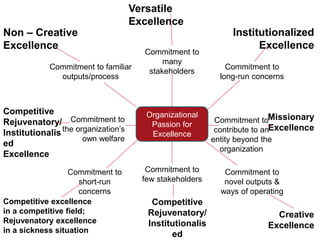
This document discusses organizational excellence, specifically competitive organizational excellence. It defines excellence as outstanding achievement that surpasses normal standards. Organizational excellence occurs when an organization promotes human excellence through merit-based practices and synchronizes individual and group efforts to achieve goals. There are different forms of organizational excellence, including competitive excellence which is important for organizations operating in competitive domains or competing for resources, where they must prioritize, develop strategies, control costs, increase productivity, and coordinate effectively. The document uses Singapore Airlines as a case study of competitive excellence, highlighting how it grew rapidly by expanding its fleet, developing routes, delivering high customer service, training staff, controlling costs, and operating as a commercial rather than prestigious enterprise.