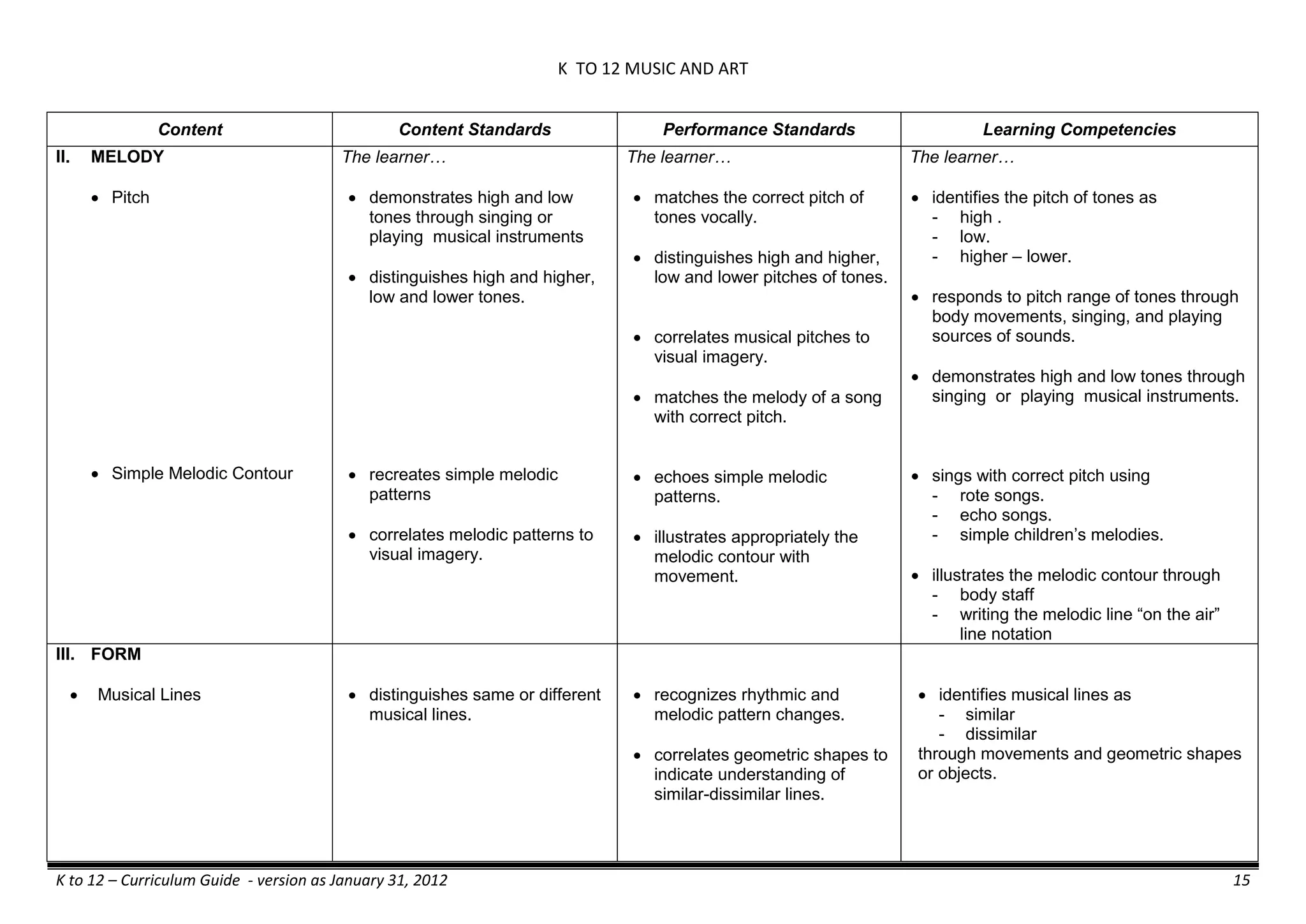
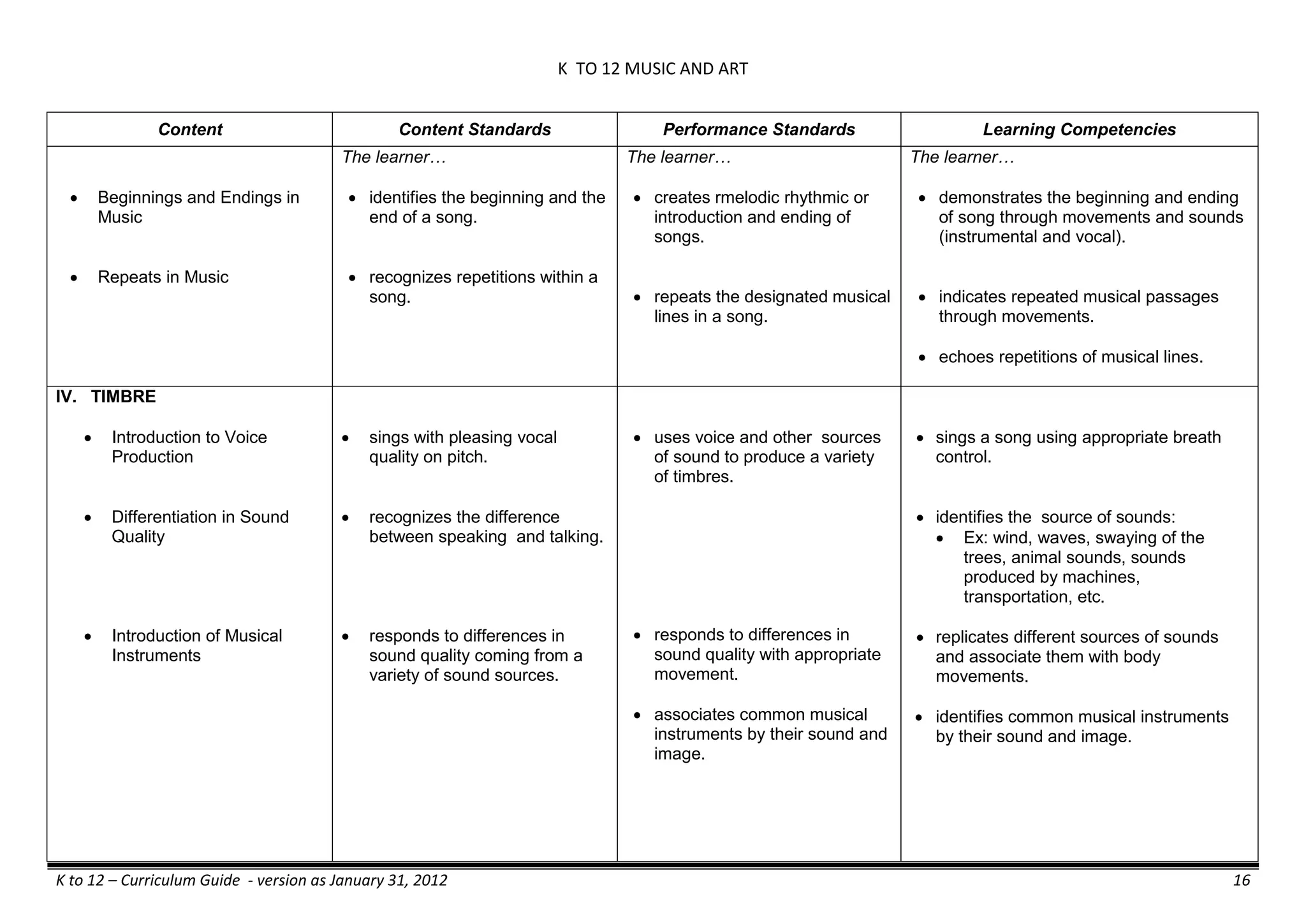
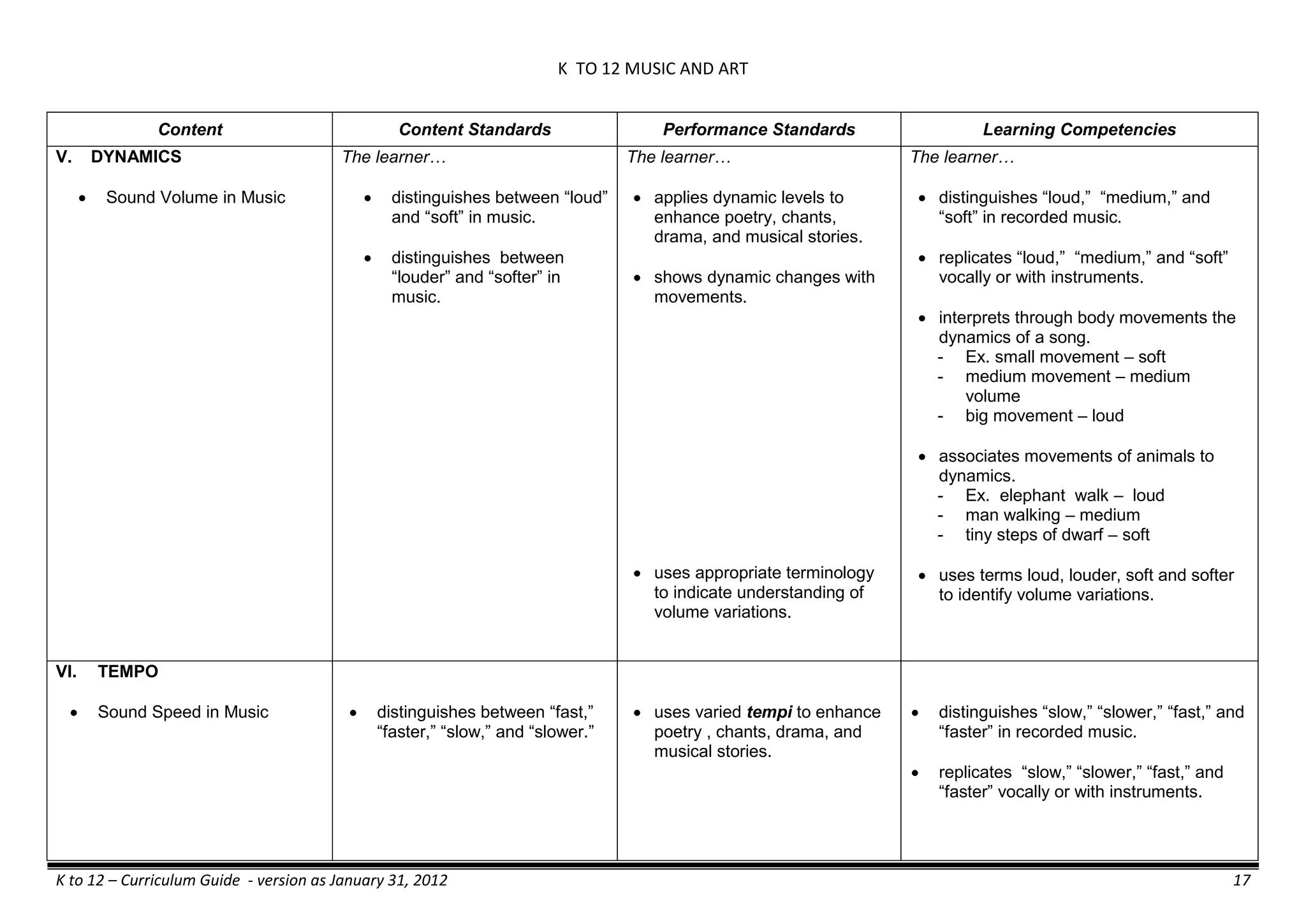
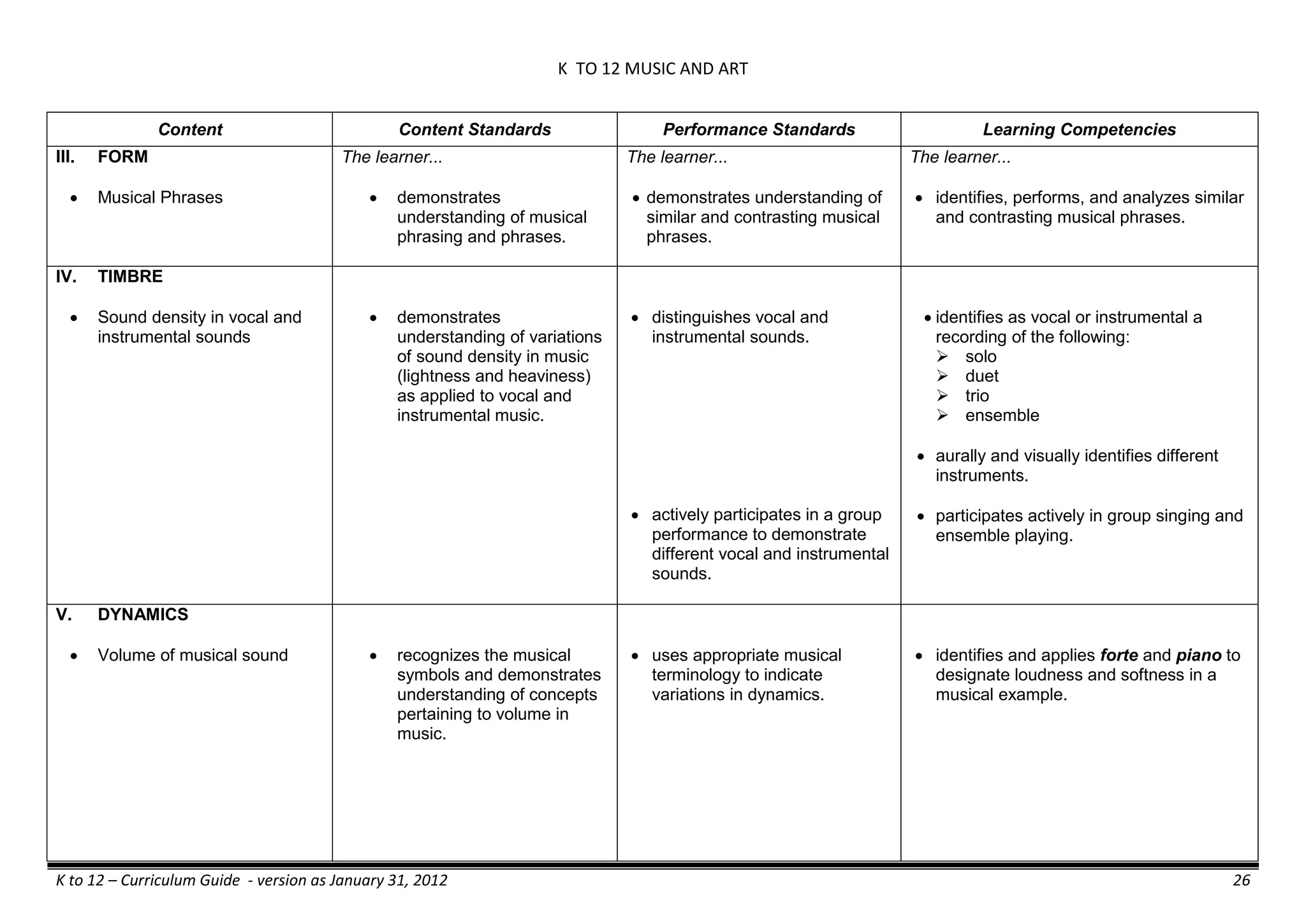
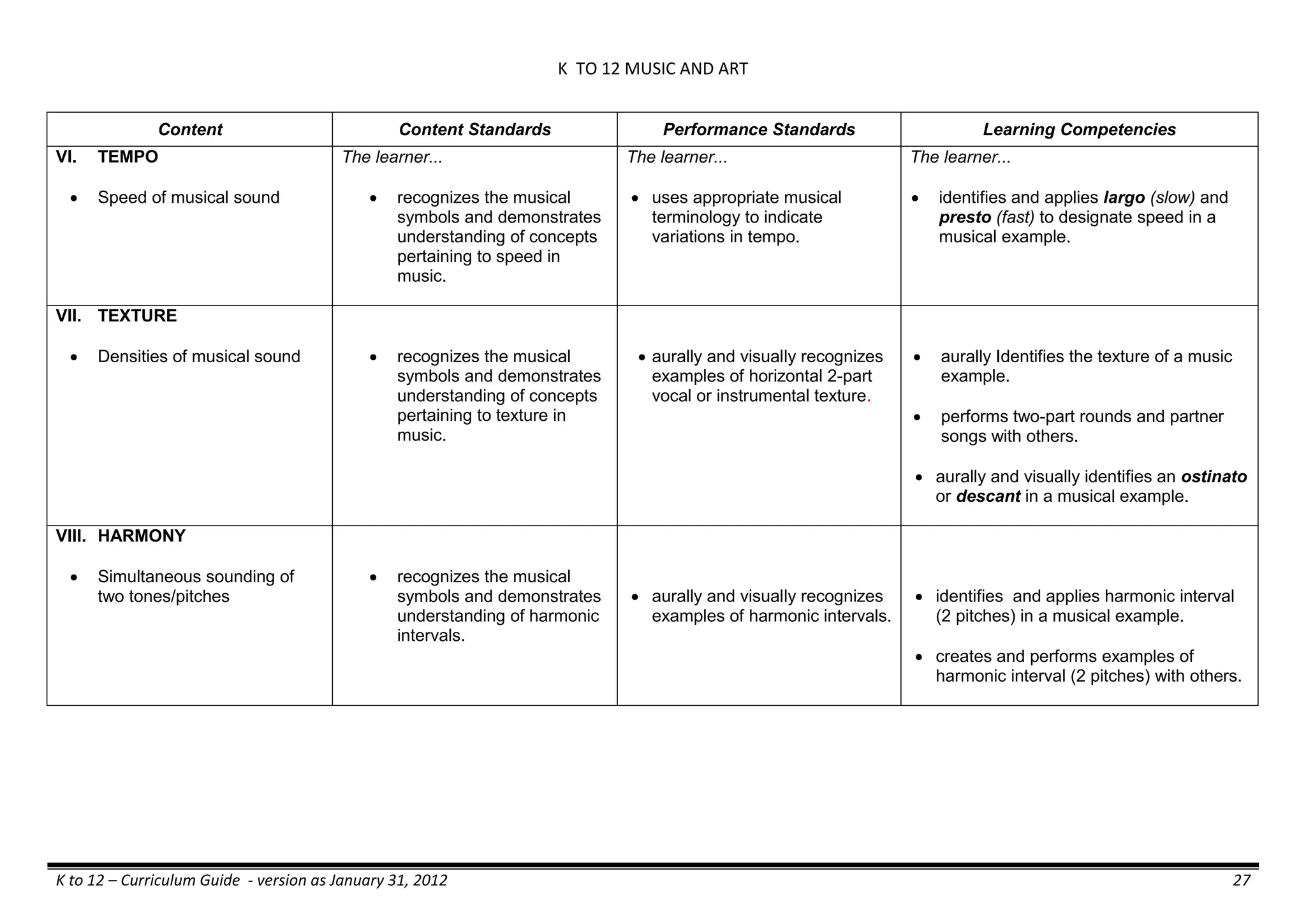
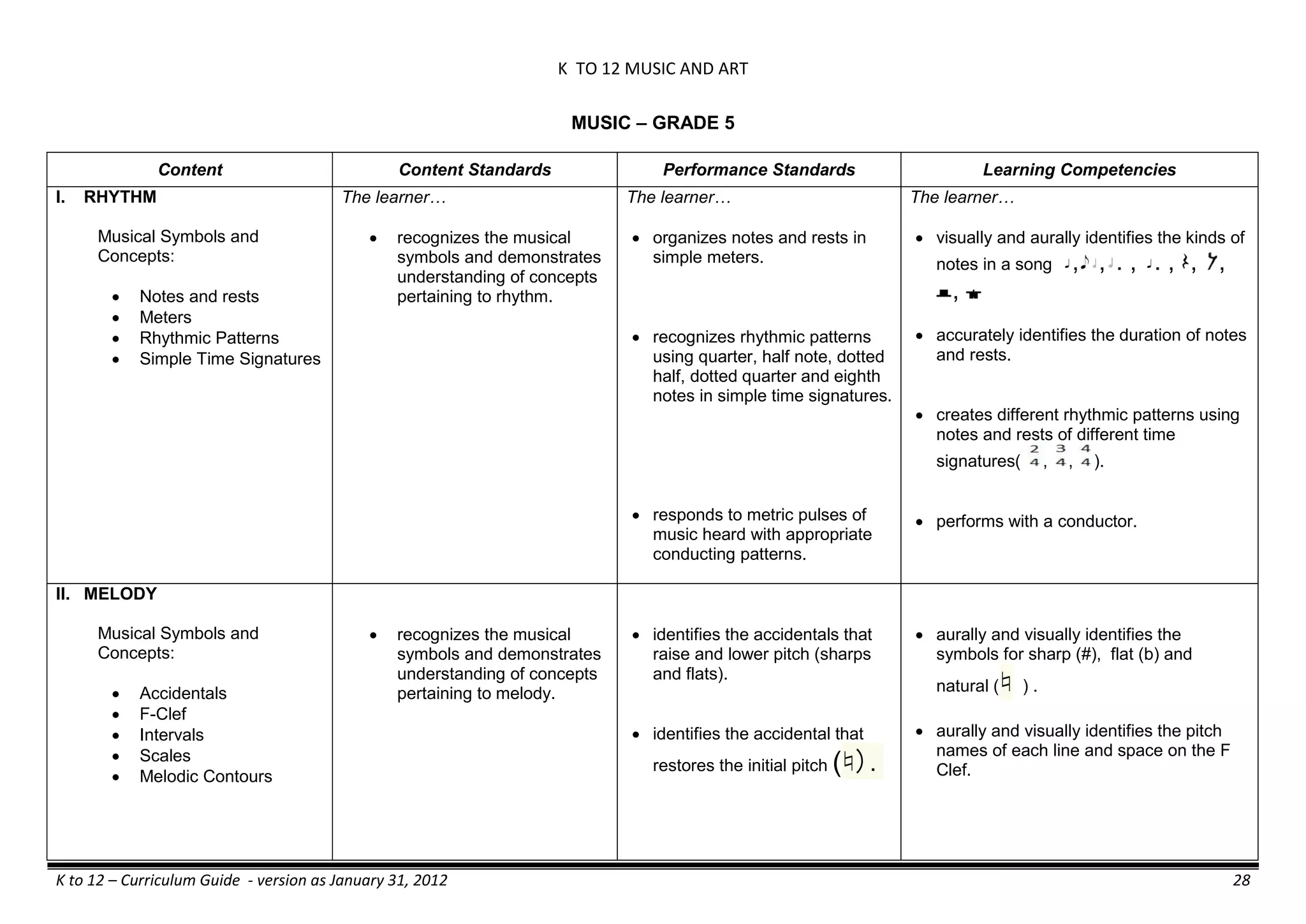
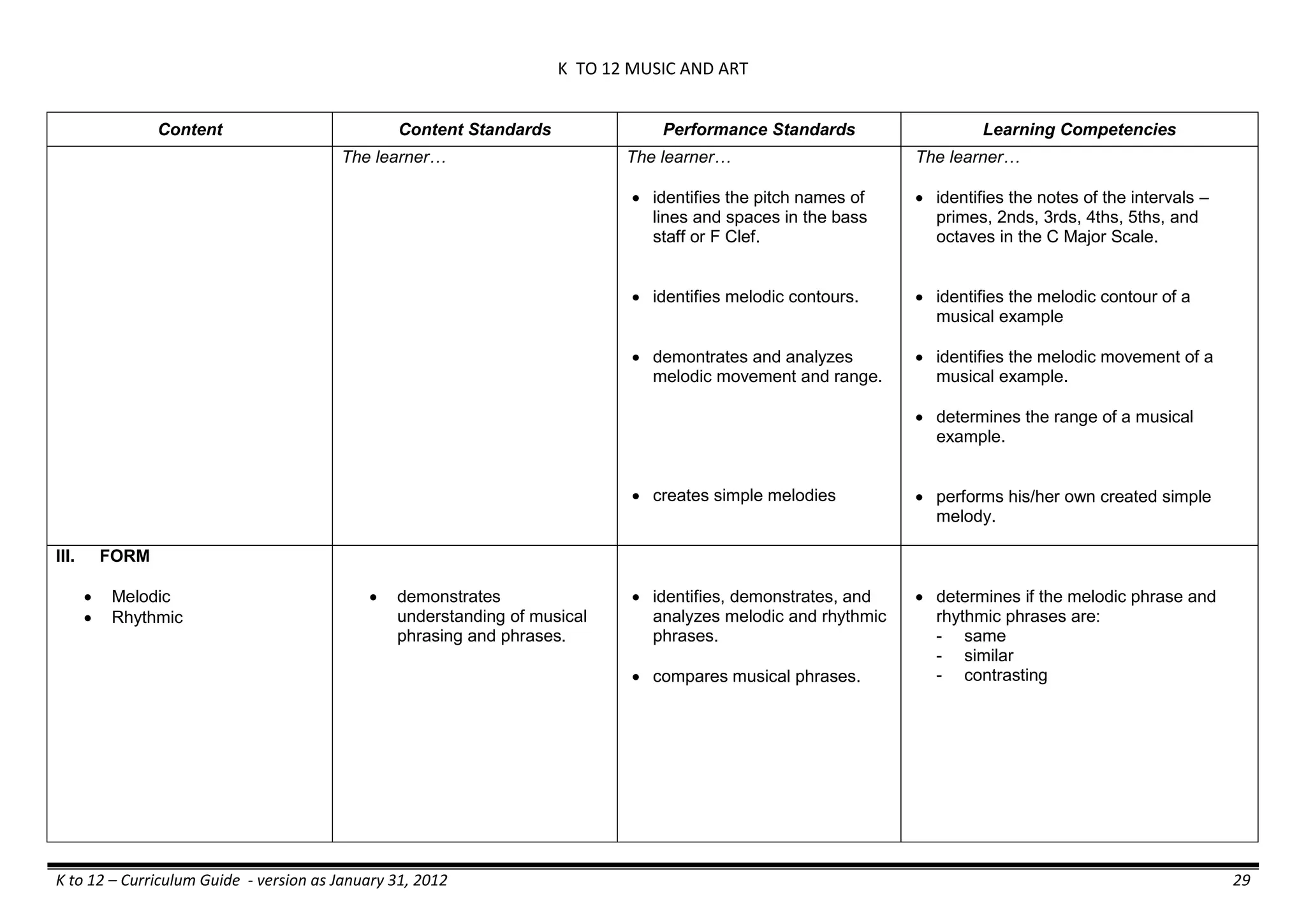
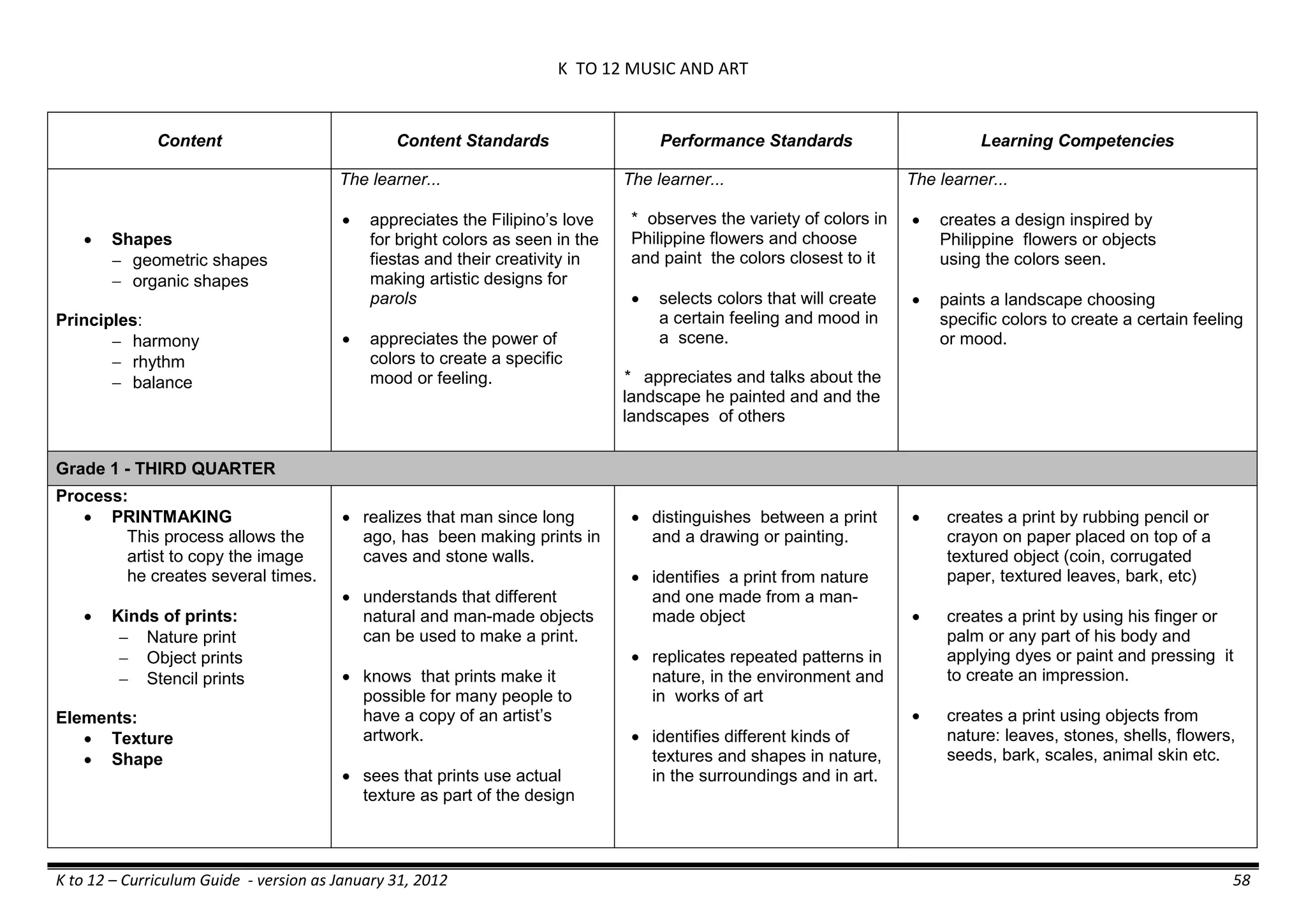
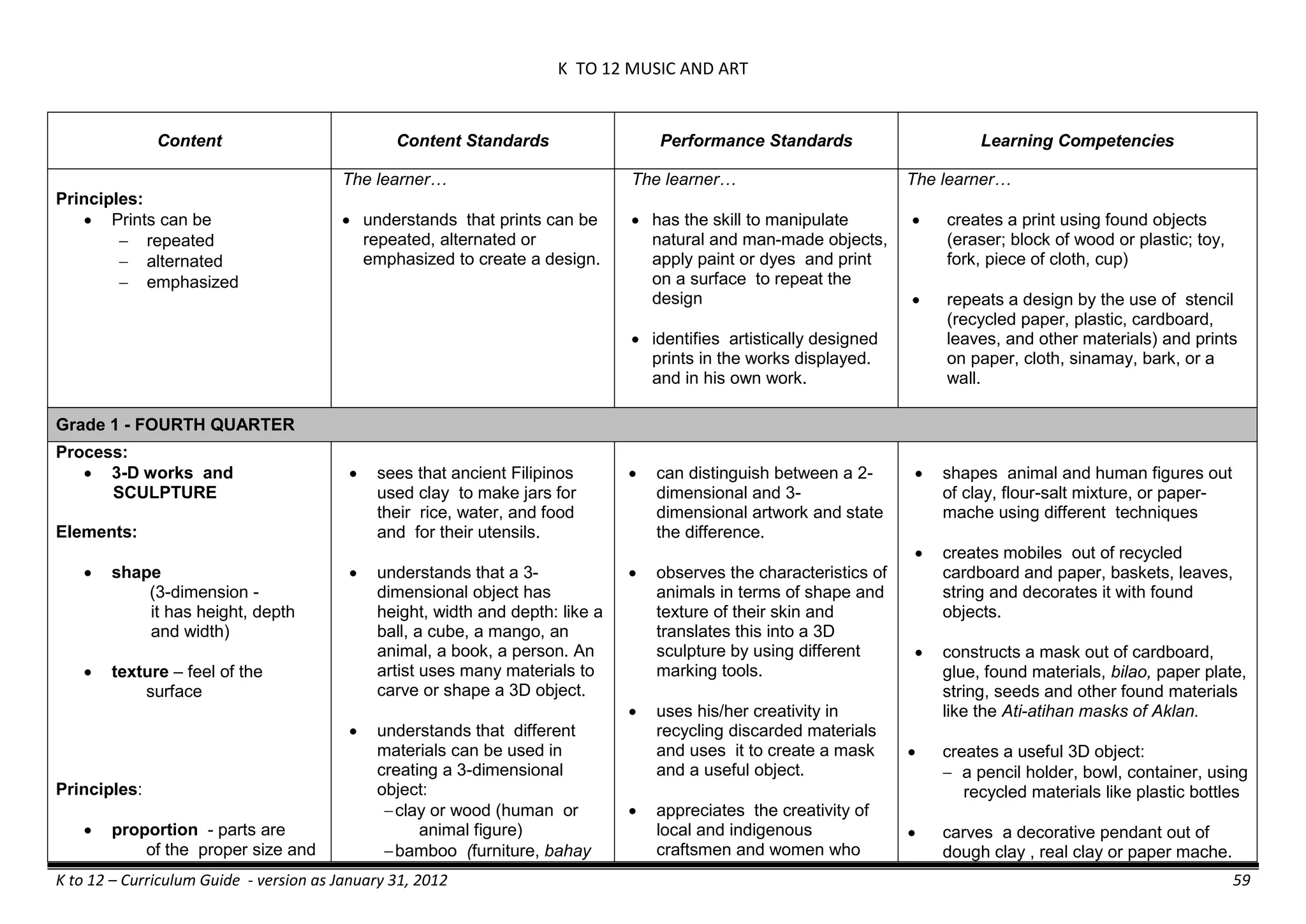
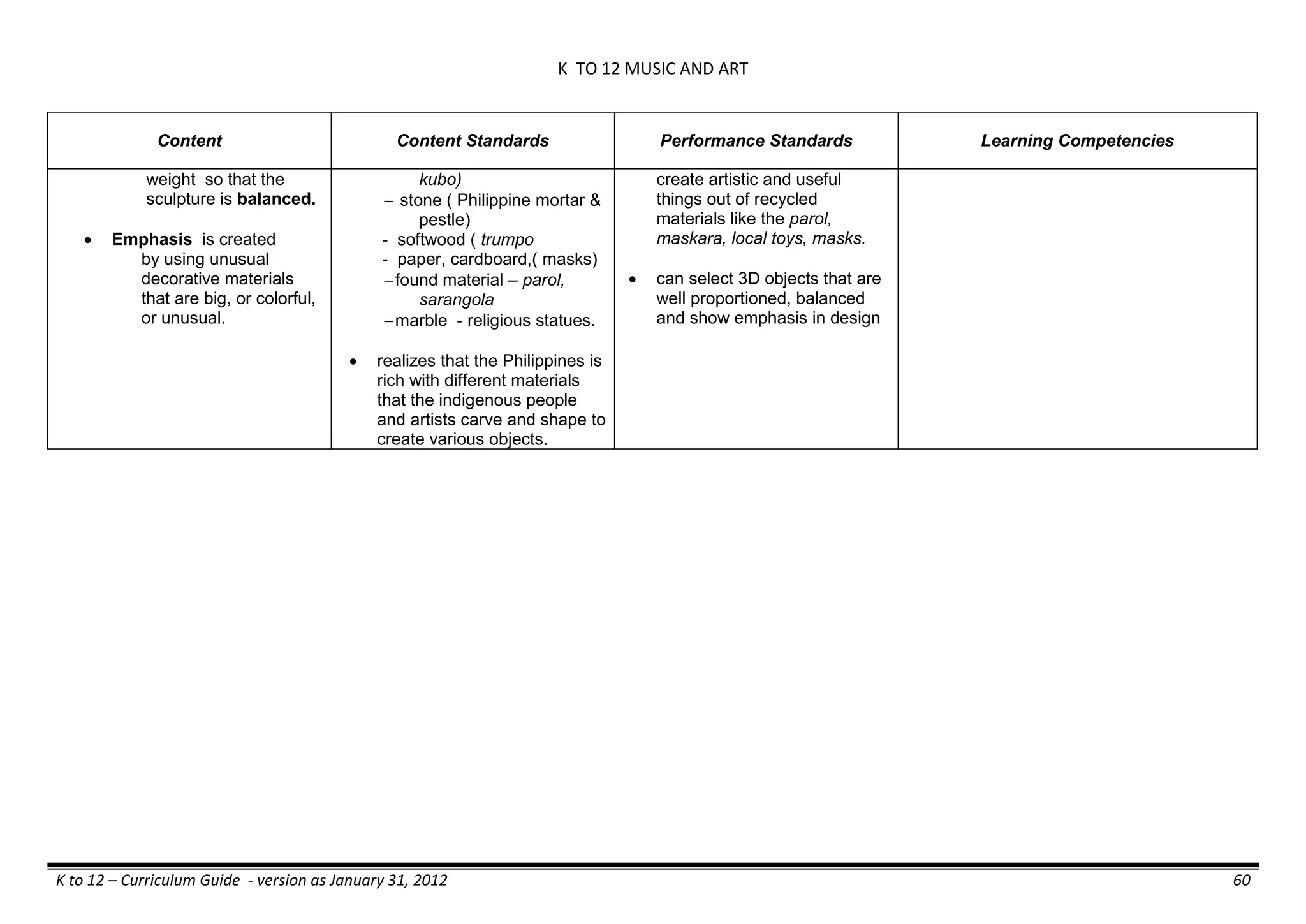
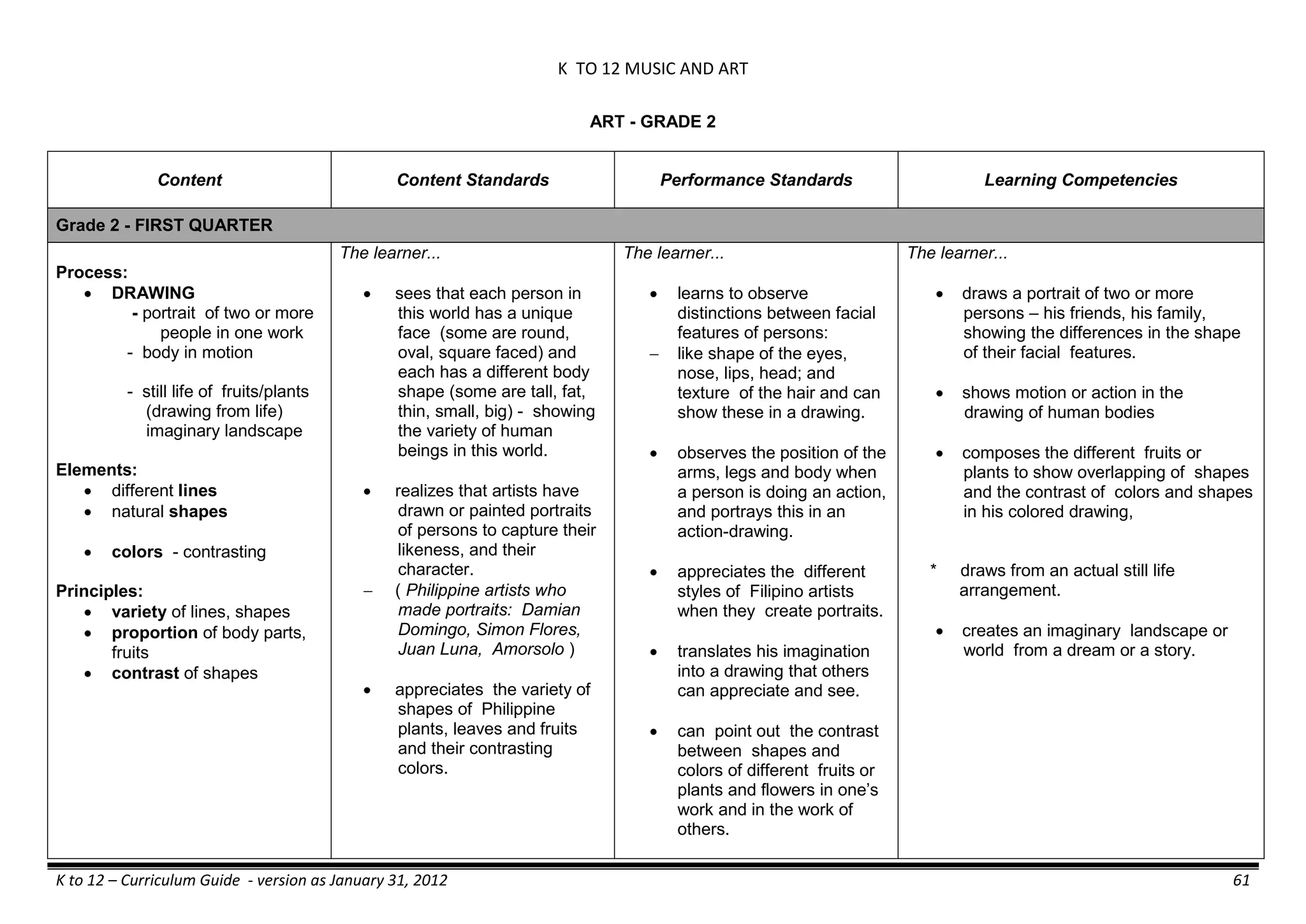
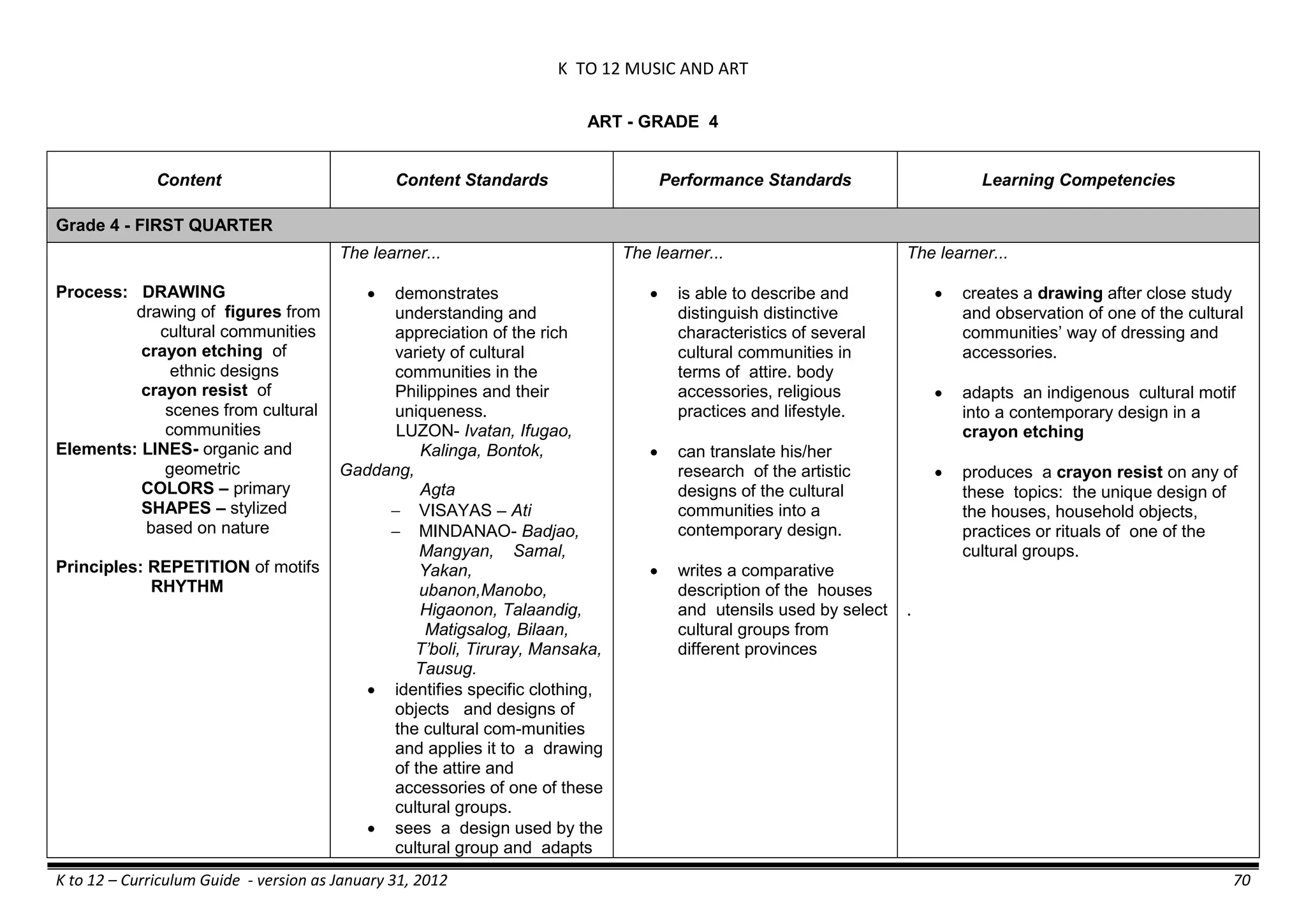
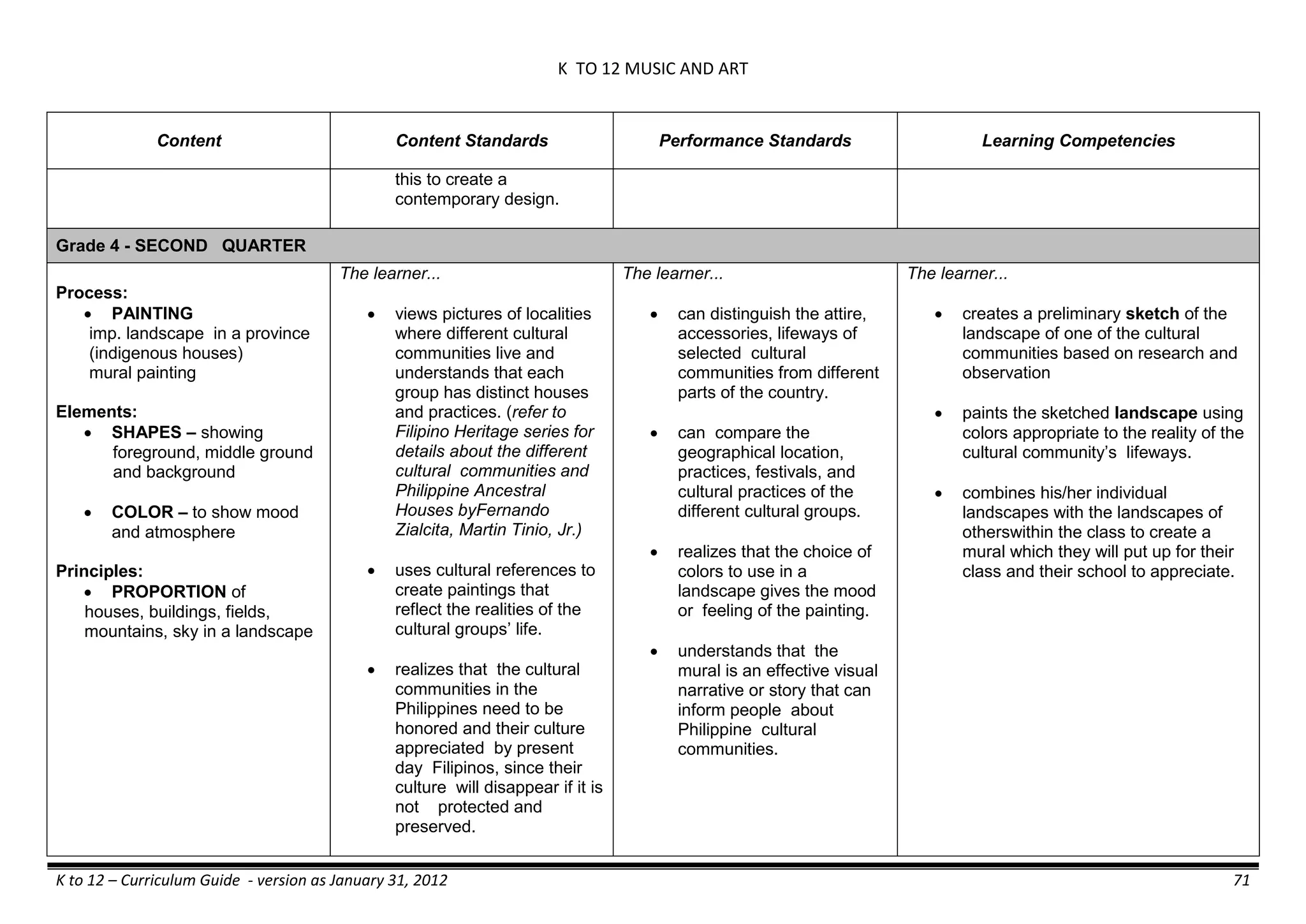
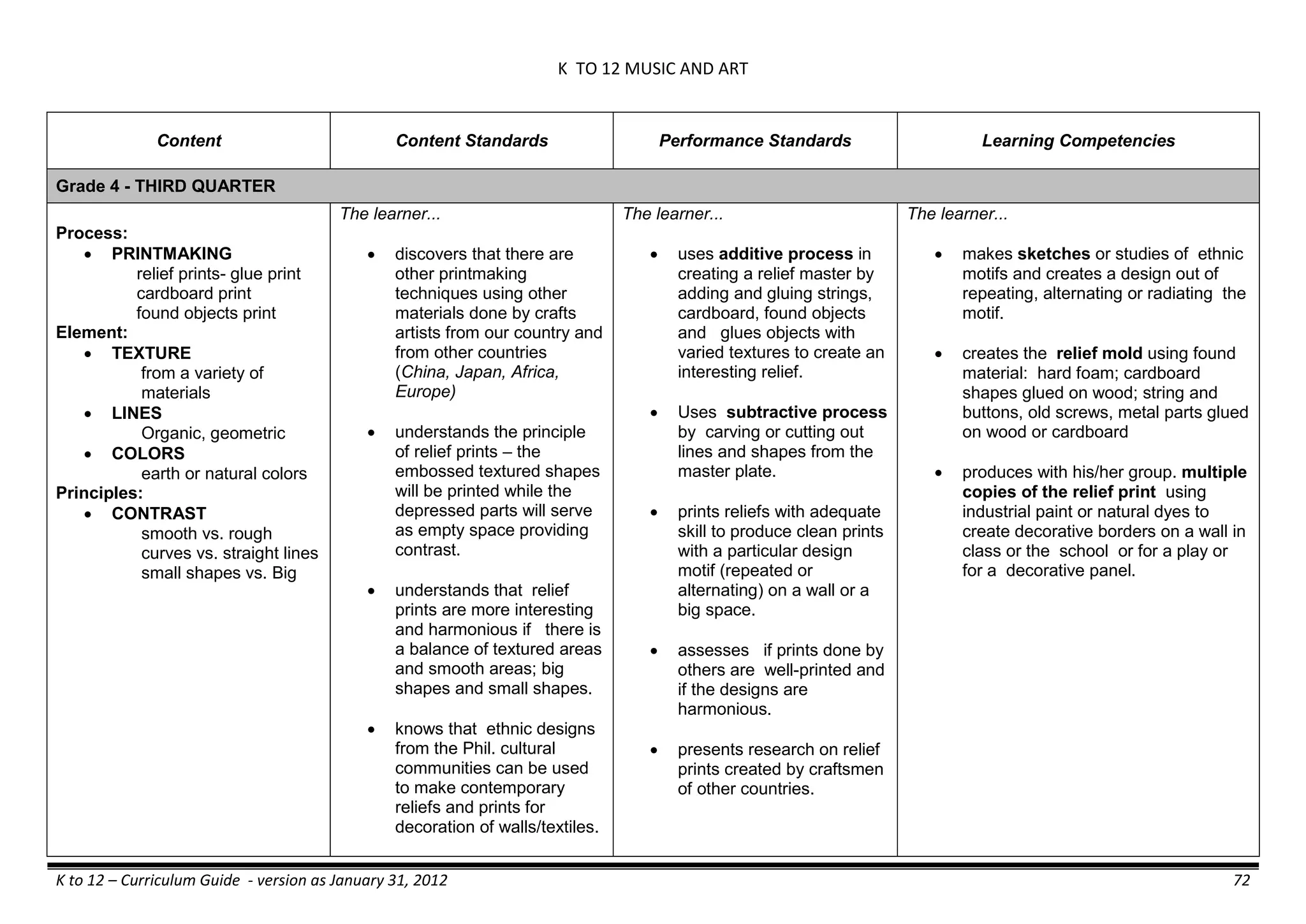
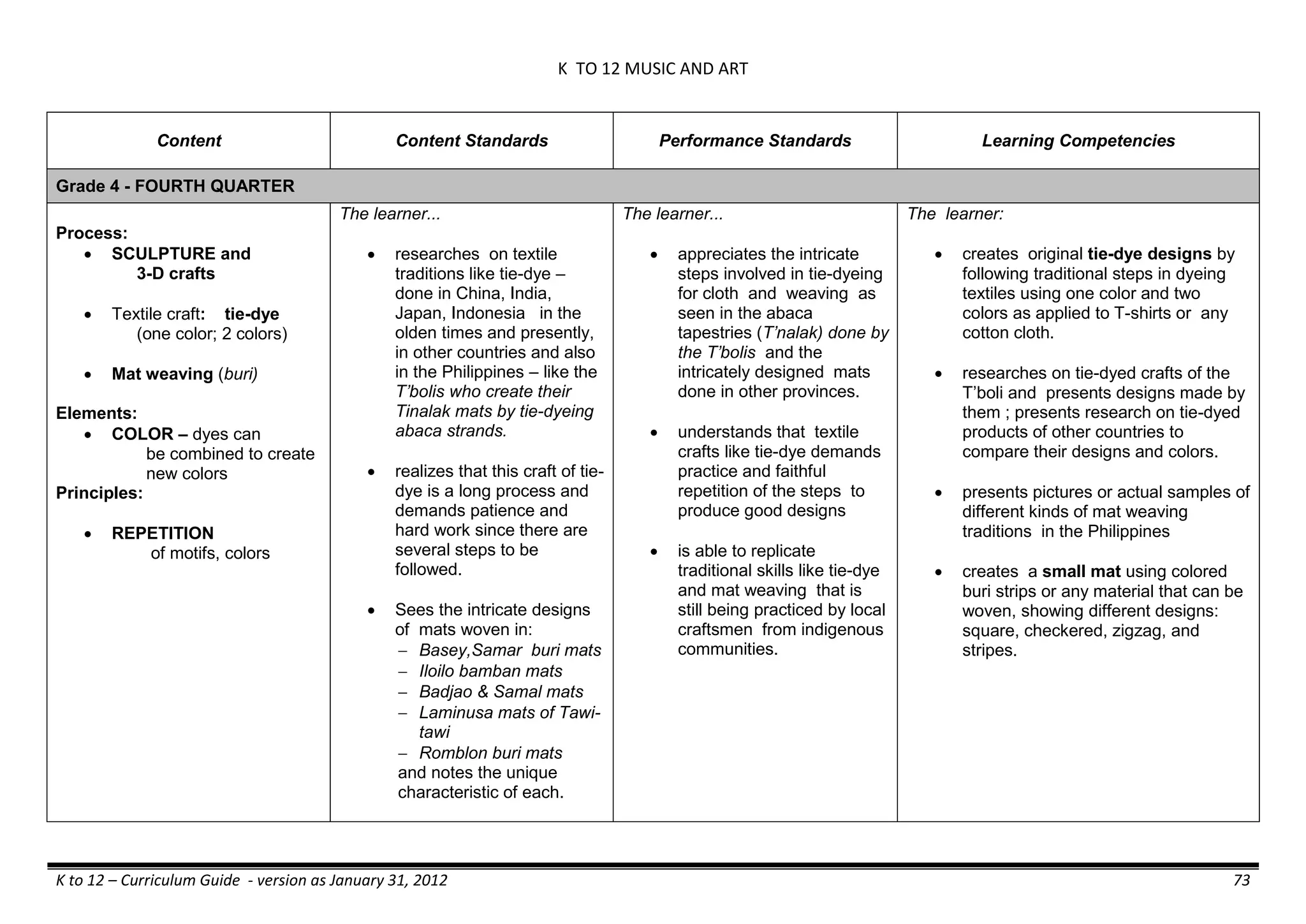
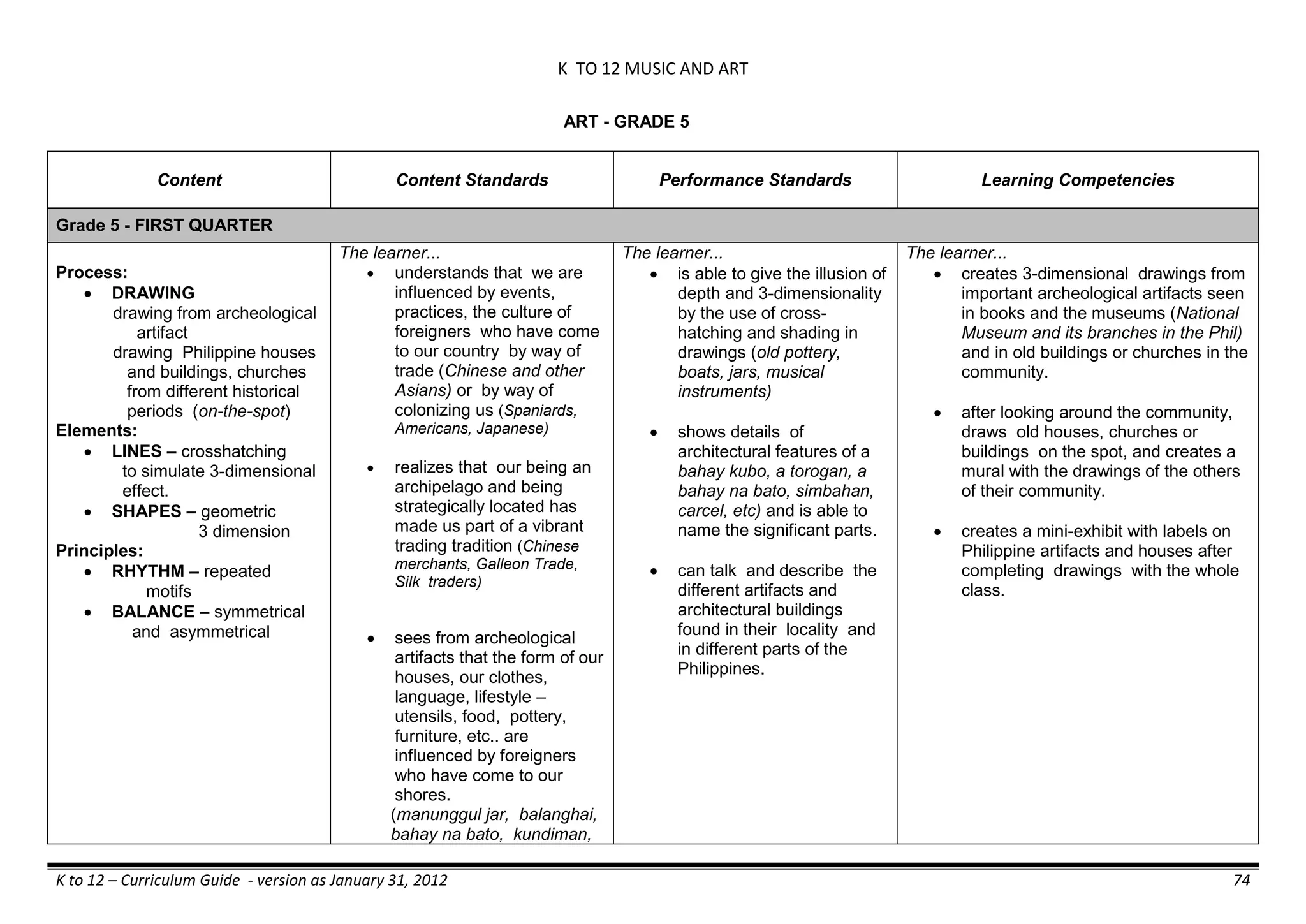
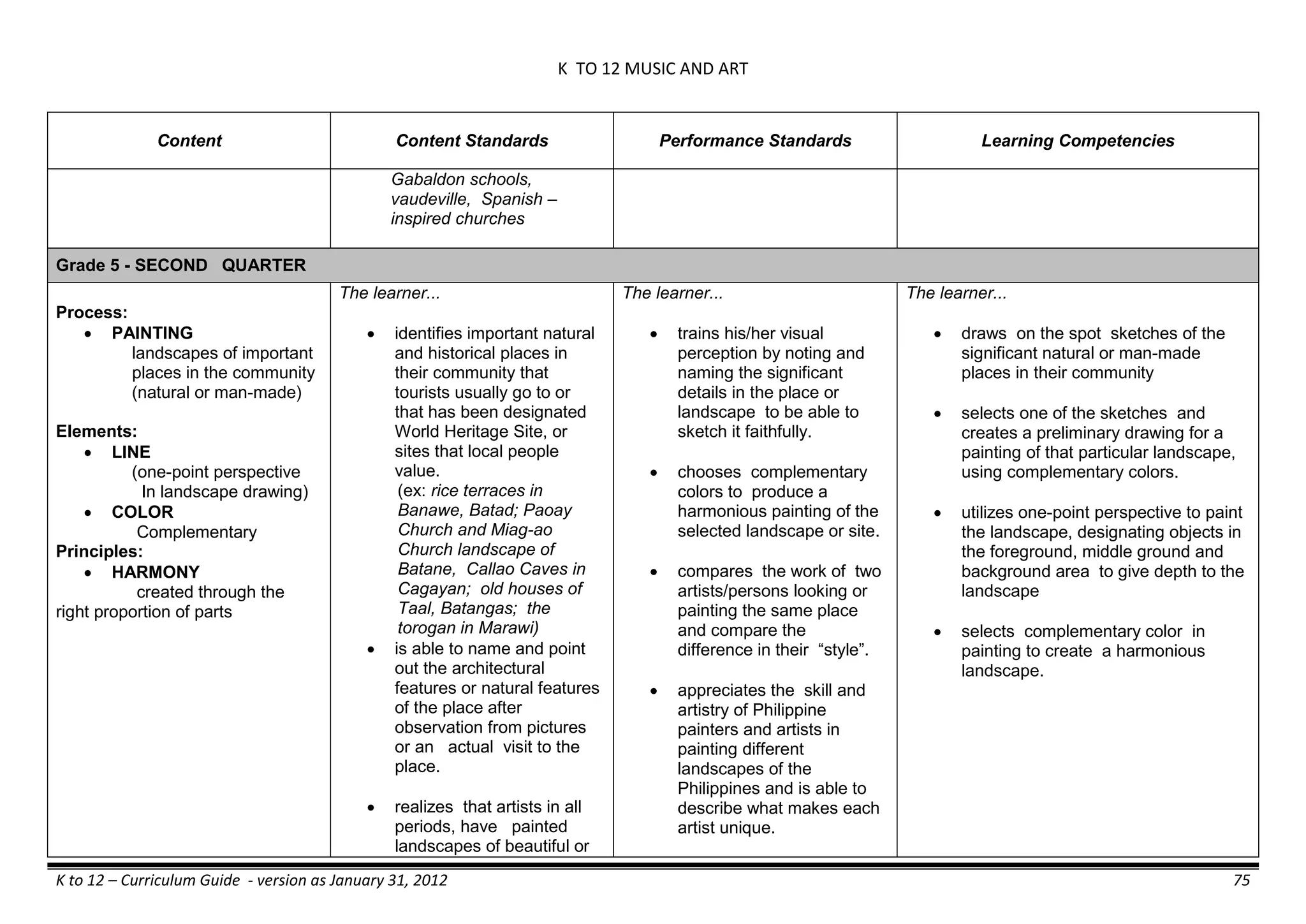
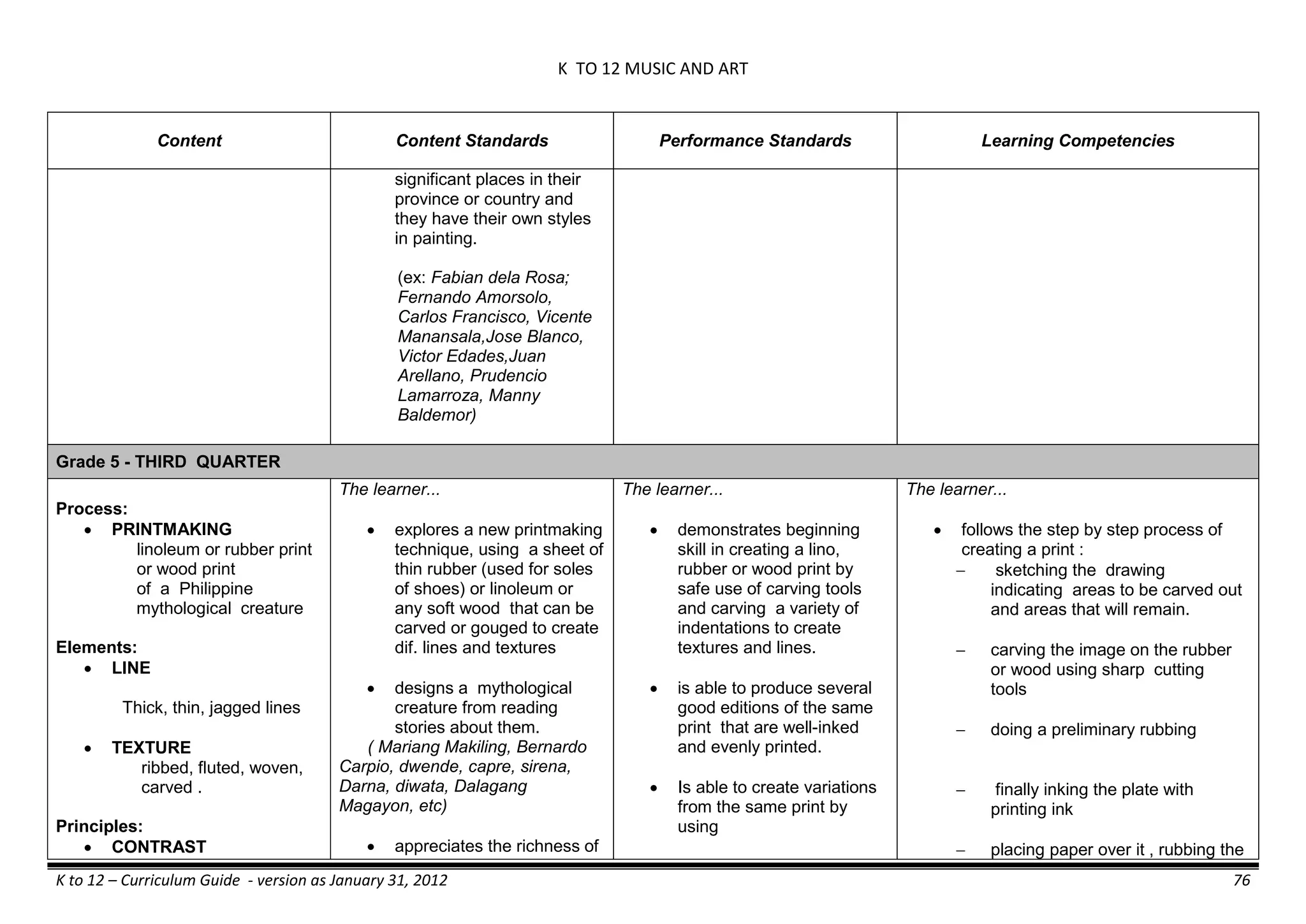
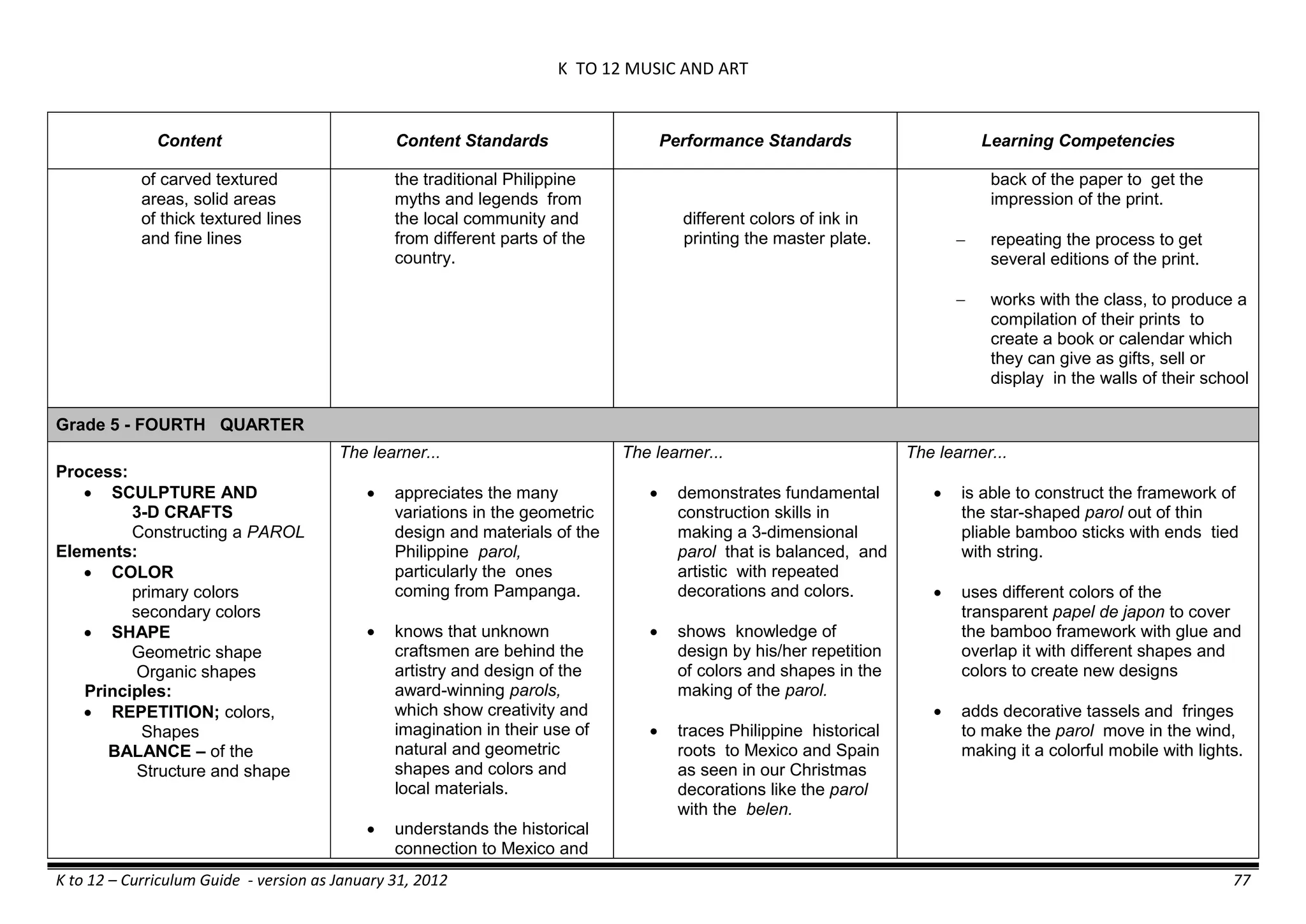
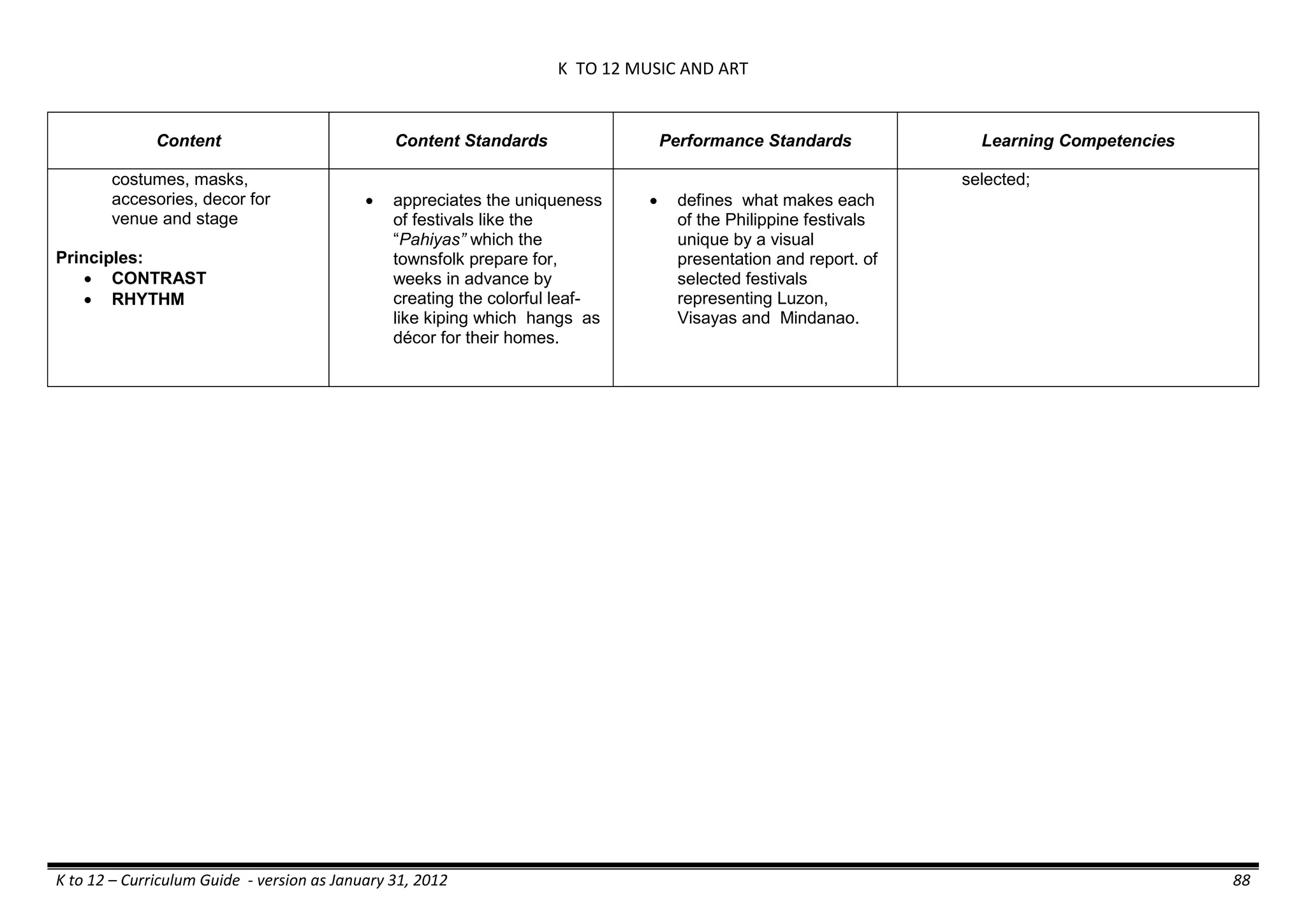
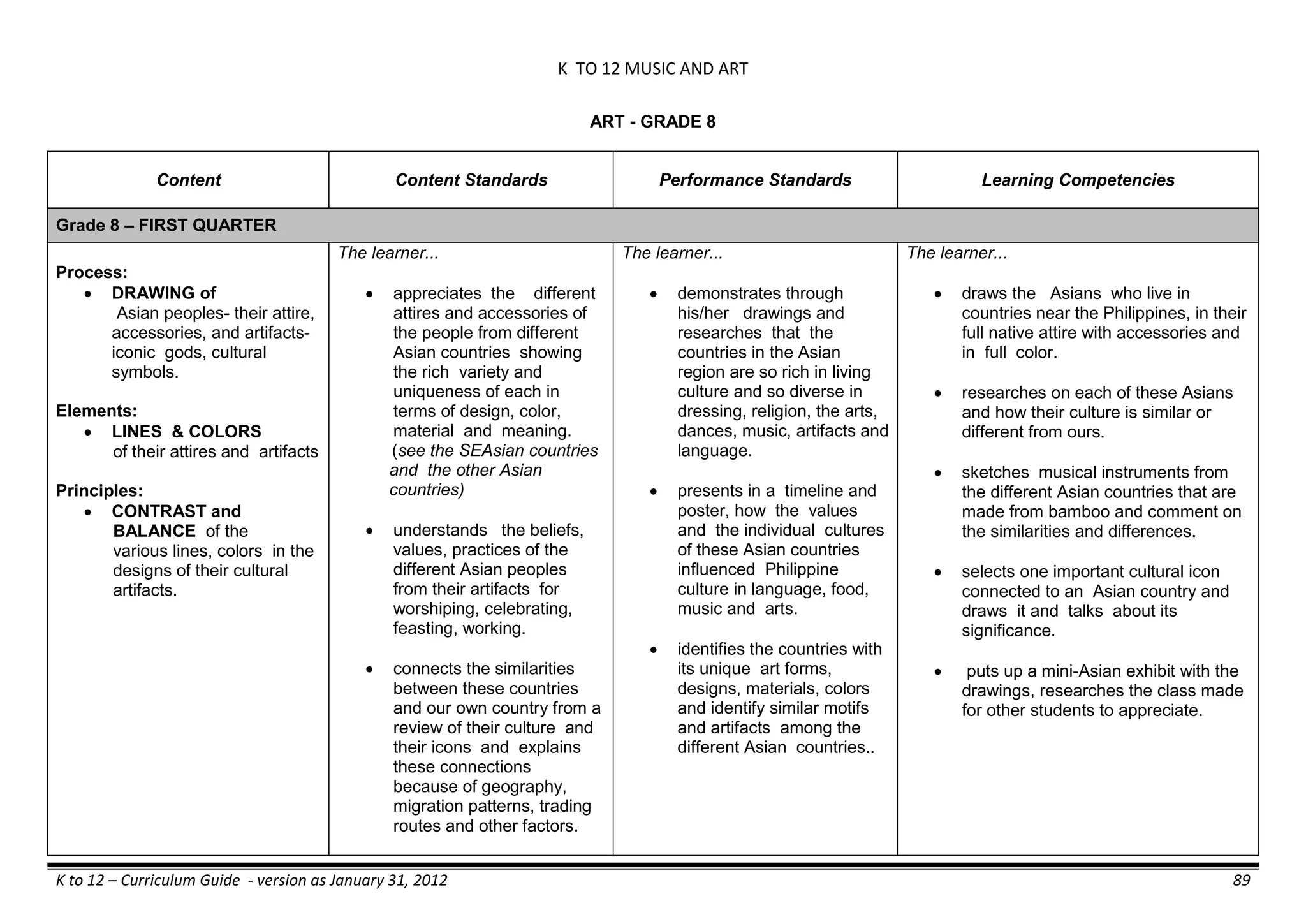
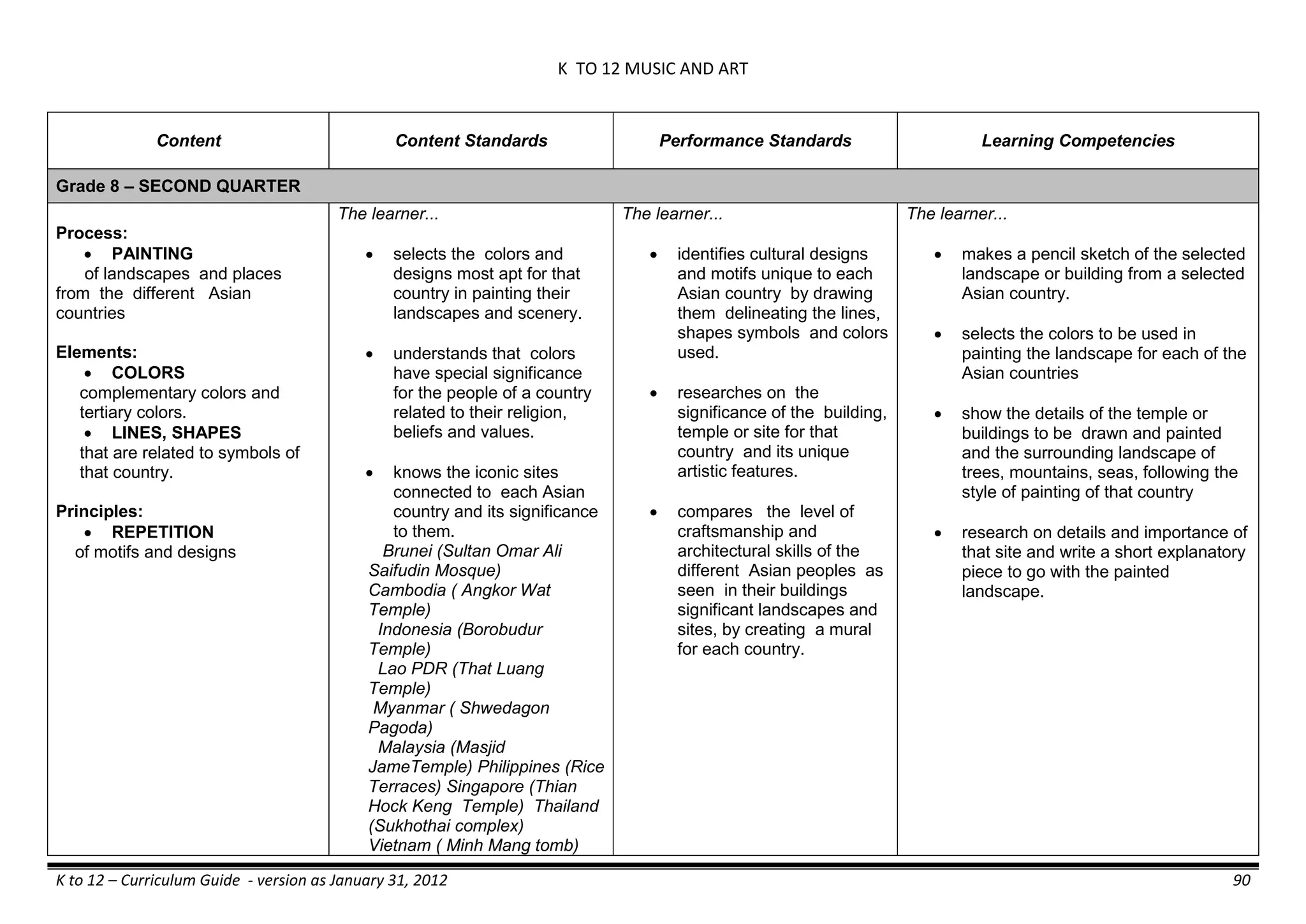
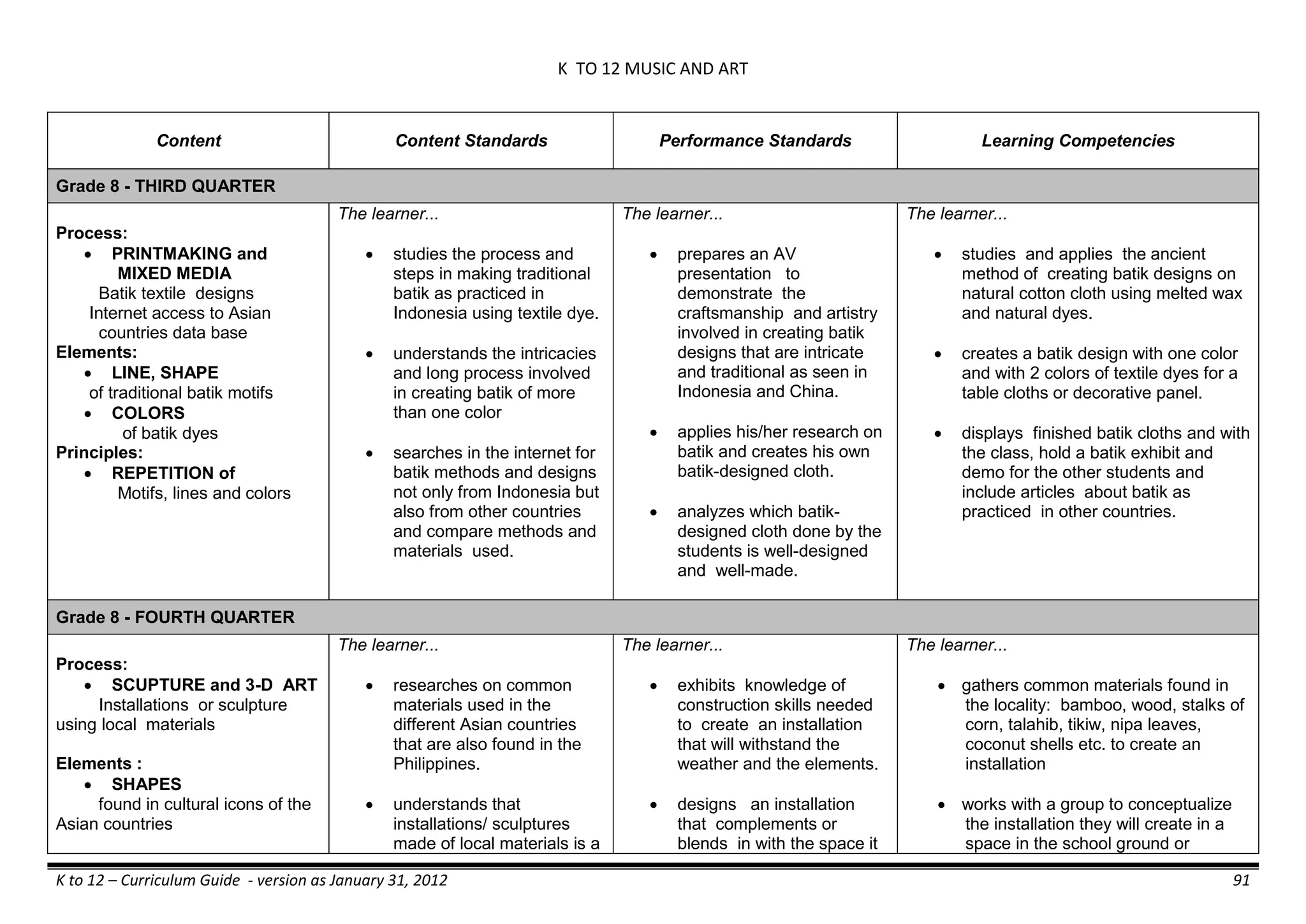
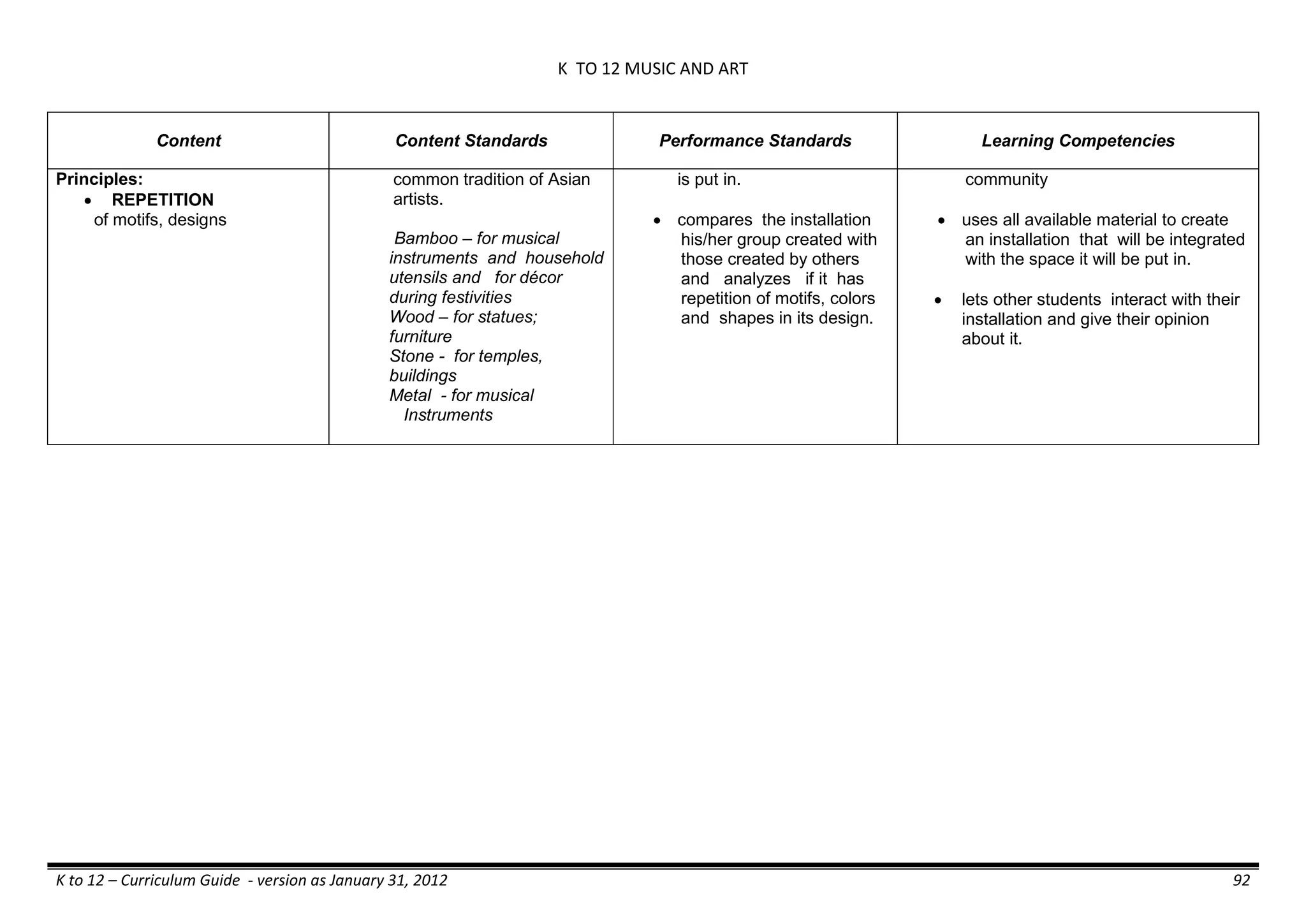
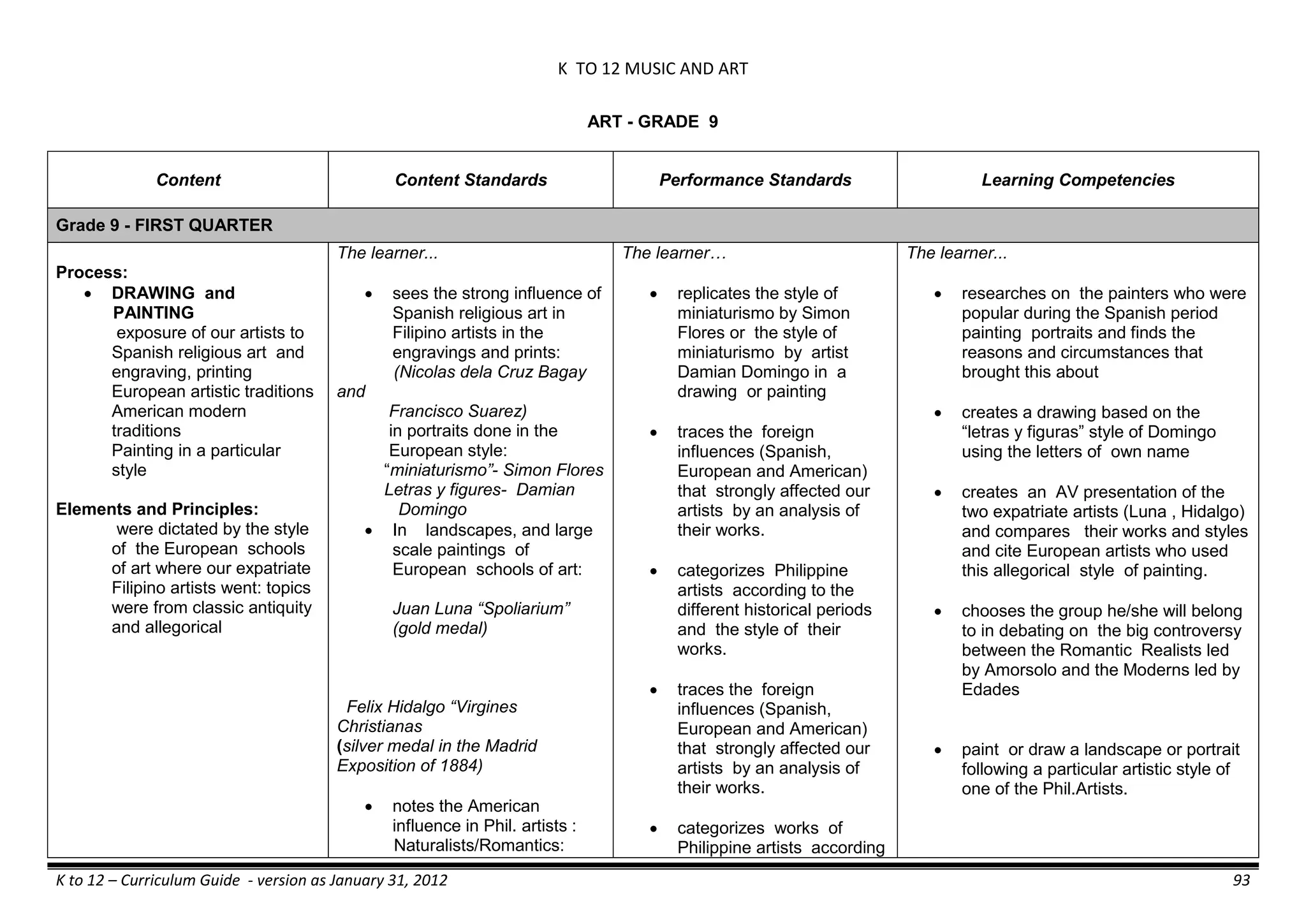
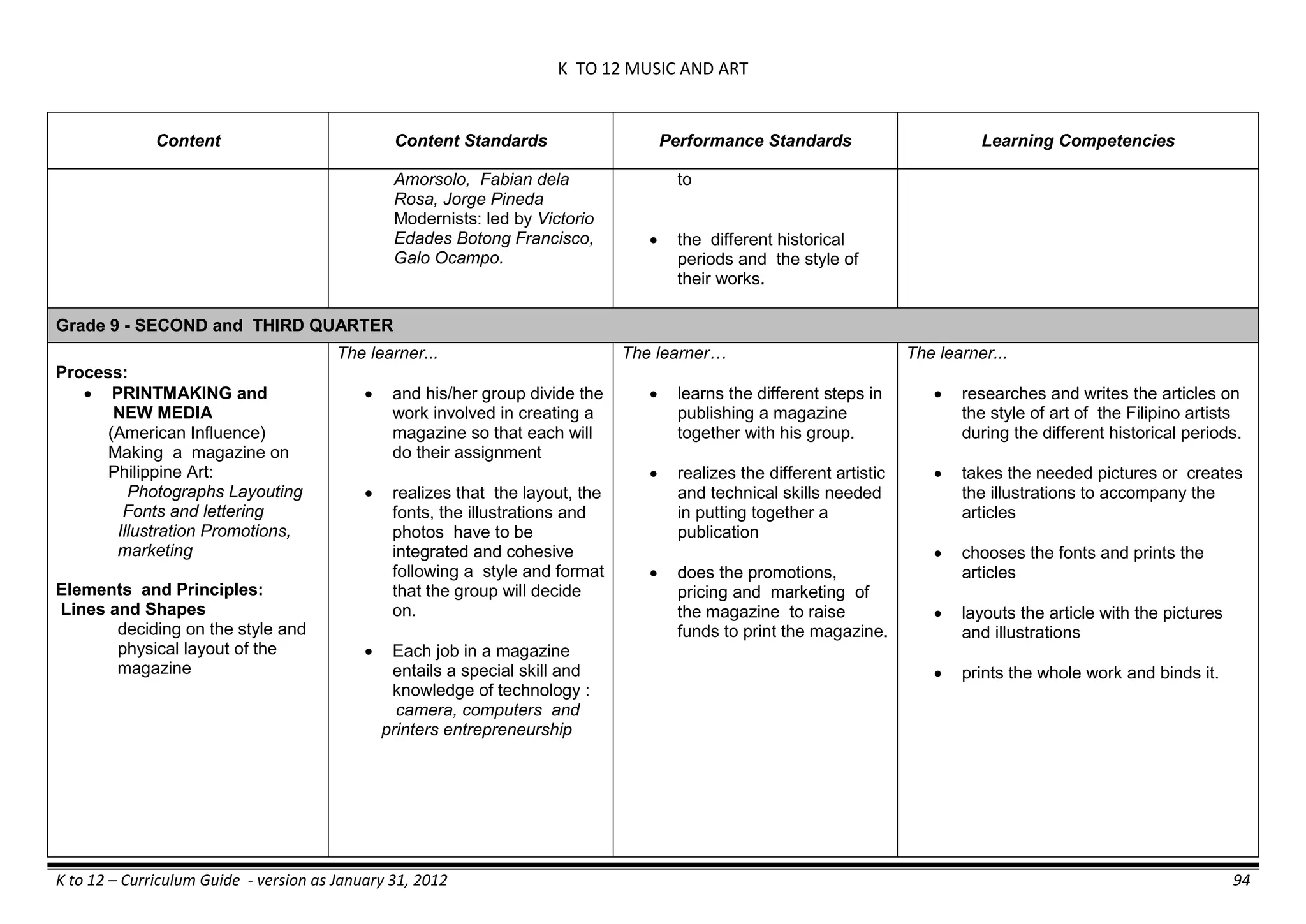
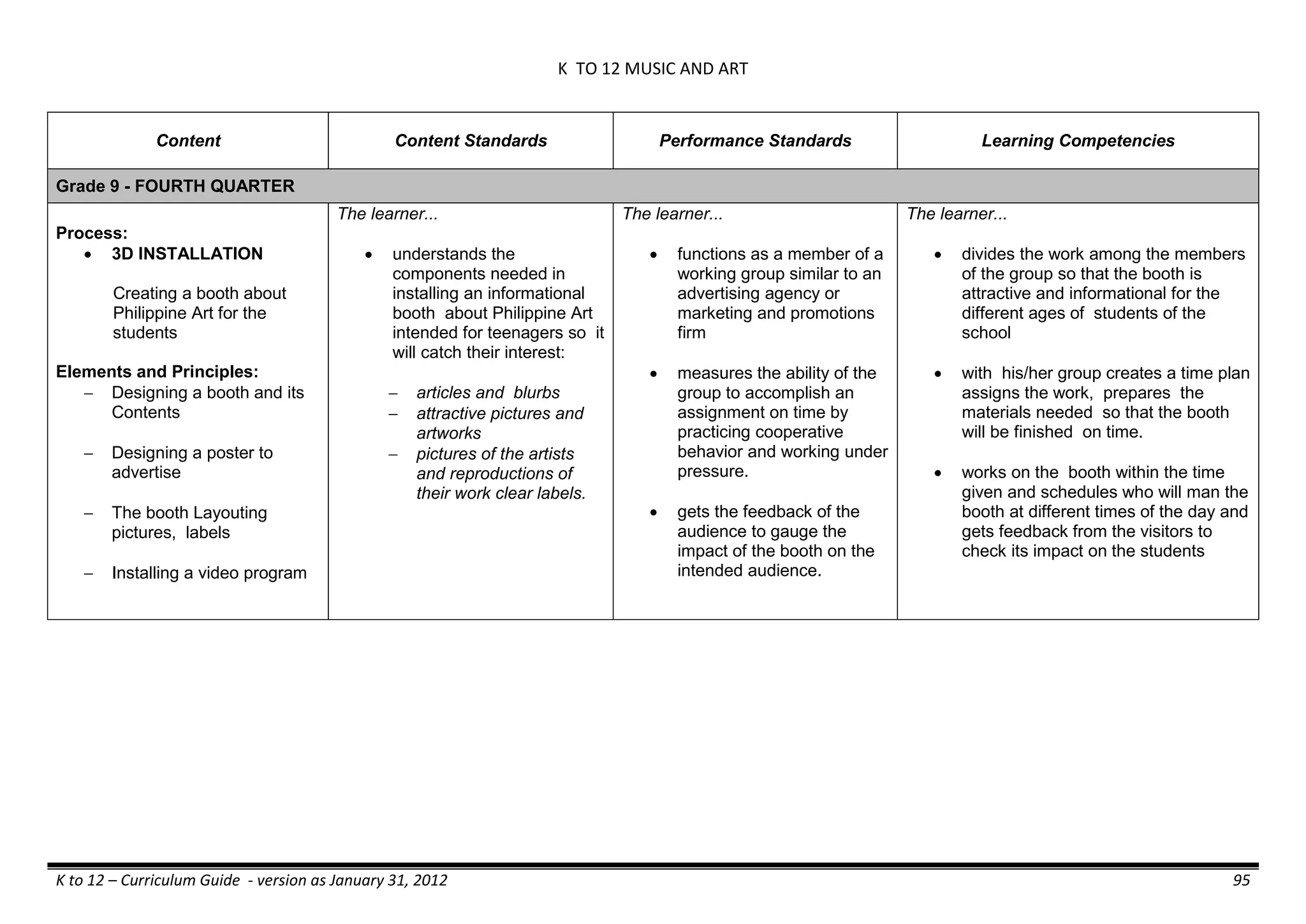
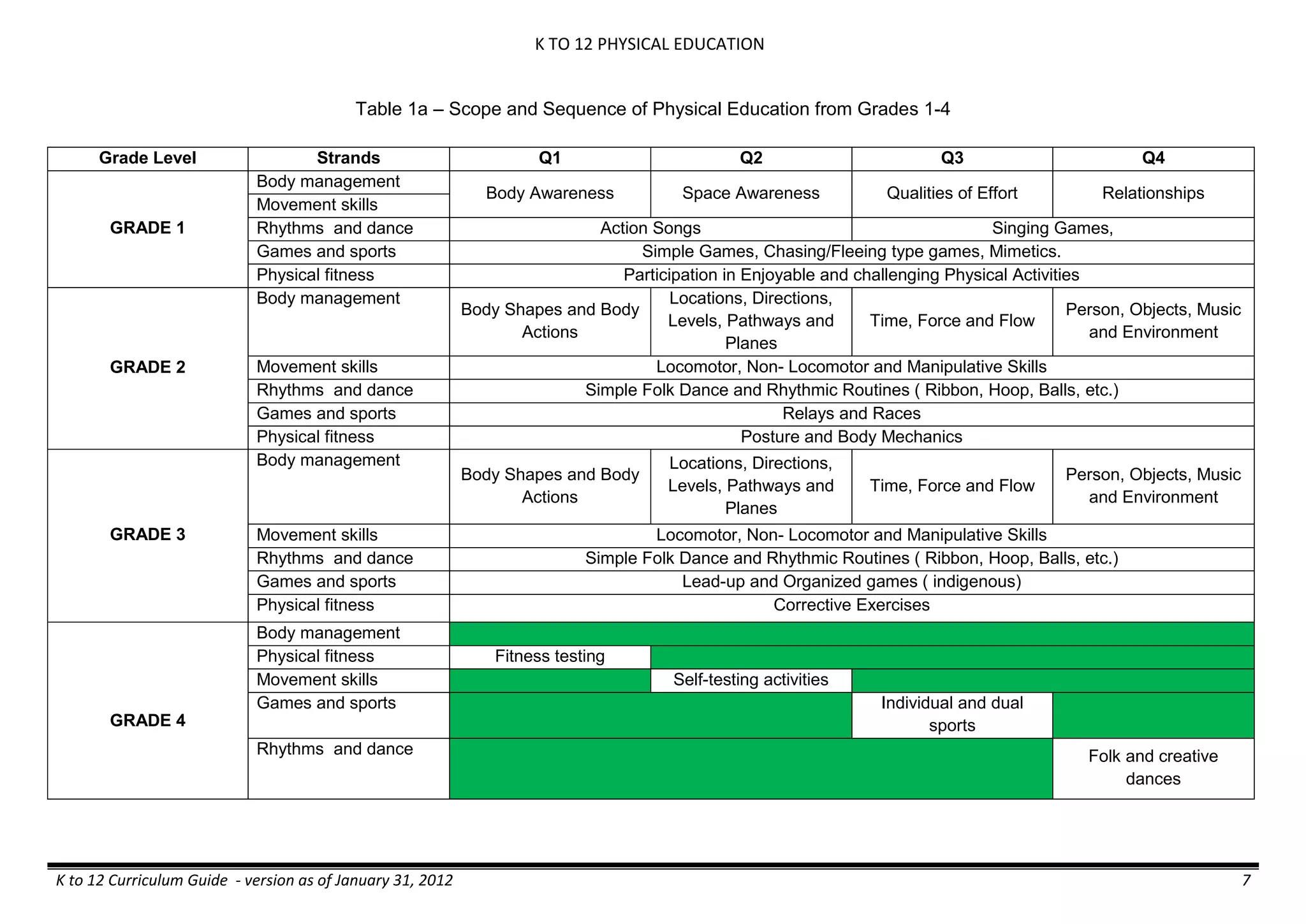
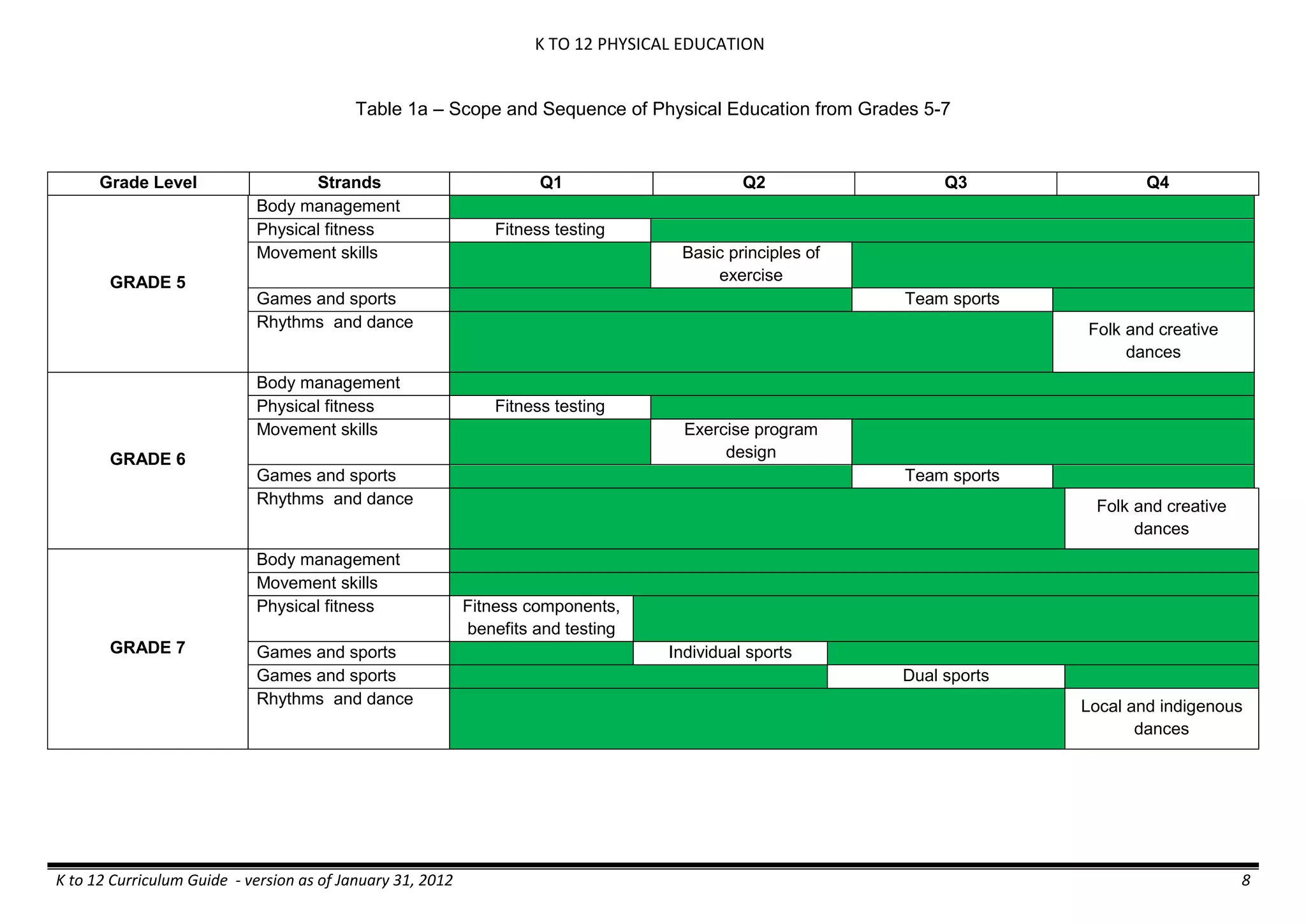
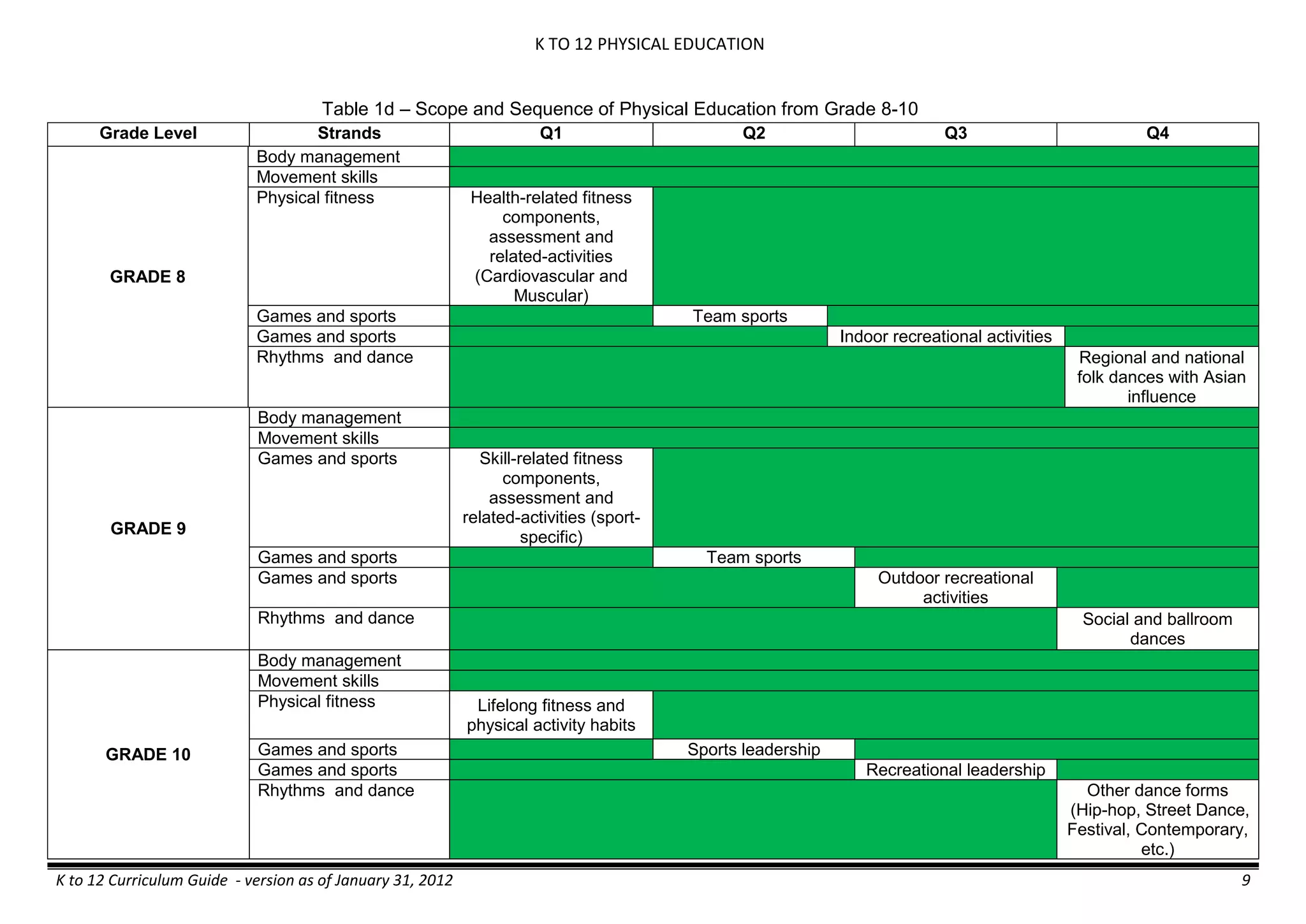
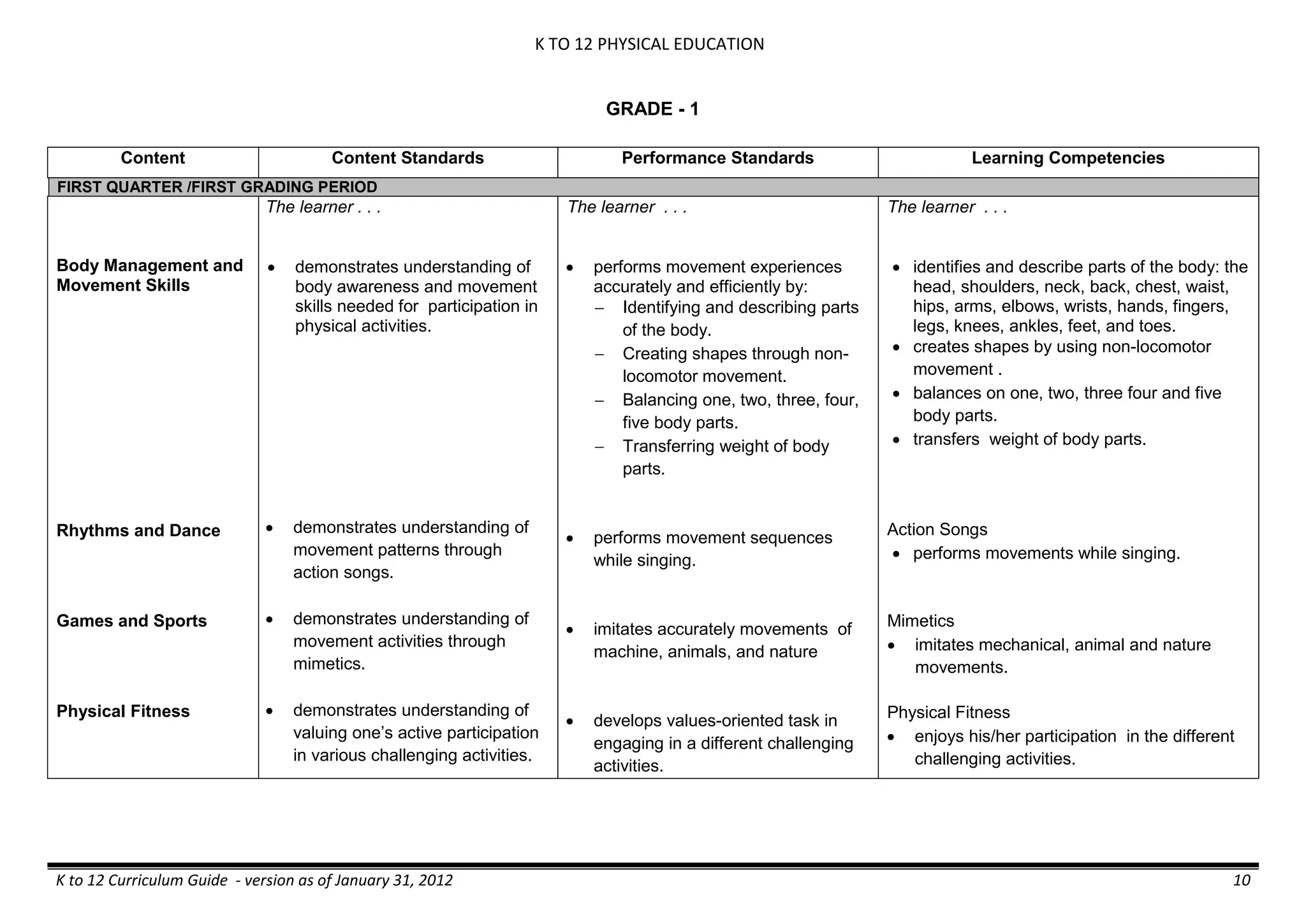
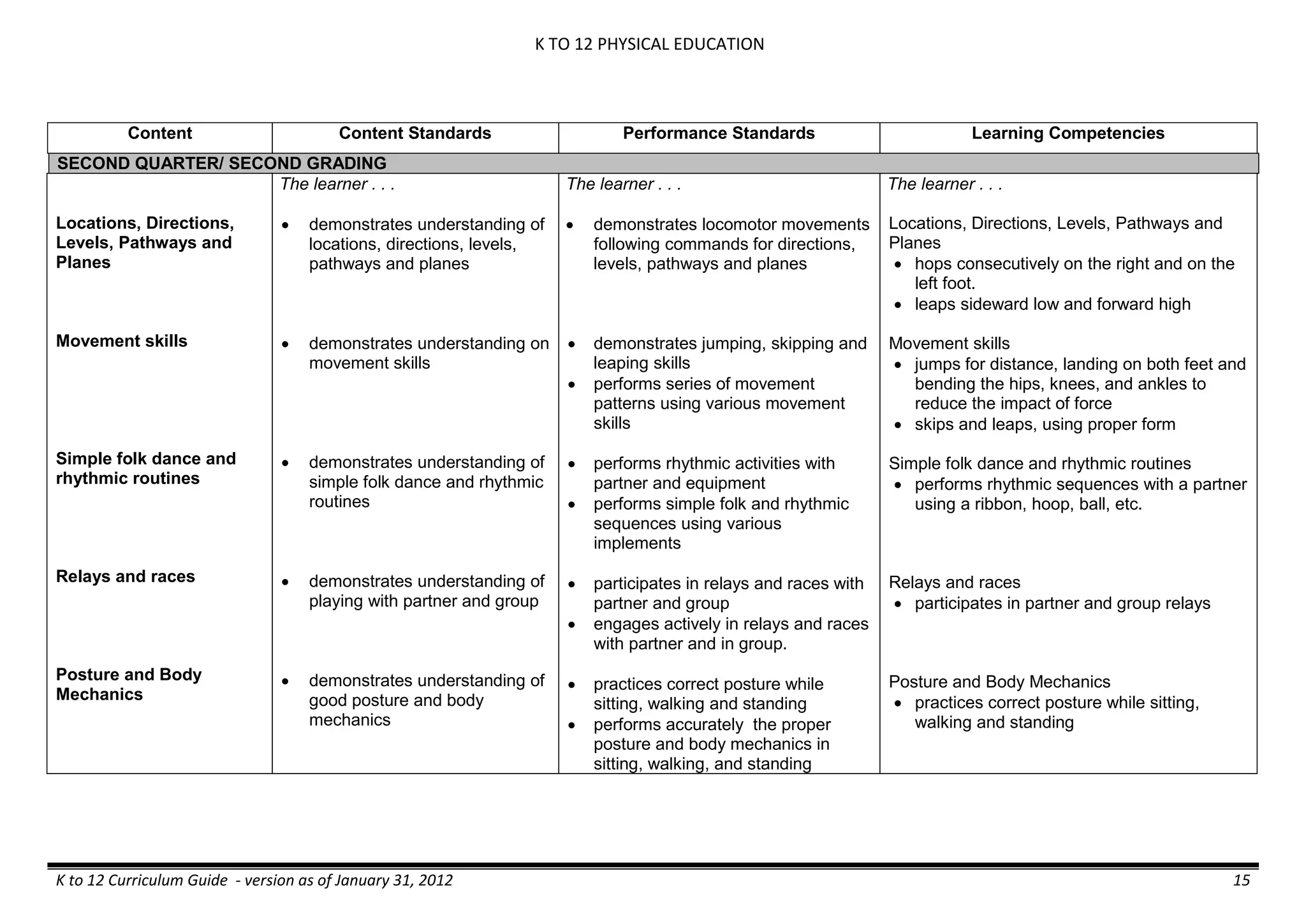
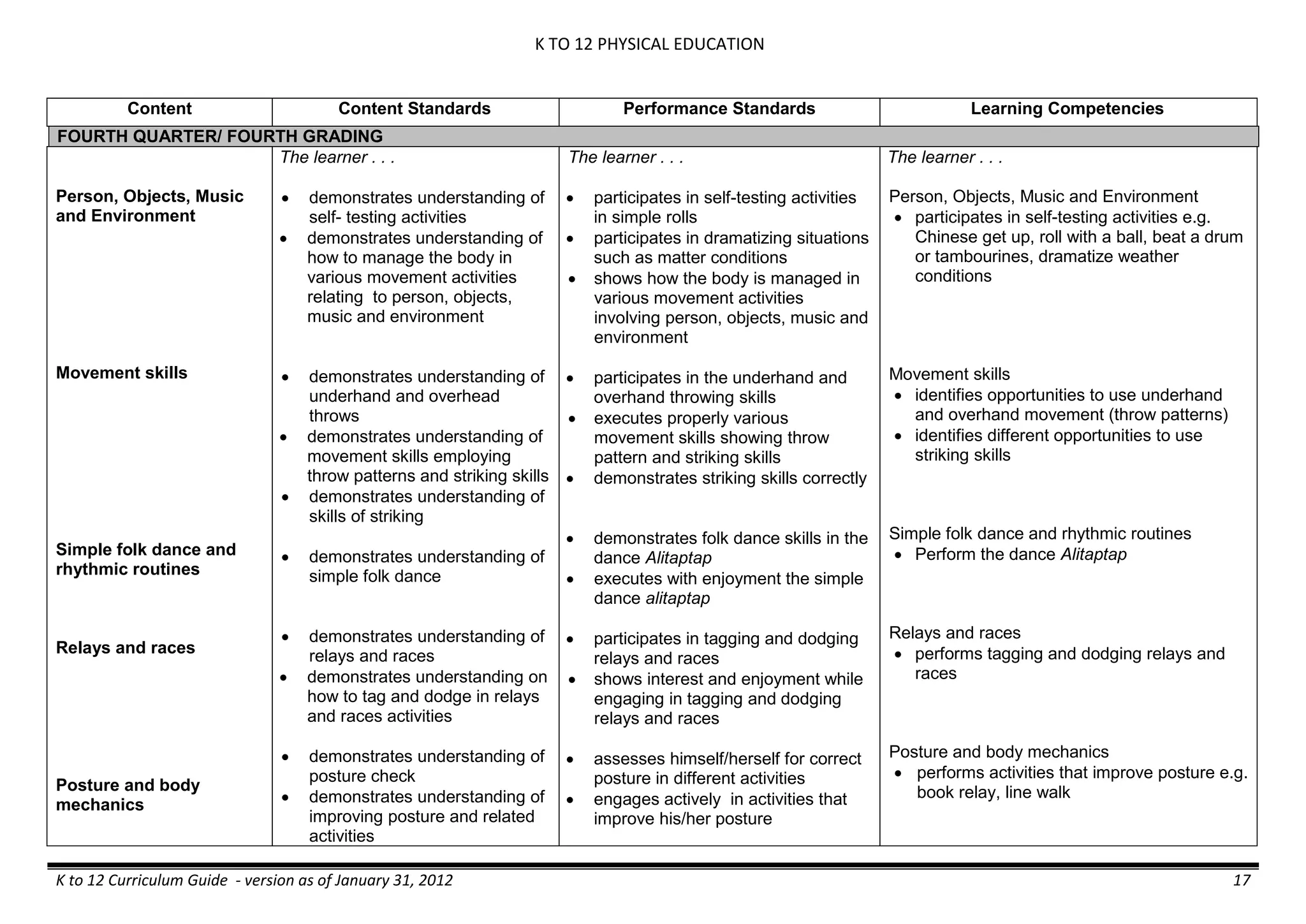
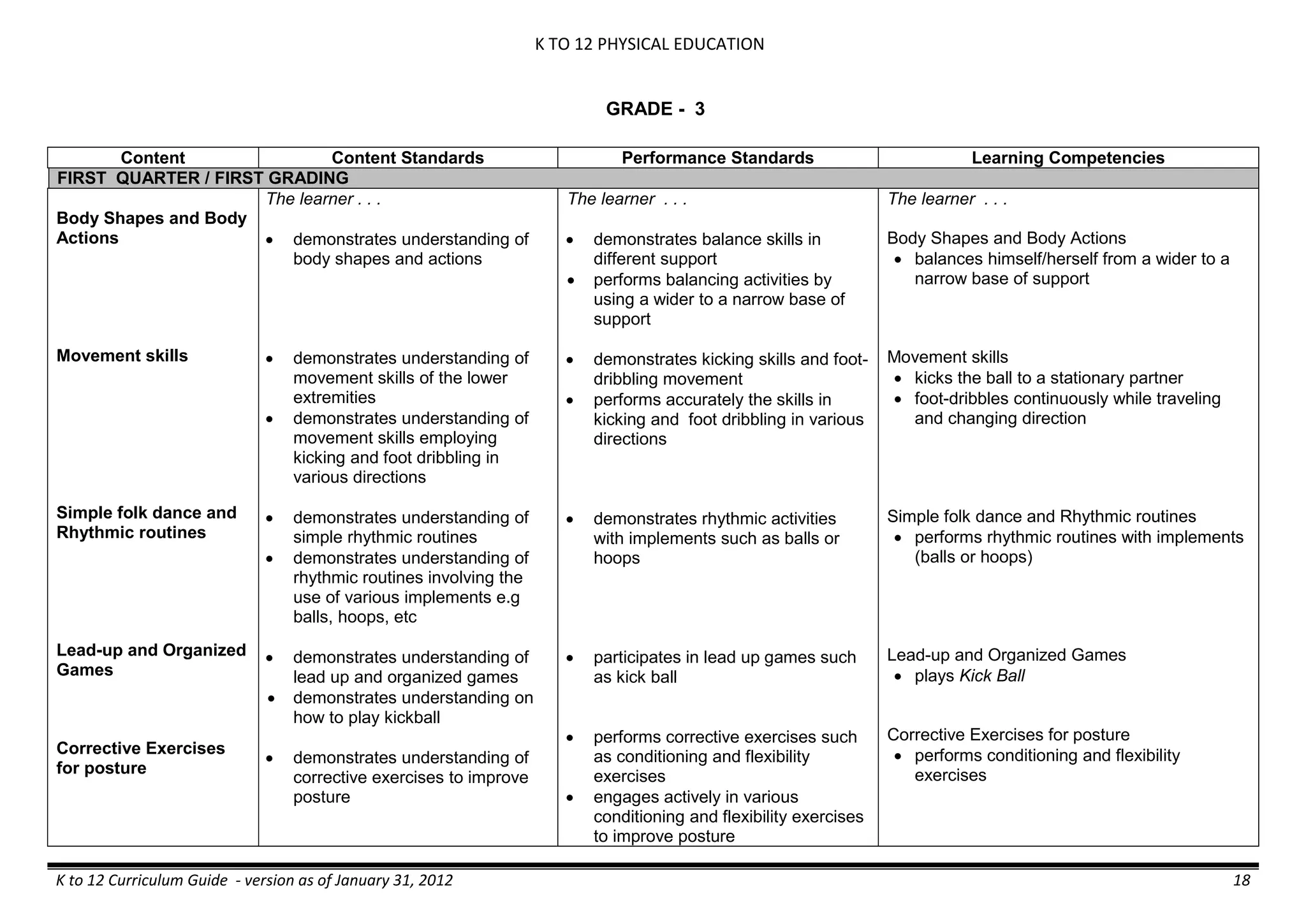
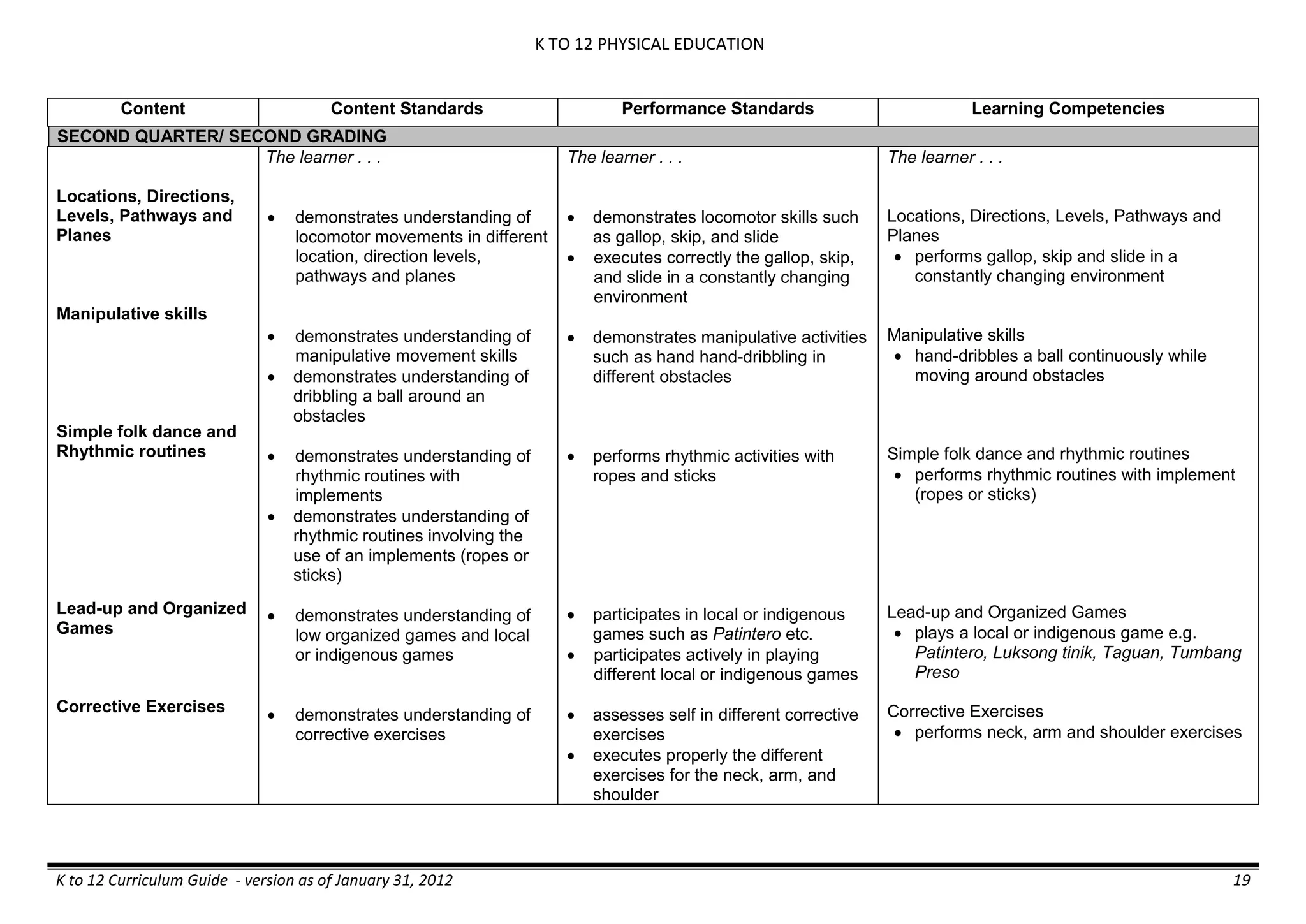
The K to 12 curriculum guide for Kindergarten in the Philippines outlines the importance of early childhood education as a foundation for lifelong learning, emphasizing holistic development through a structured, creative, and developmentally appropriate curriculum. It includes principles for teacher guidance and developmental benchmarks focused on areas such as physical health, social-emotional skills, cognitive growth, language acquisition, and values formation. The Kindergarten Education Act mandates one year of free preschool education, making it a compulsory stage of formal schooling.




















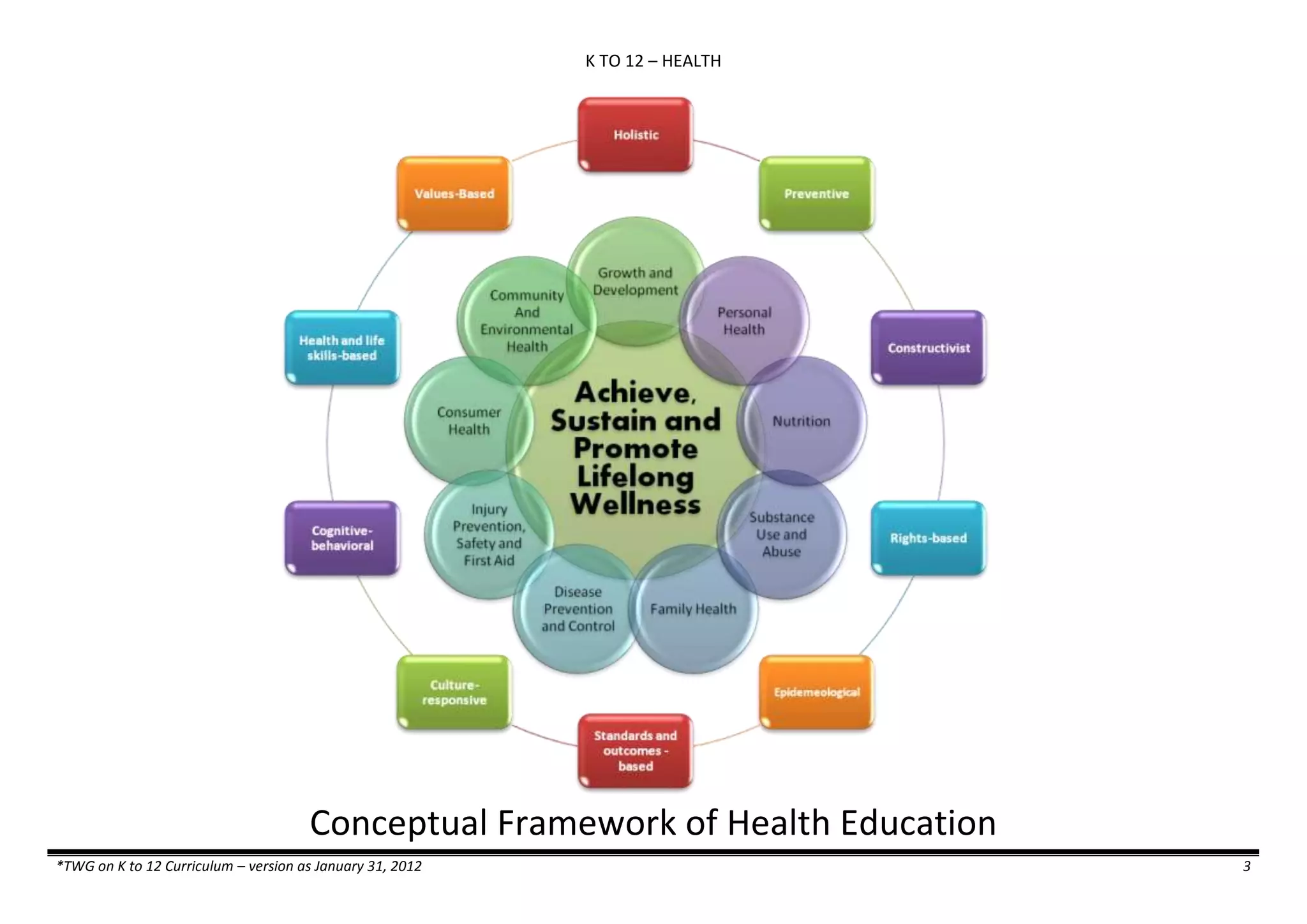
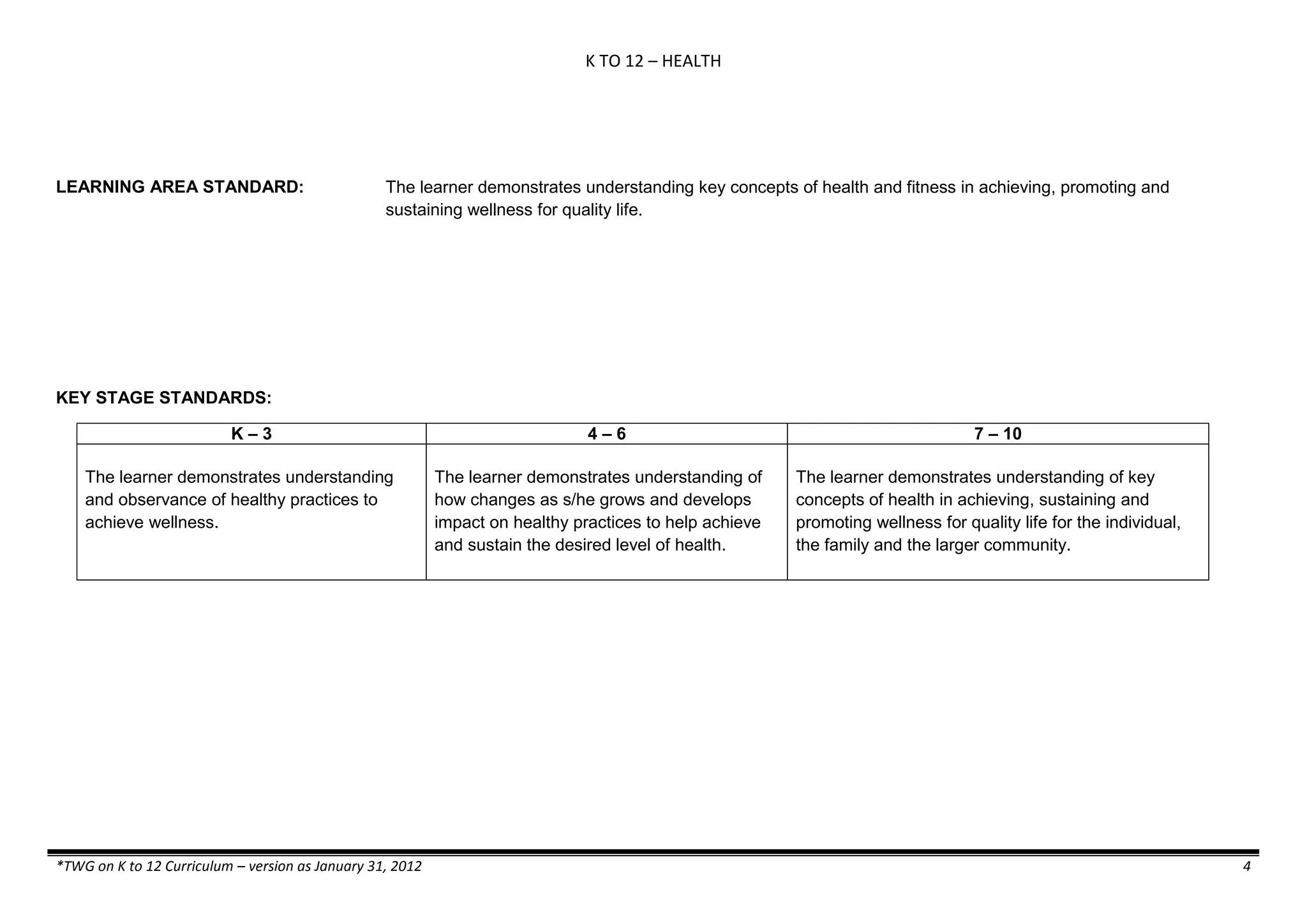
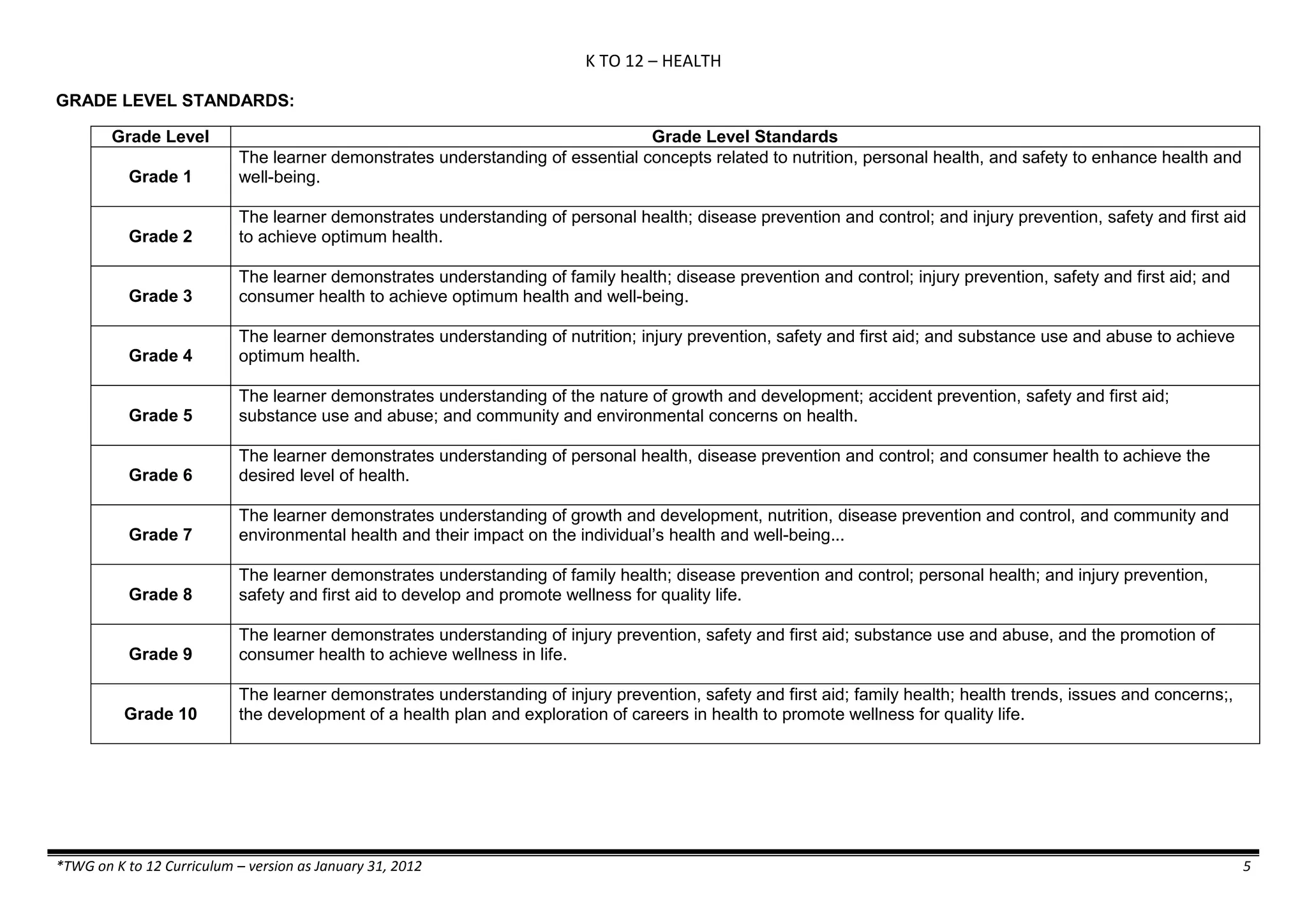
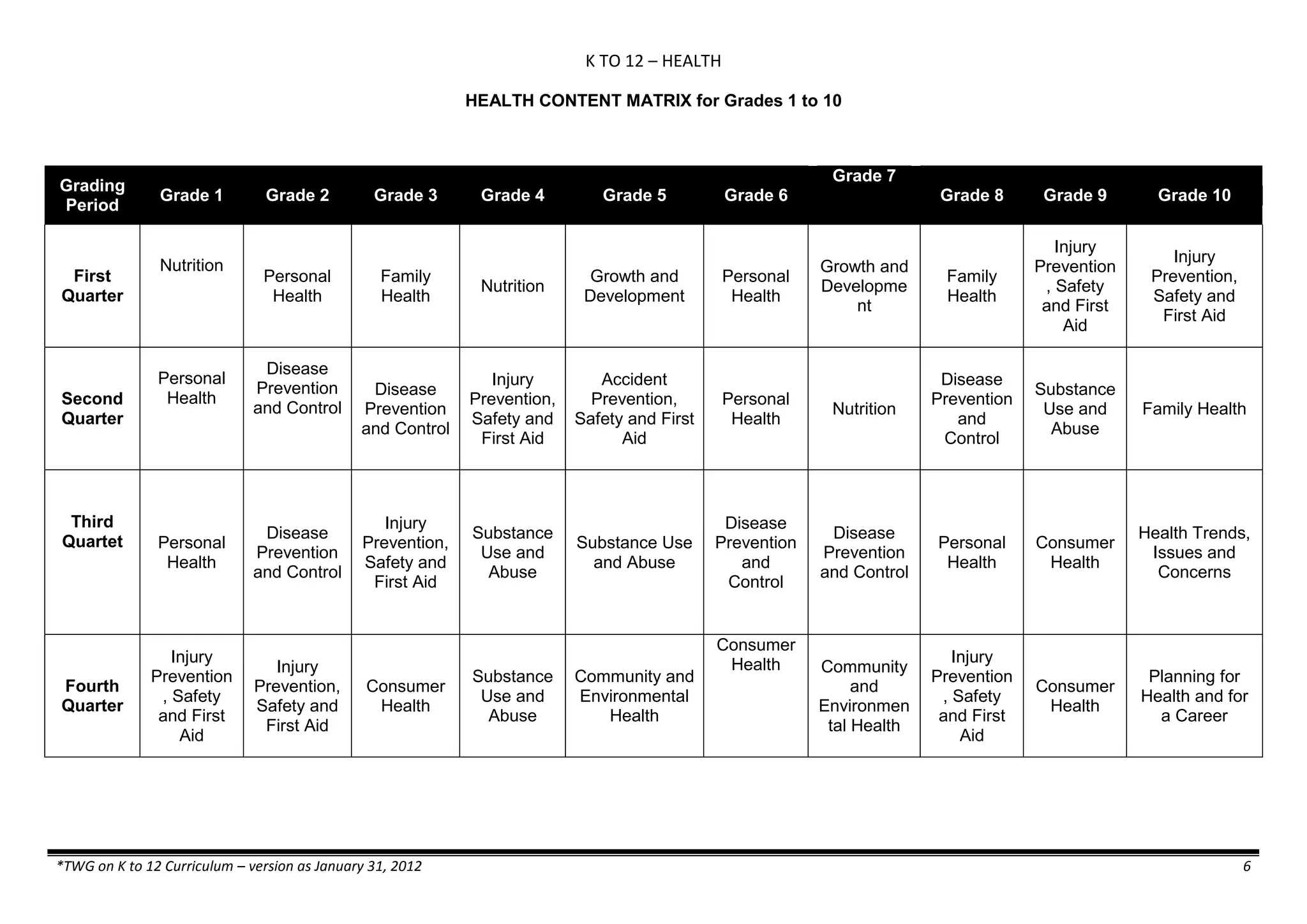





















































![K TO 12 SCIENCE
K to 12 Curriculum Guide Science – version as of January 31, 2012 33
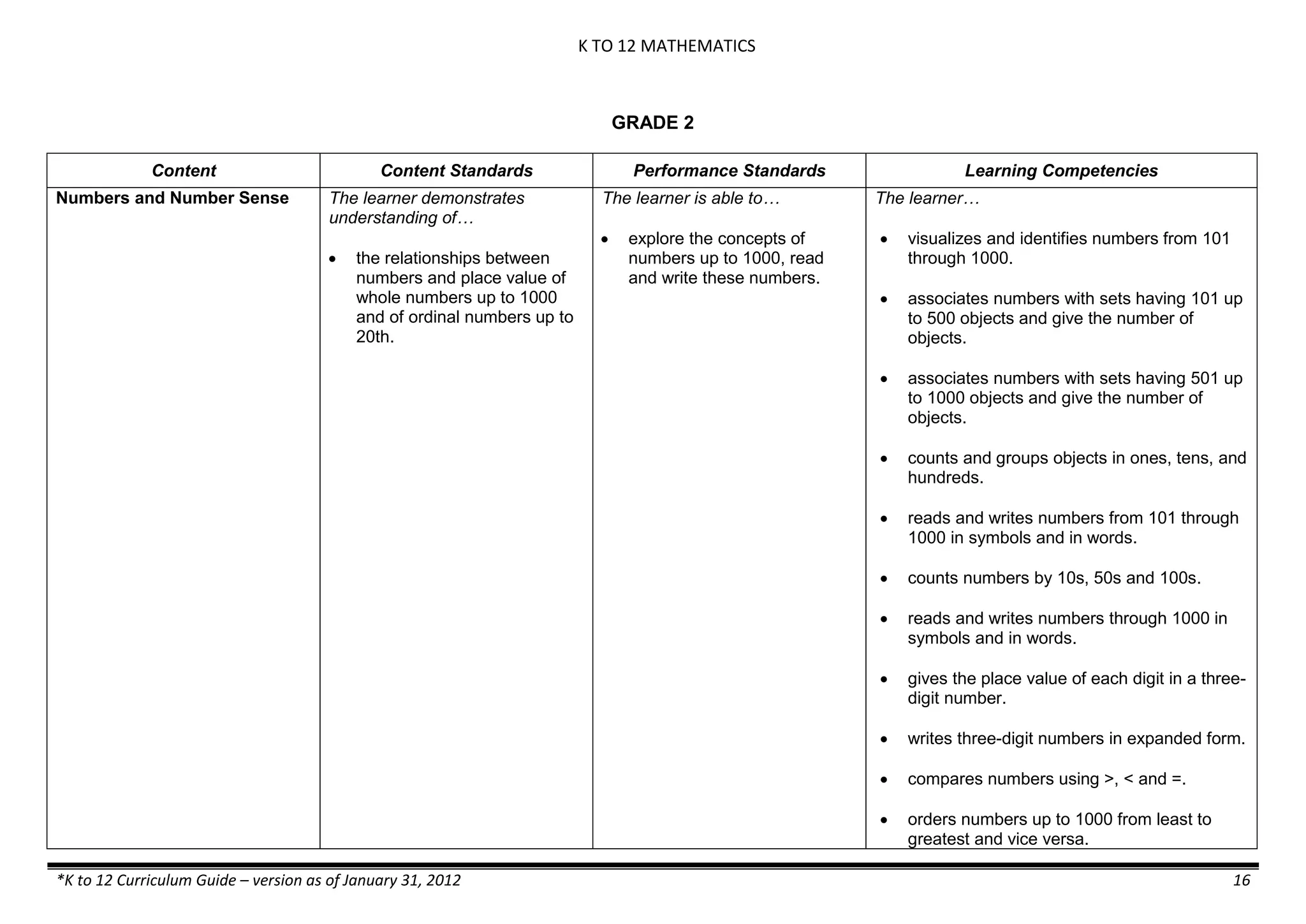
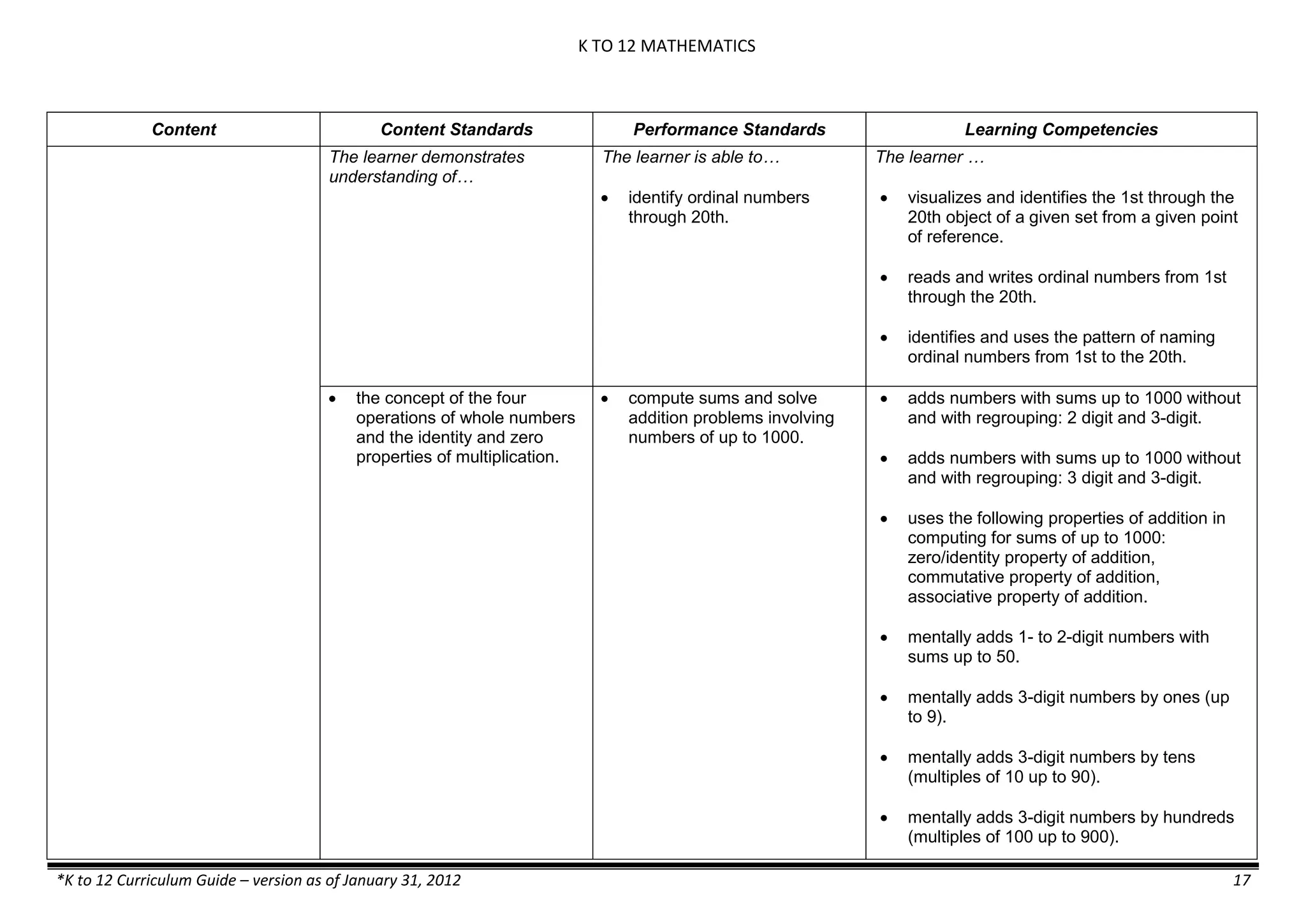
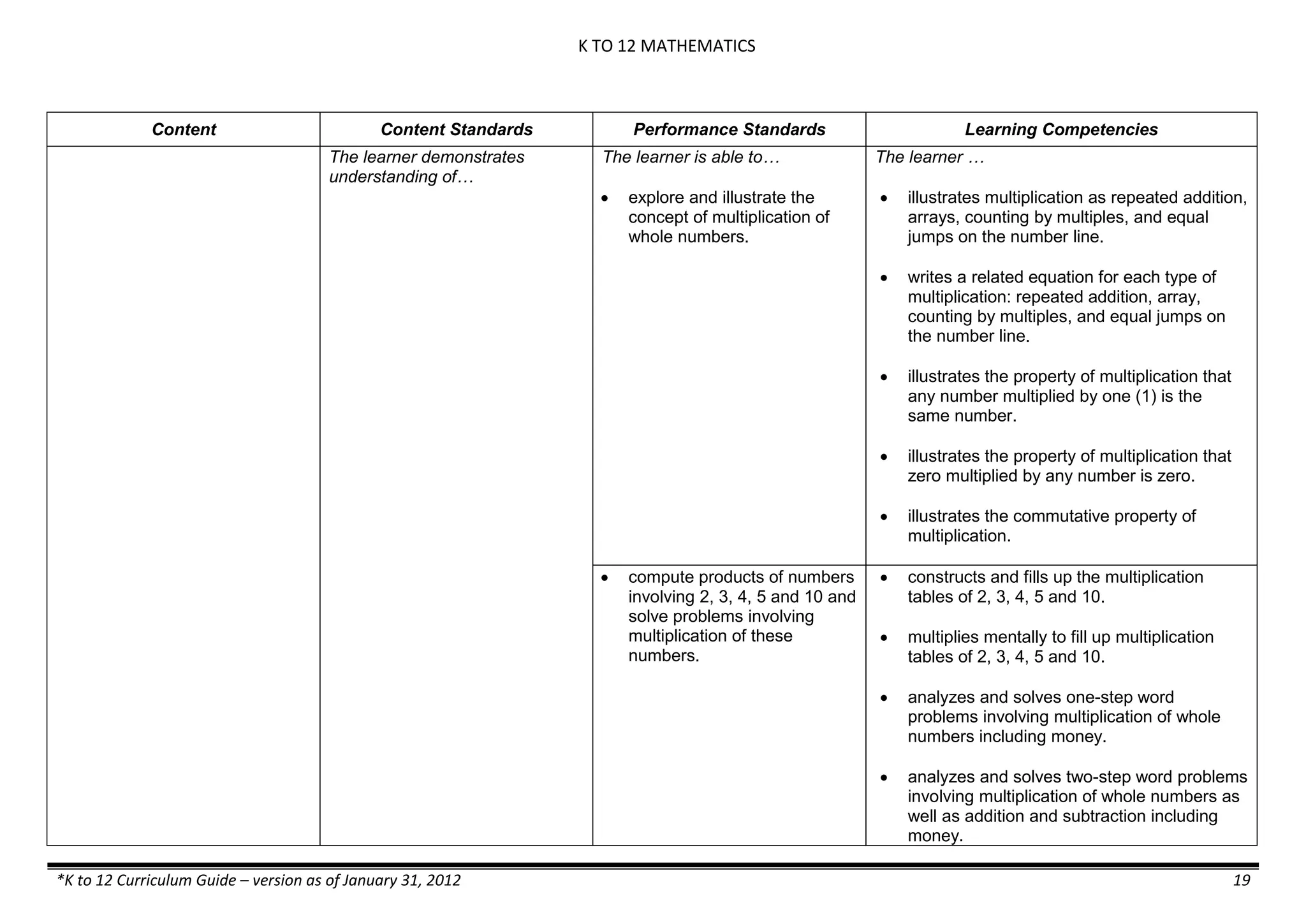
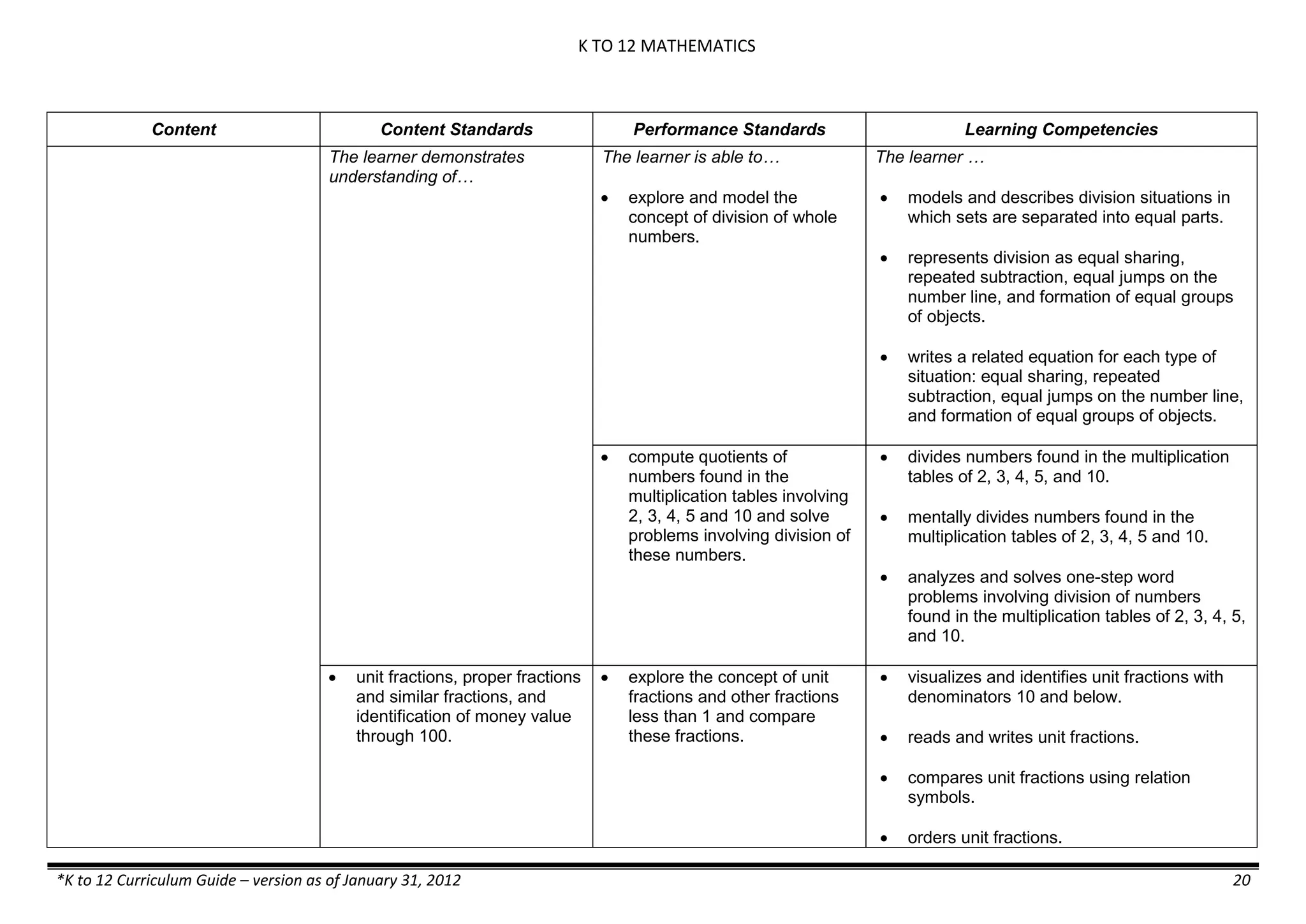
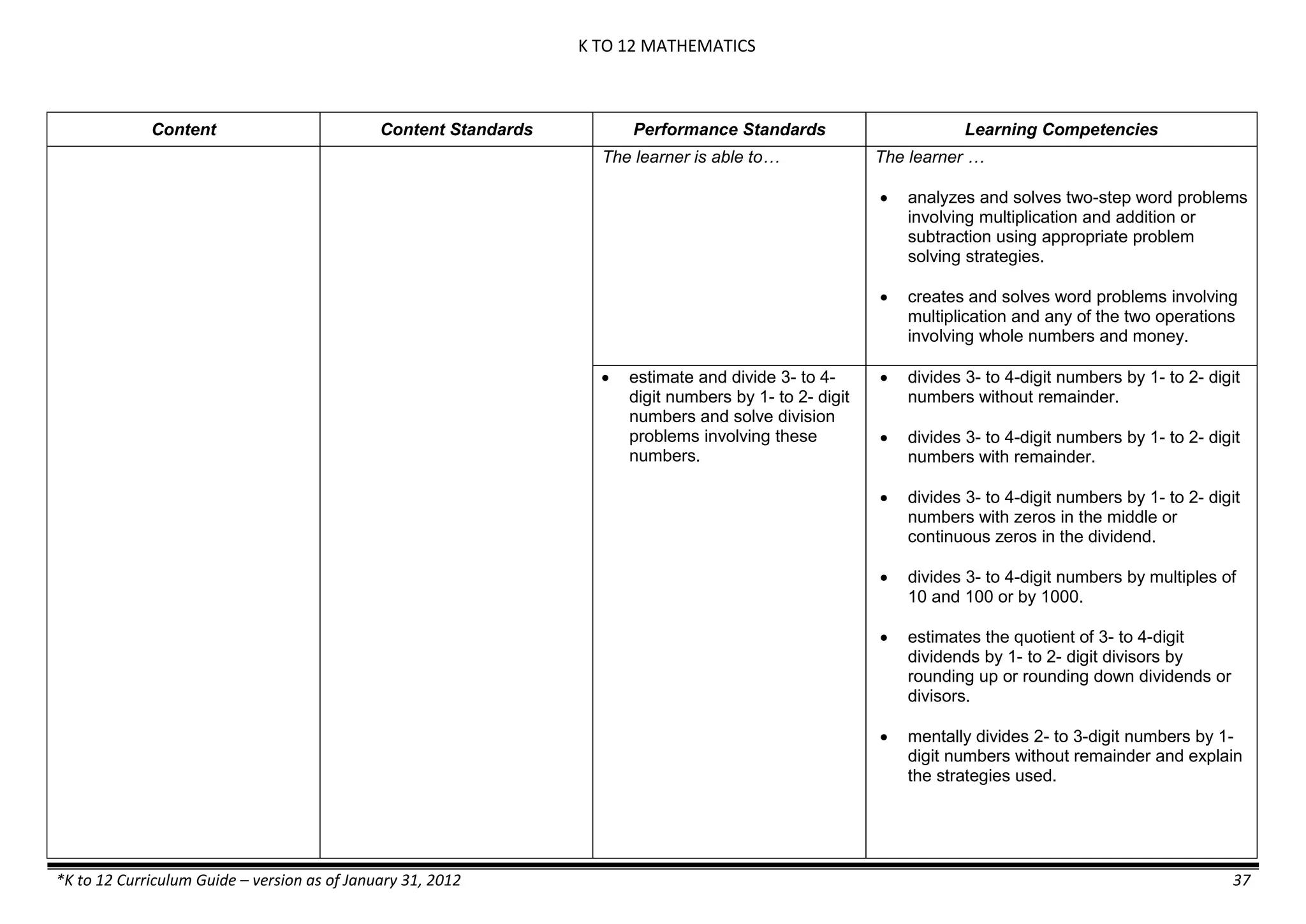
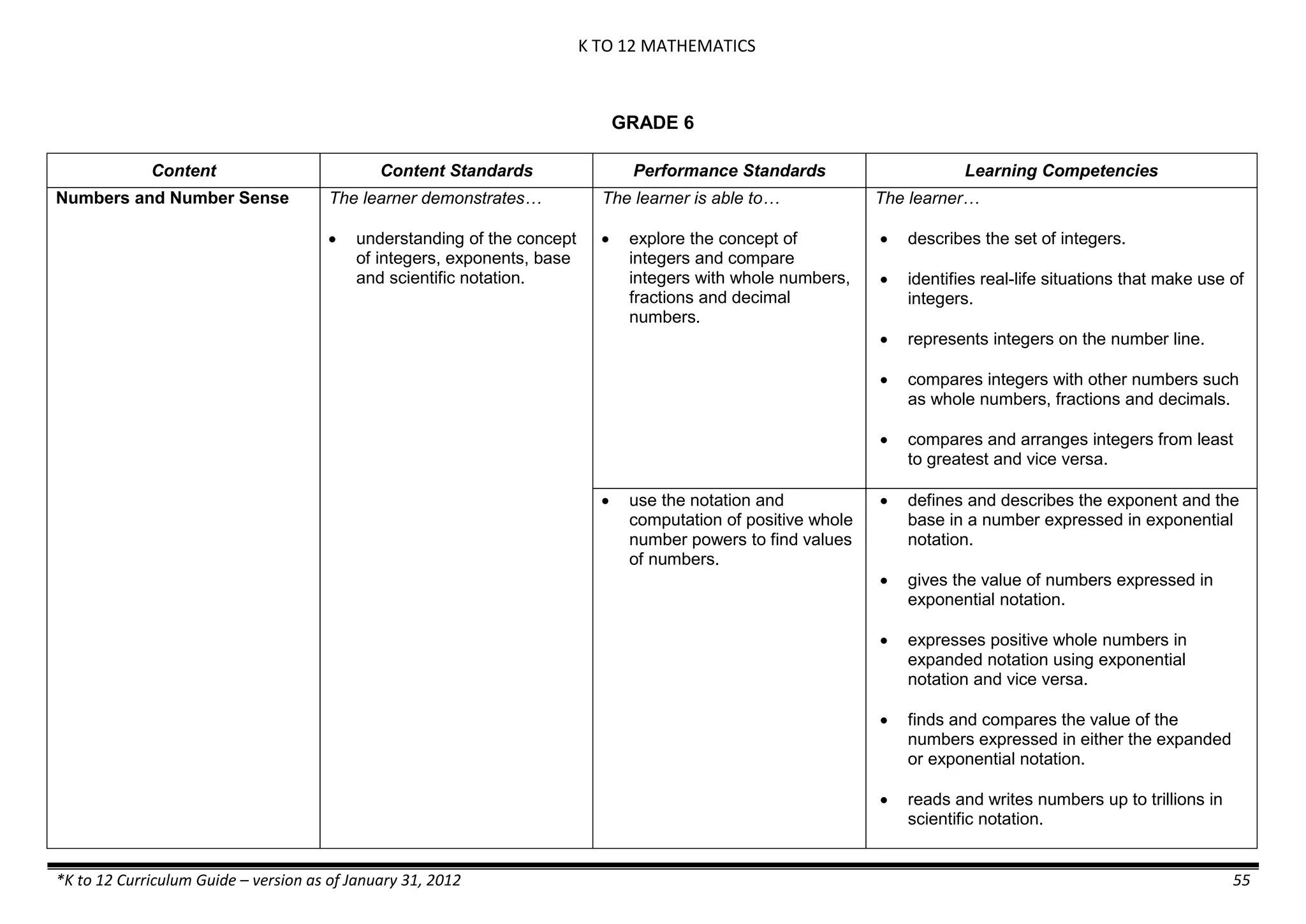
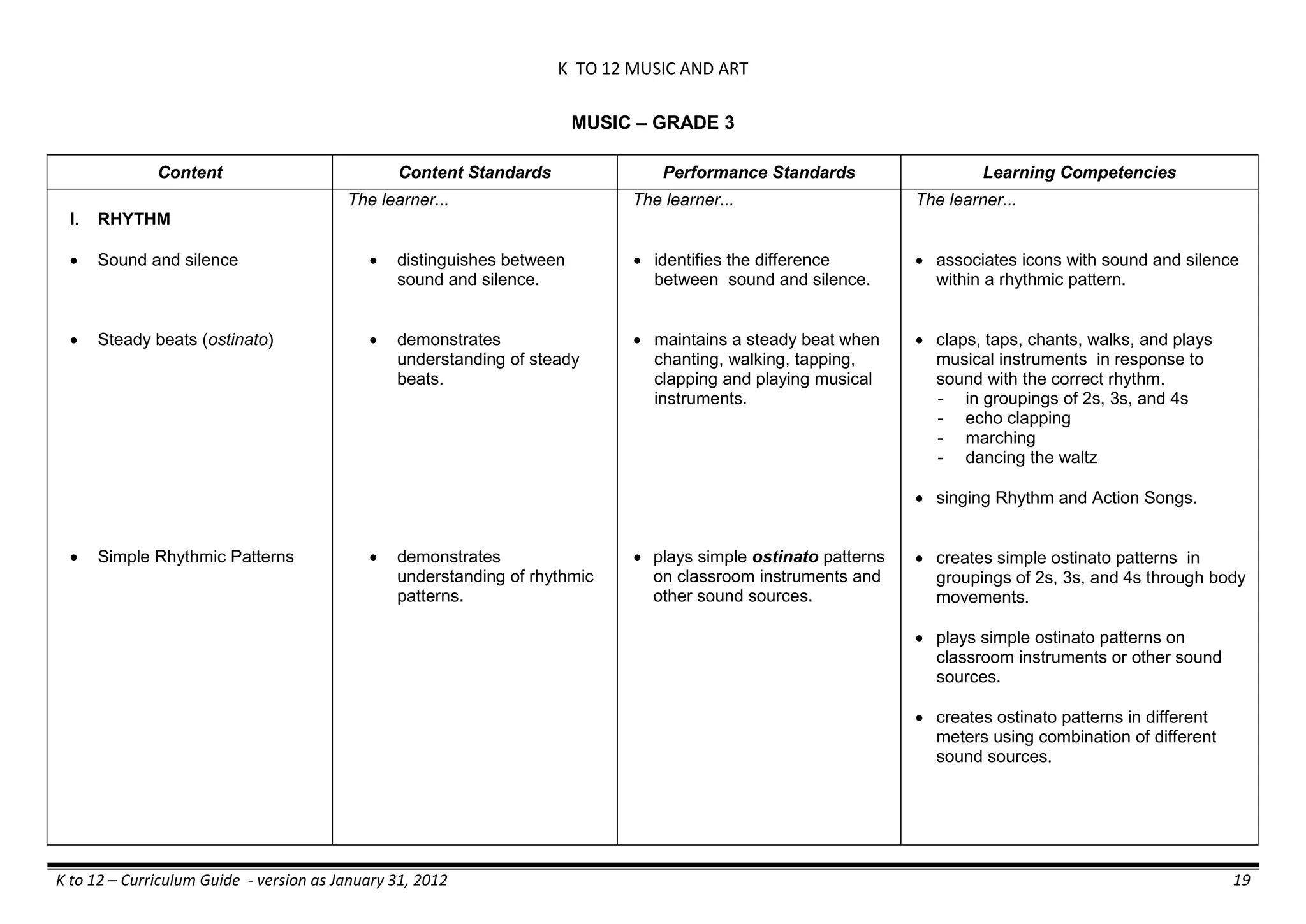
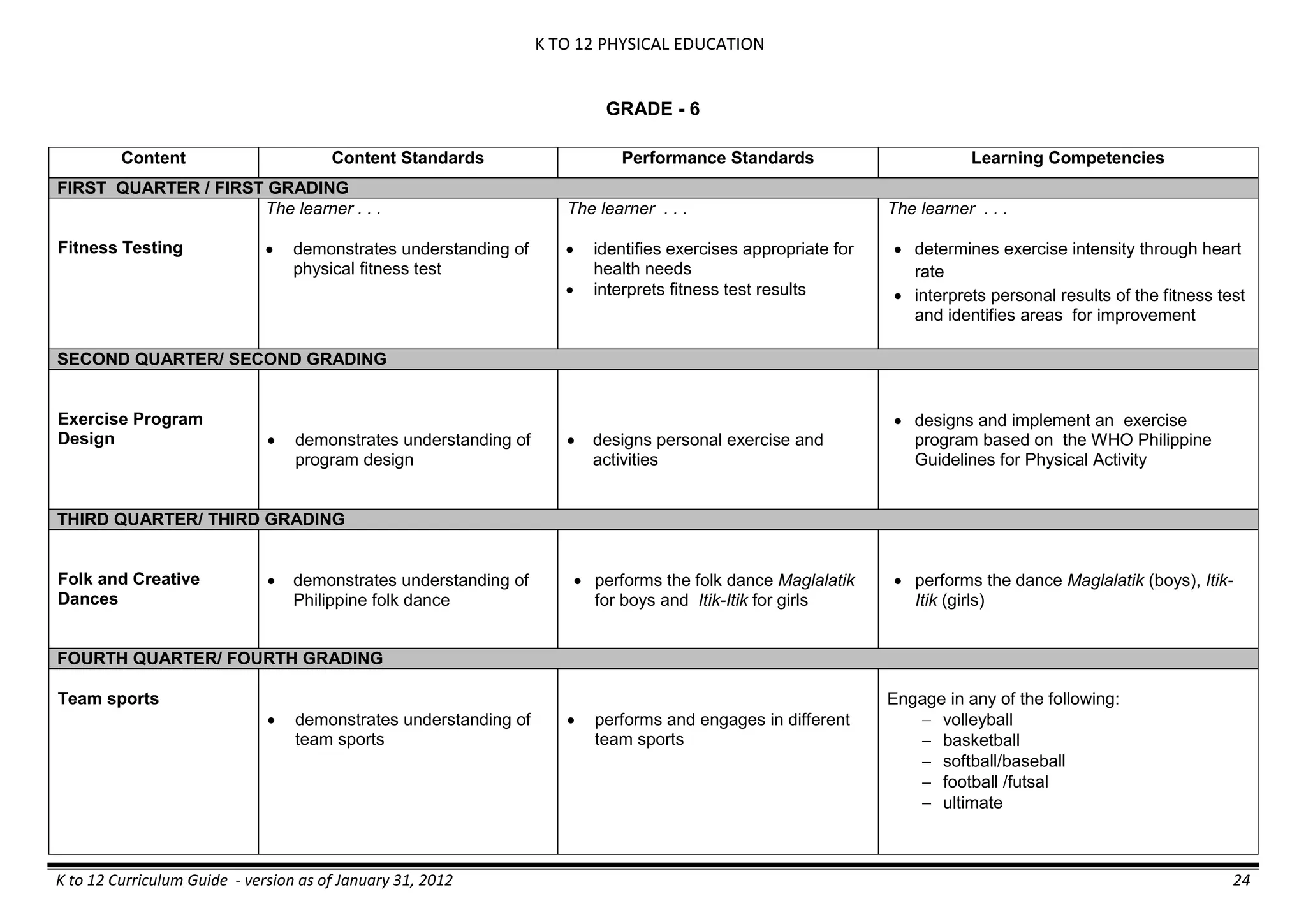
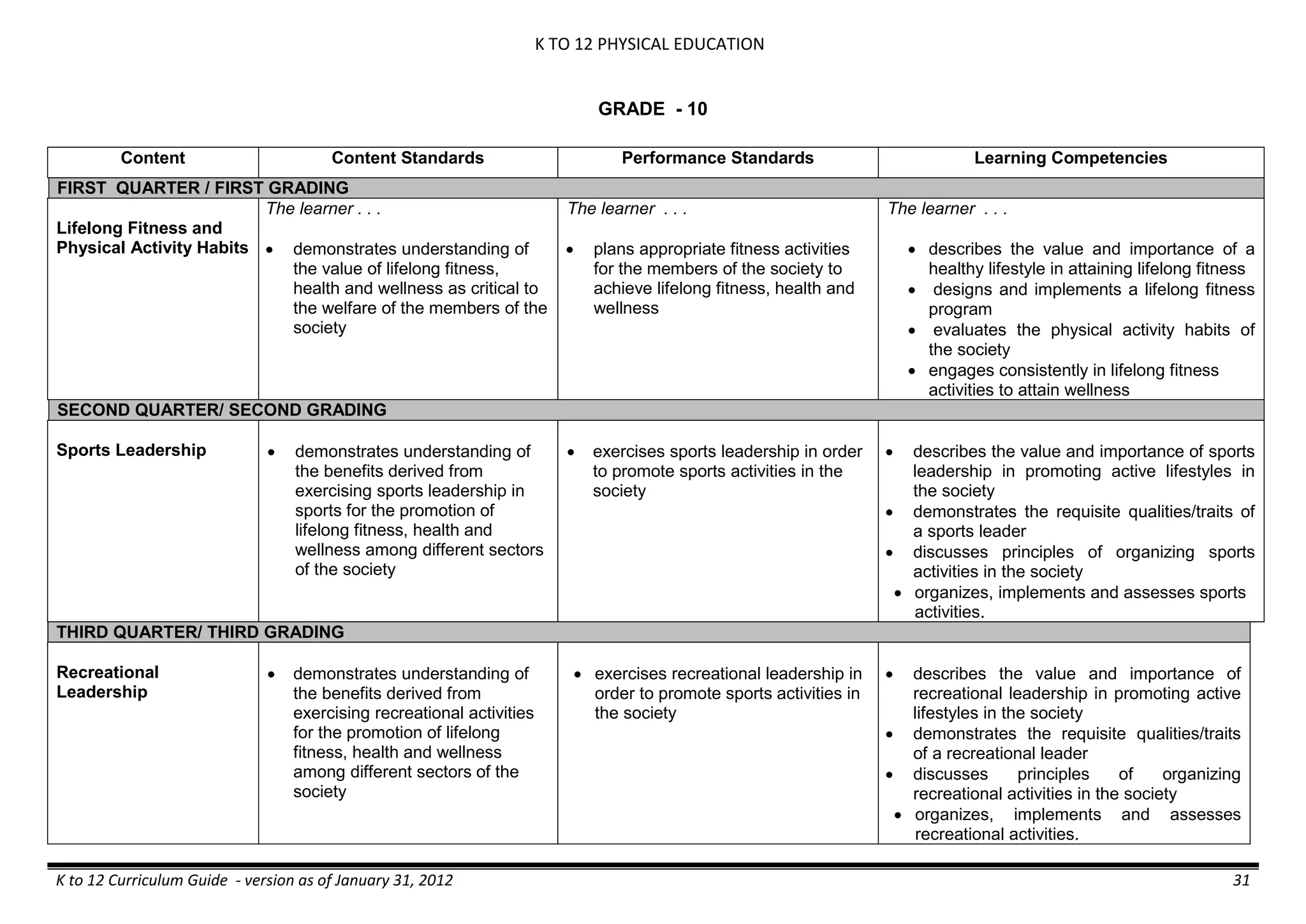
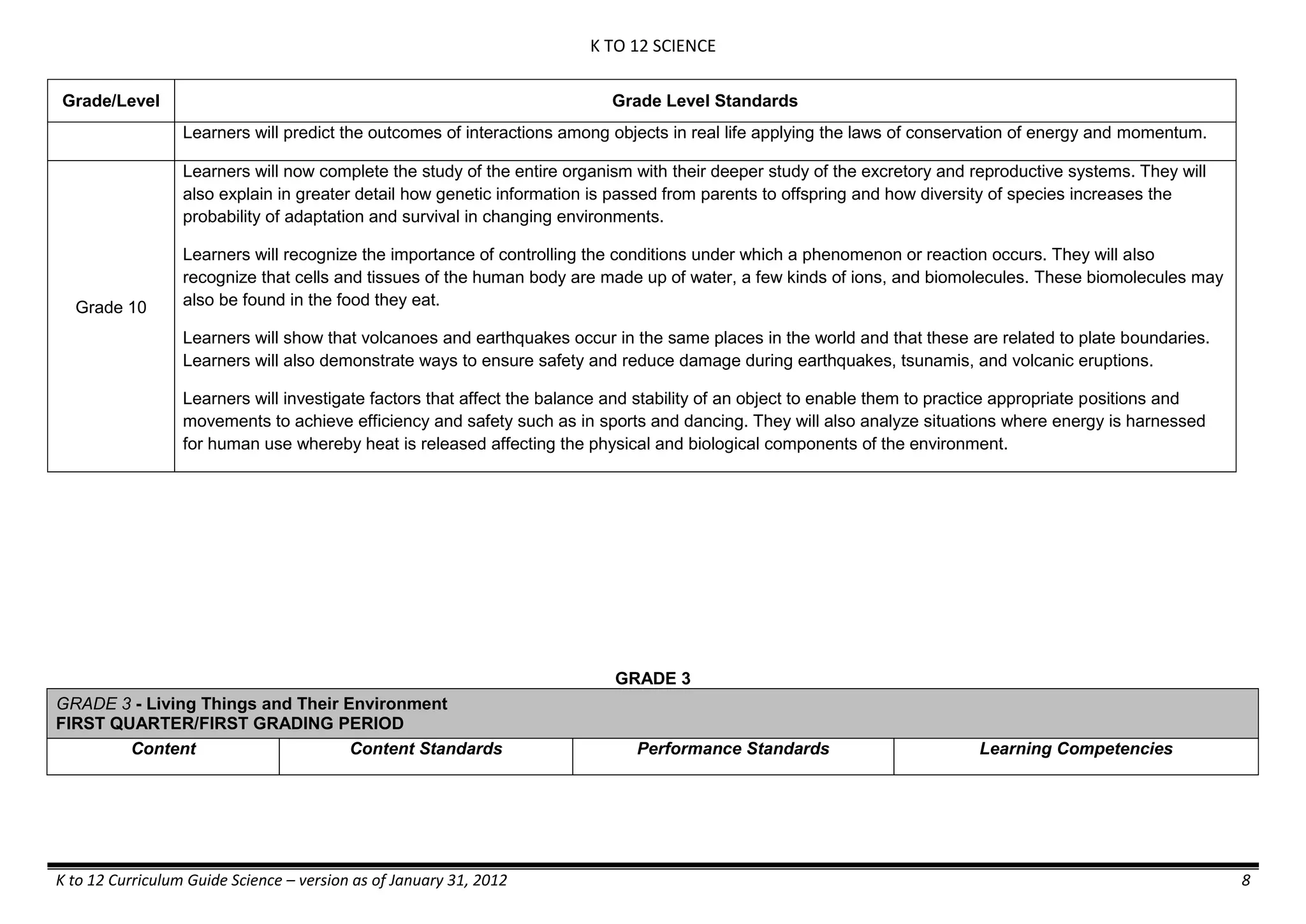
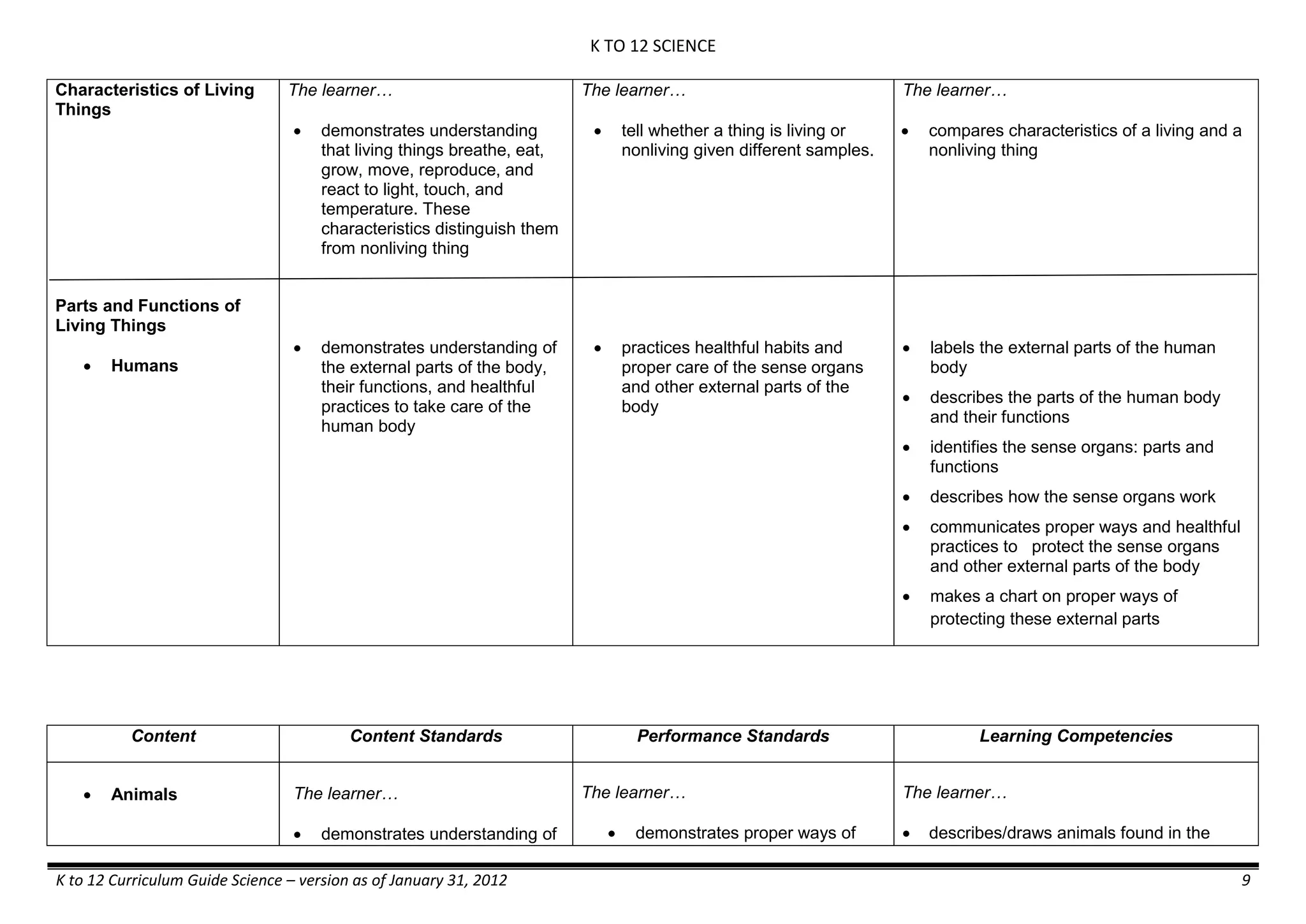
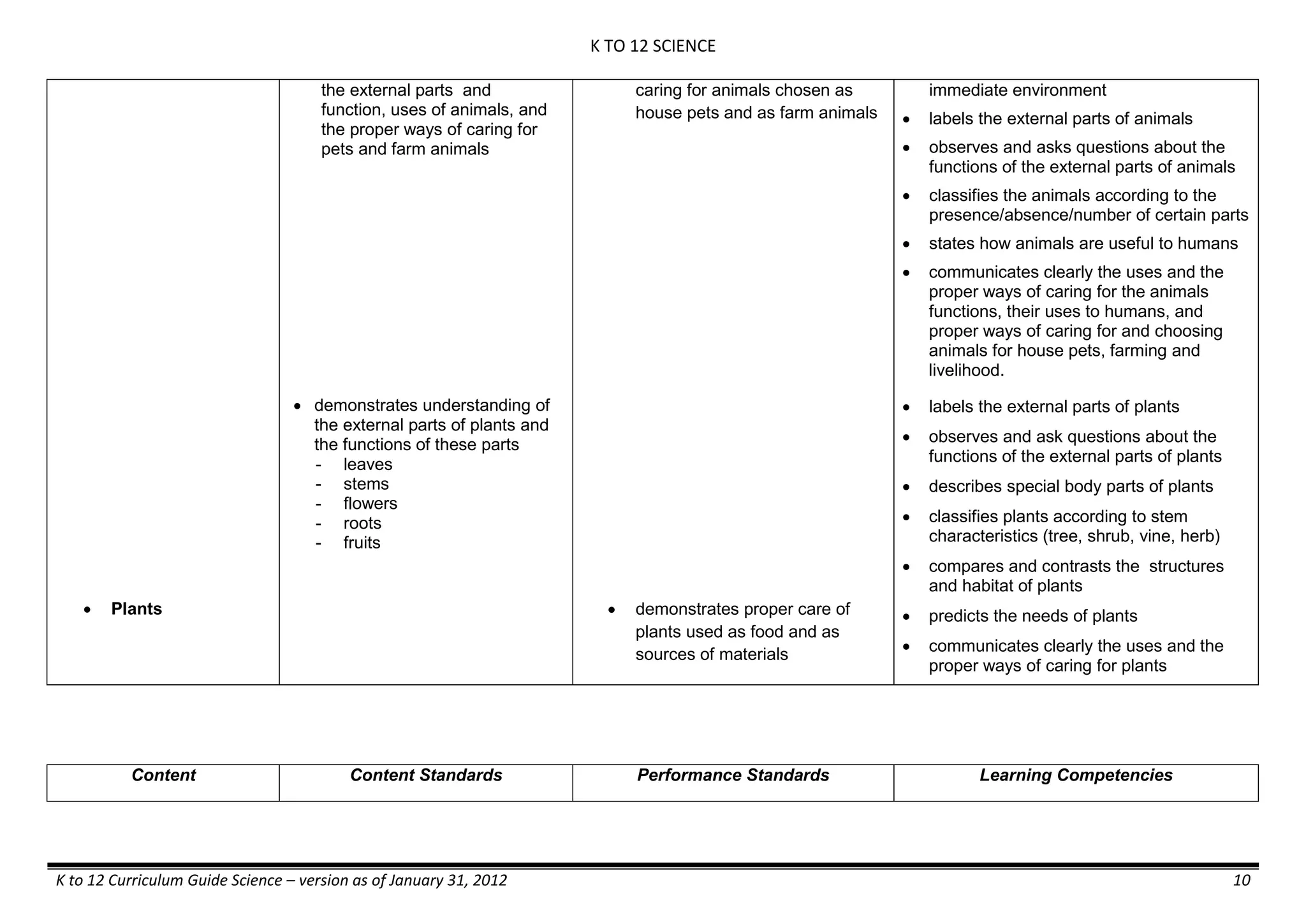
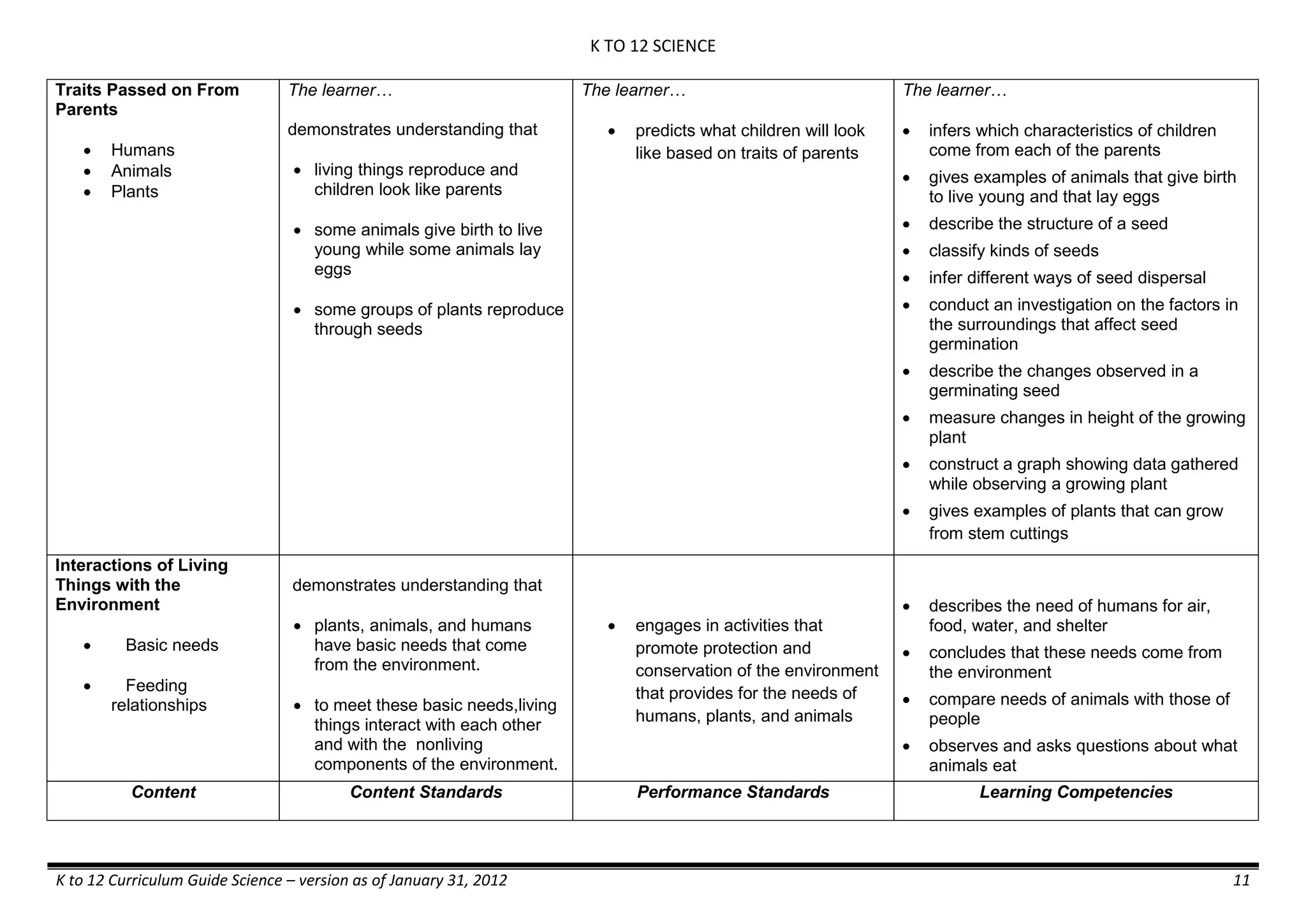
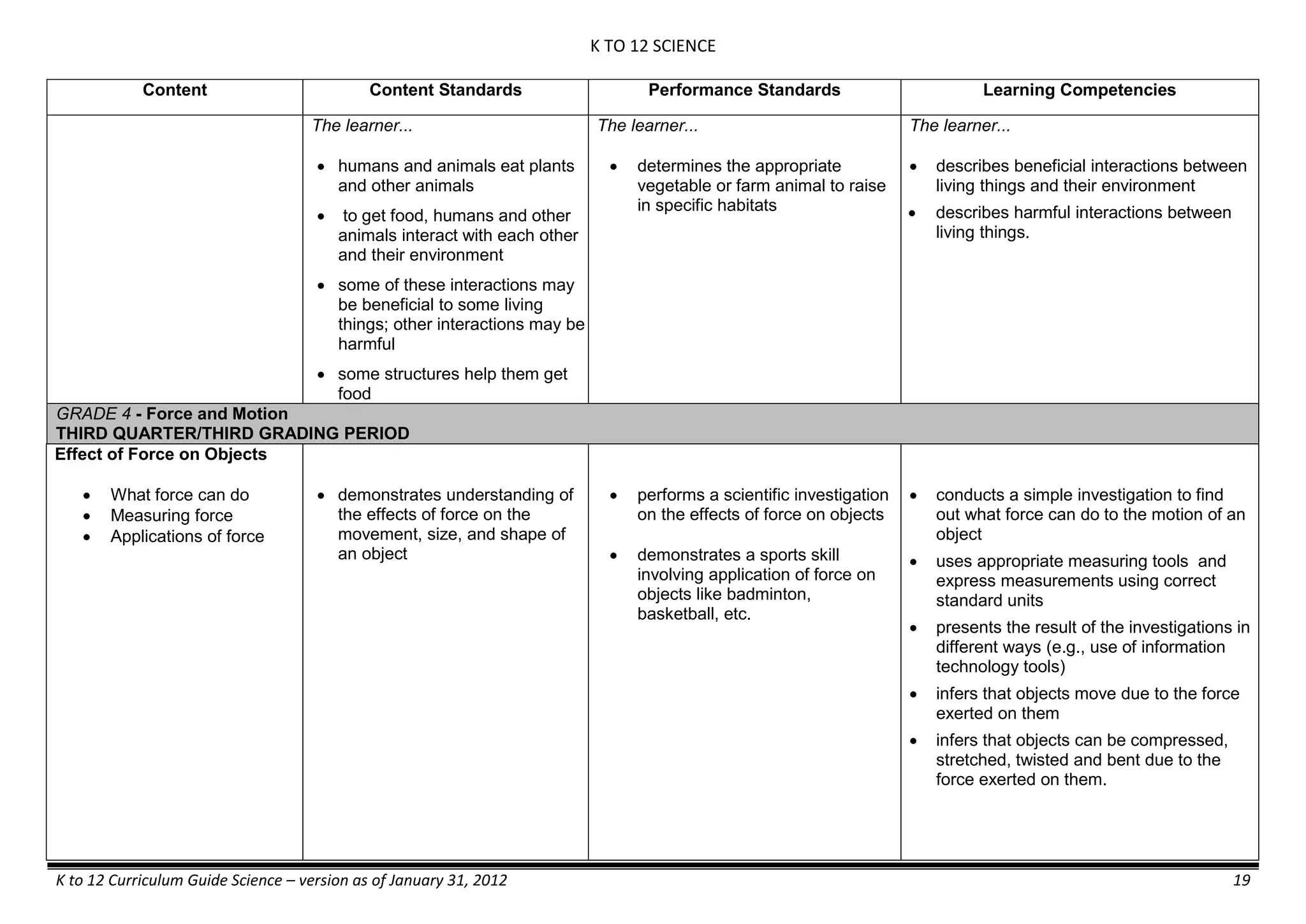
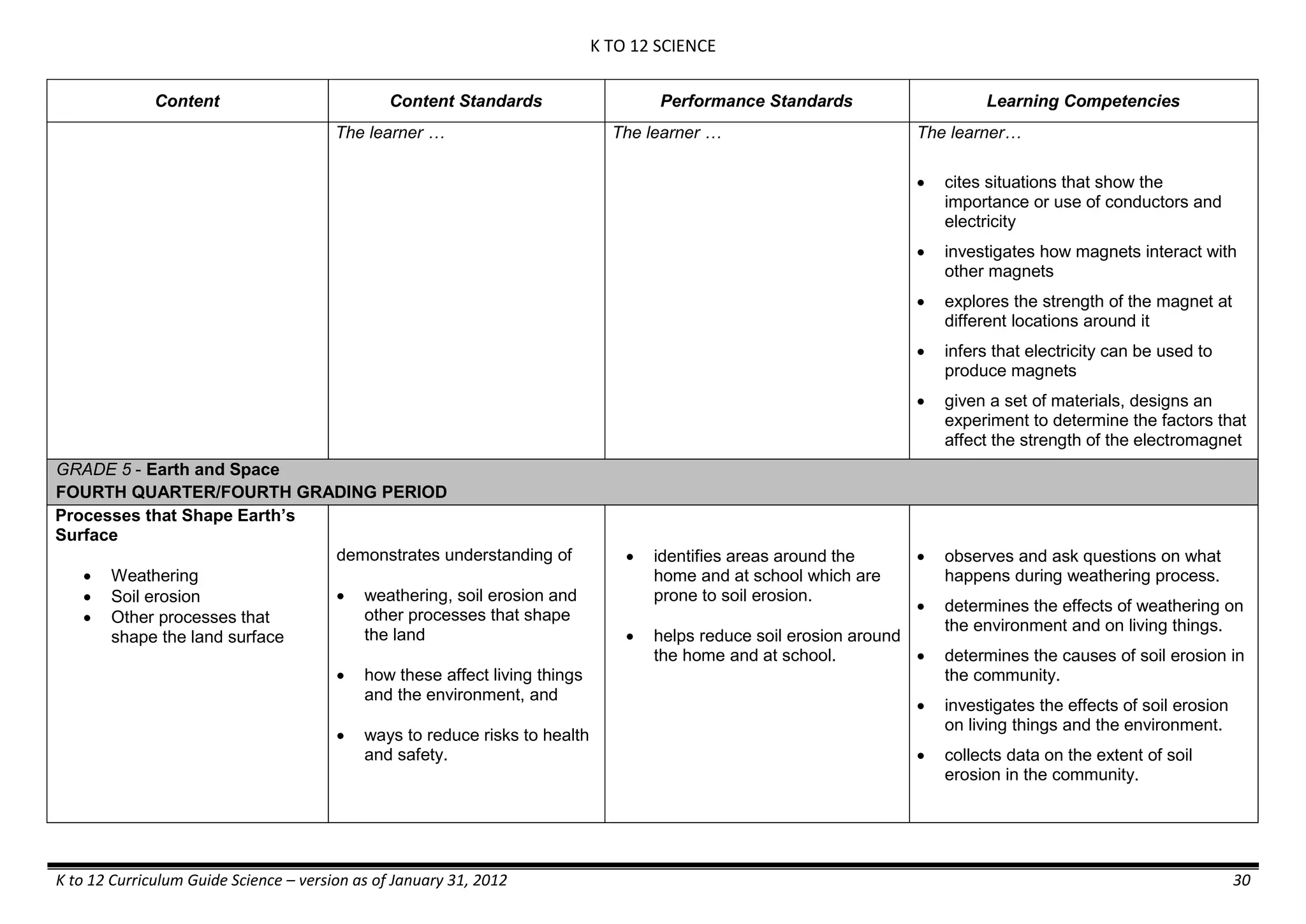
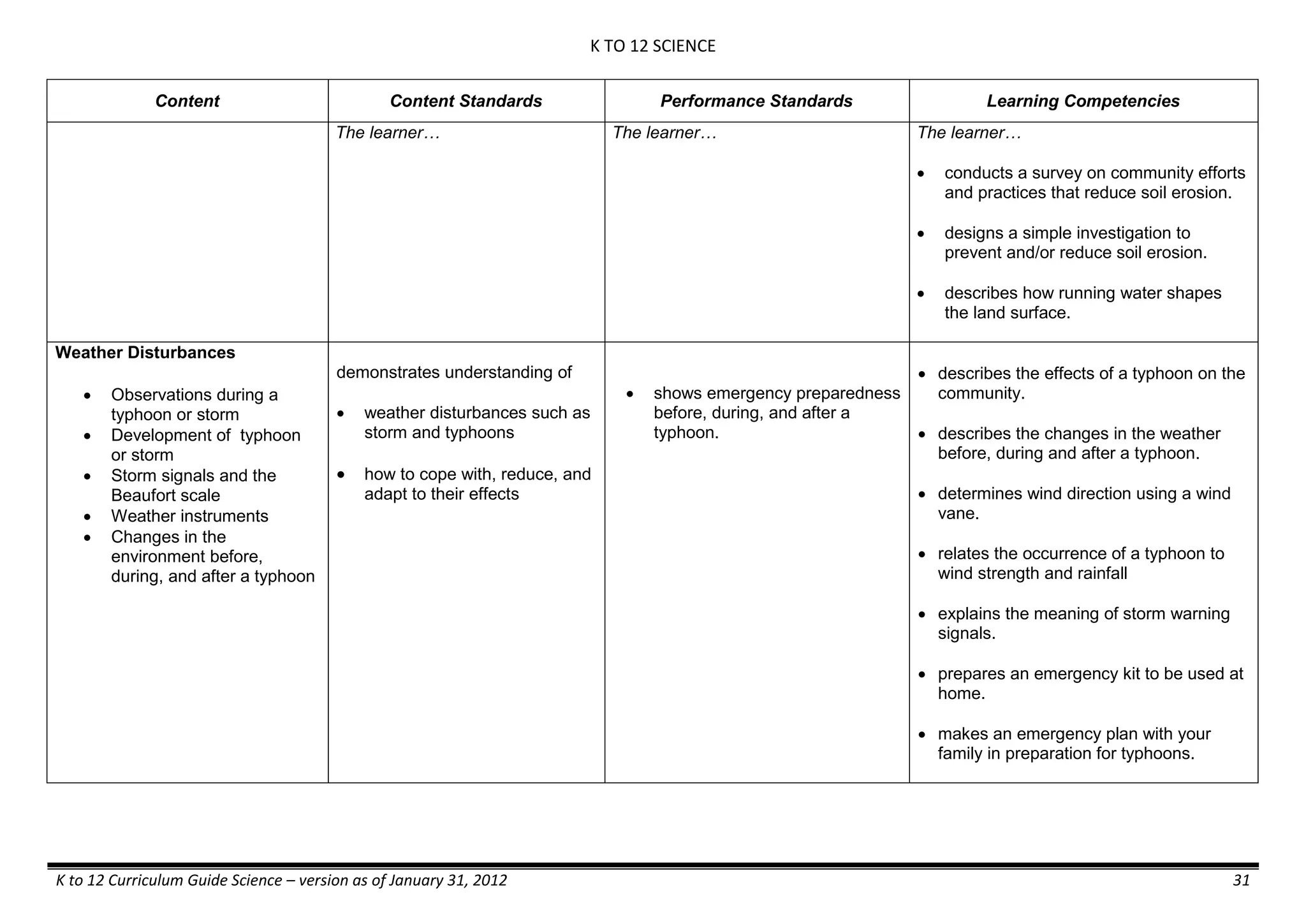
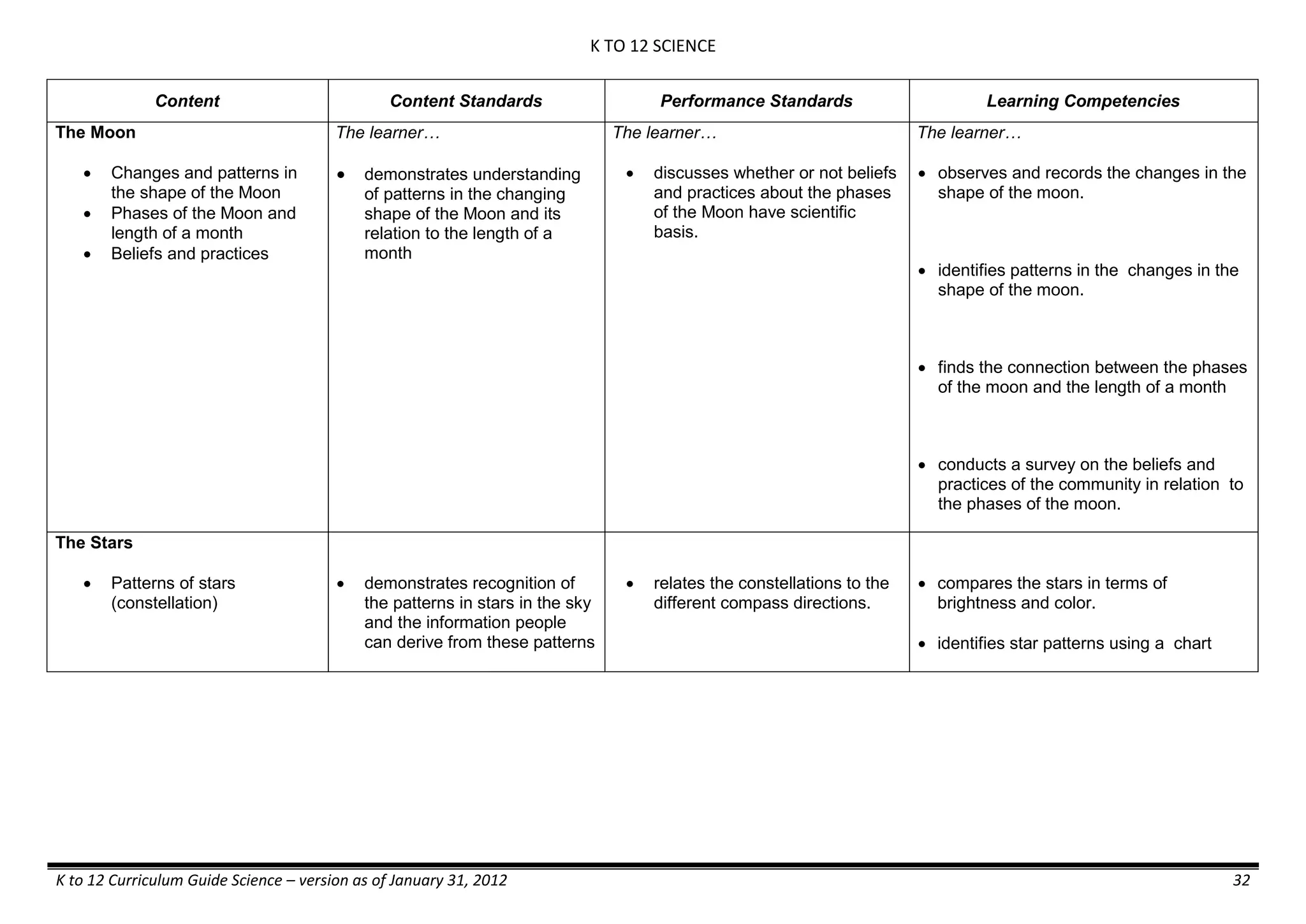
GRADE 6
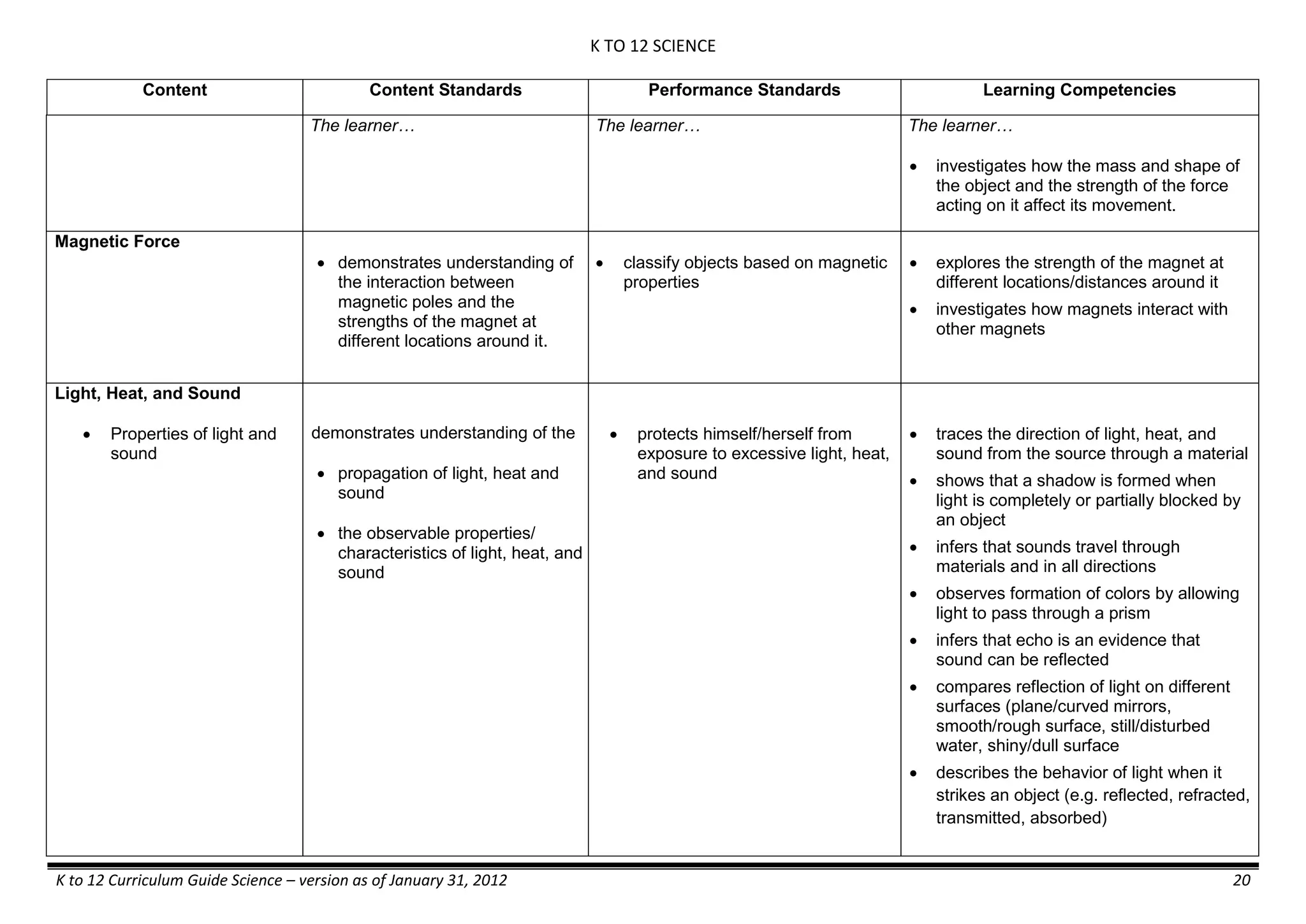
GRADE 6 - Matter
FIRST QUARTER/FIRST GRADING PERIOD
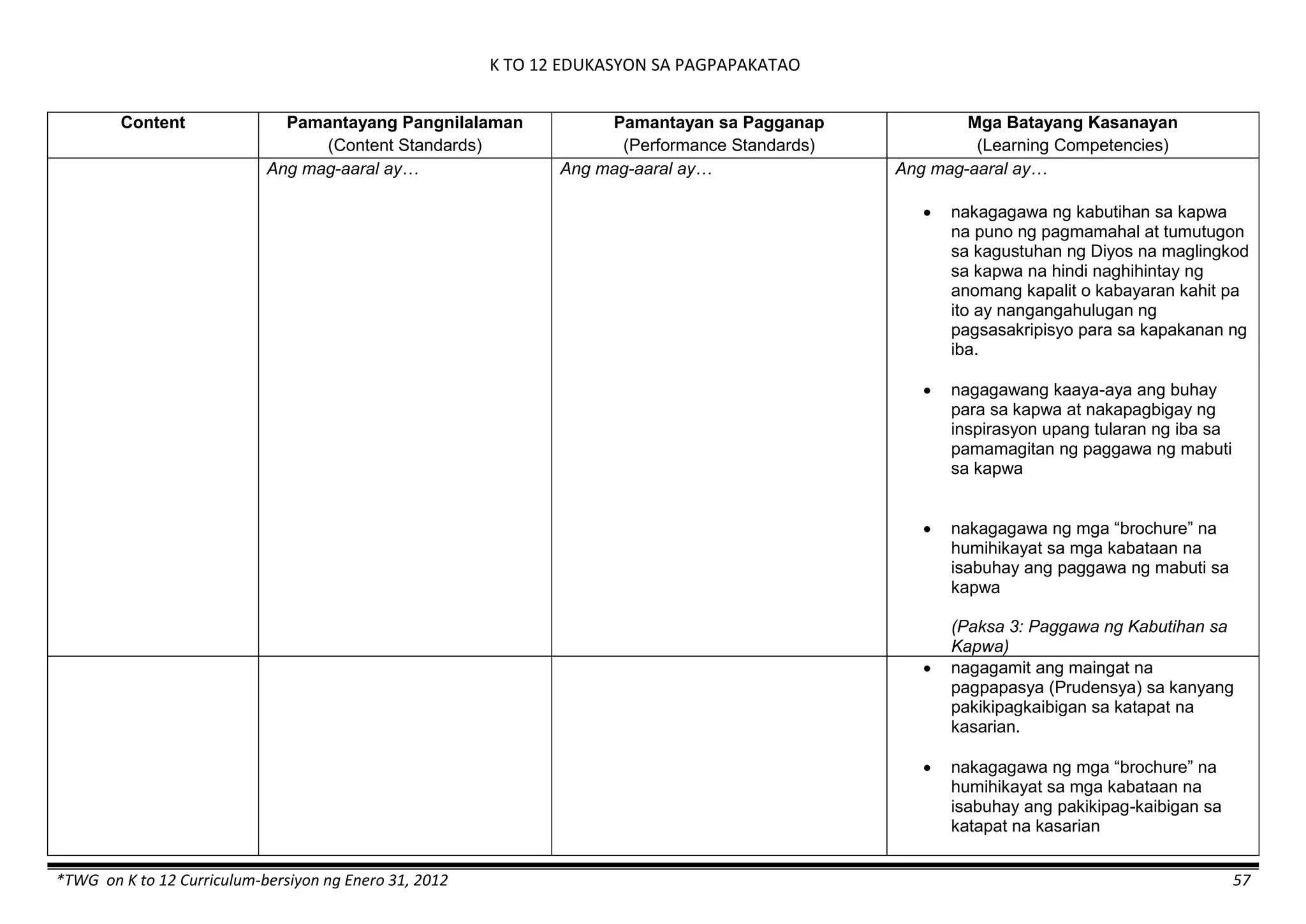
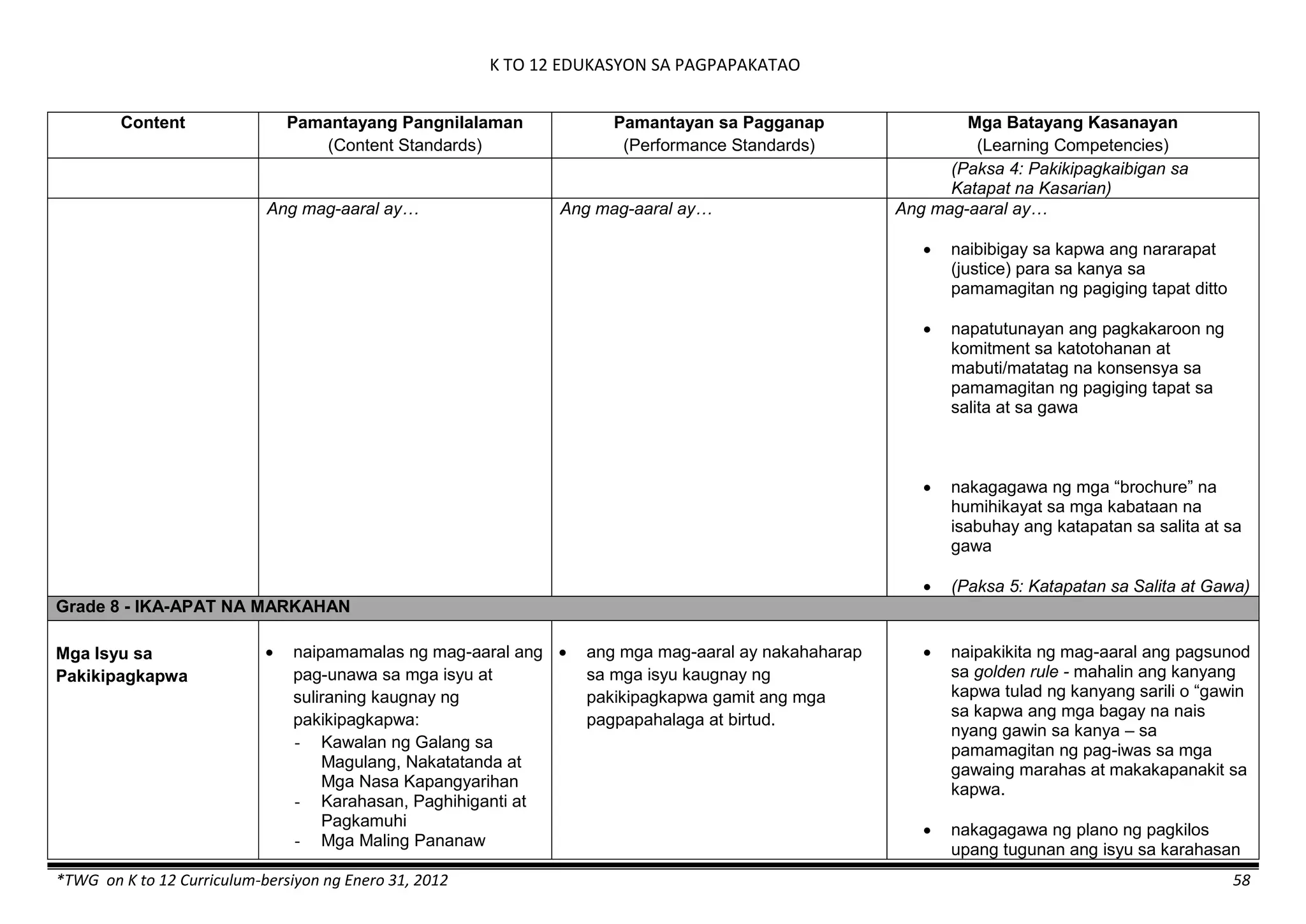
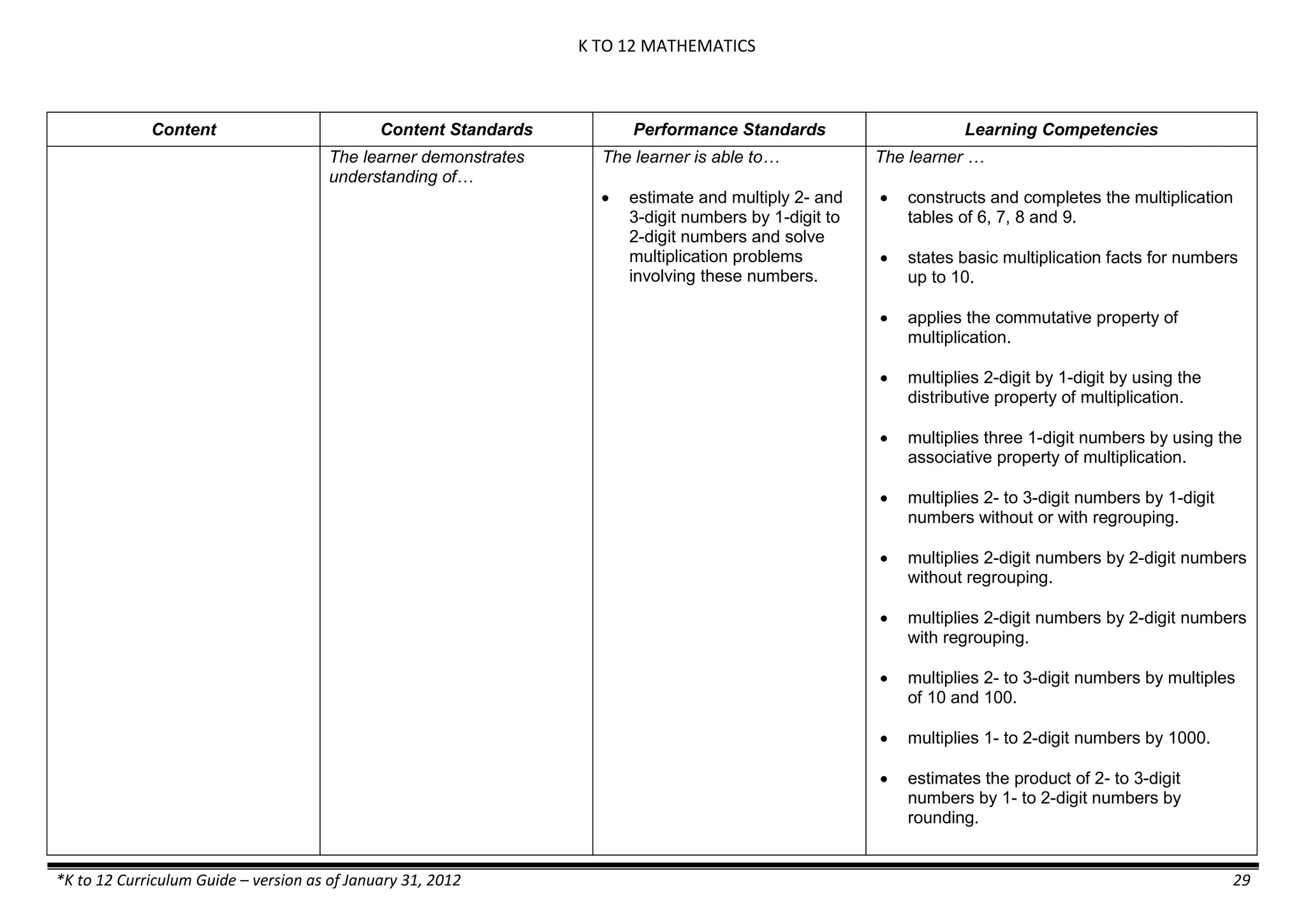
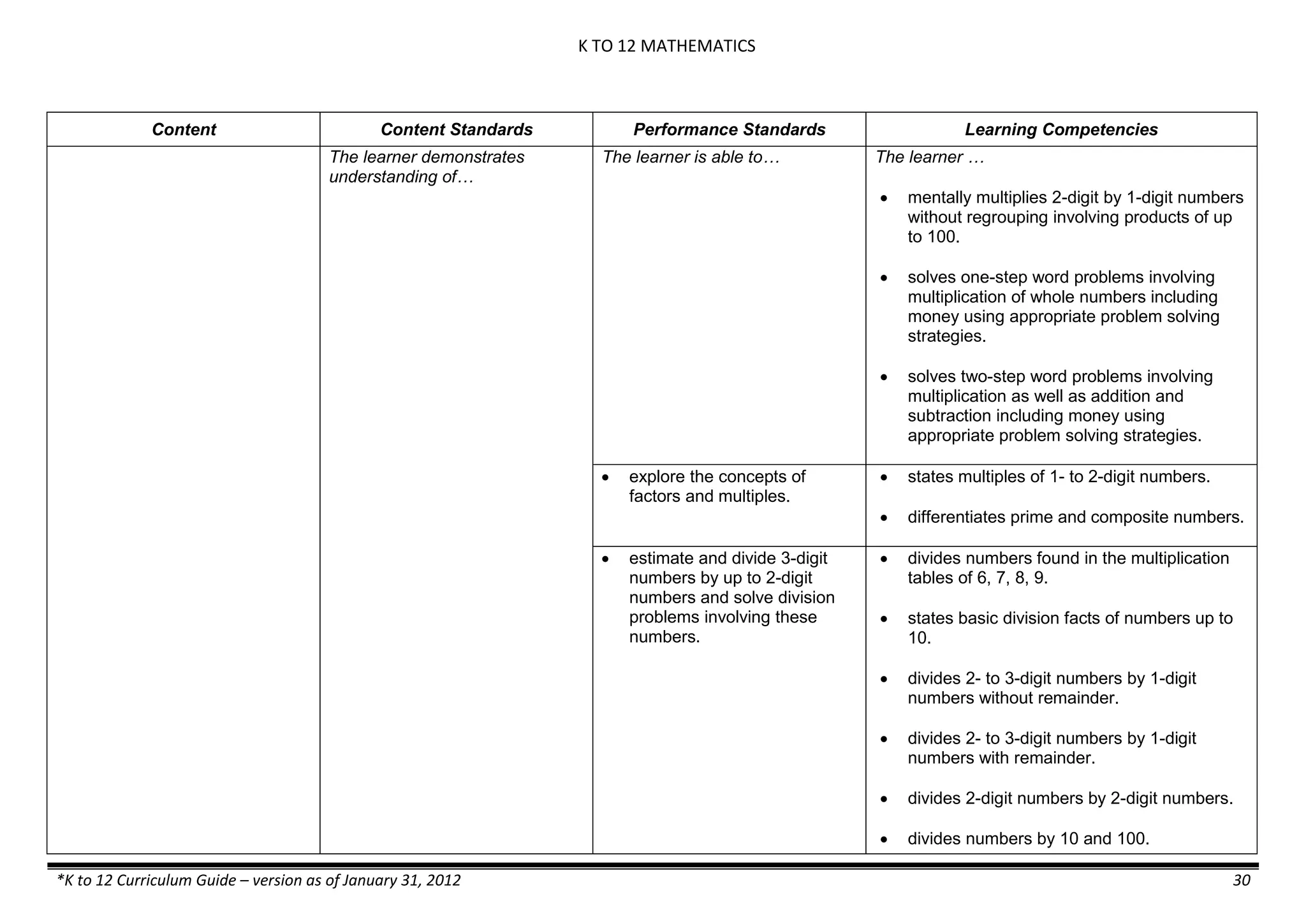
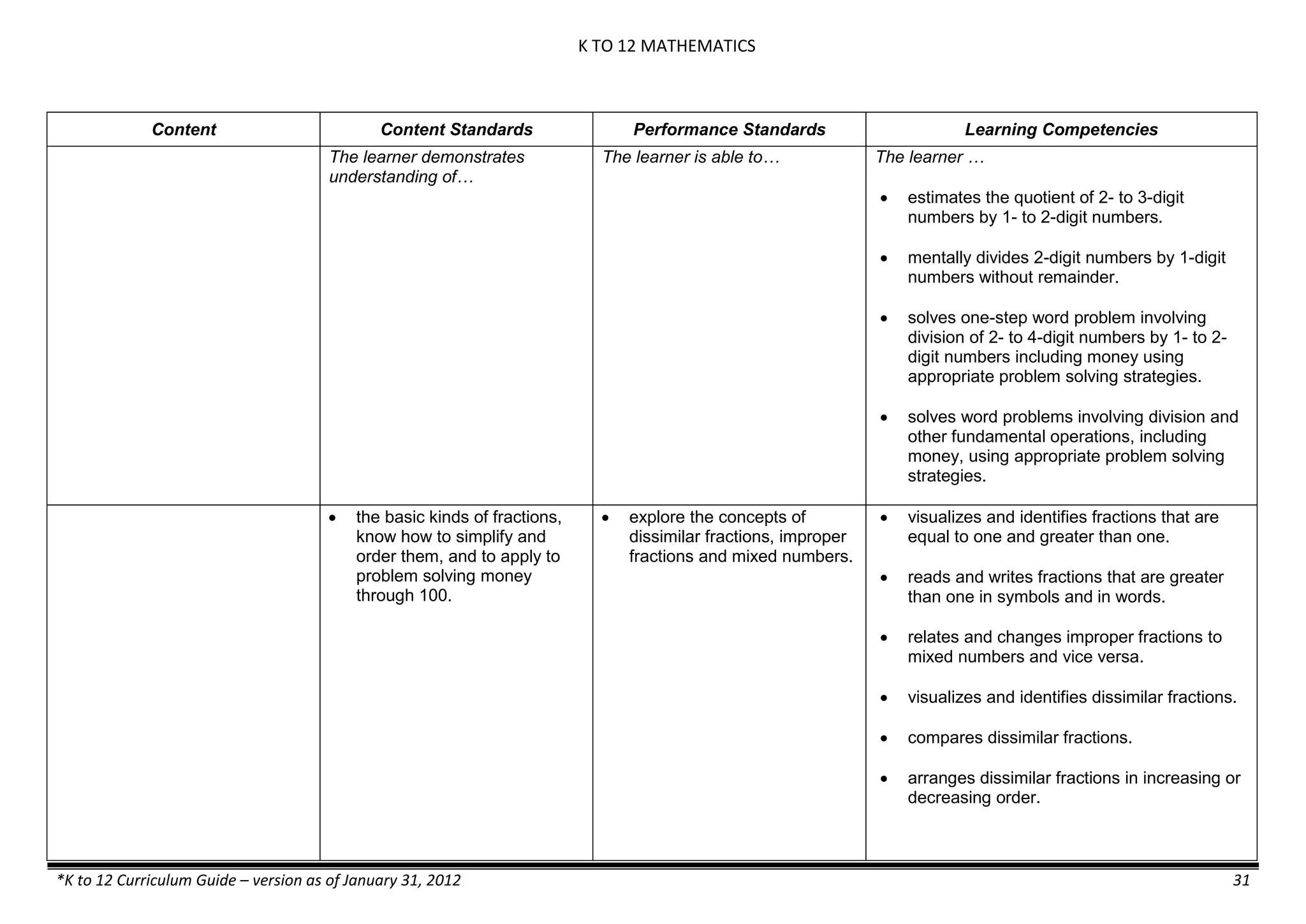
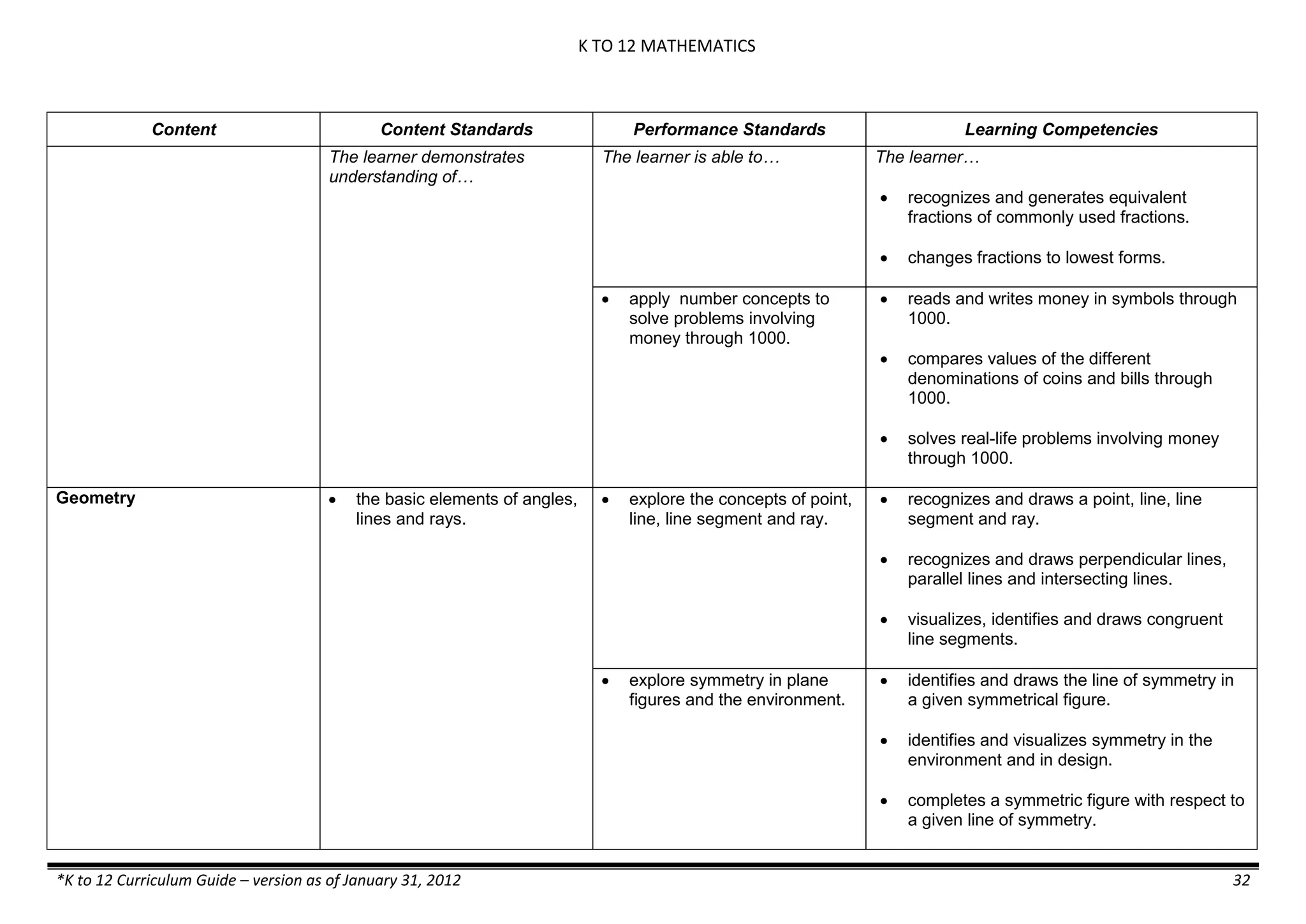
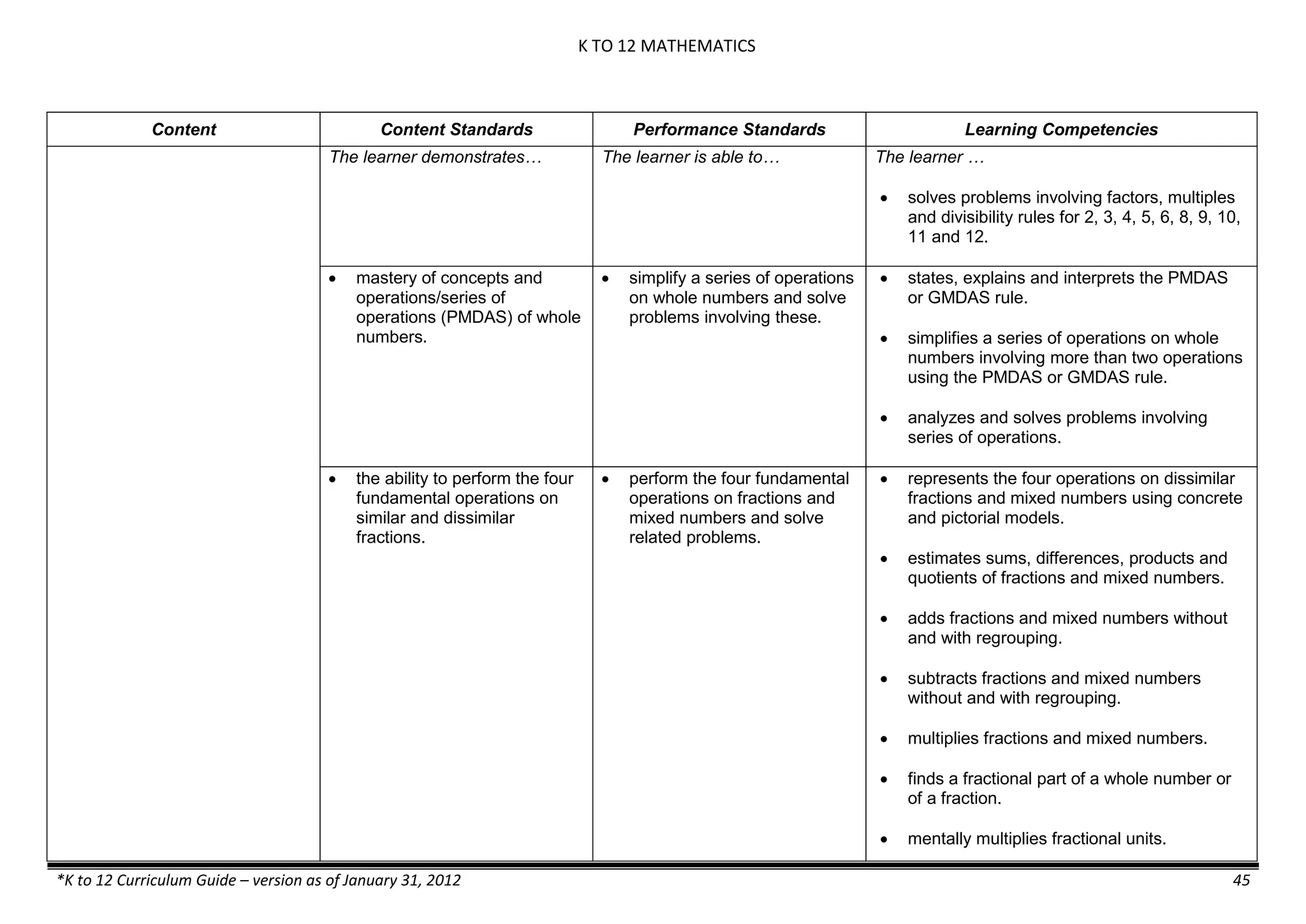
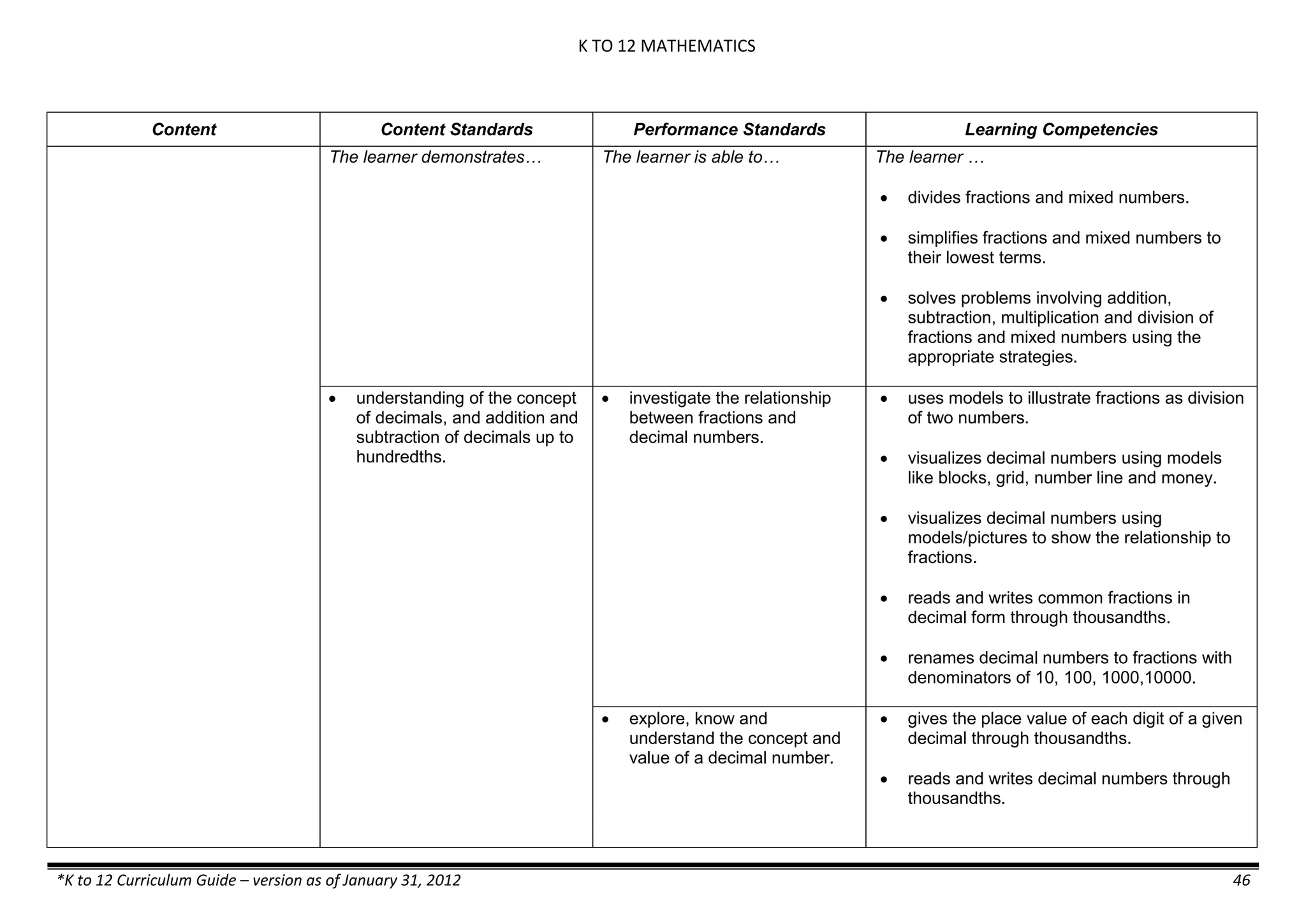
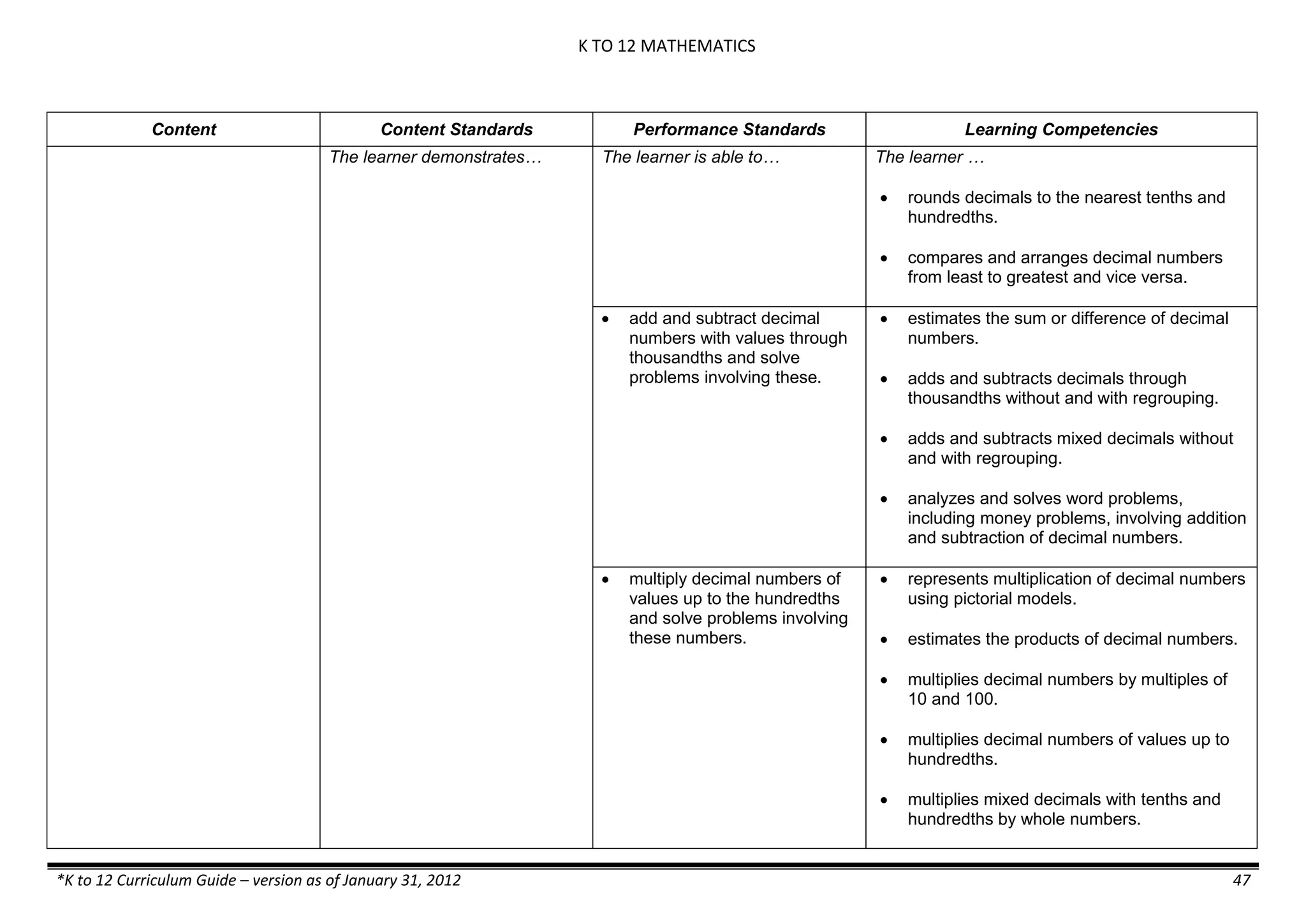
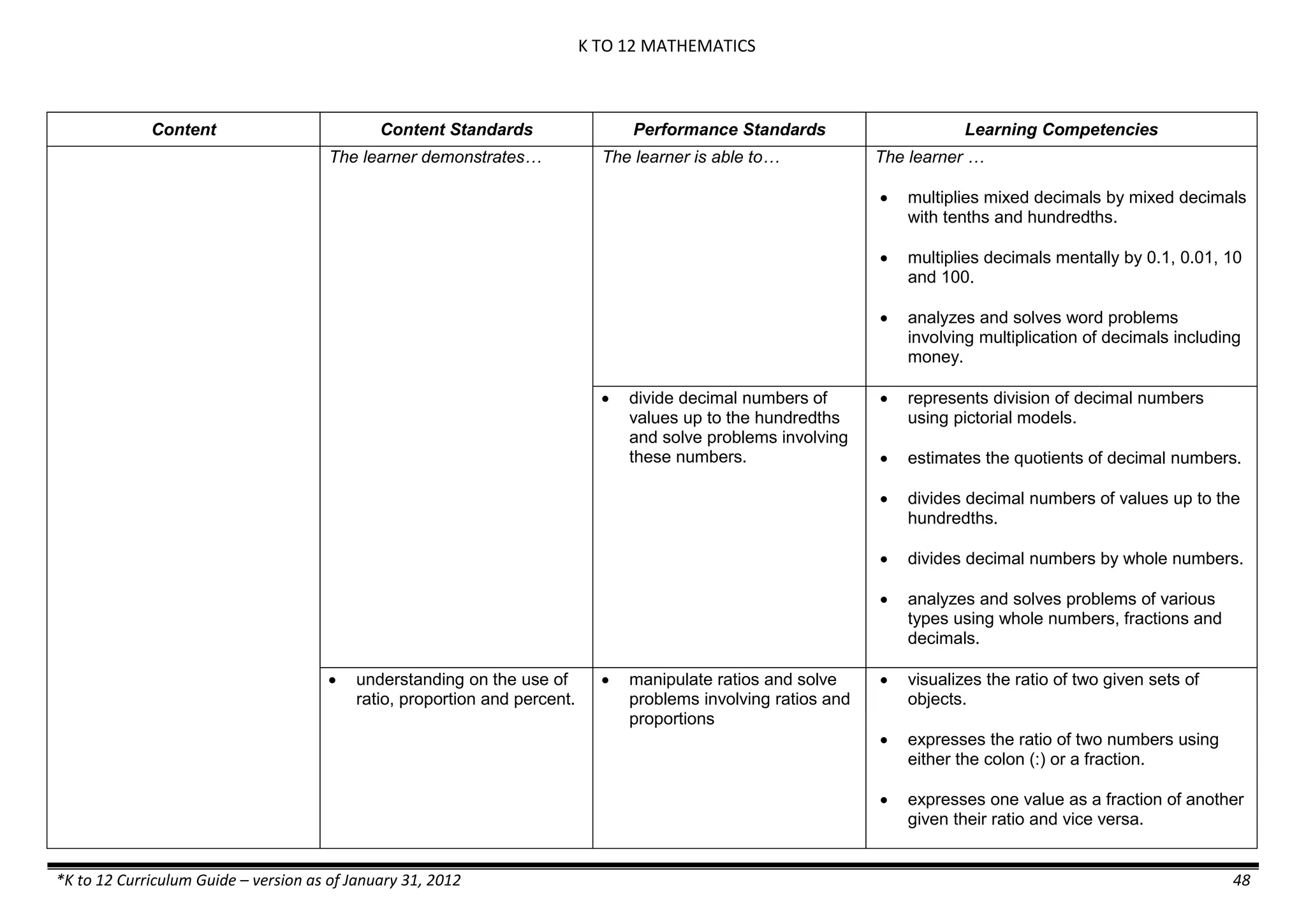
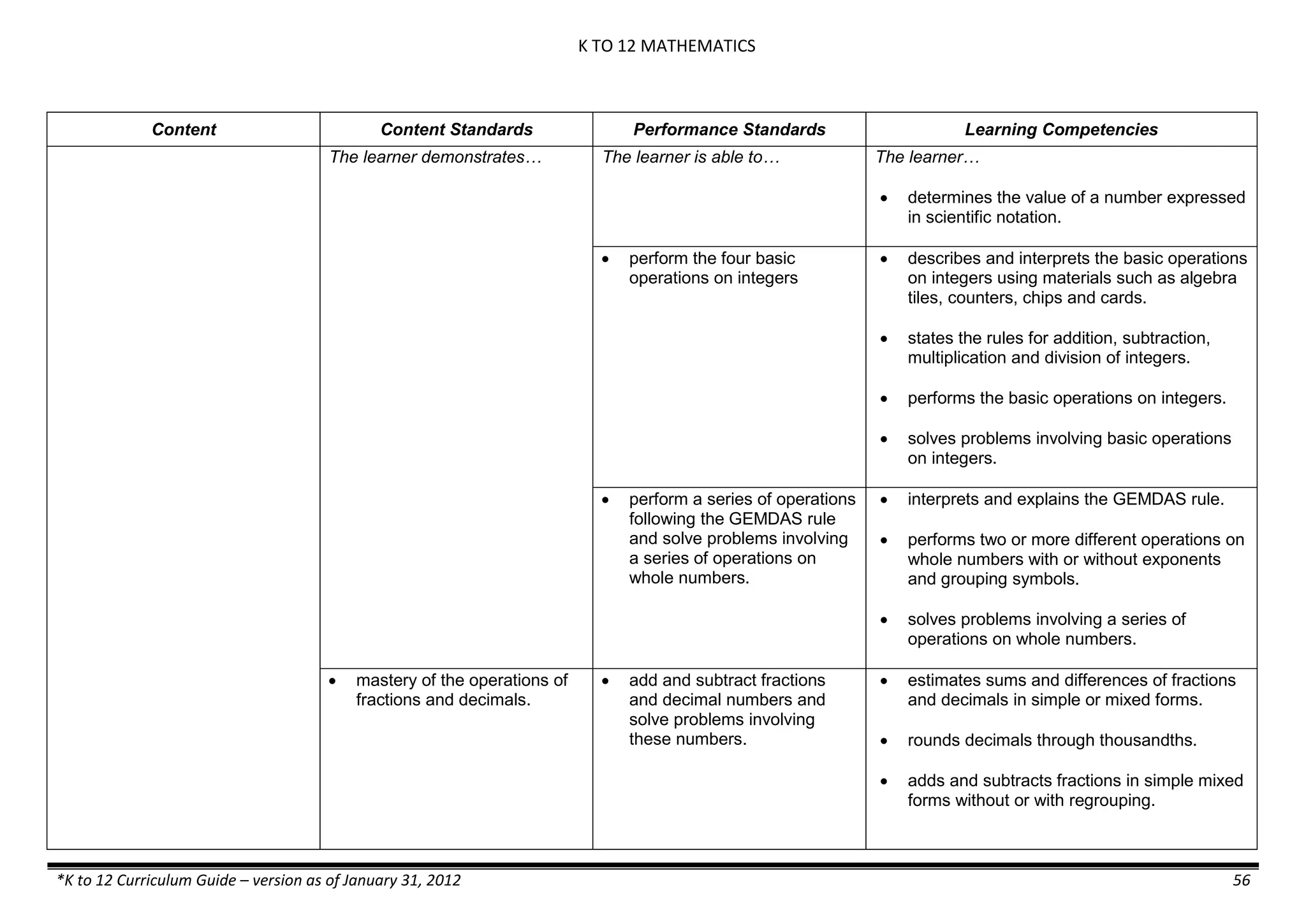
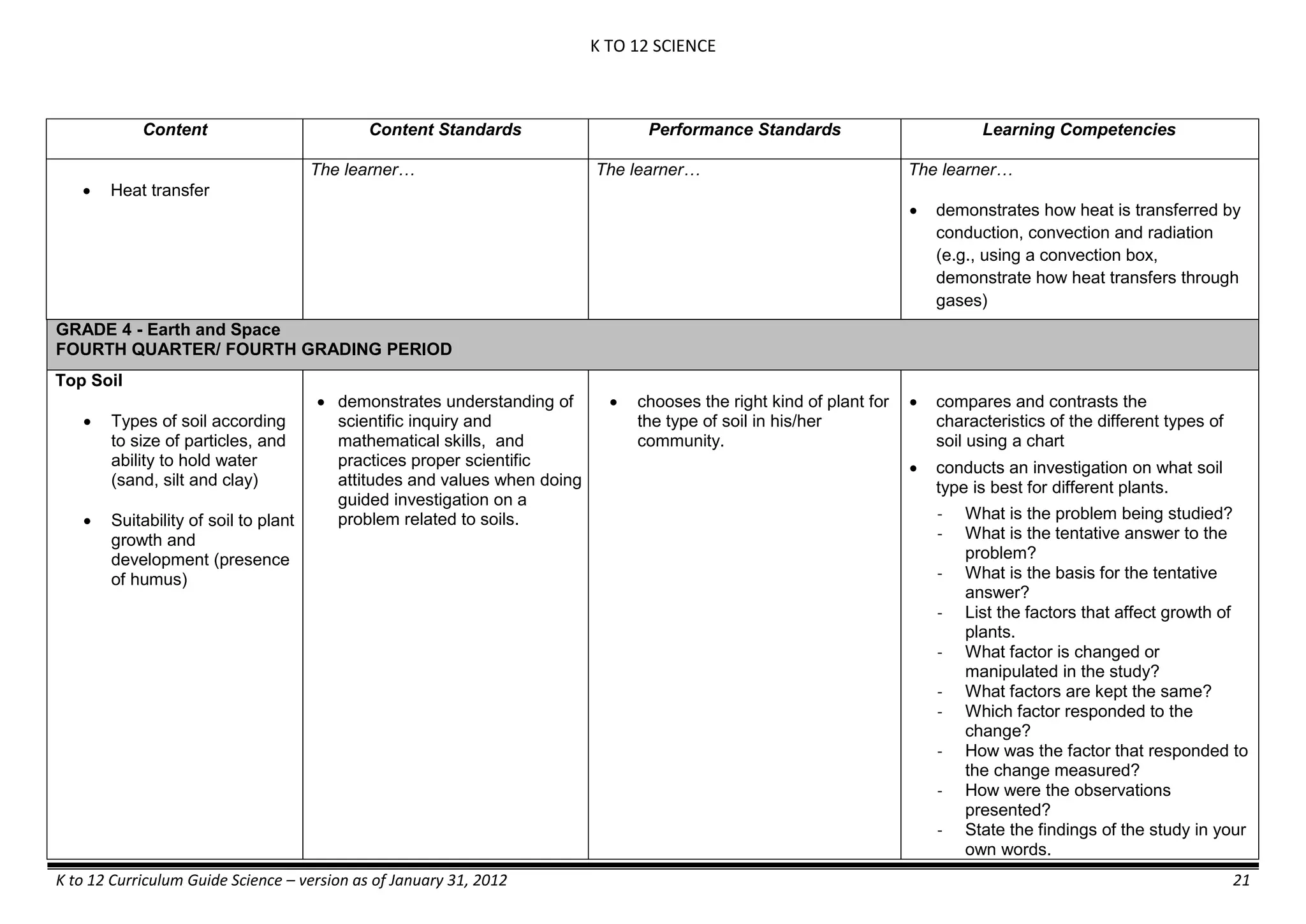
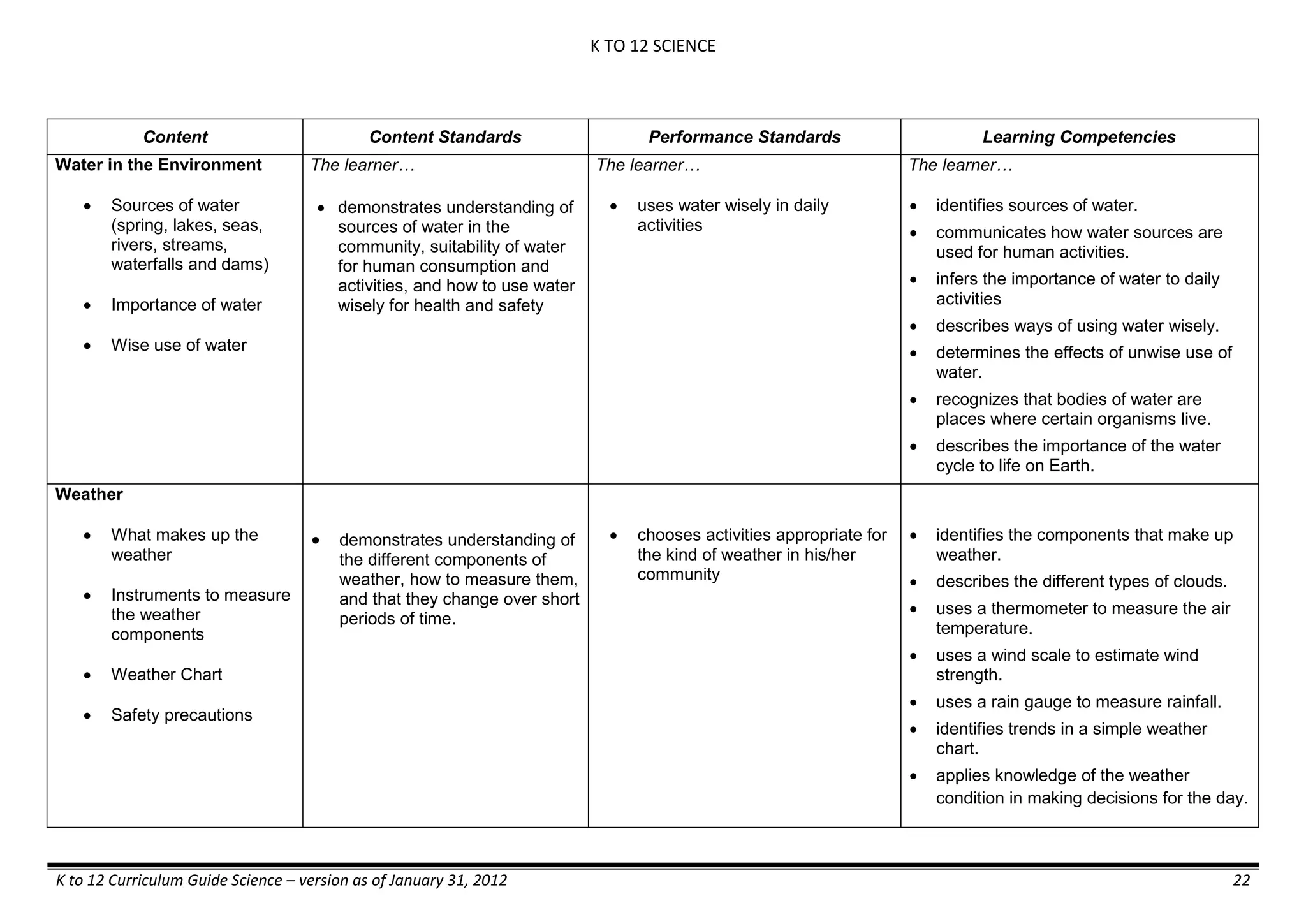
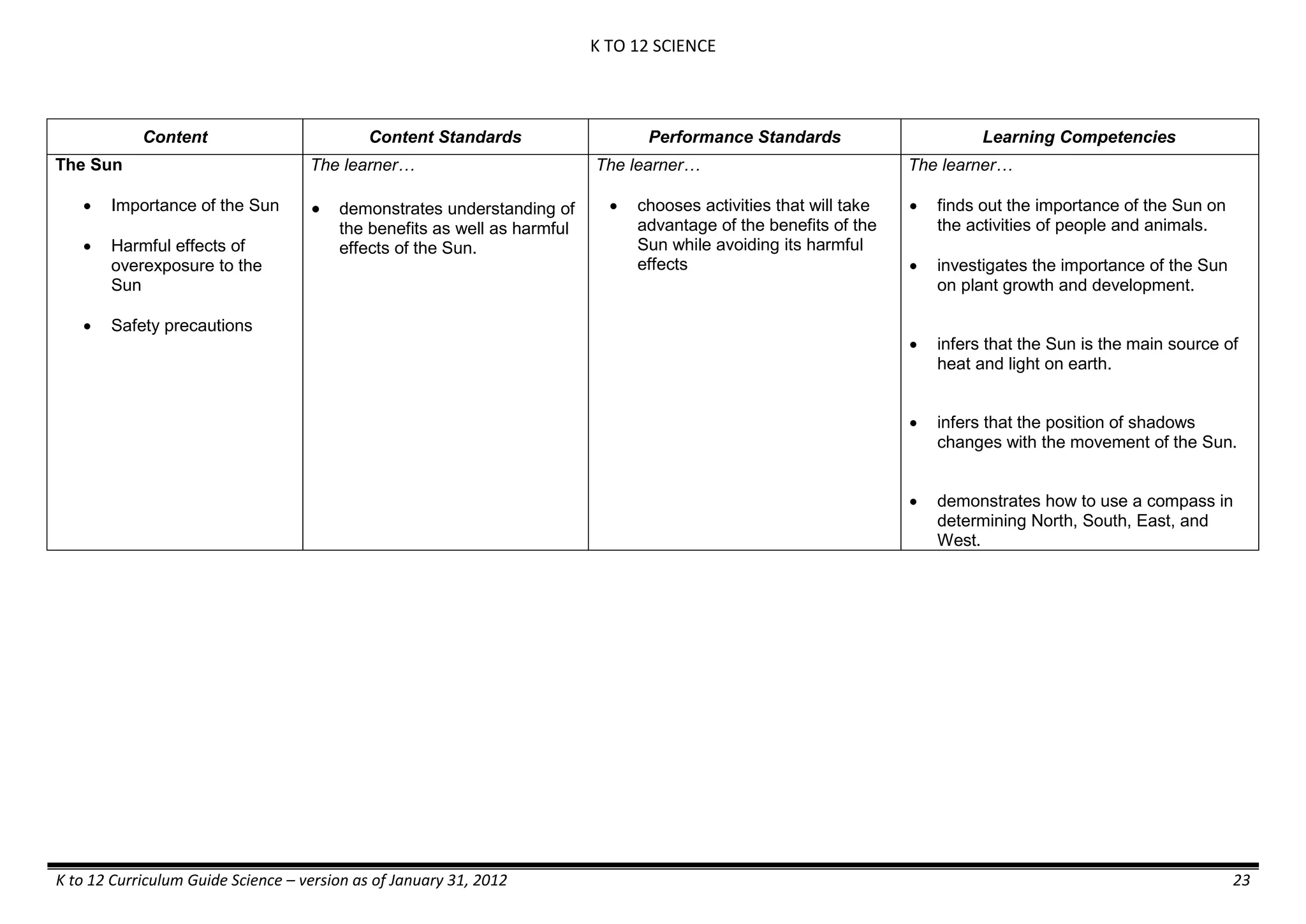
Content Content Standards Performance Standards Learning Competencies
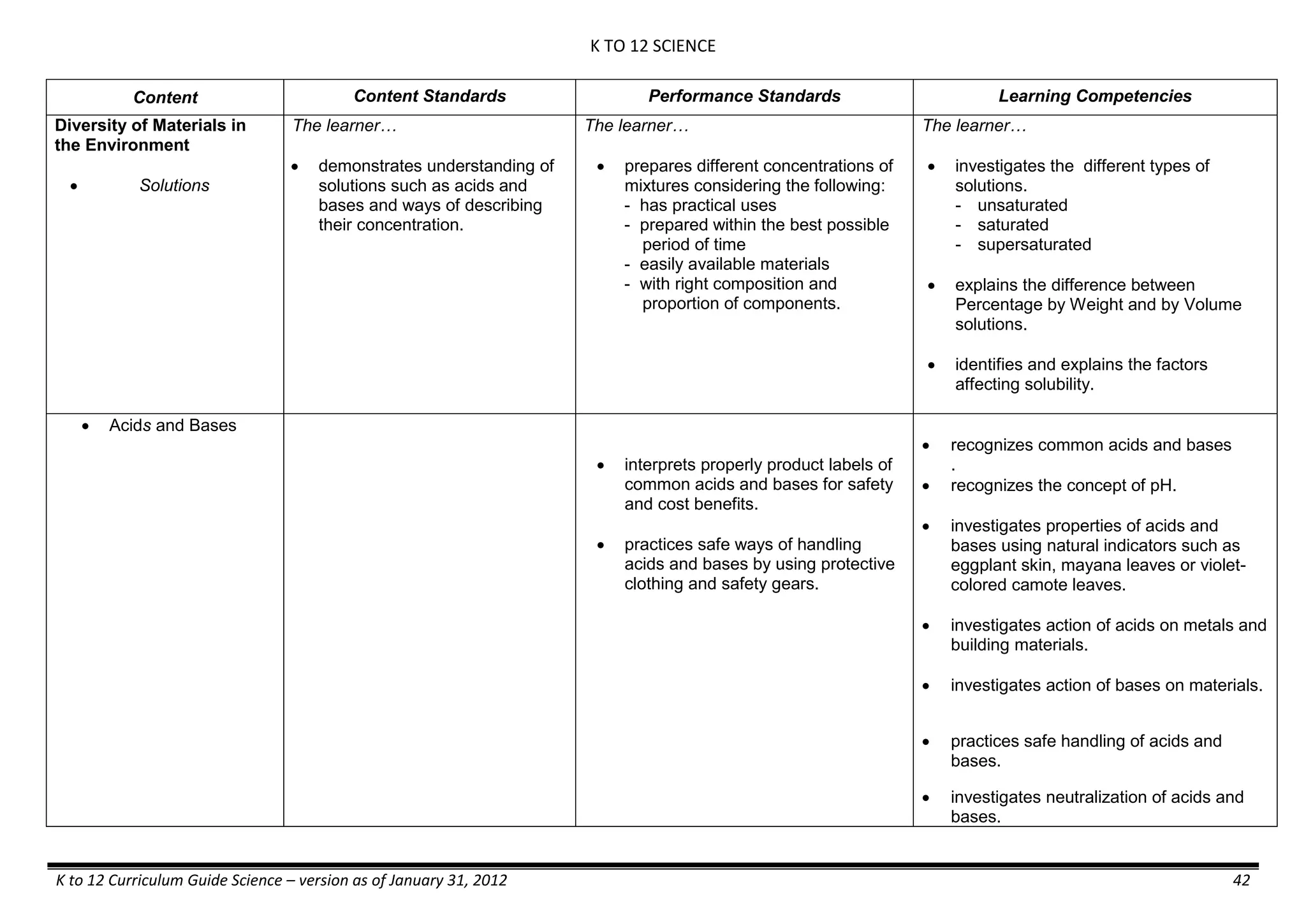
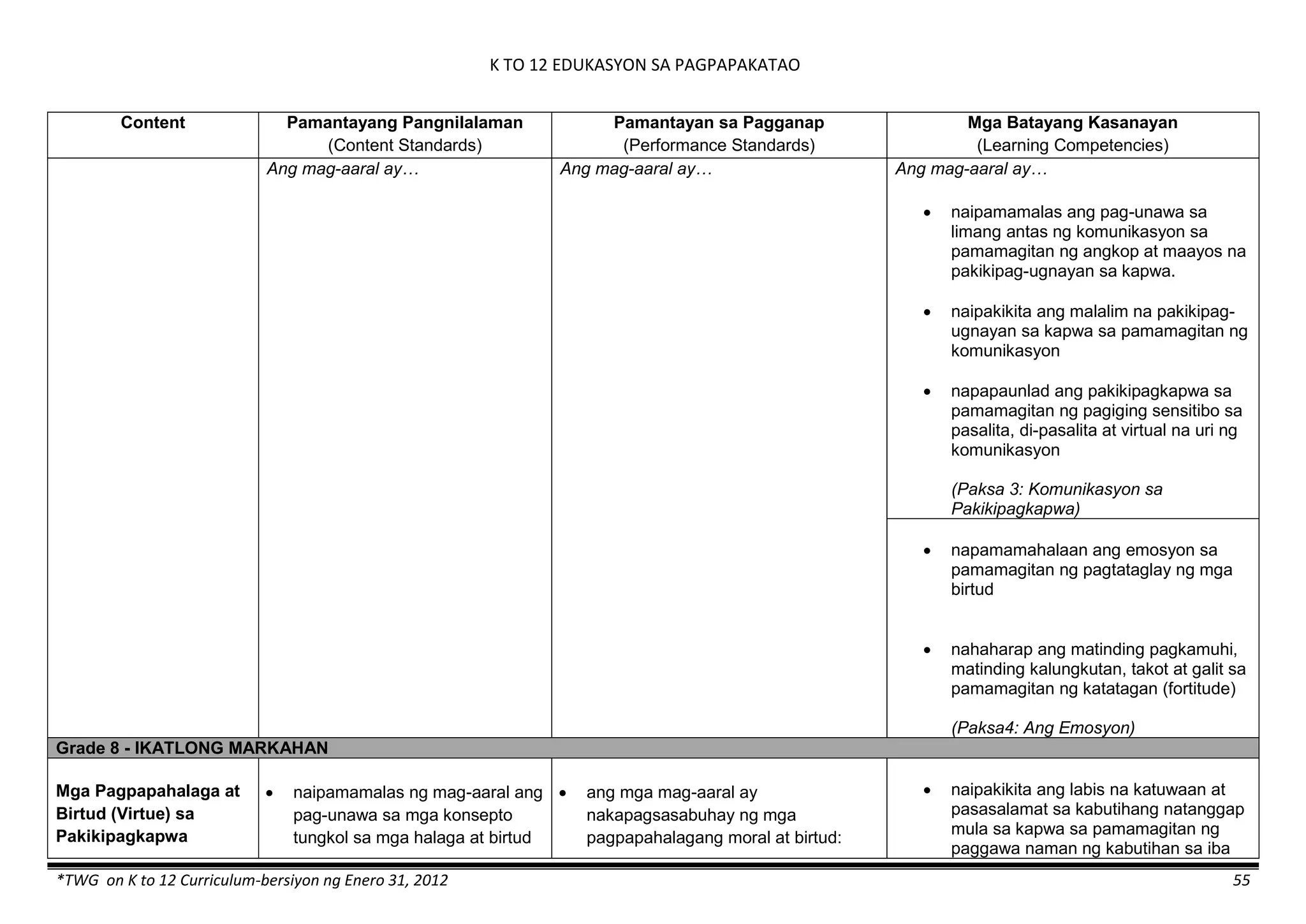
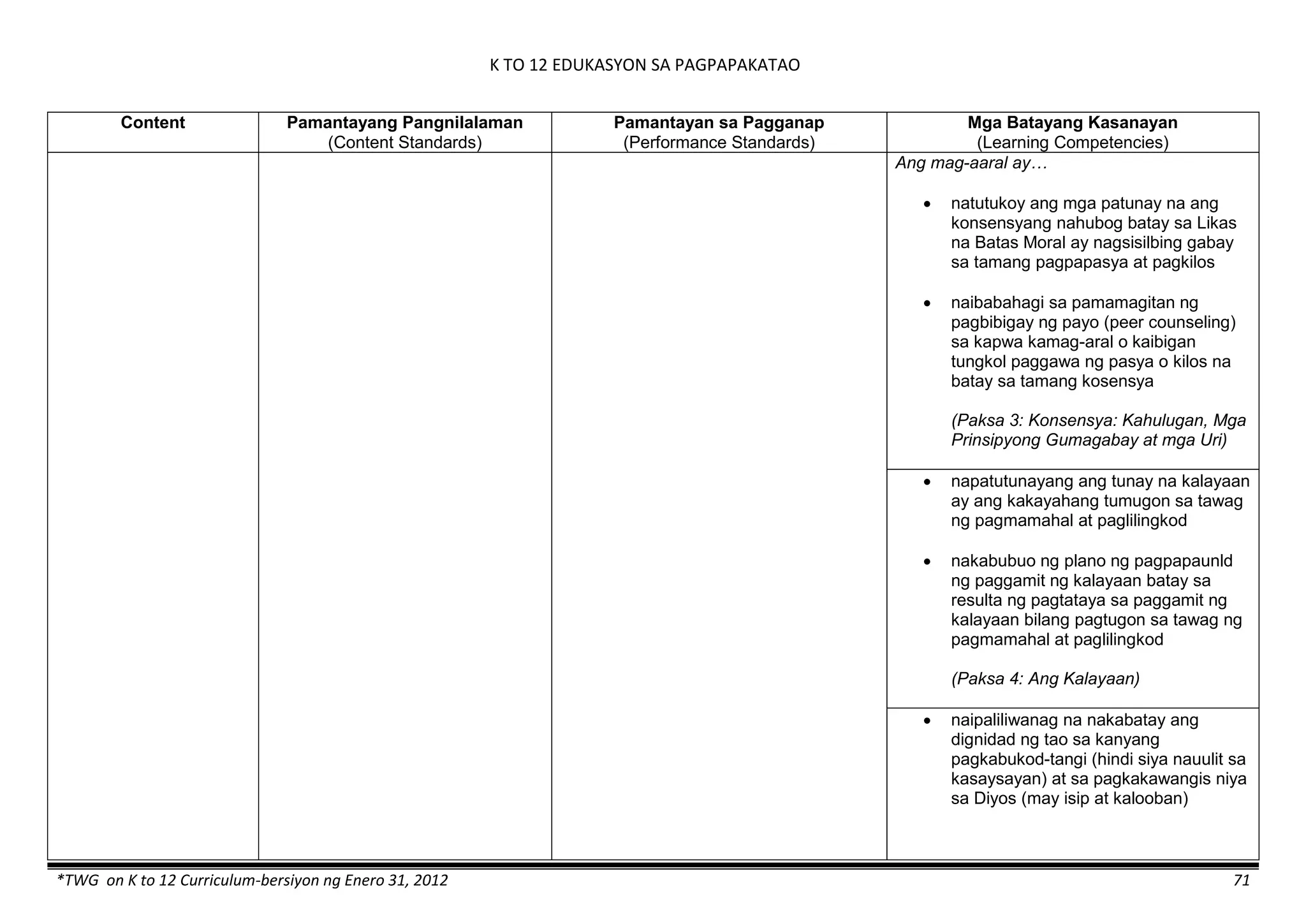
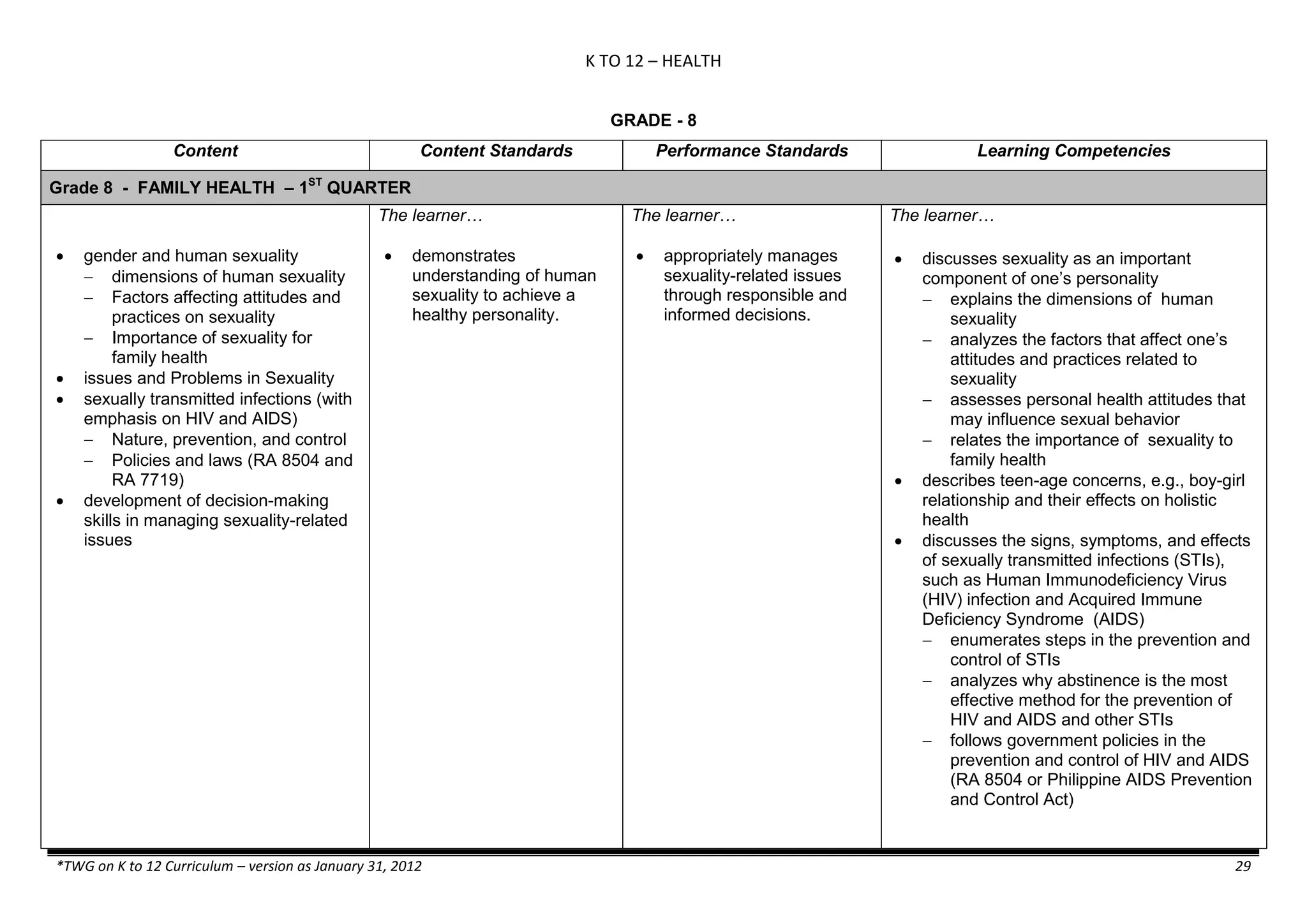
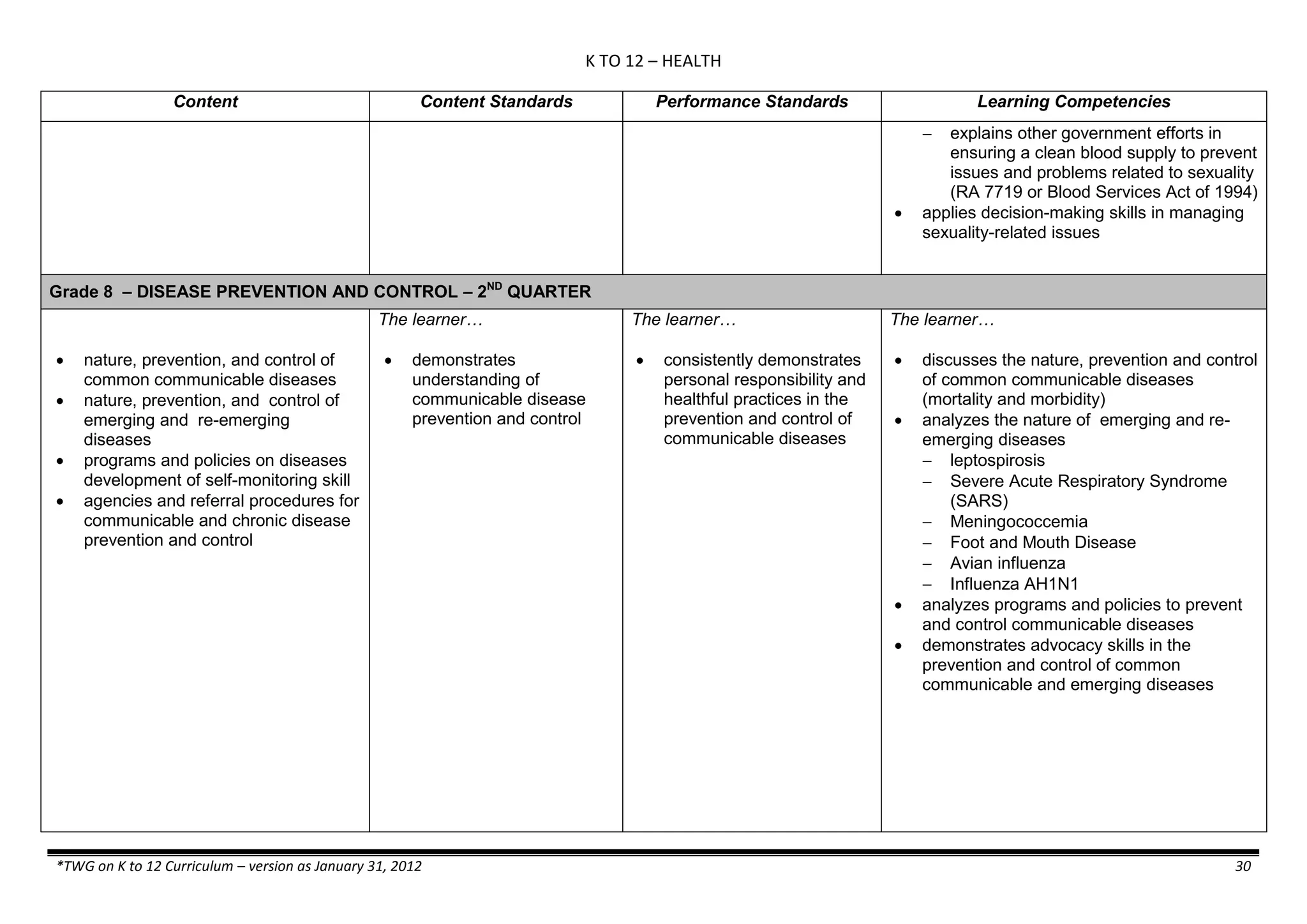
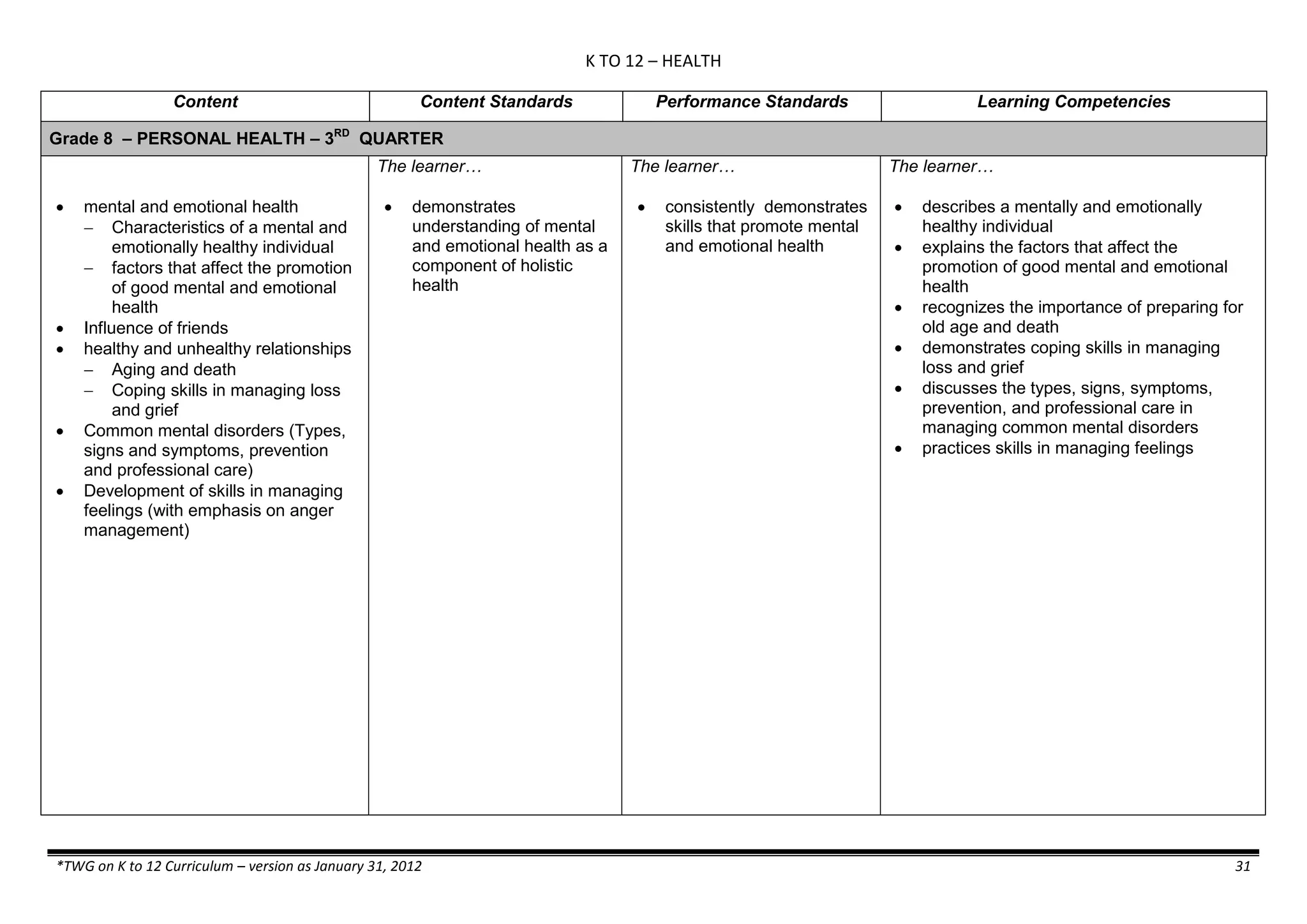
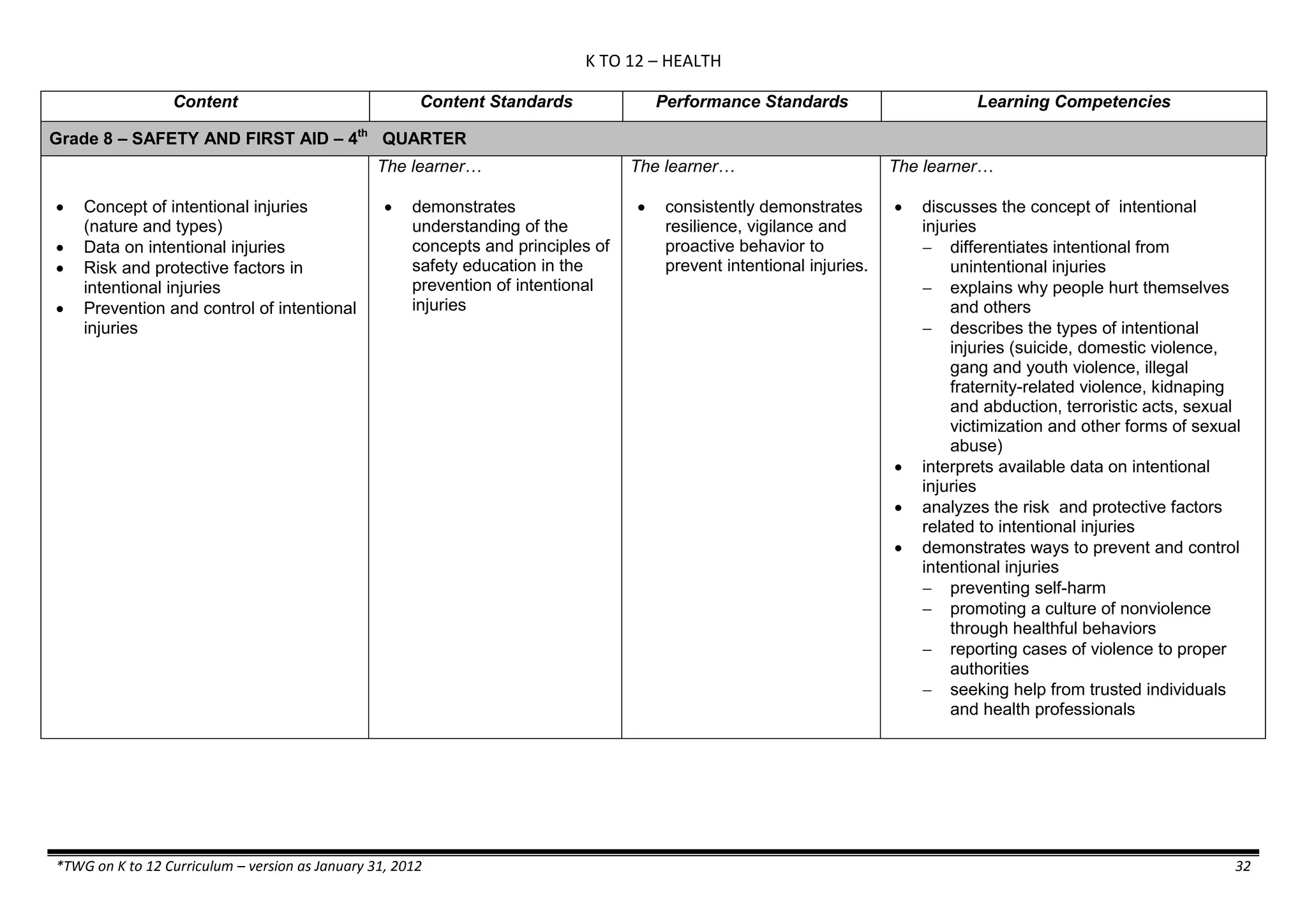
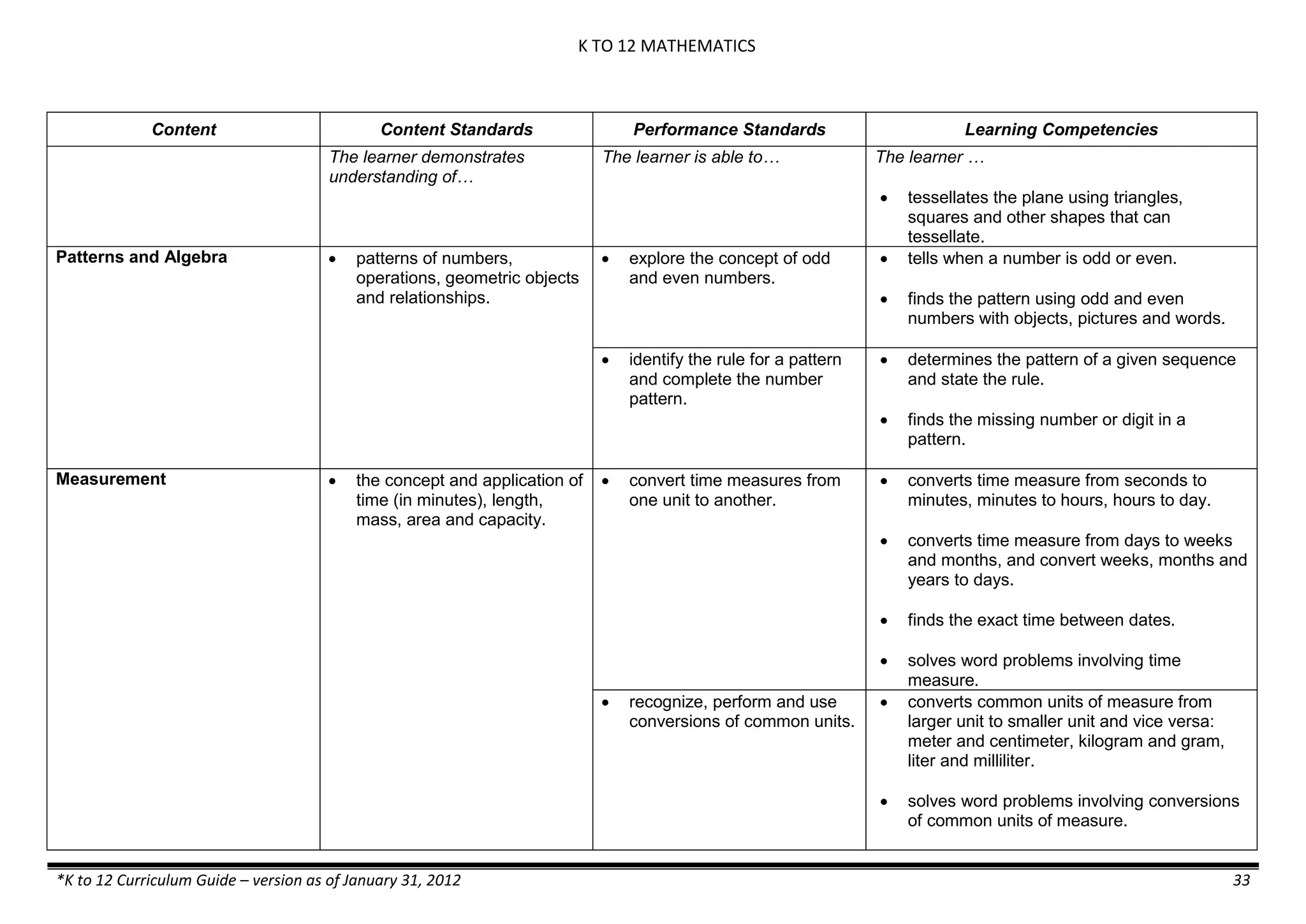
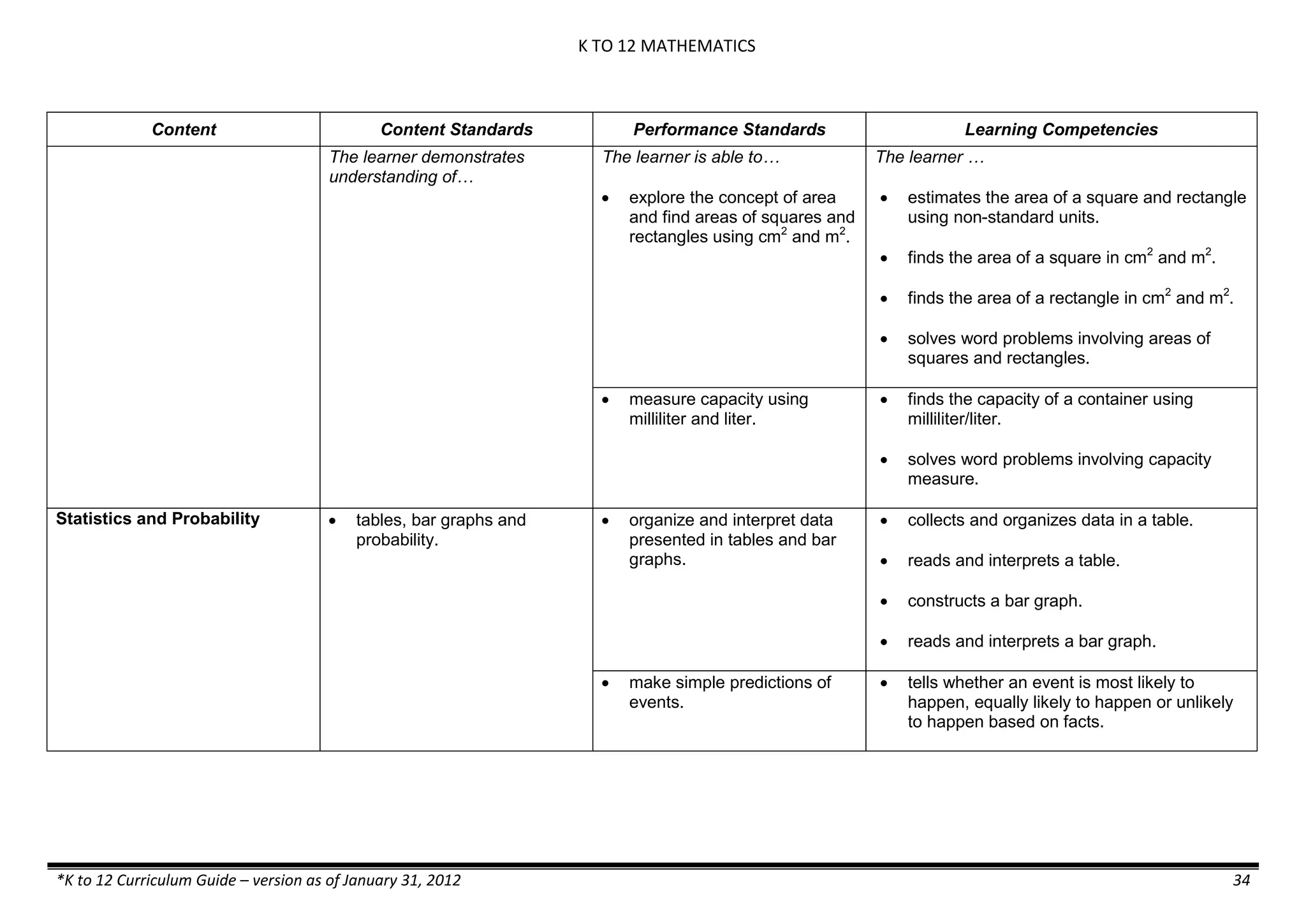
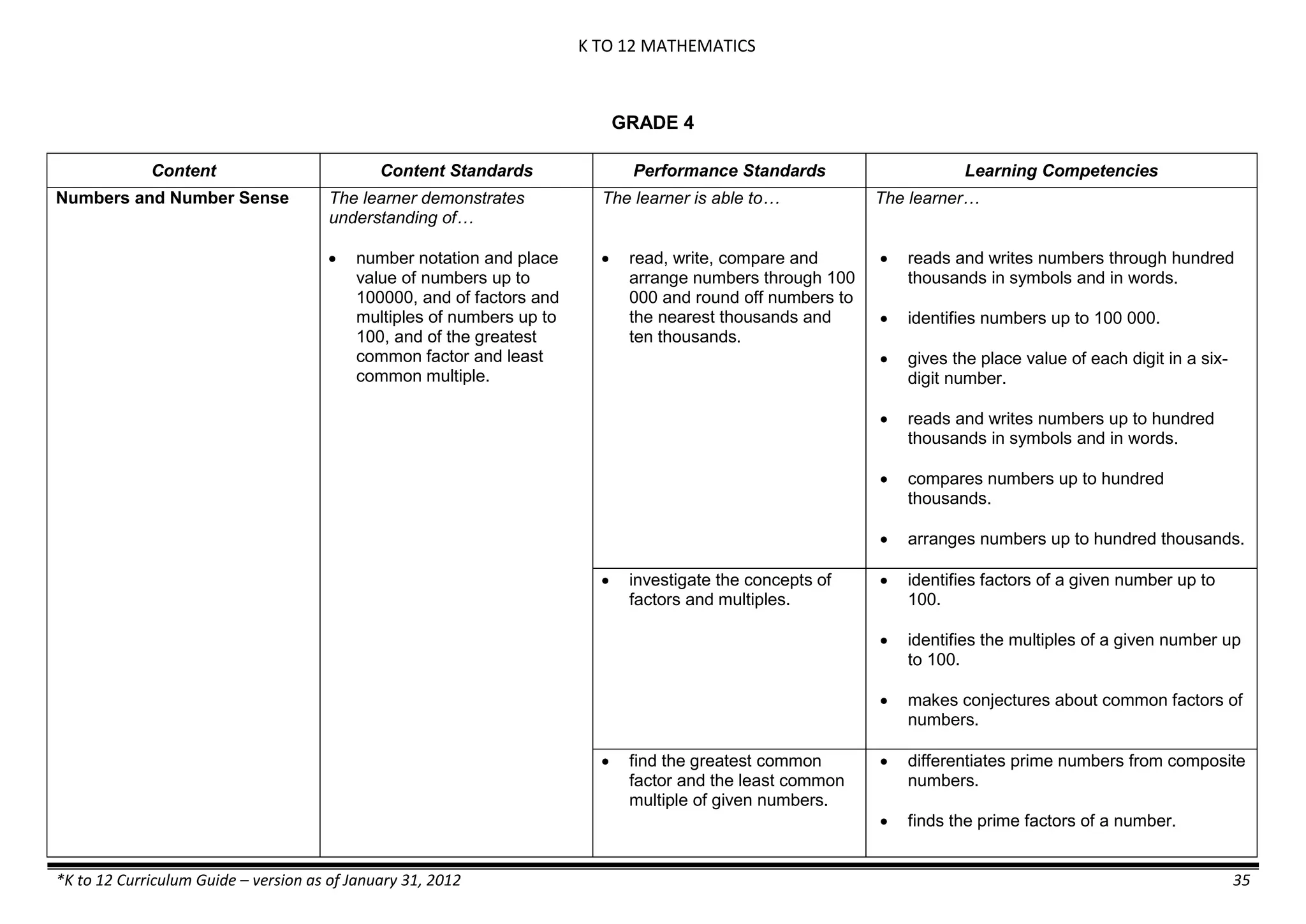
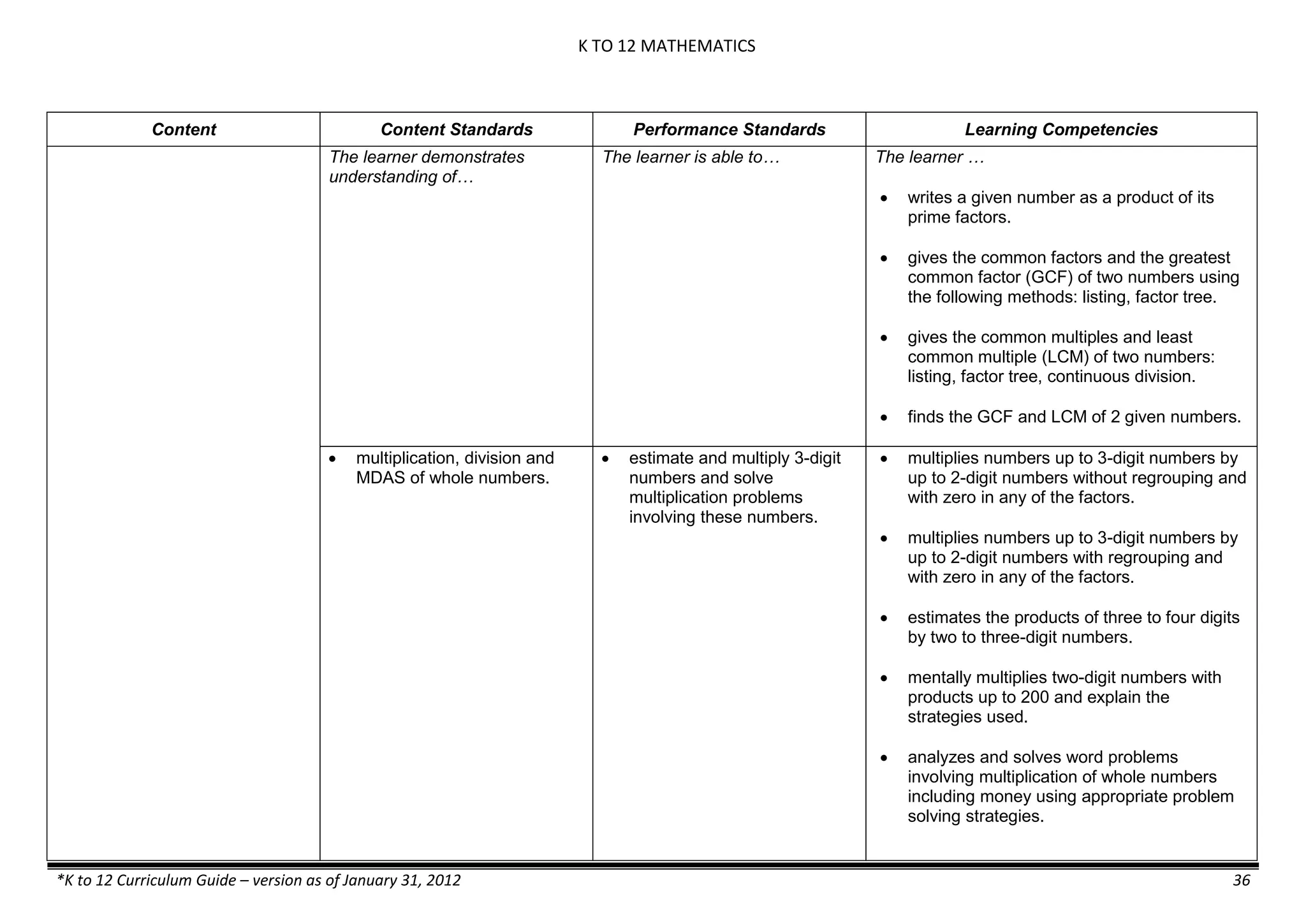
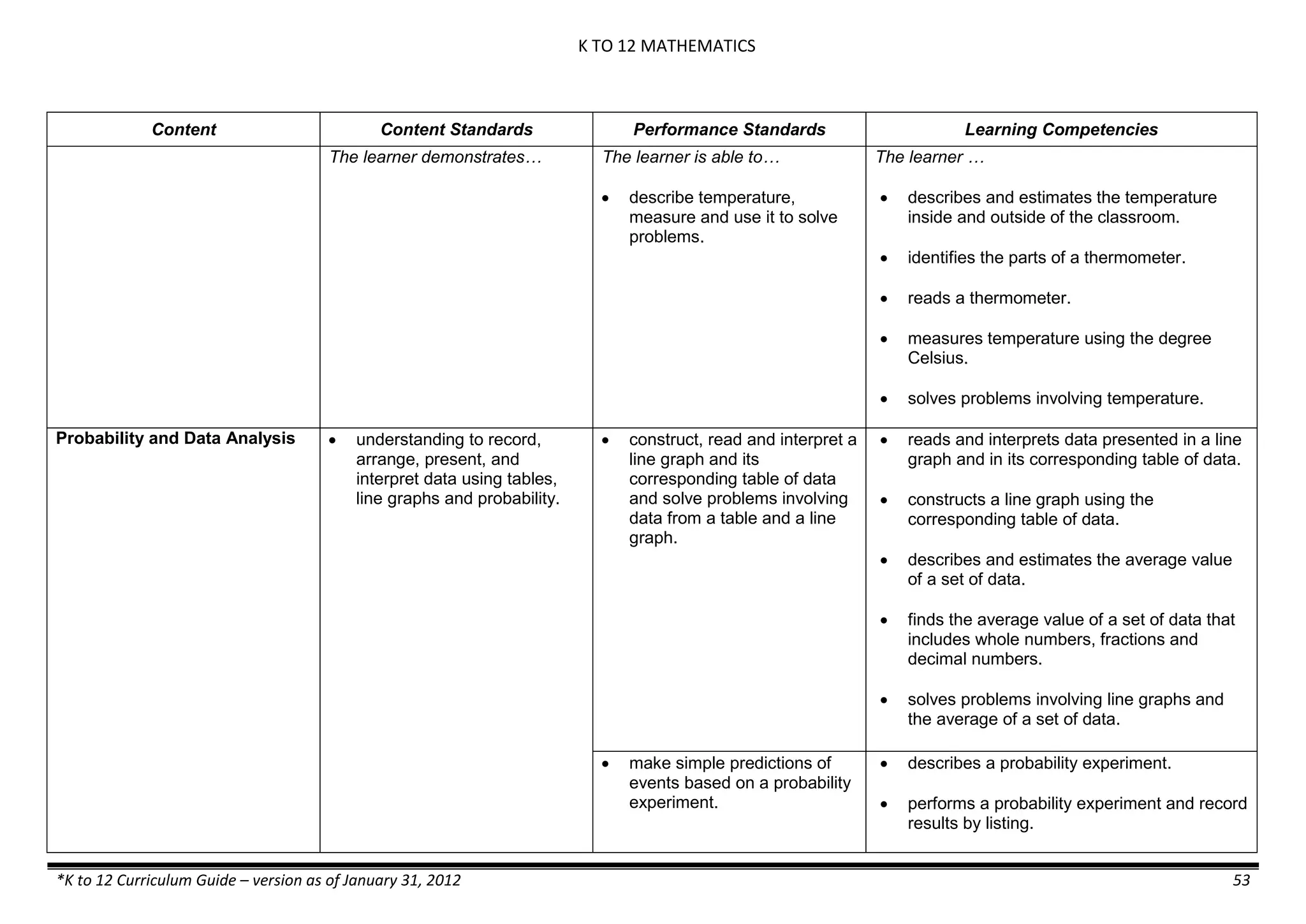
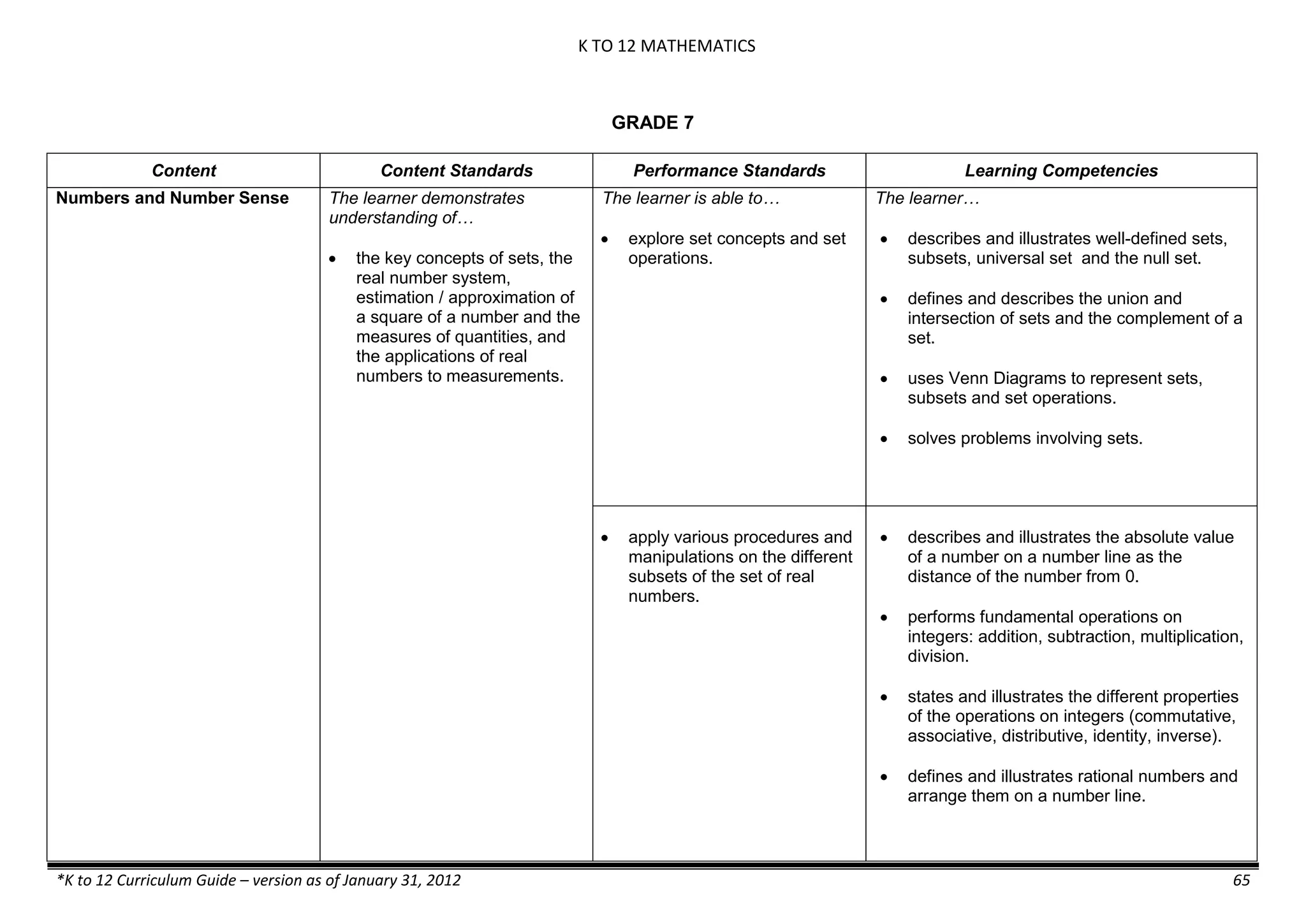
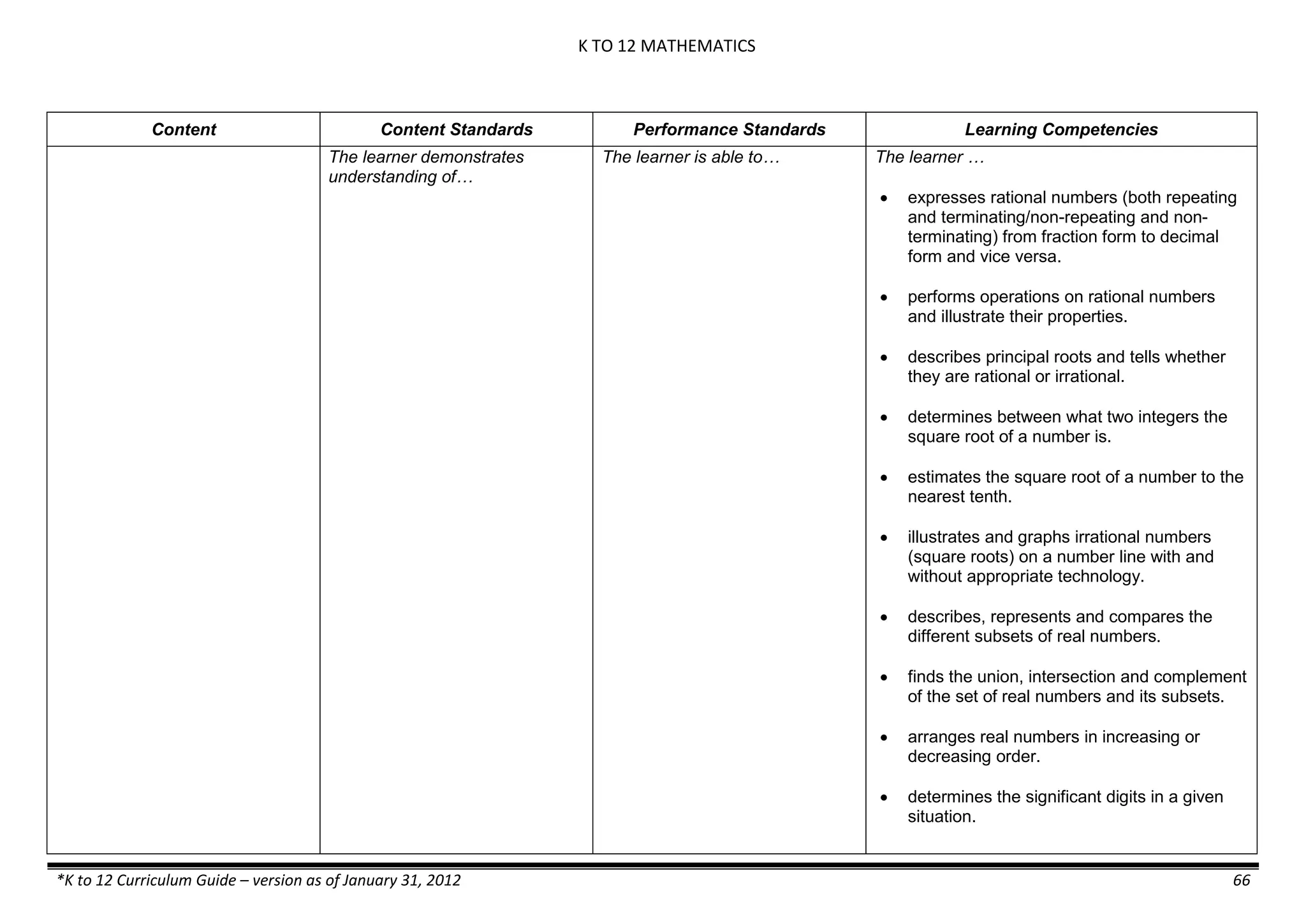
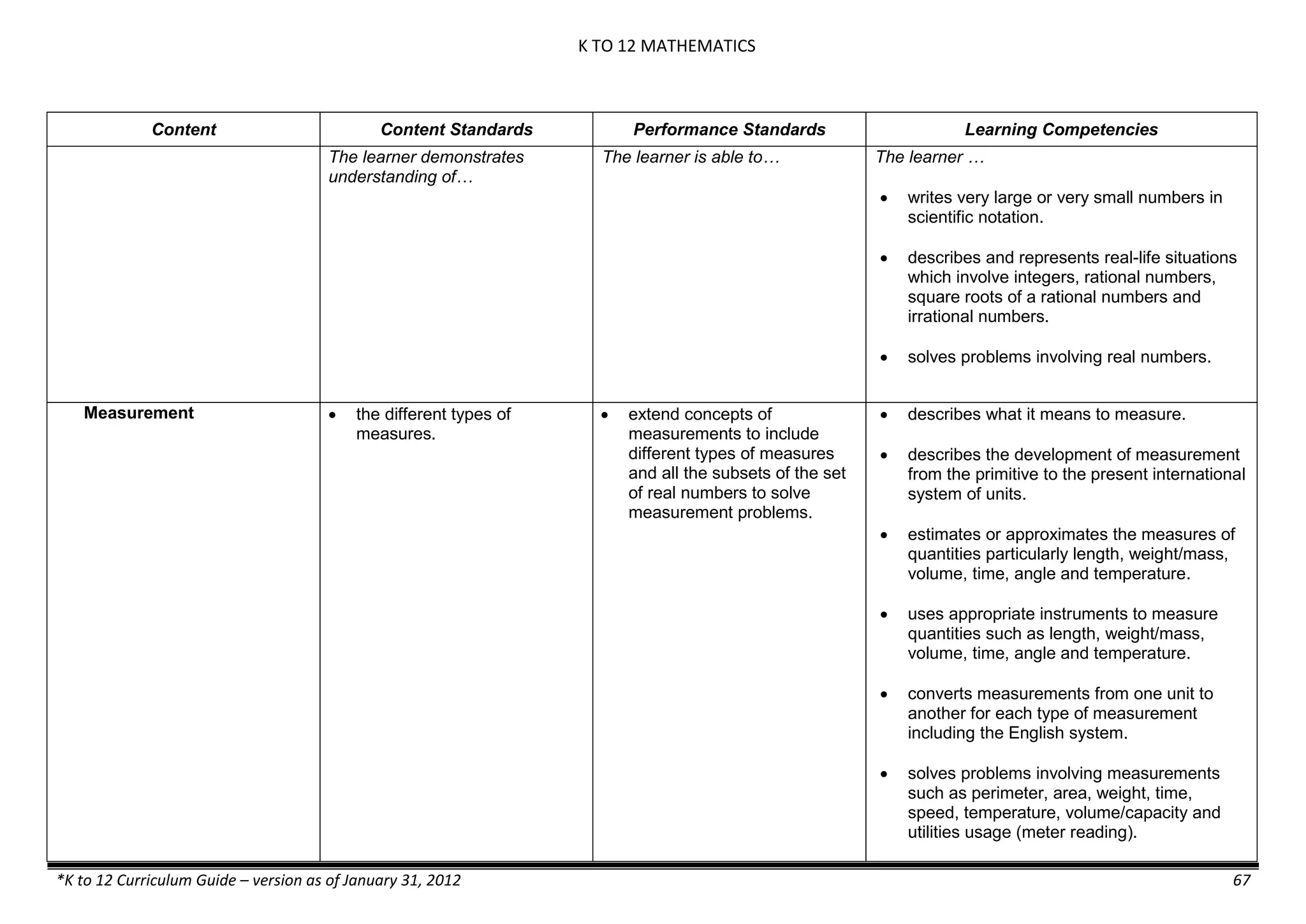
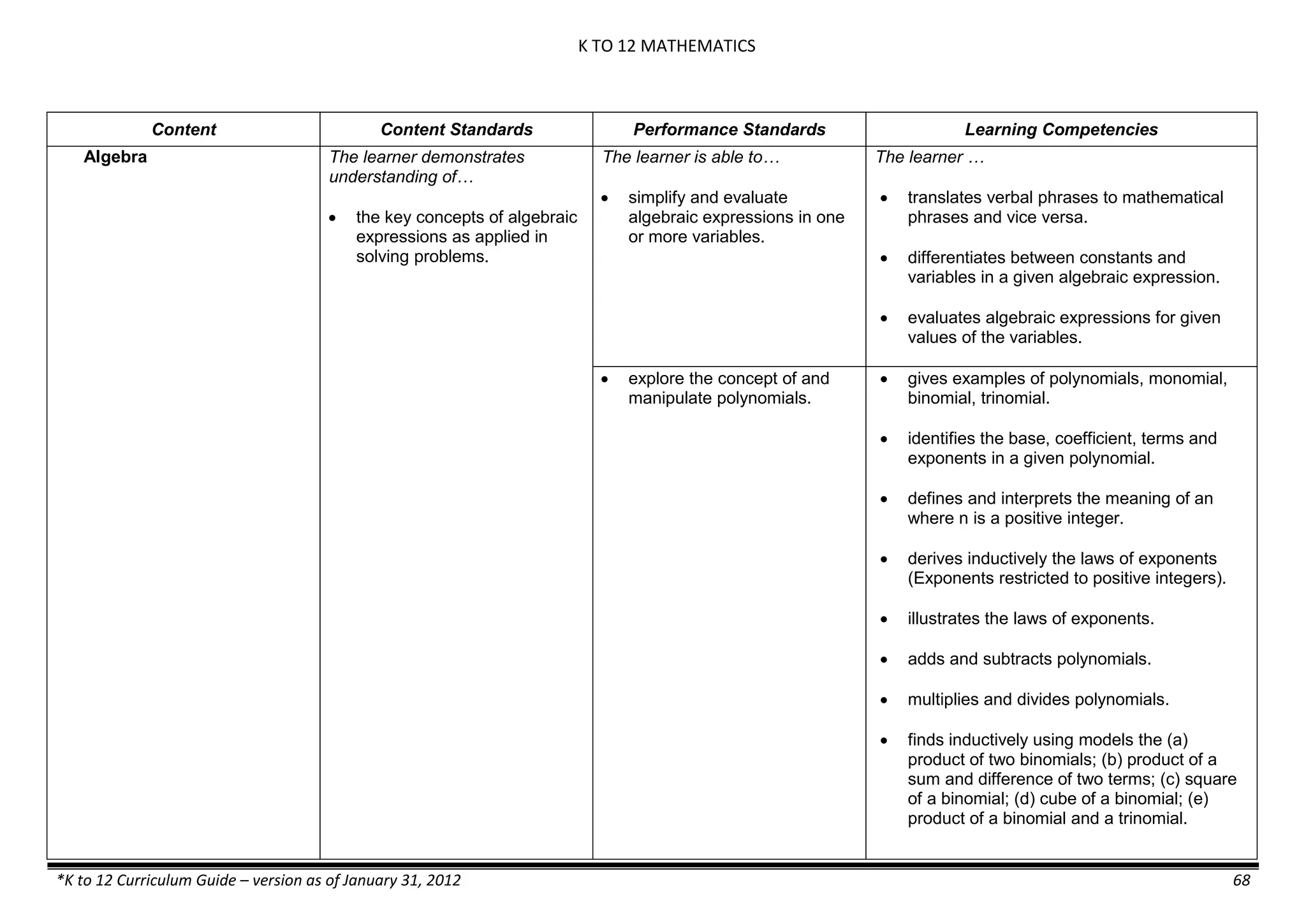
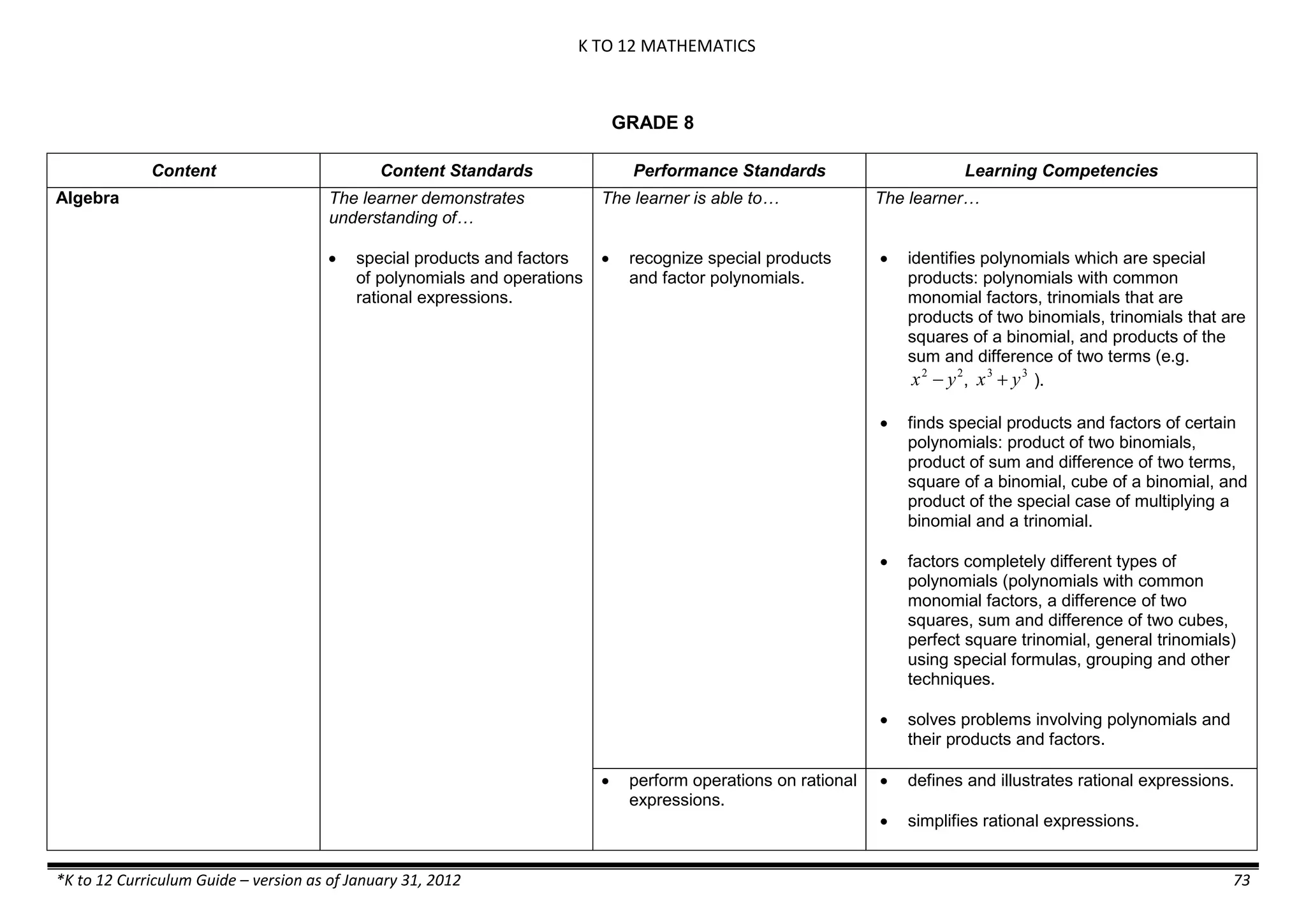
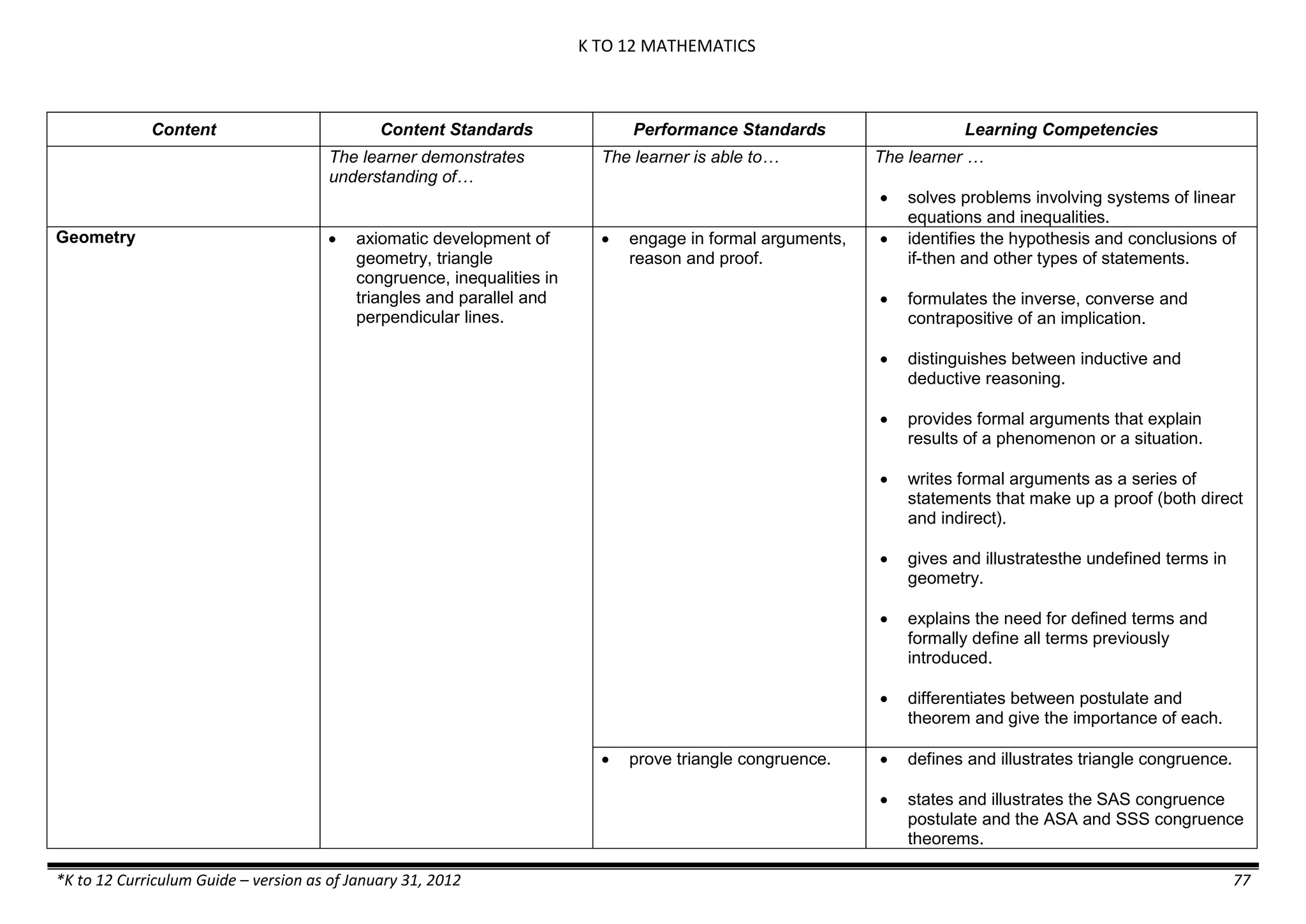
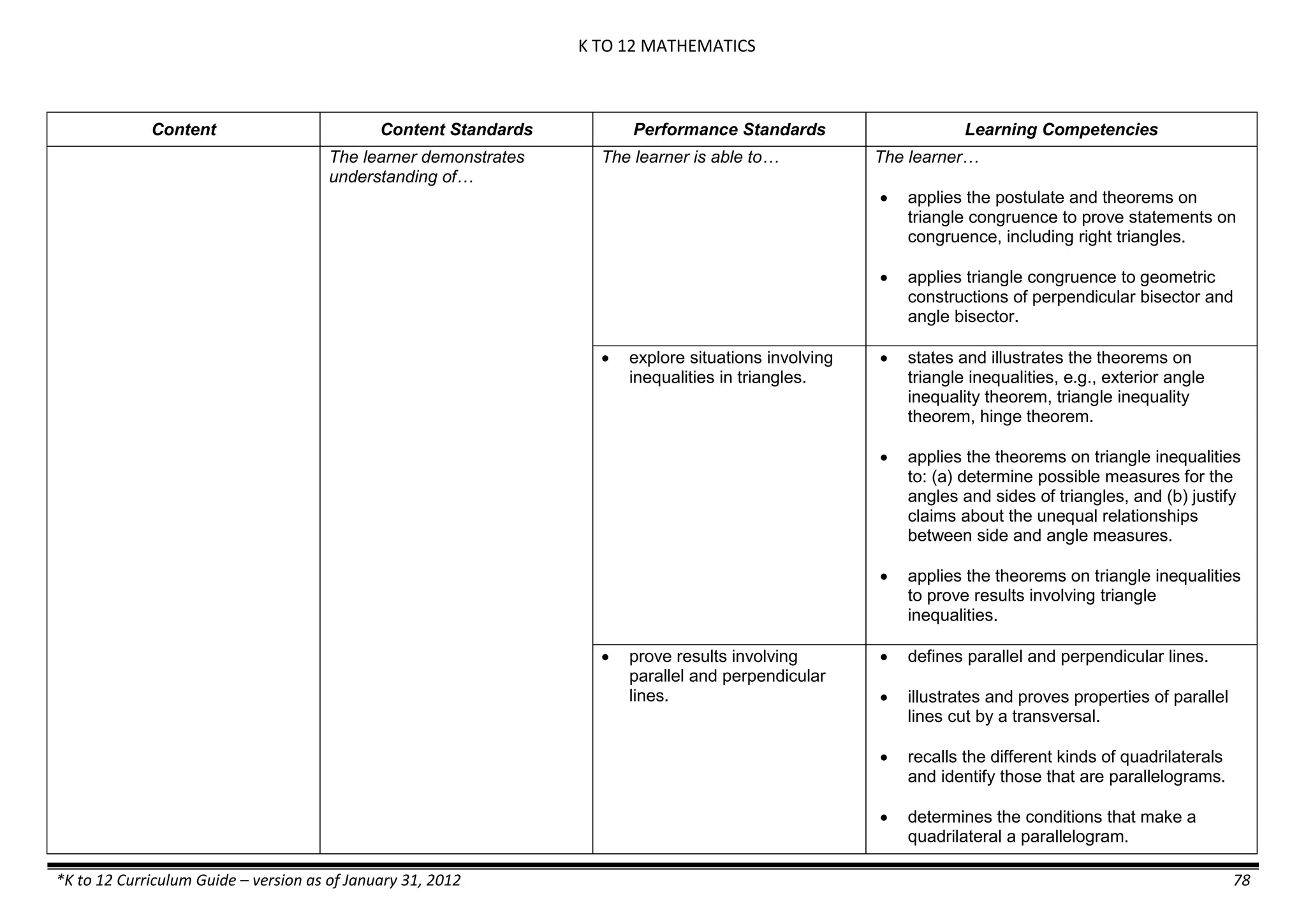
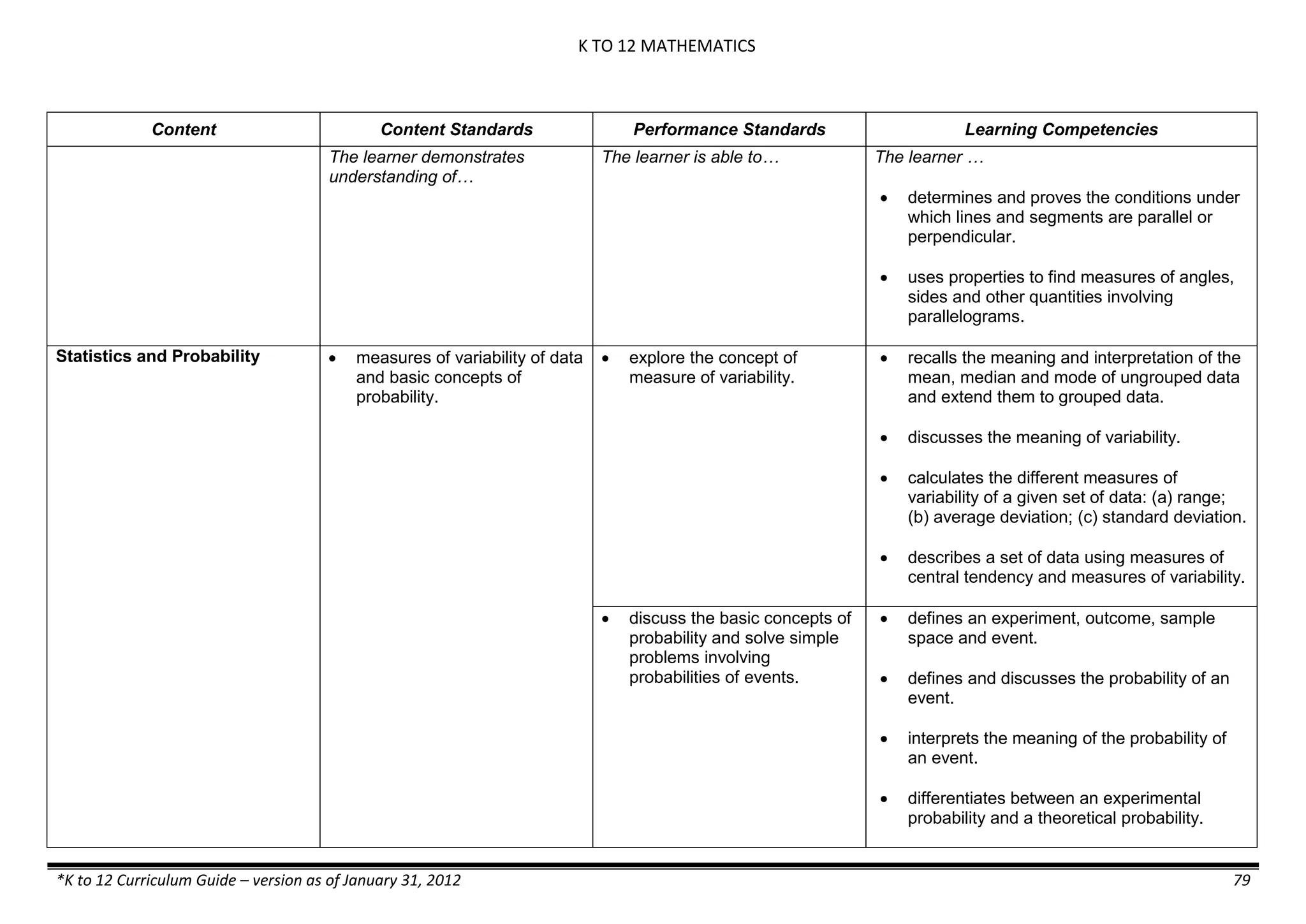
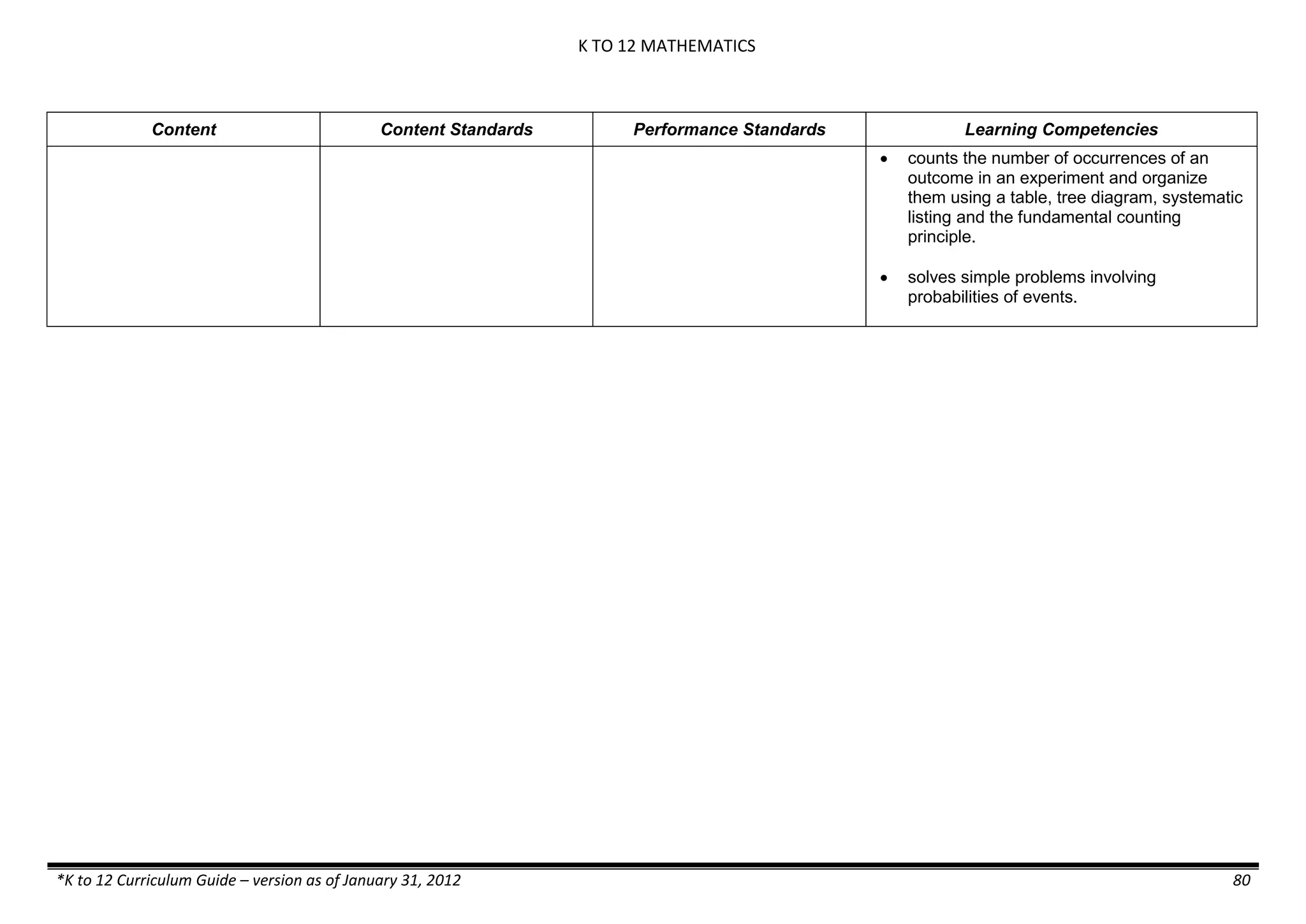
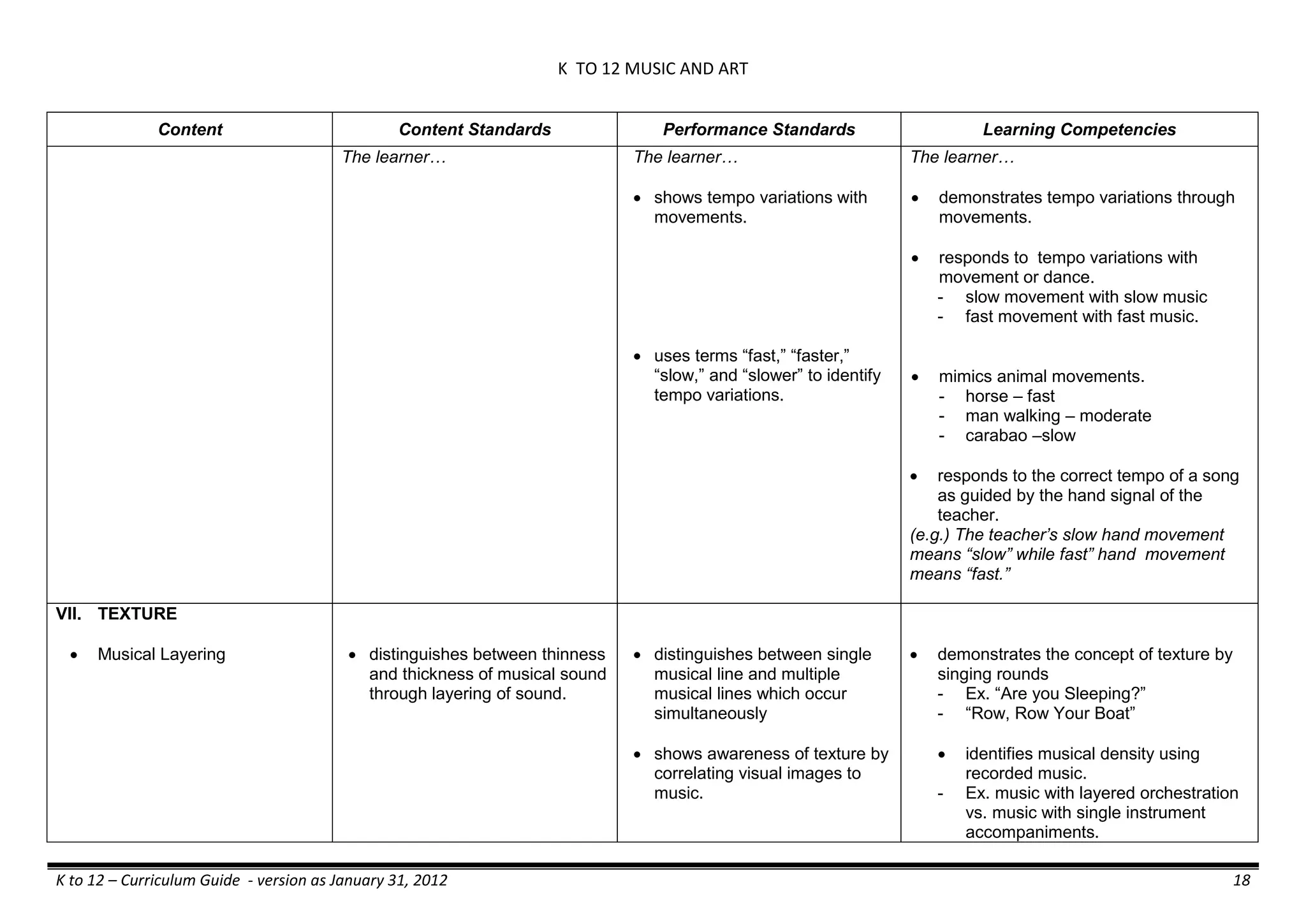
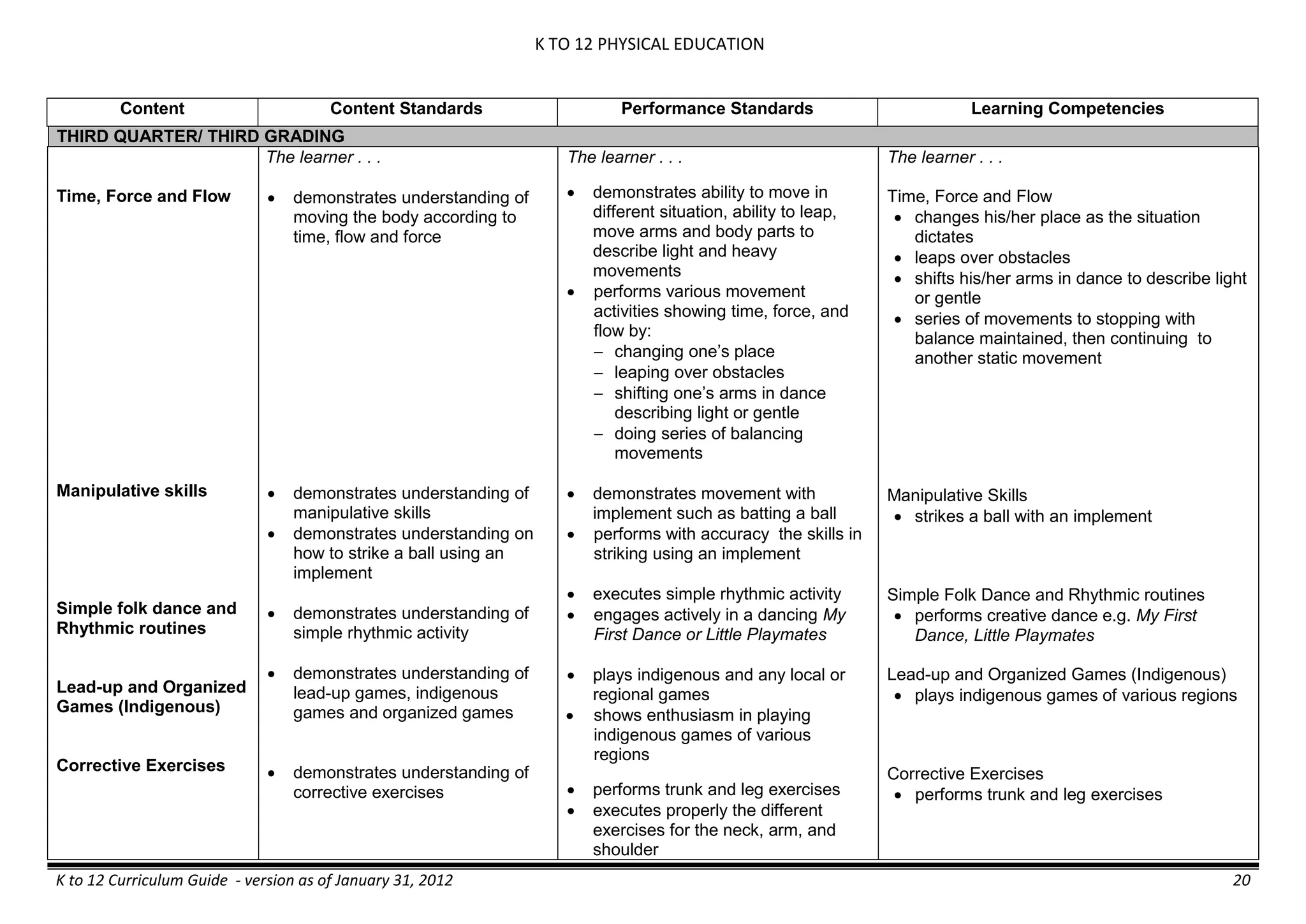
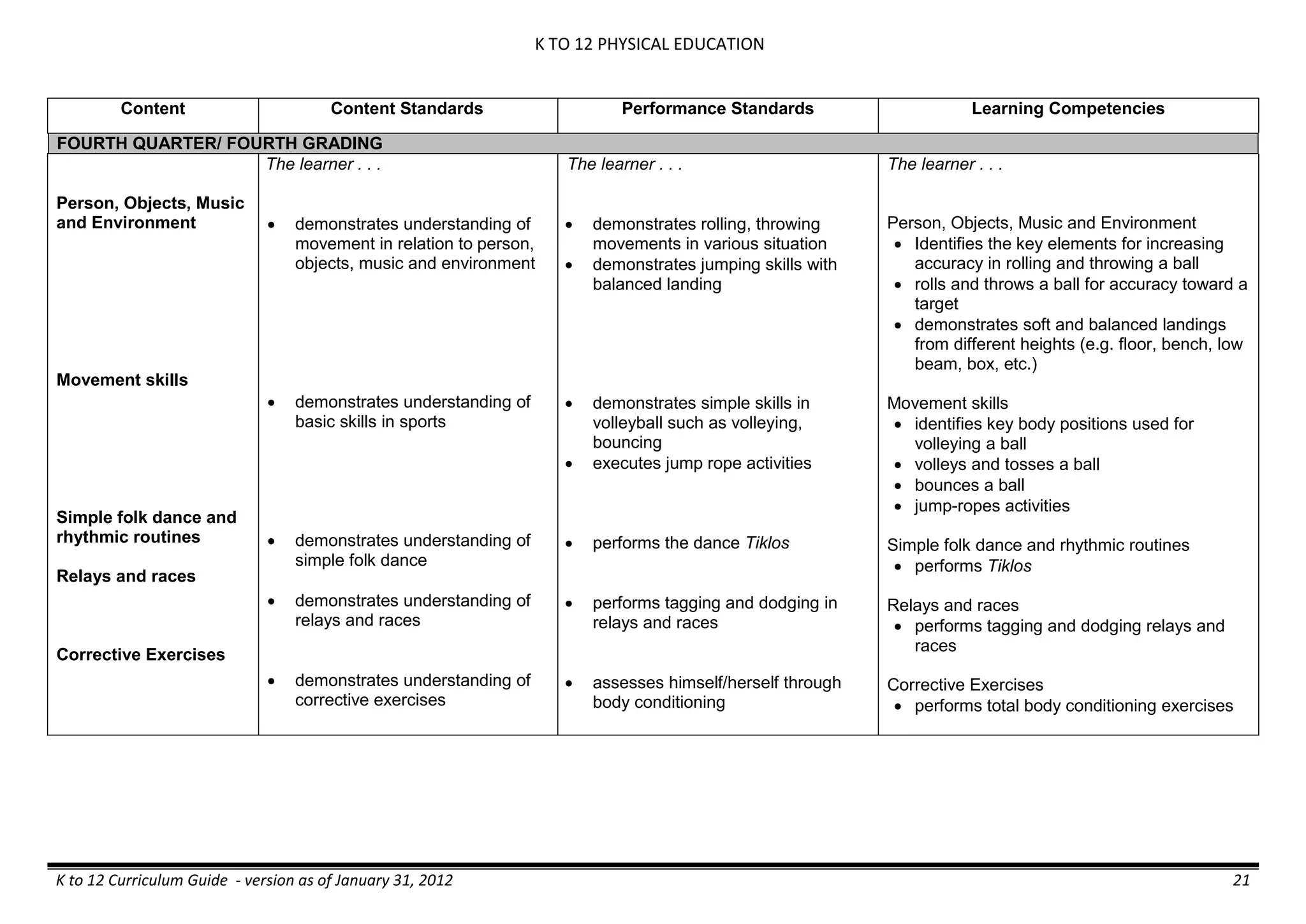
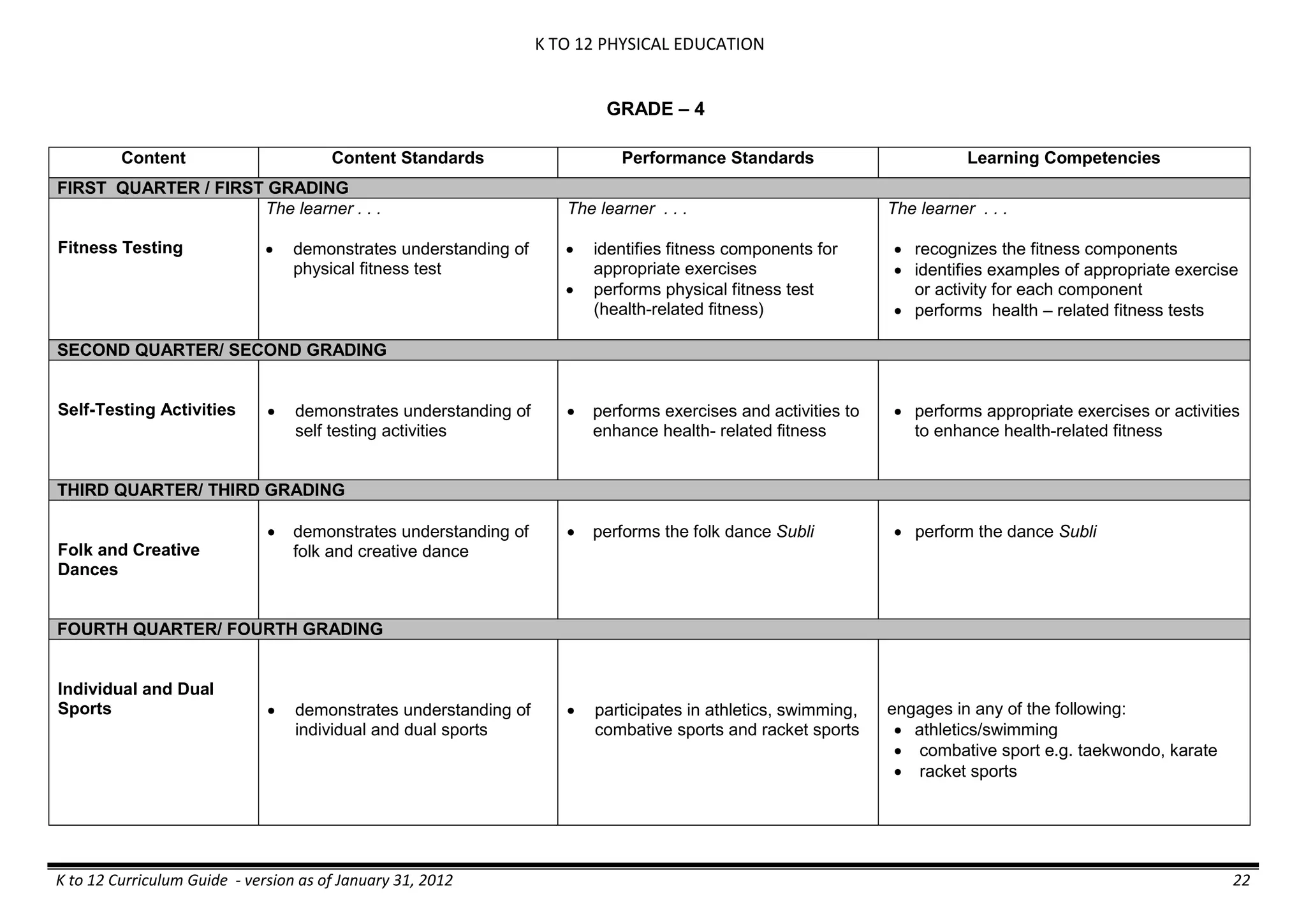
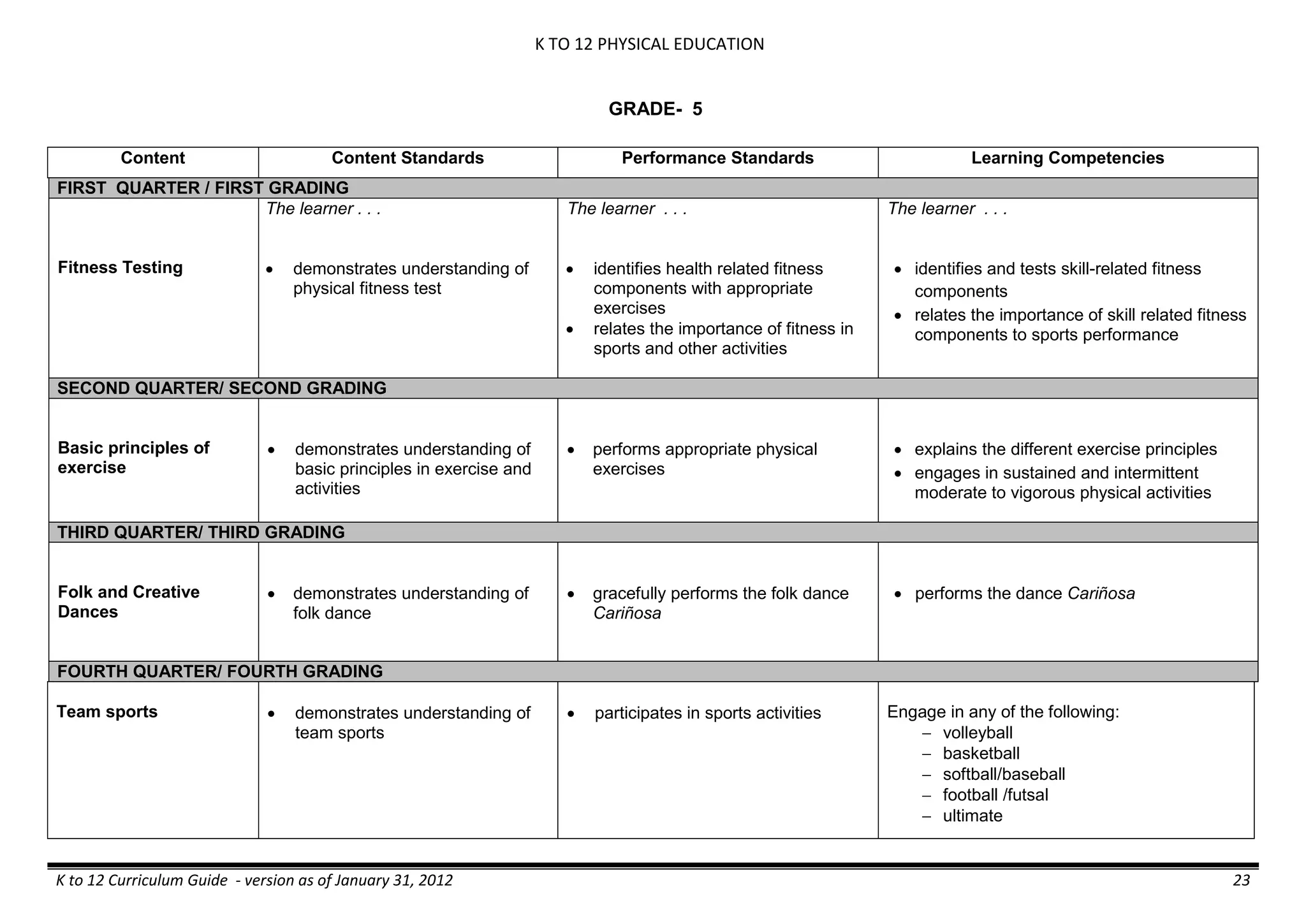
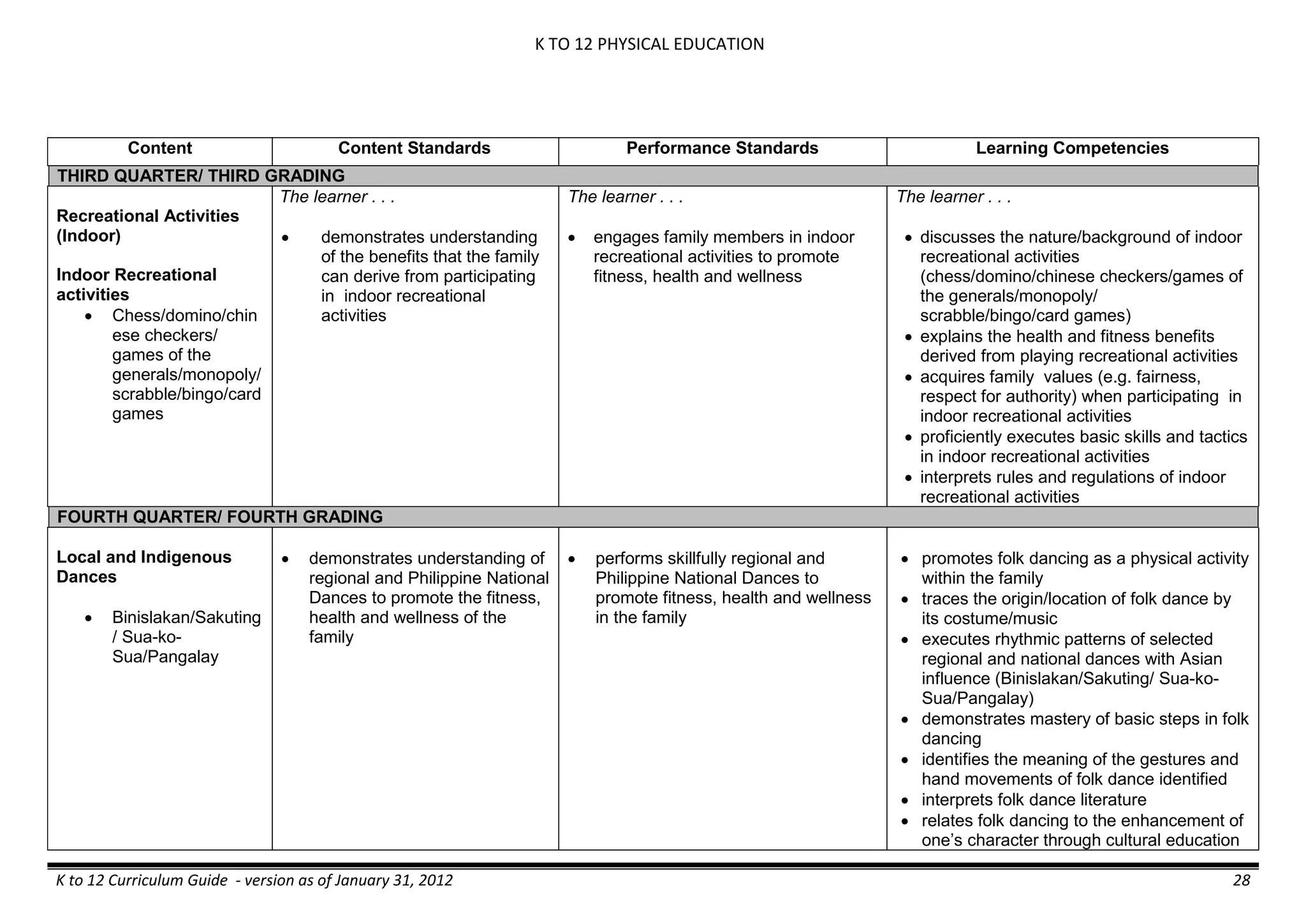
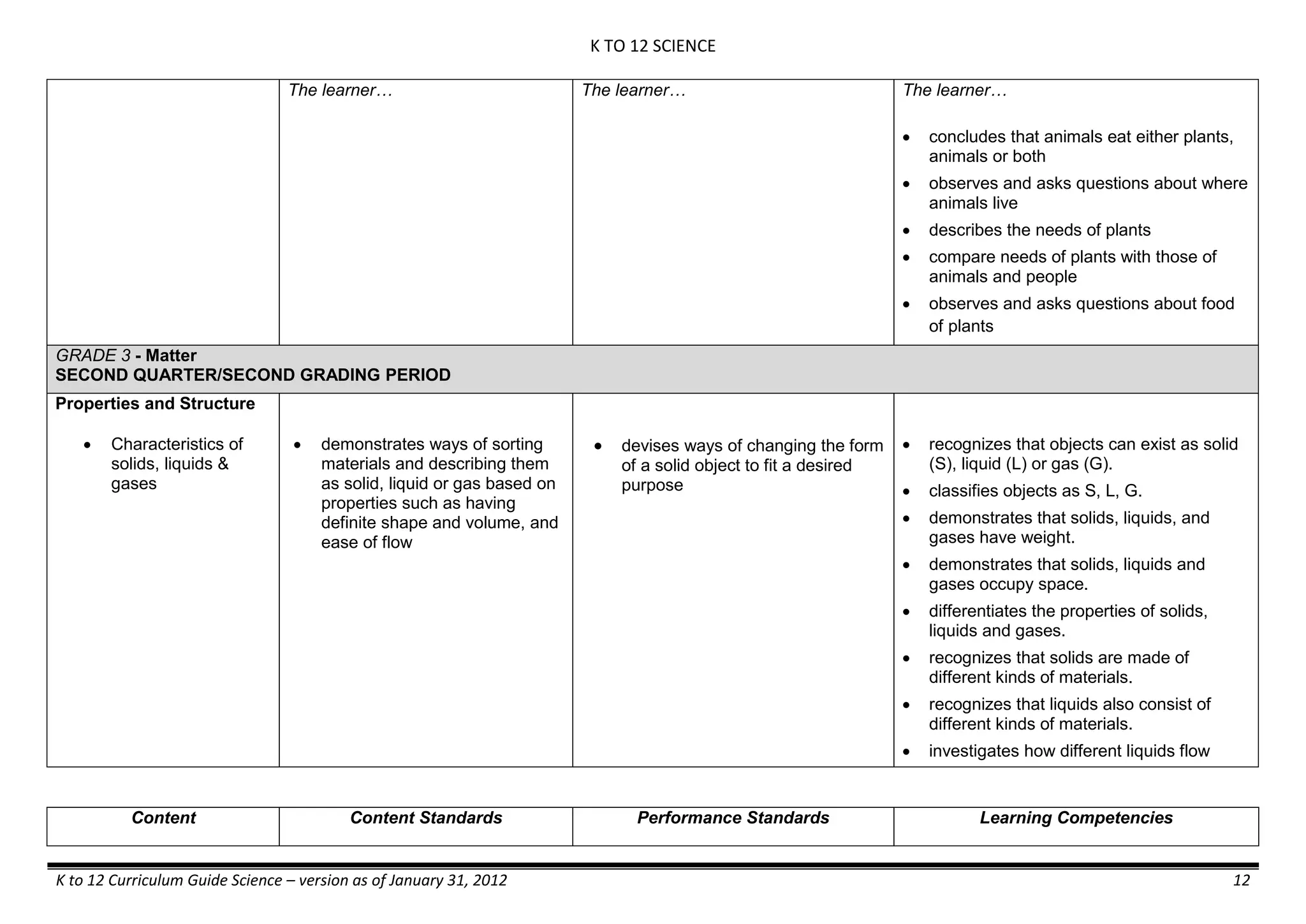
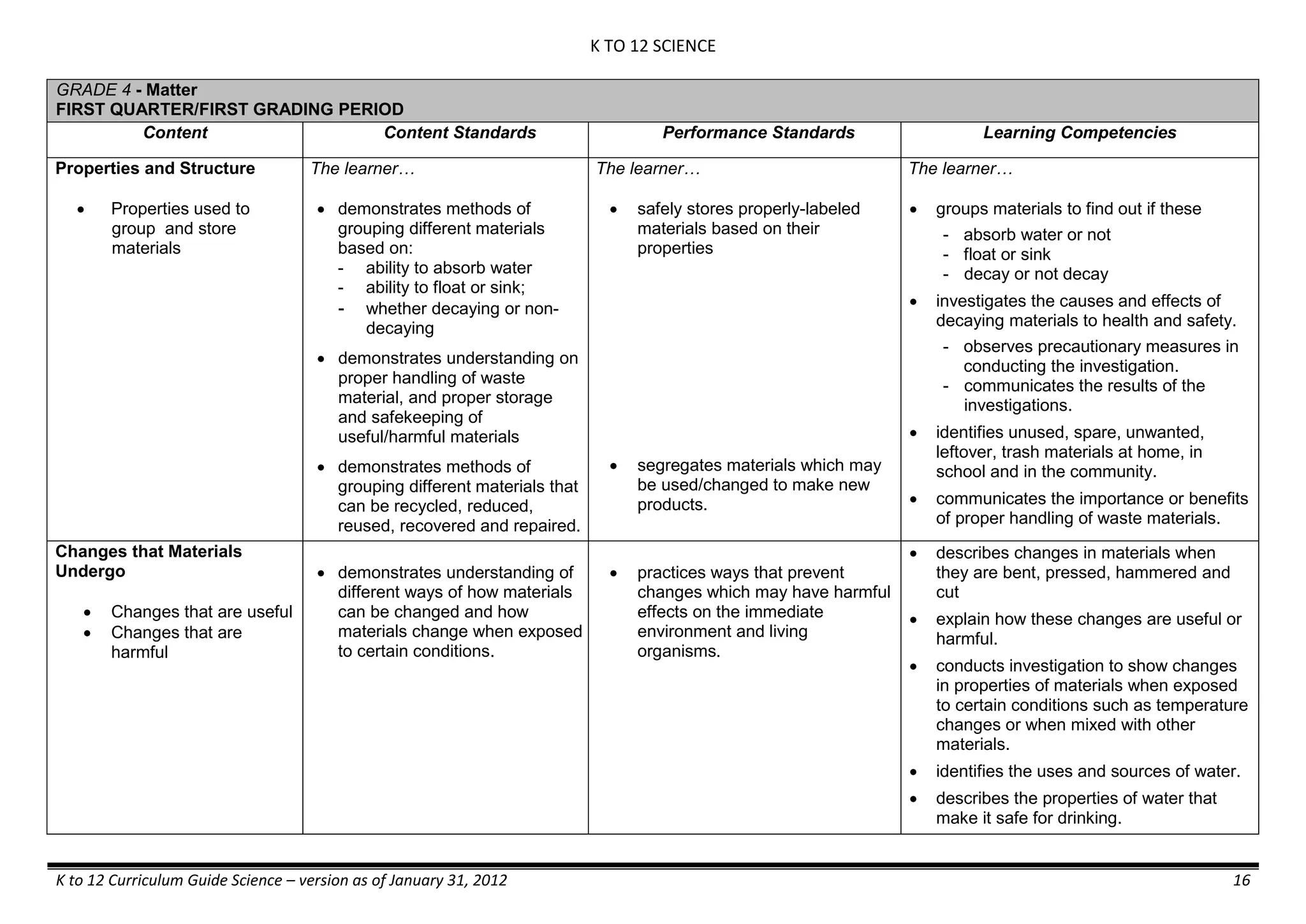
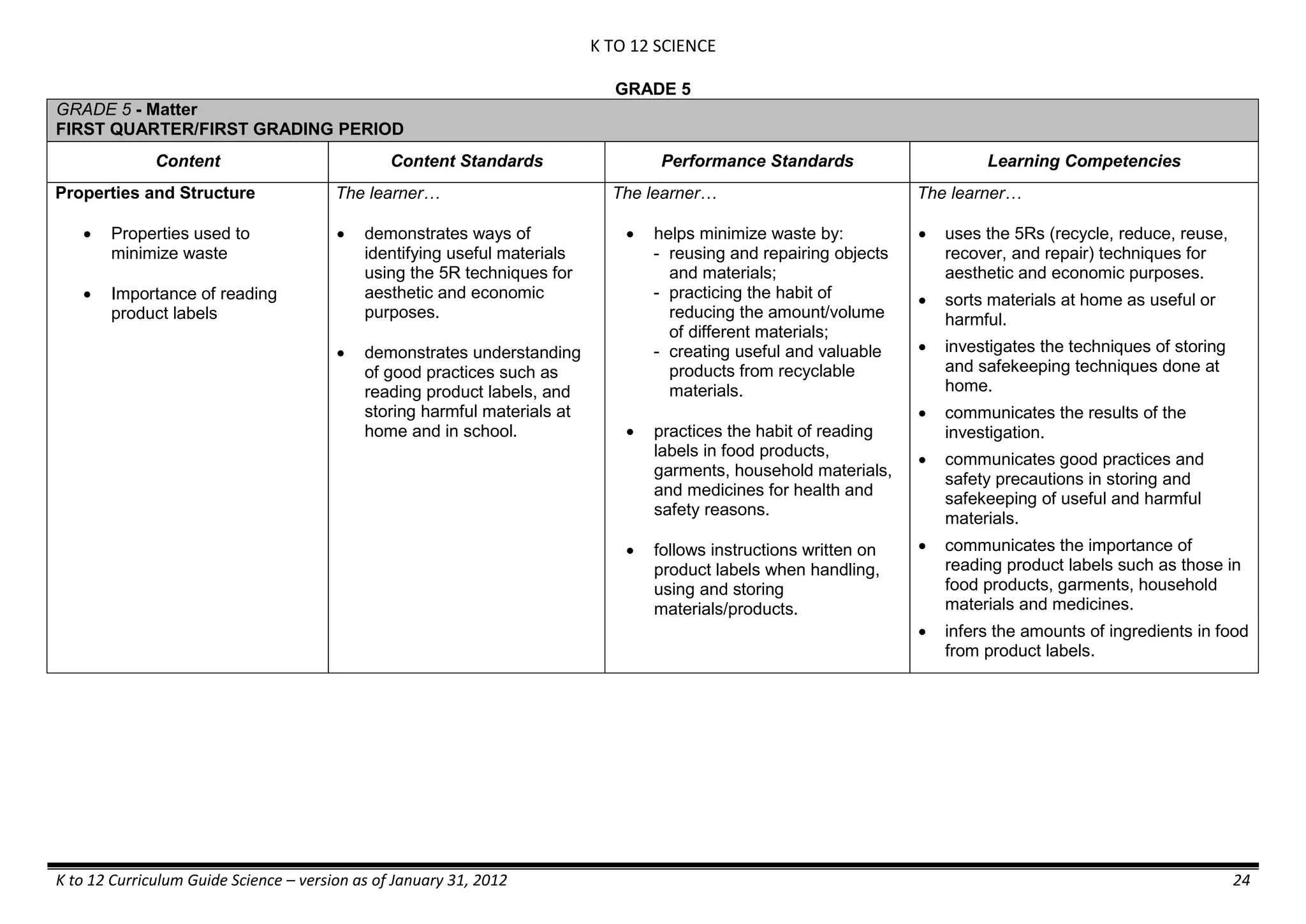
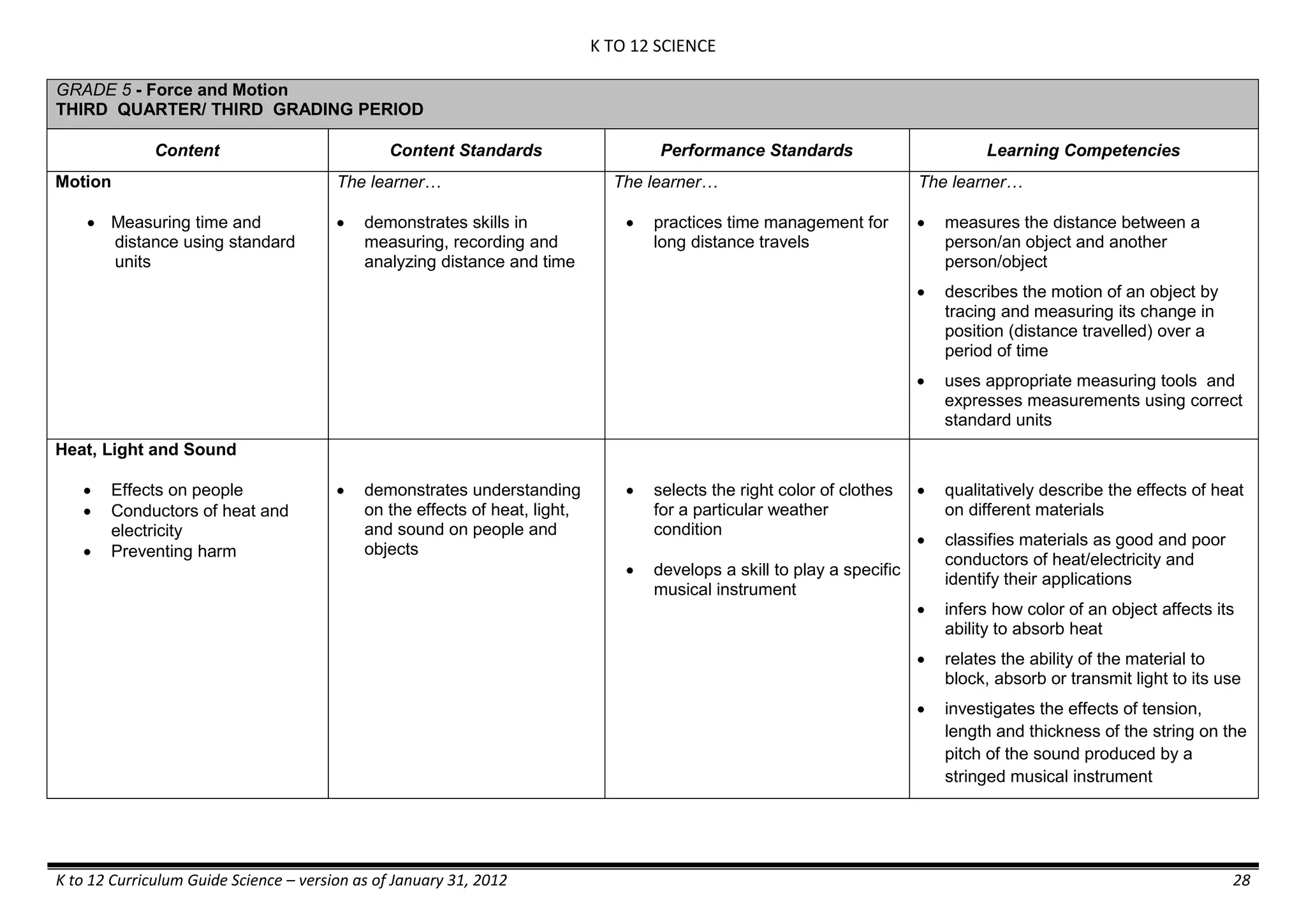
Properties and Structure
Mixtures and their
Characteristics
- Heterogeneous
mixtures
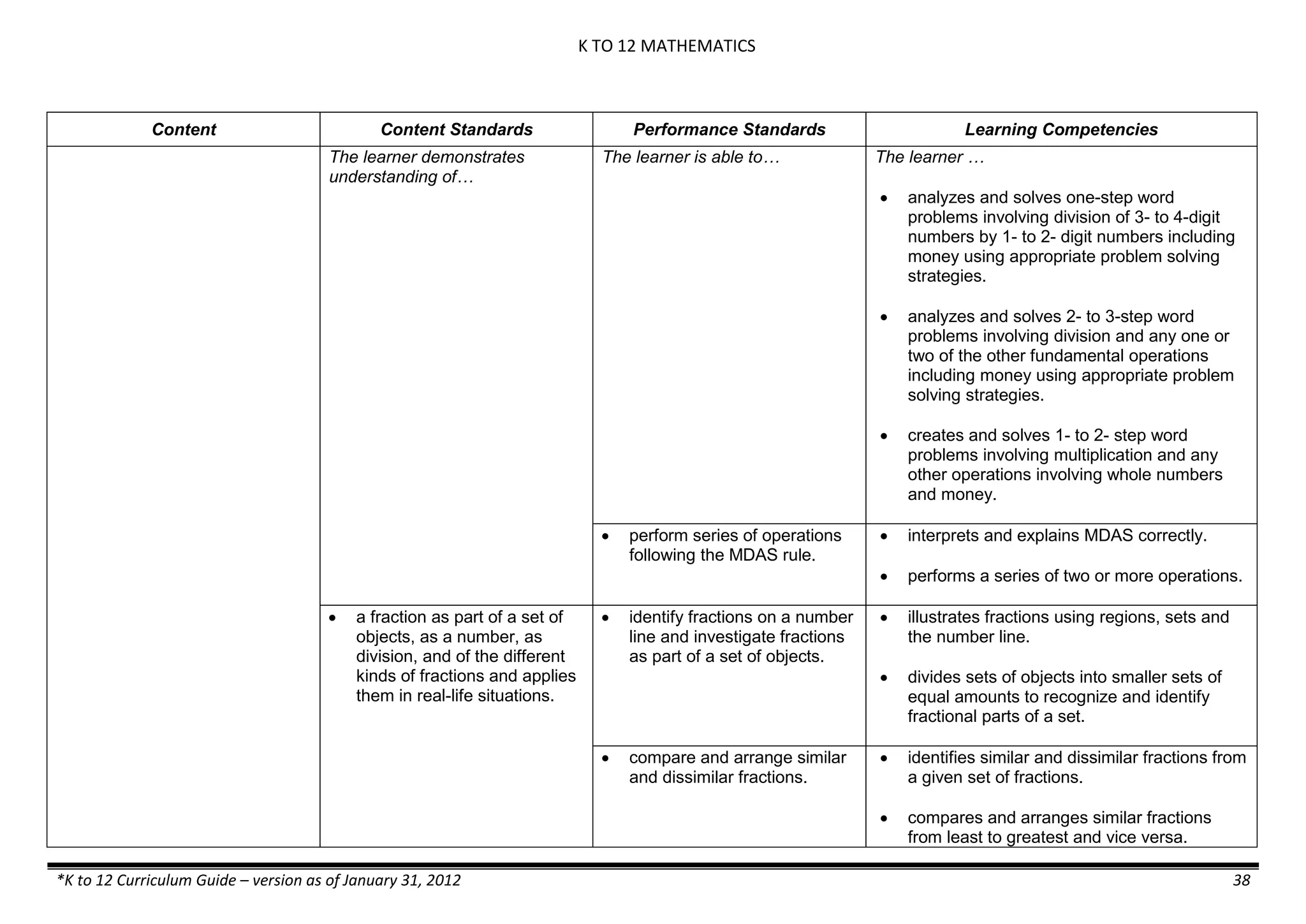
The learner…
demonstrates understanding
of the forms [solid (S), liquid
(L), gas (G)], and
classification of mixtures
(solutions, colloids and
suspensions), and
The learner…
prepares beneficial and useful
mixtures such as drinks, food, and
herbal medicines.
The learner…
recognizes that mixtures are made of
different forms (S,L, and G) of
substances.
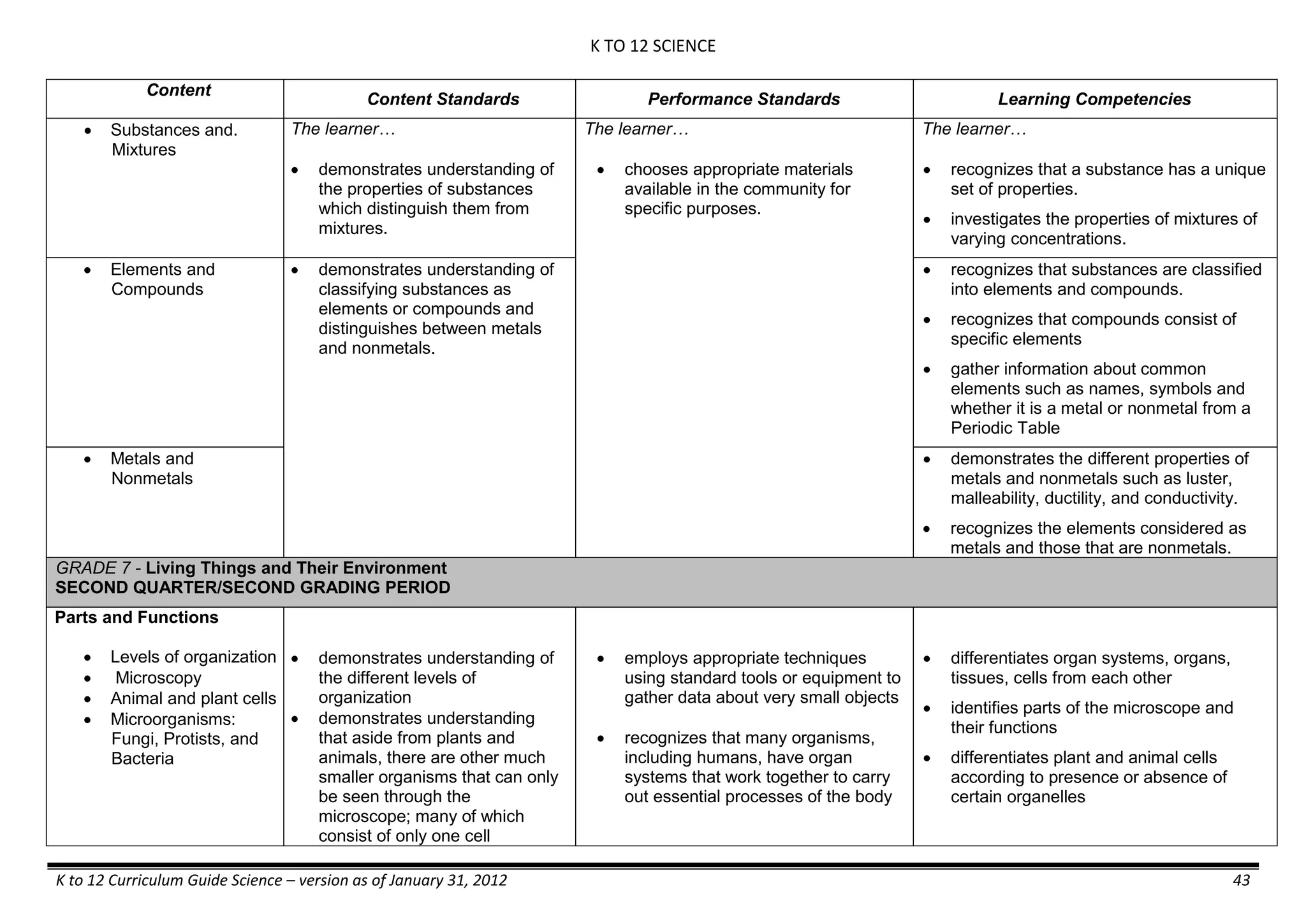
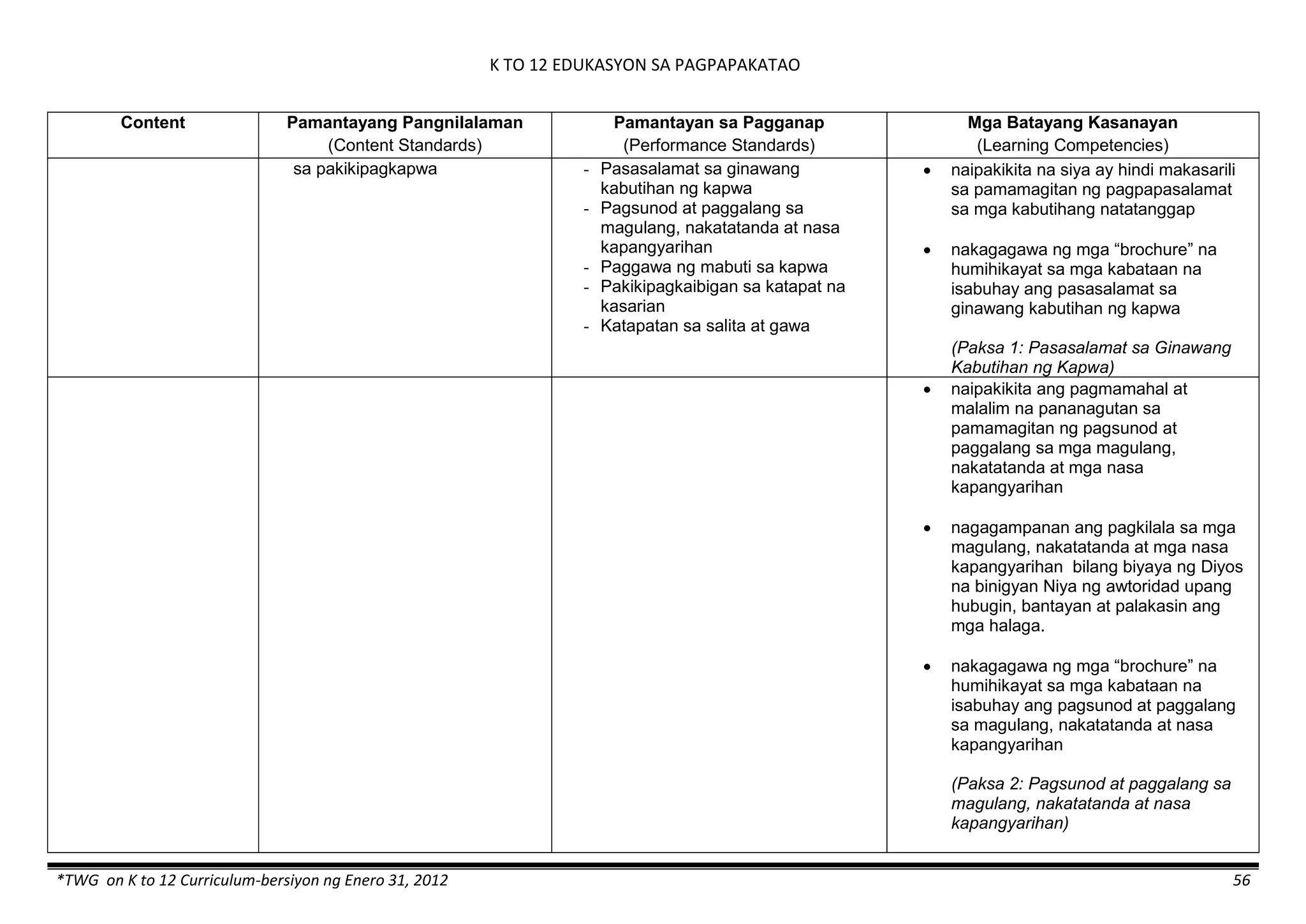
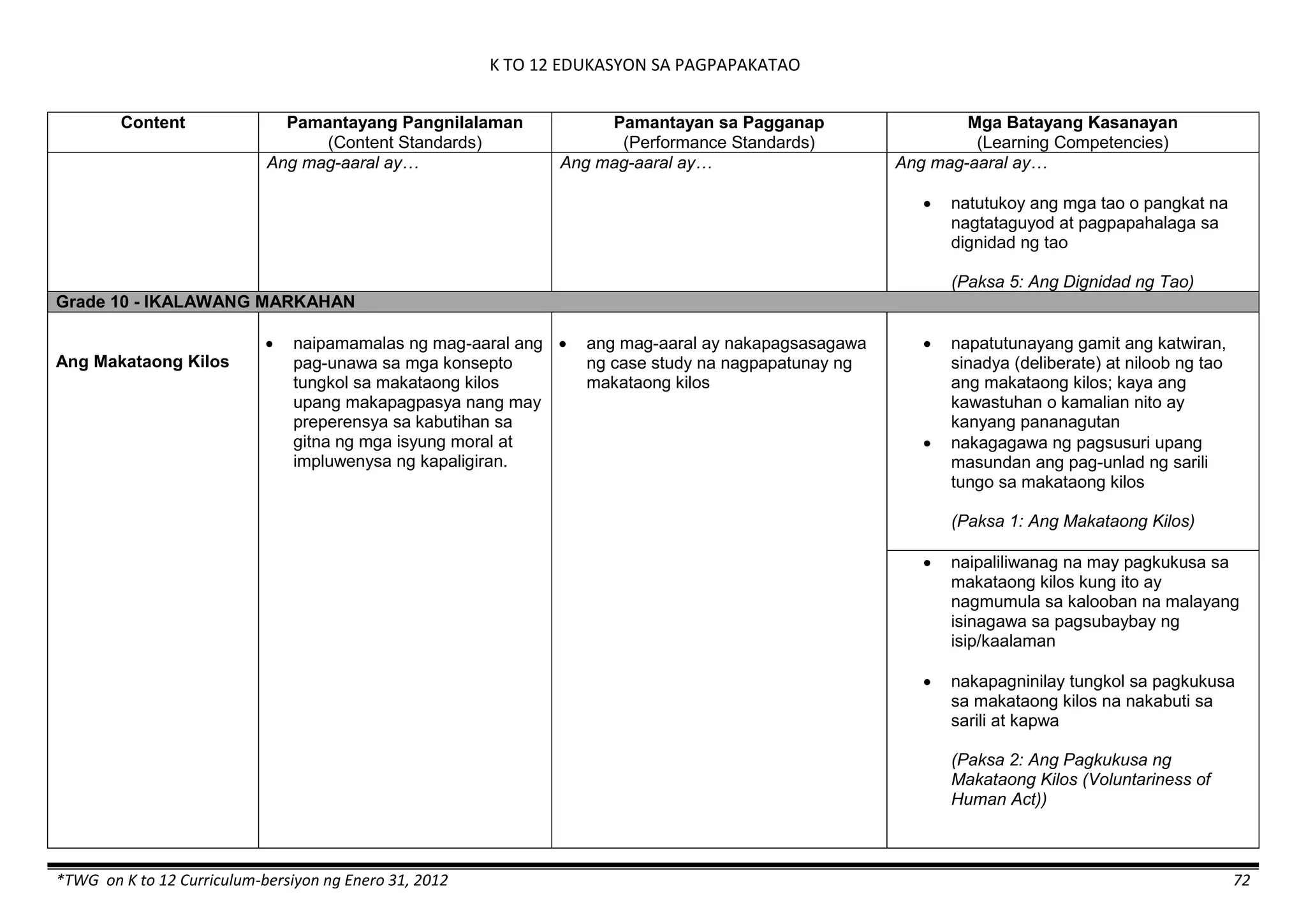
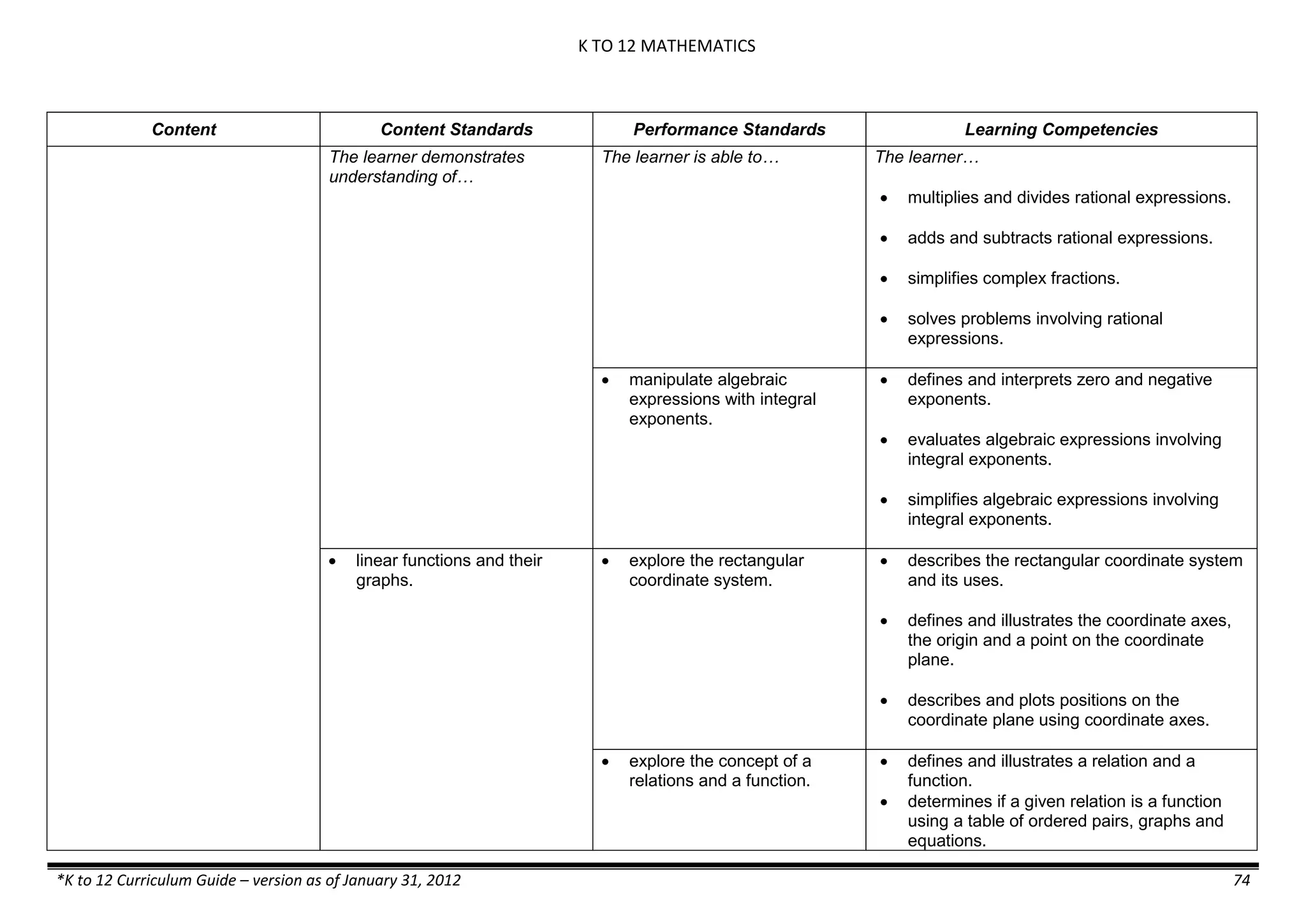
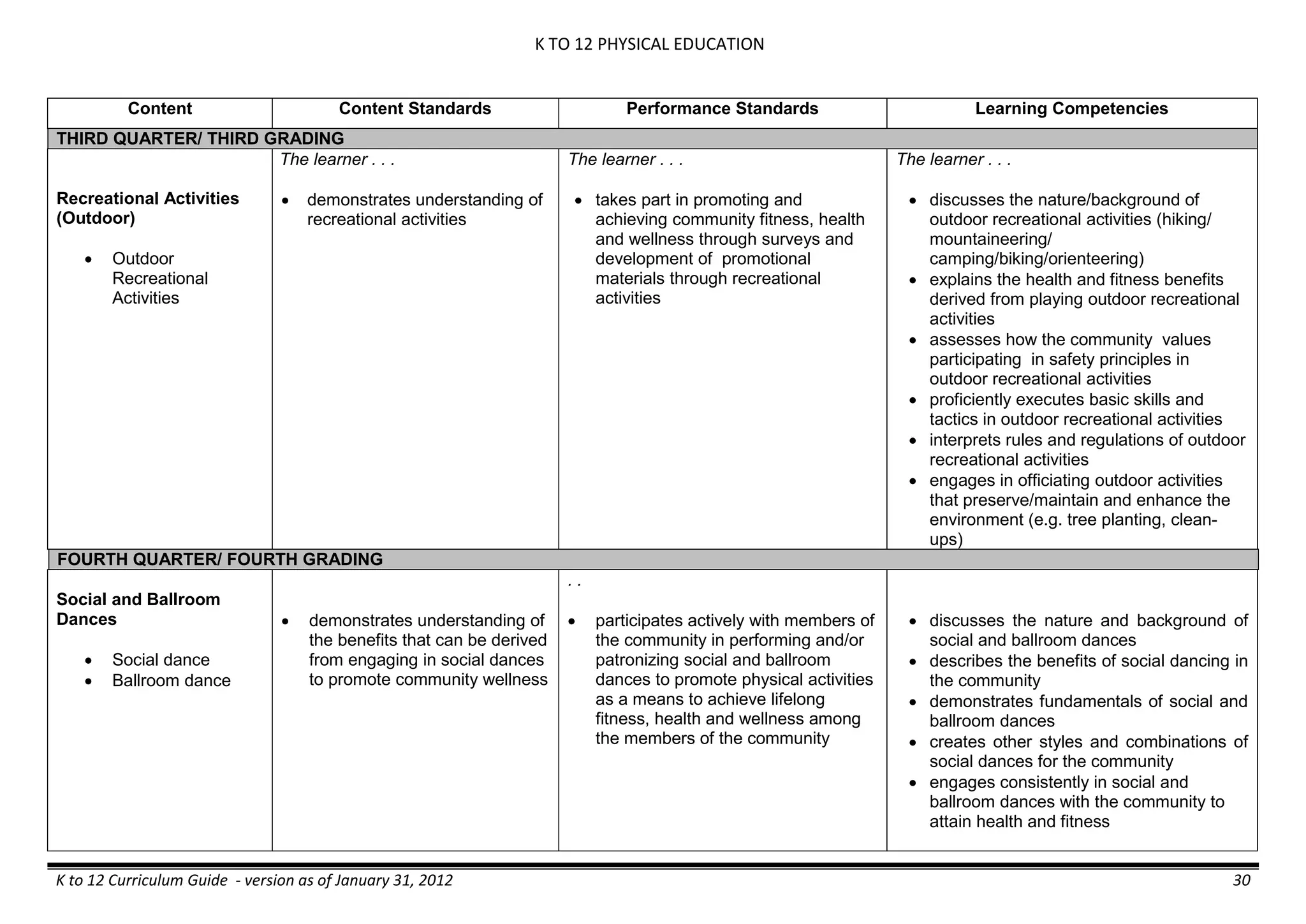
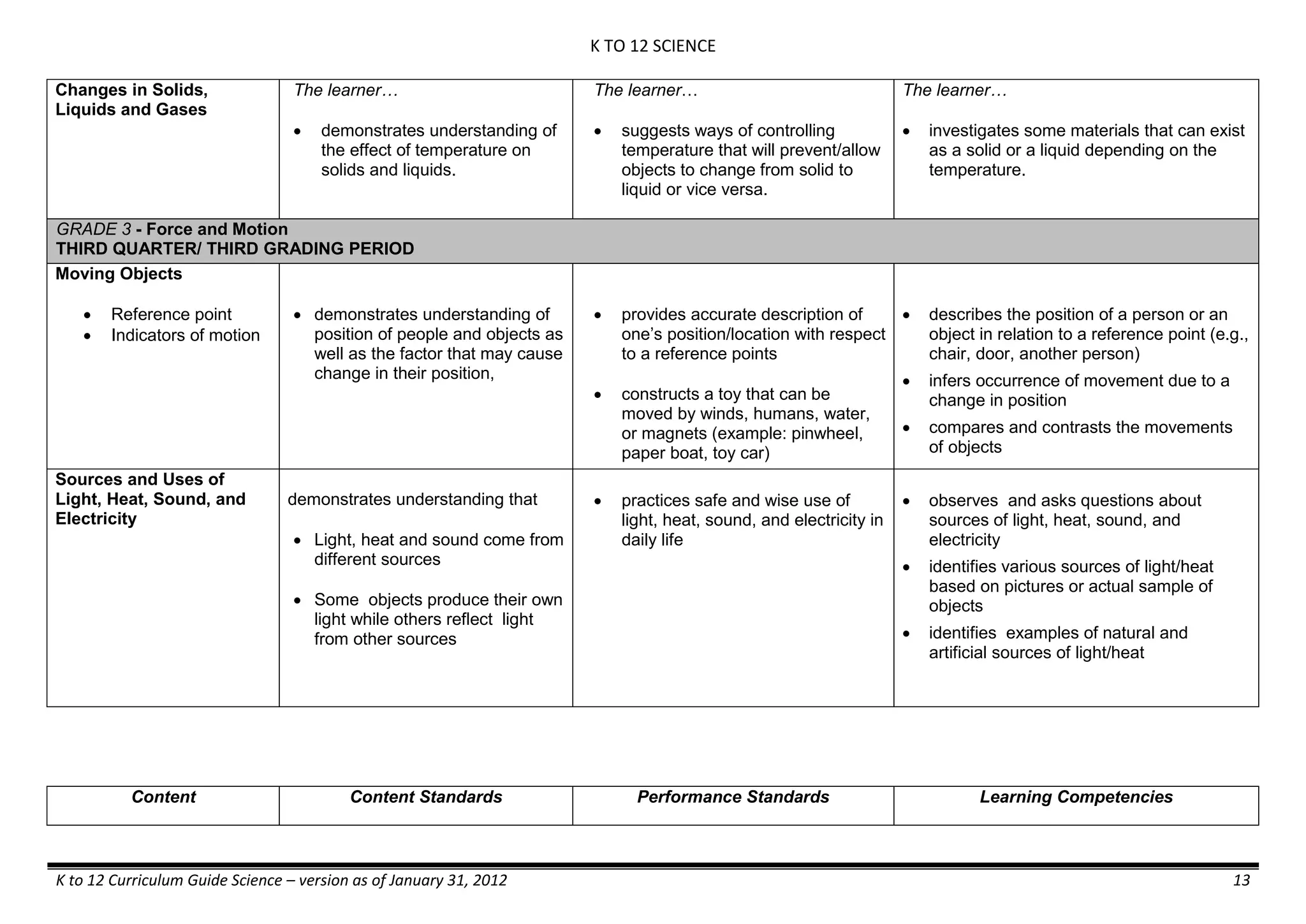
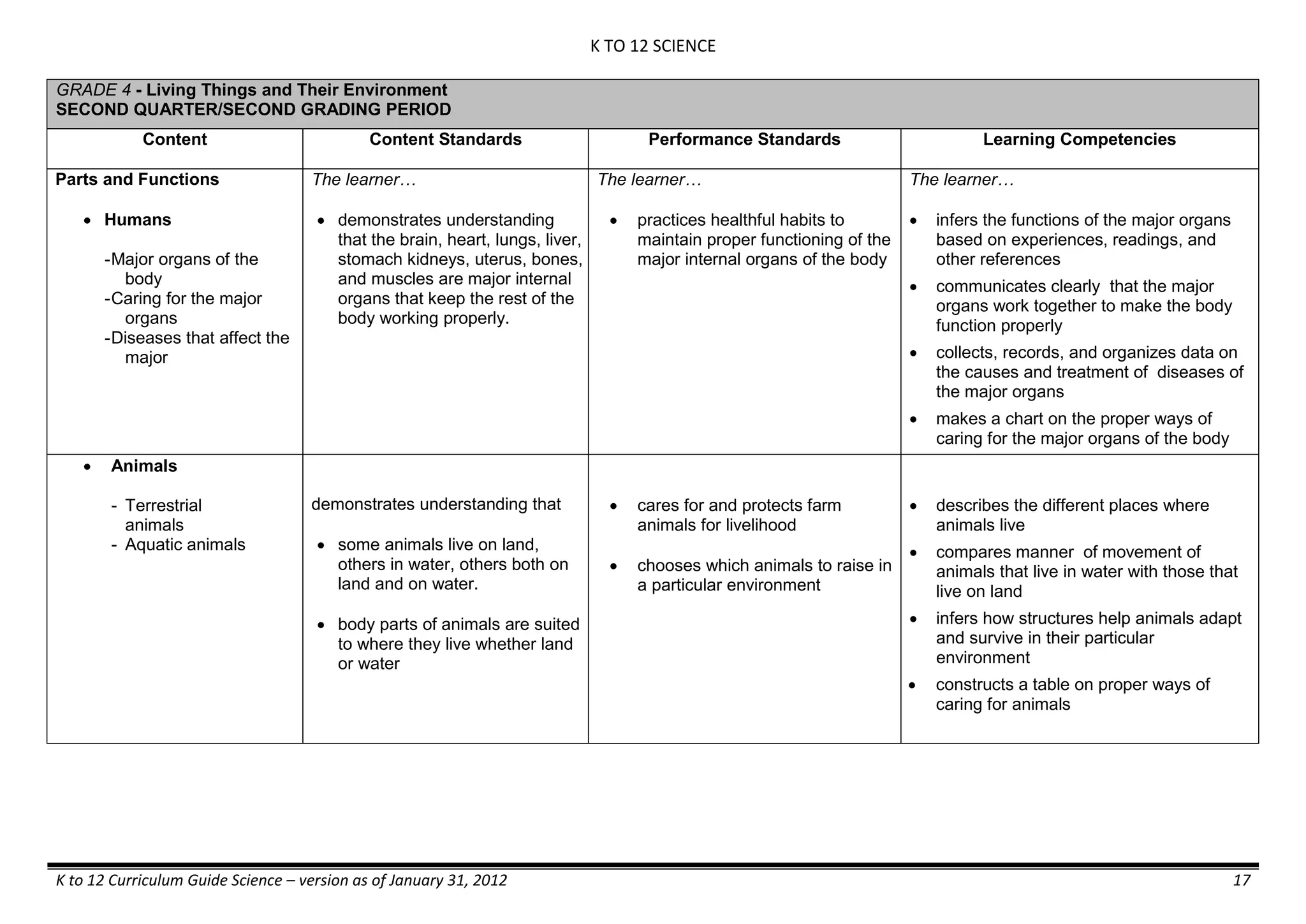
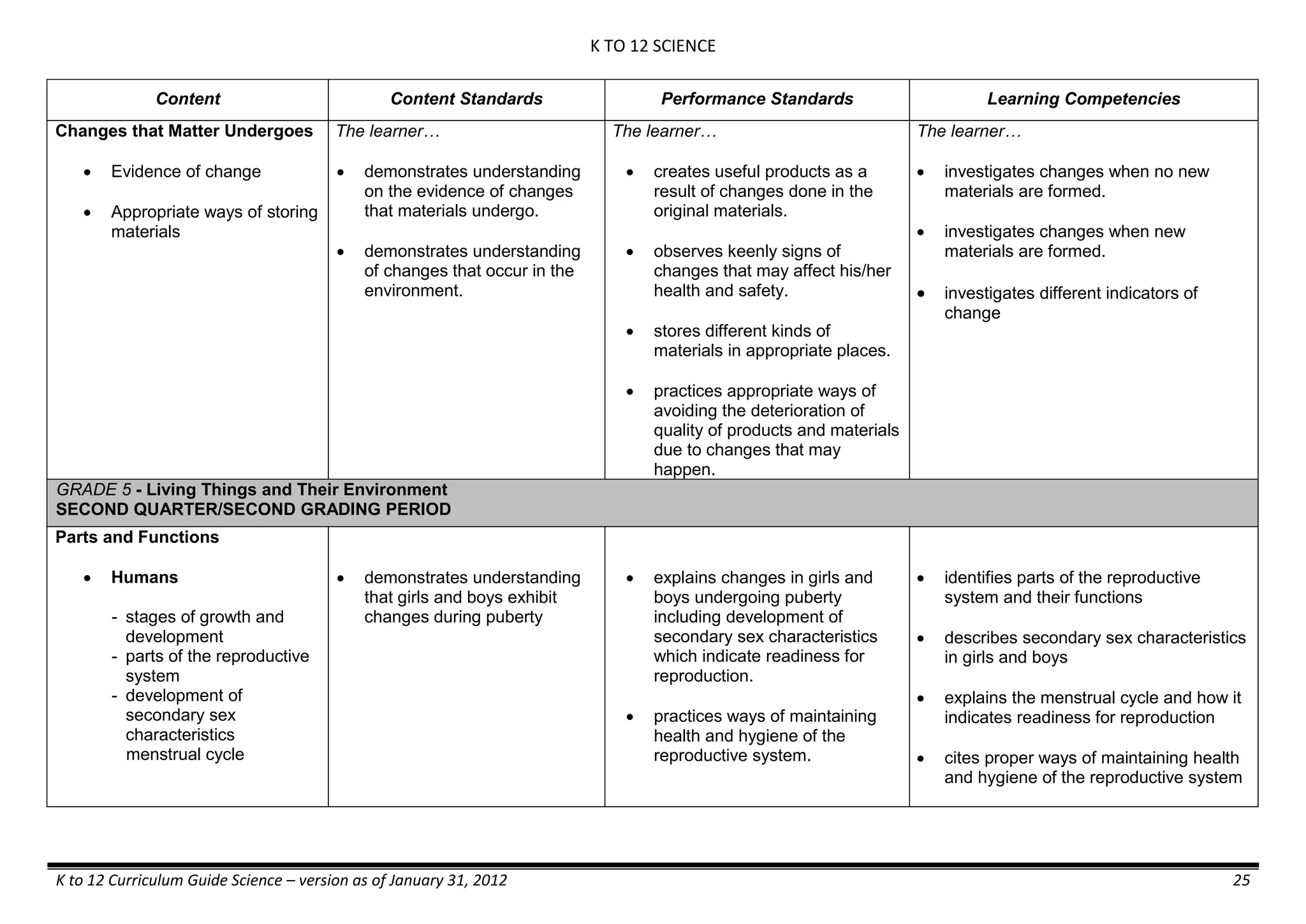
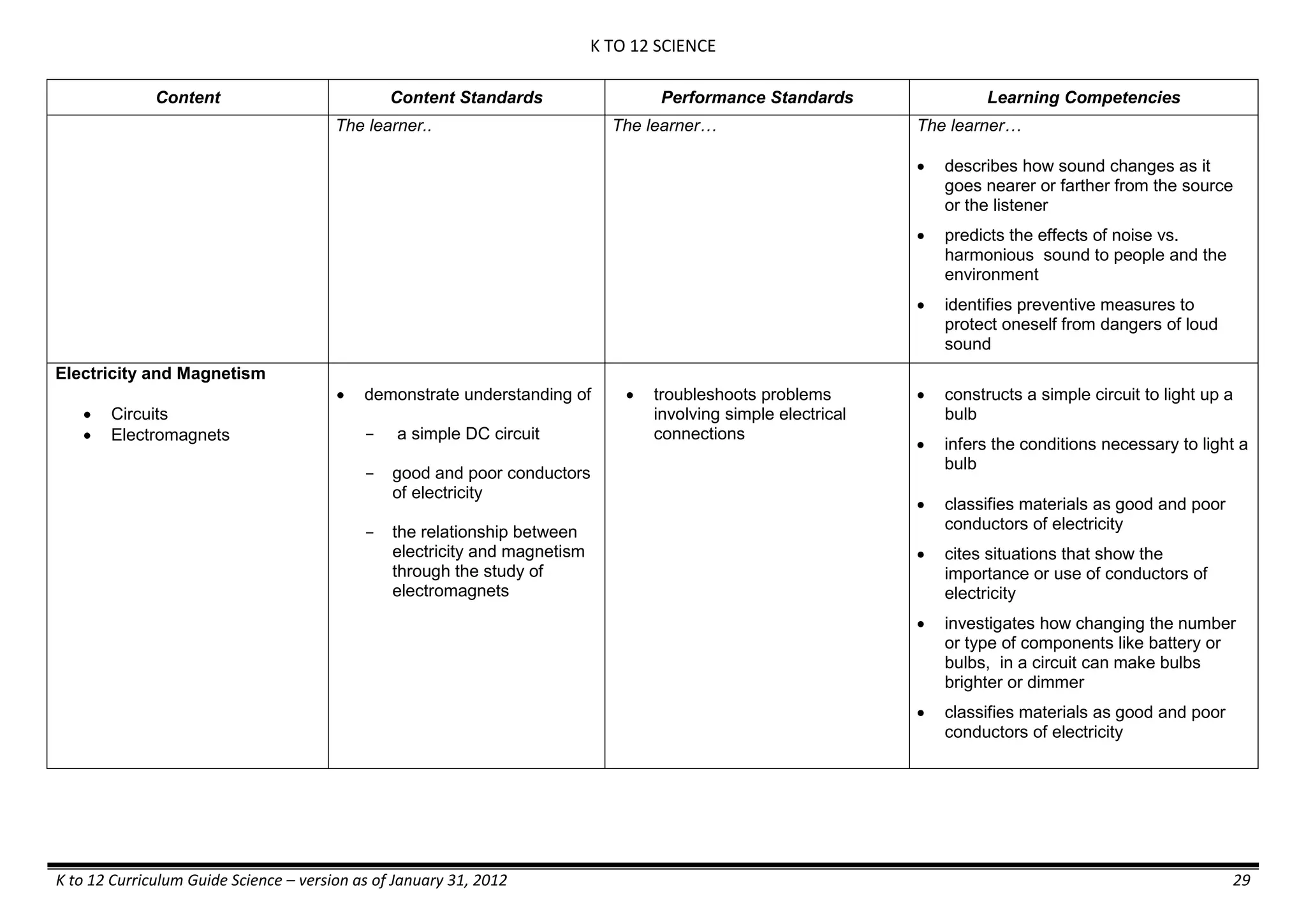
- liquid mixtures (S,L)
- liquid mixtures (S,L,G)
- solid mixtures
- gas mixtures
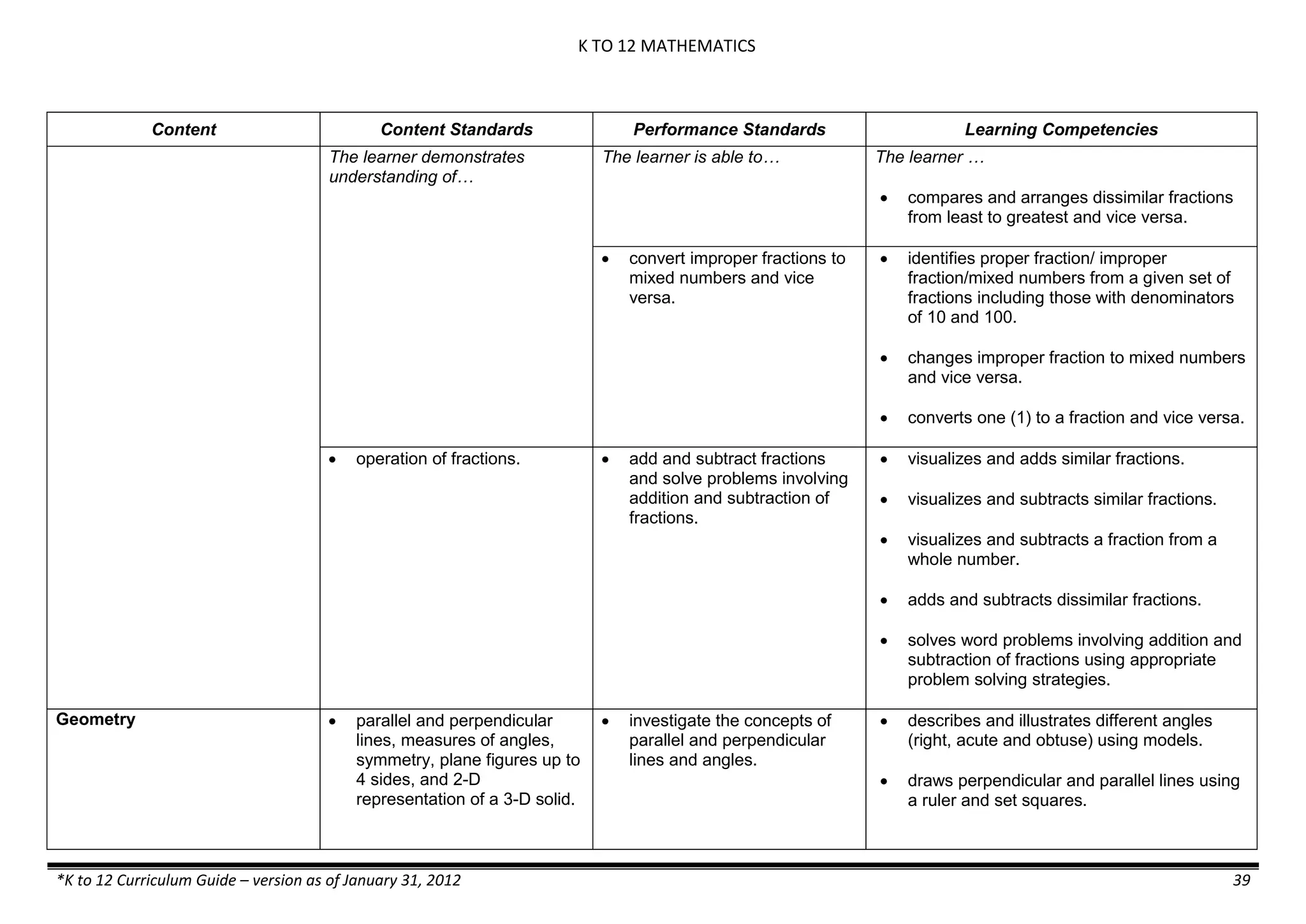
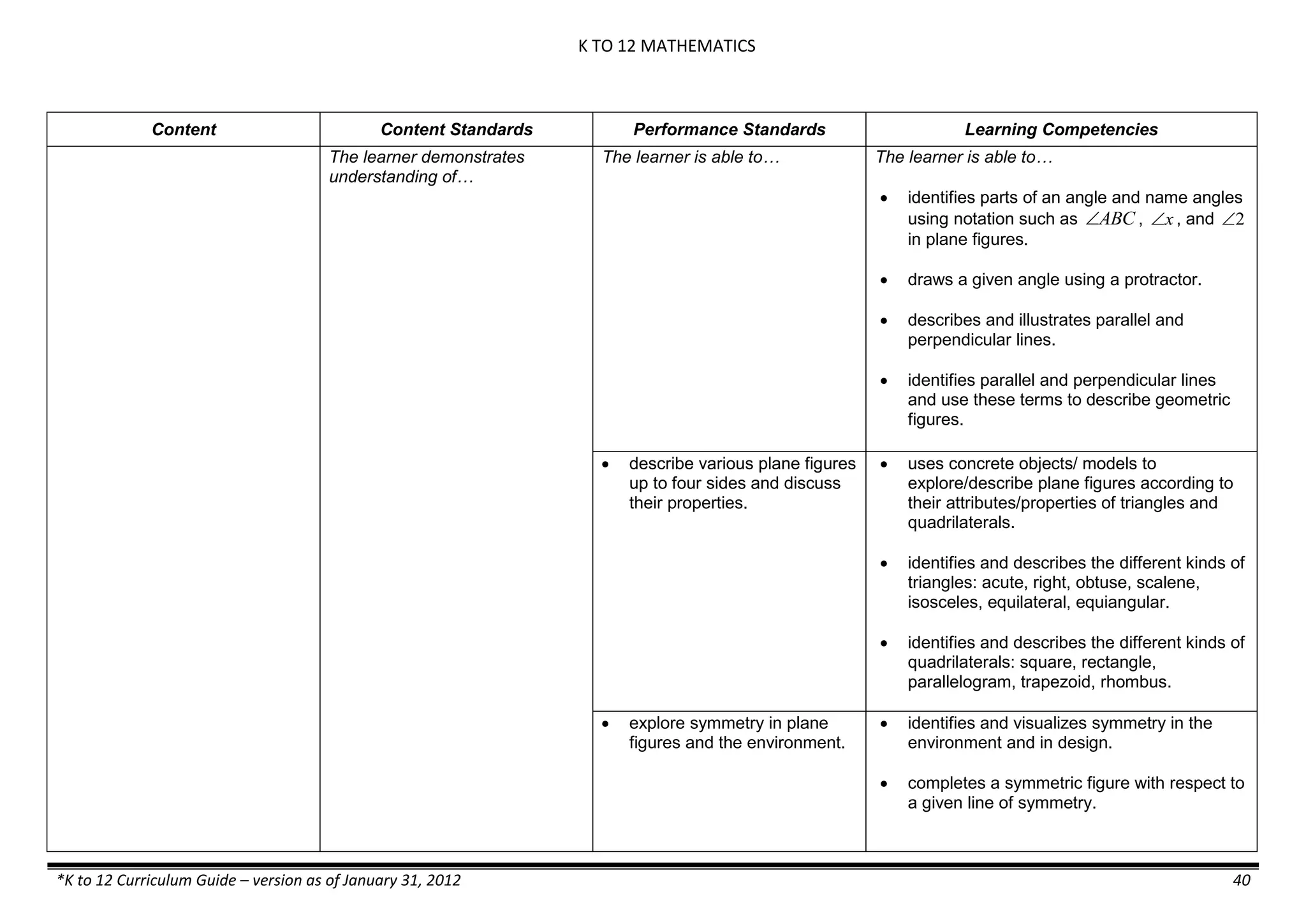
demonstrates that some materials when
mixed together form homogeneous
(solutions) or heterogeneous
(suspensions) mixtures.
communicates the uses of different
mixtures.
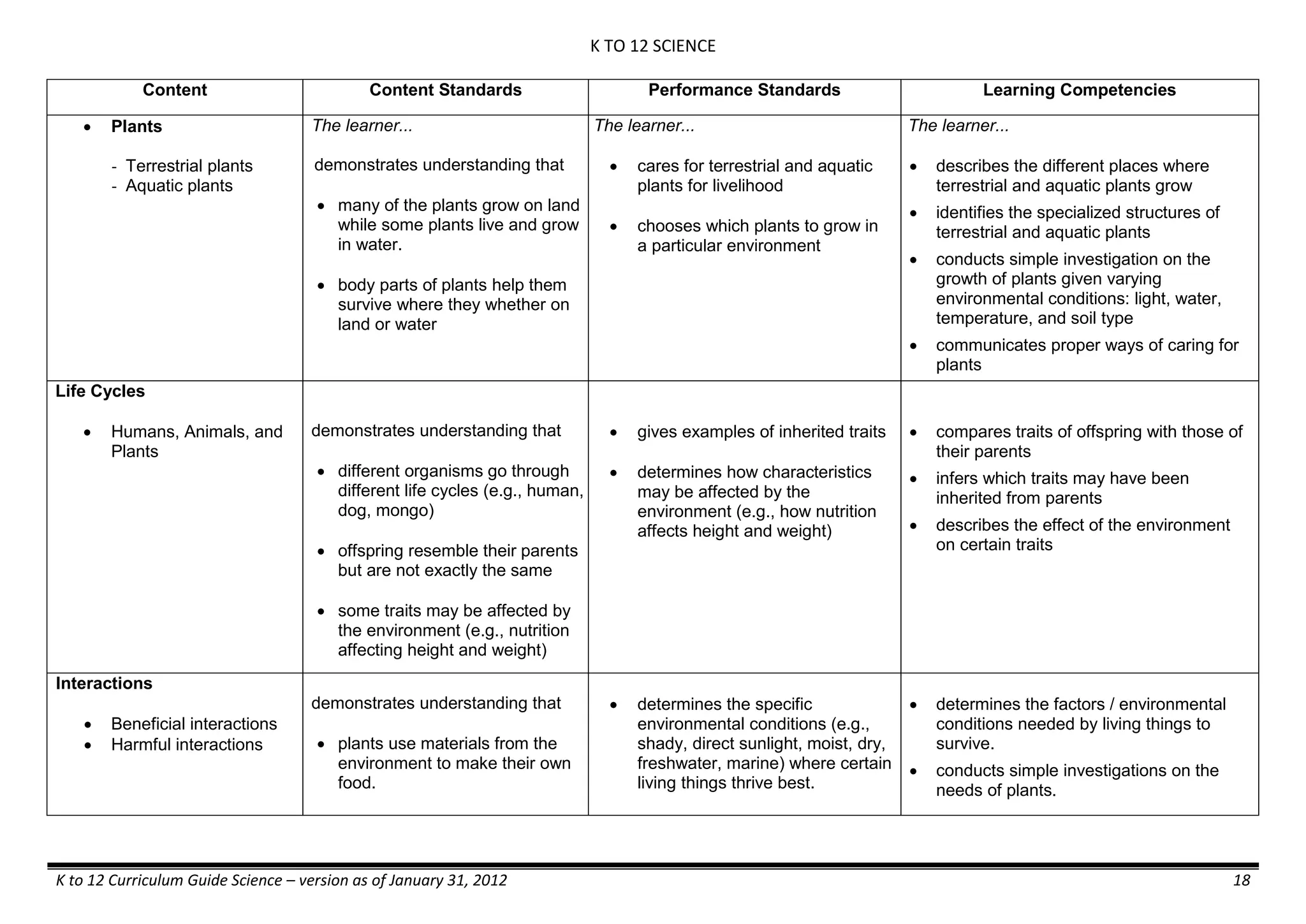
- Colloids demonstrates the formation of colloids.
classifies colloids.
prepares useful colloids.
explains how colloids are utilized in
technology.
evaluates the importance of colloids to
daily life.
describes the biological and
environmental impact of colloids like
aerosol sprays, hair gel, and smoke.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kto12curriculumguide2012-140630070203-phpapp02/75/Compilation-of-K-to-12-Curriculum-Guides-S-Y-2012-490-2048.jpg)