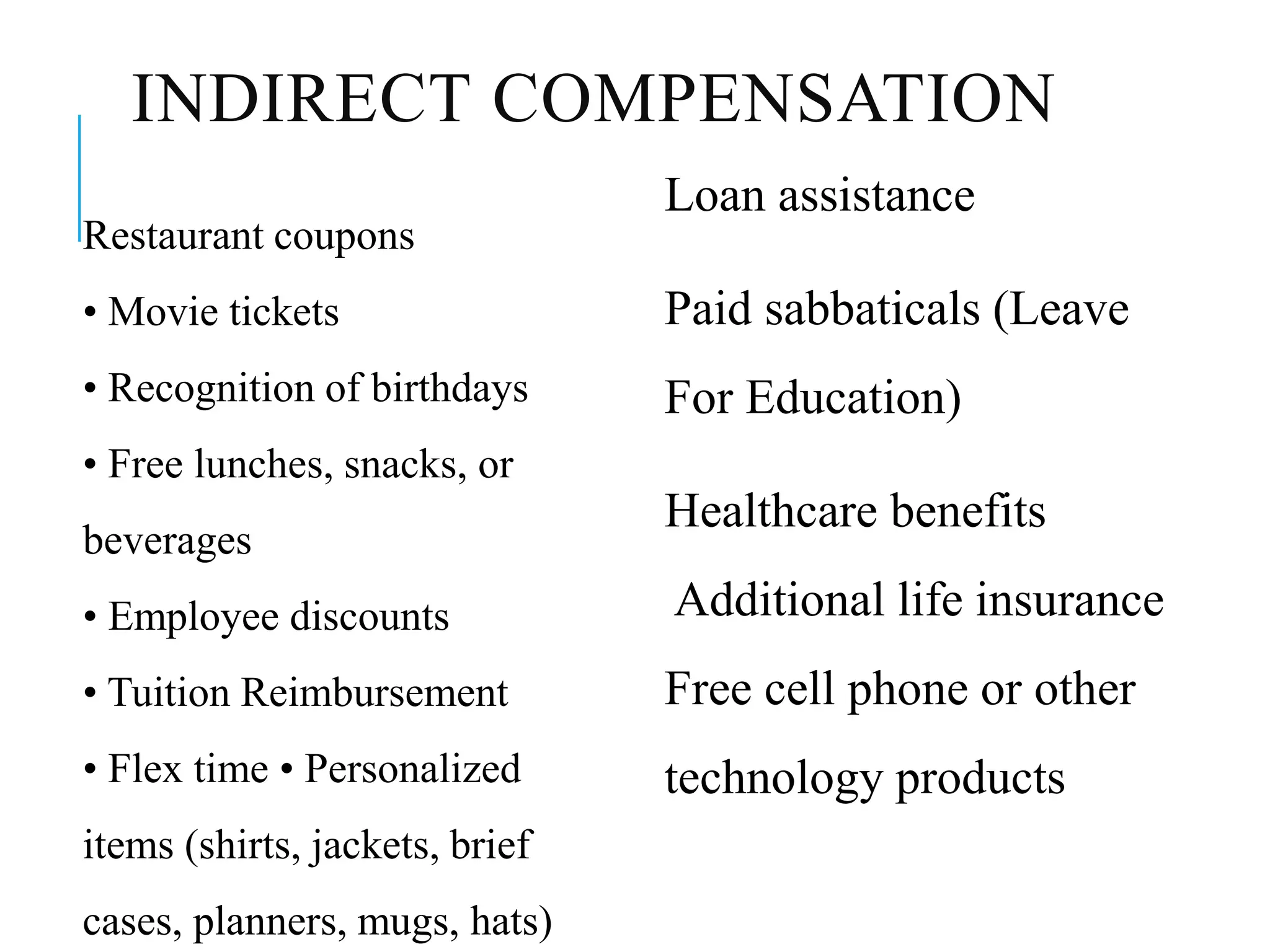
This document defines compensation and its objectives, discusses factors that influence compensation, and describes the various types of direct and indirect compensation. The key objectives of compensation are to attract, retain, and motivate qualified employees. Compensation includes direct wages/salaries as well as indirect benefits and is influenced by market rates, cost of living, productivity, and other economic factors. Common types of direct compensation are salary, wages, bonuses, and commissions, while indirect compensation includes benefits like healthcare, paid time off, and retirement plans.