The document discusses various compensation policies and philosophies. It provides information on:
1) Factors that determine compensation including supply and demand, prevailing wages, ability to pay, and cost of living.
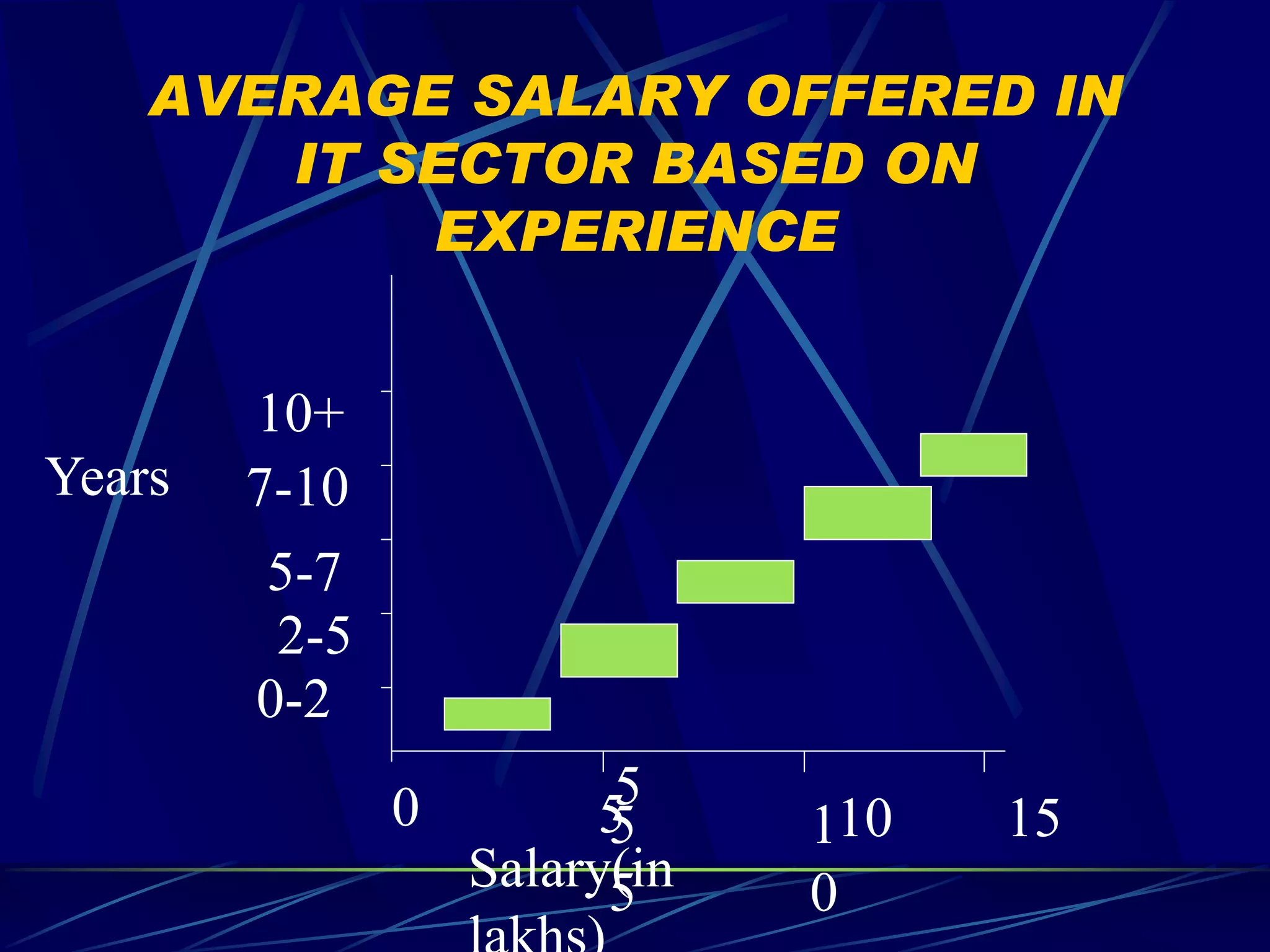
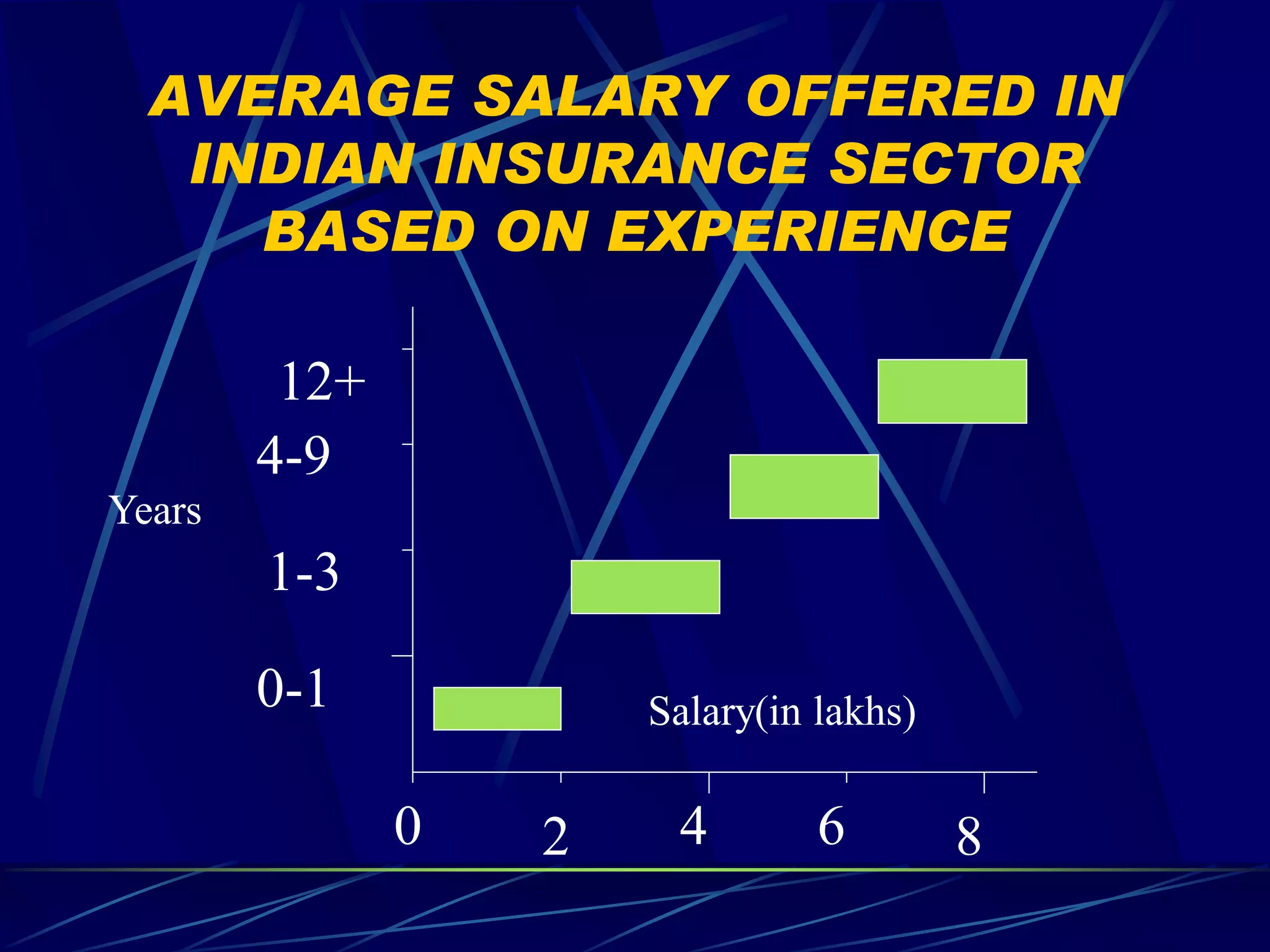
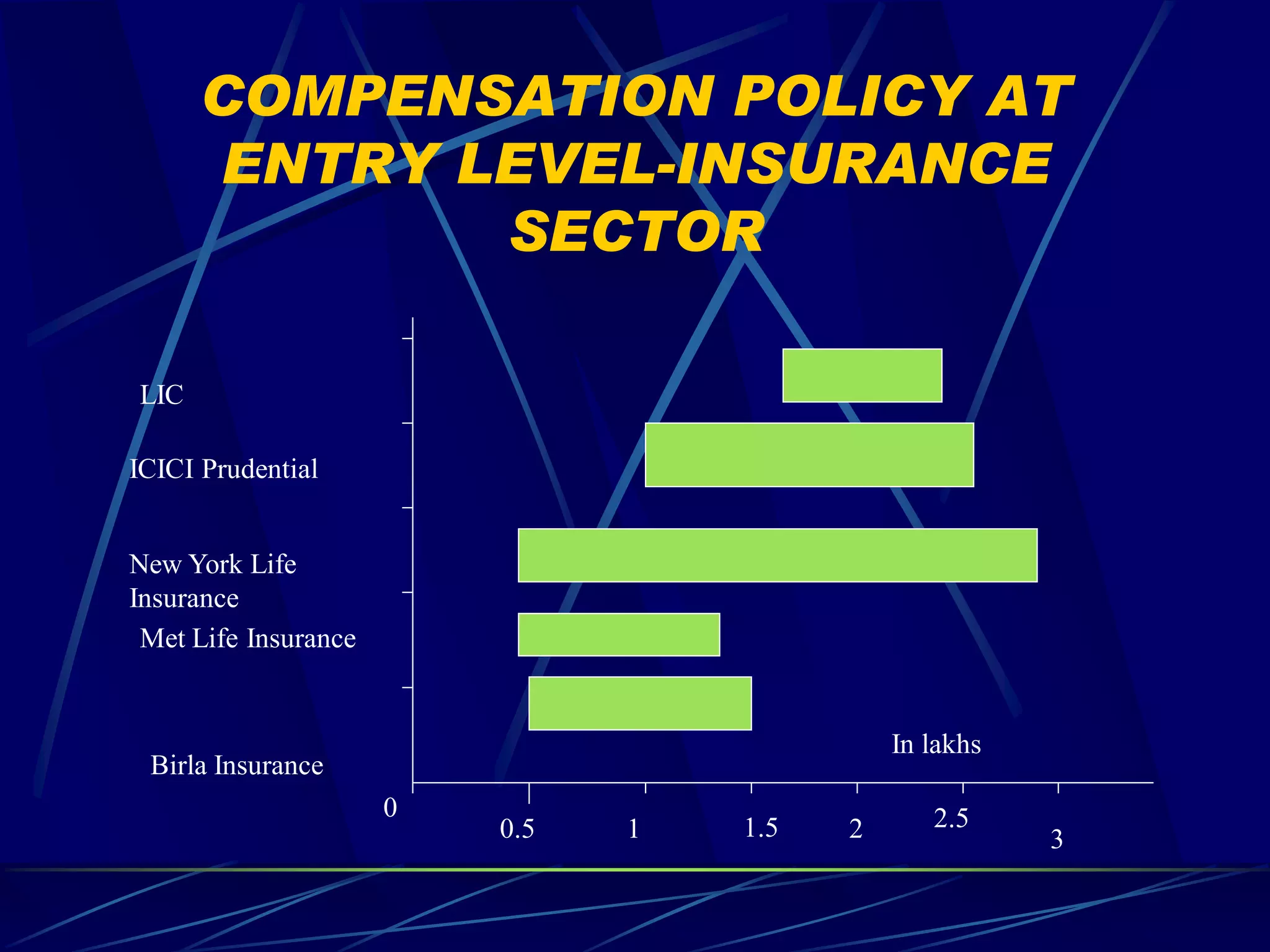
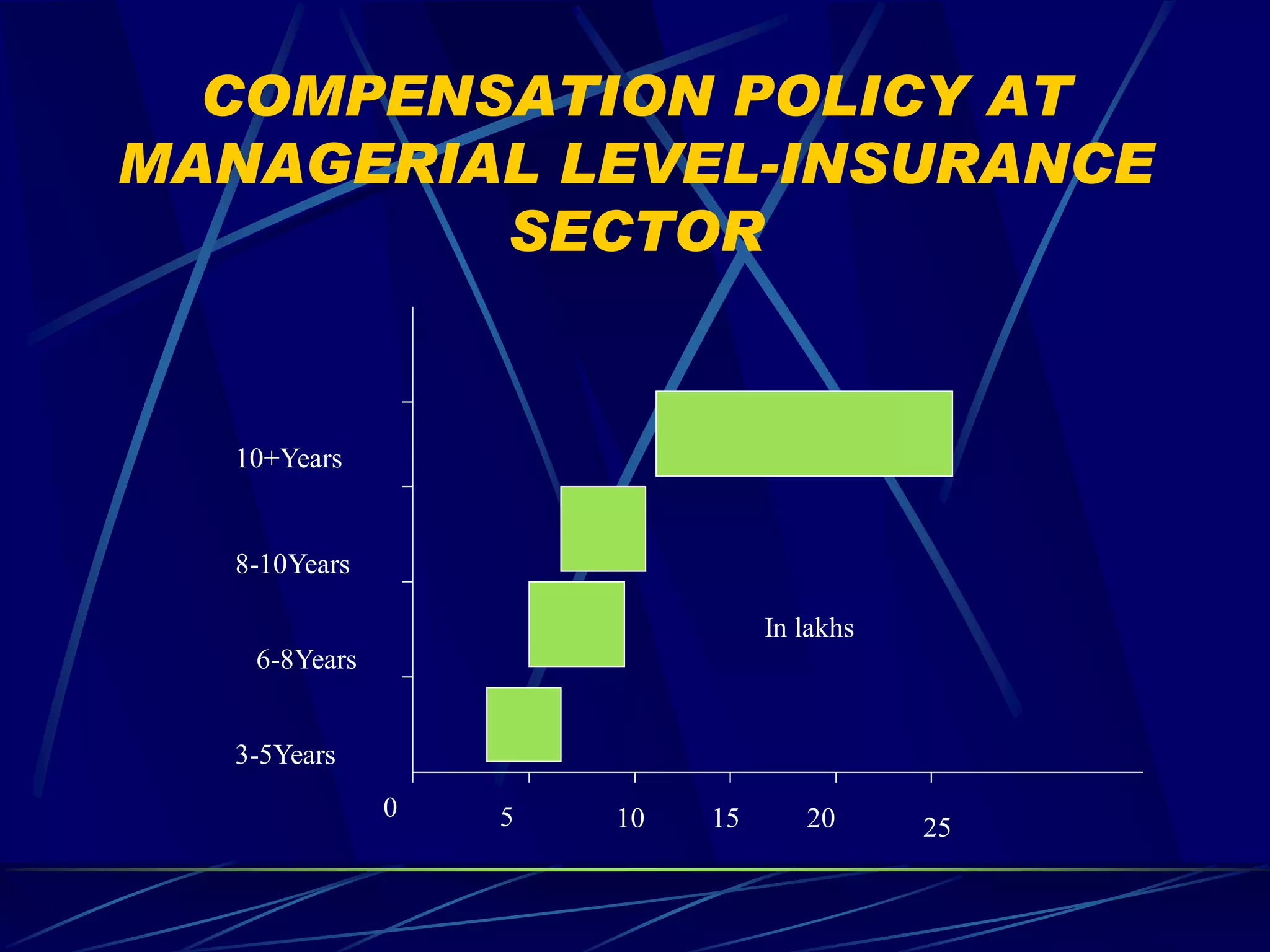
2) Different compensation policies for industries like IT, insurance, and telecommunications that consider education, experience, and performance.
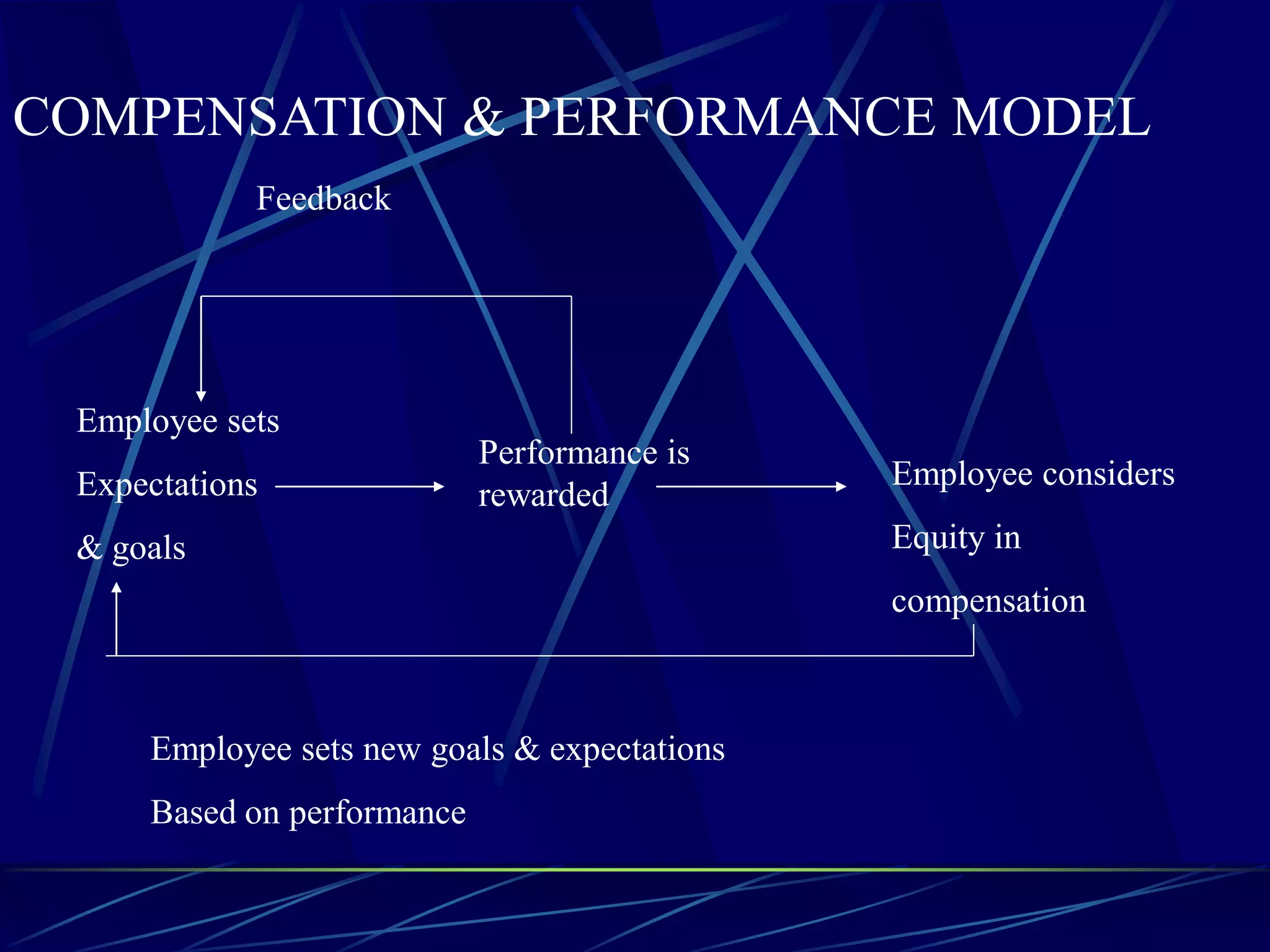
3) Compensation philosophies like productivity philosophy which links pay to productivity and purchasing power philosophy which aims to increase standards of living.
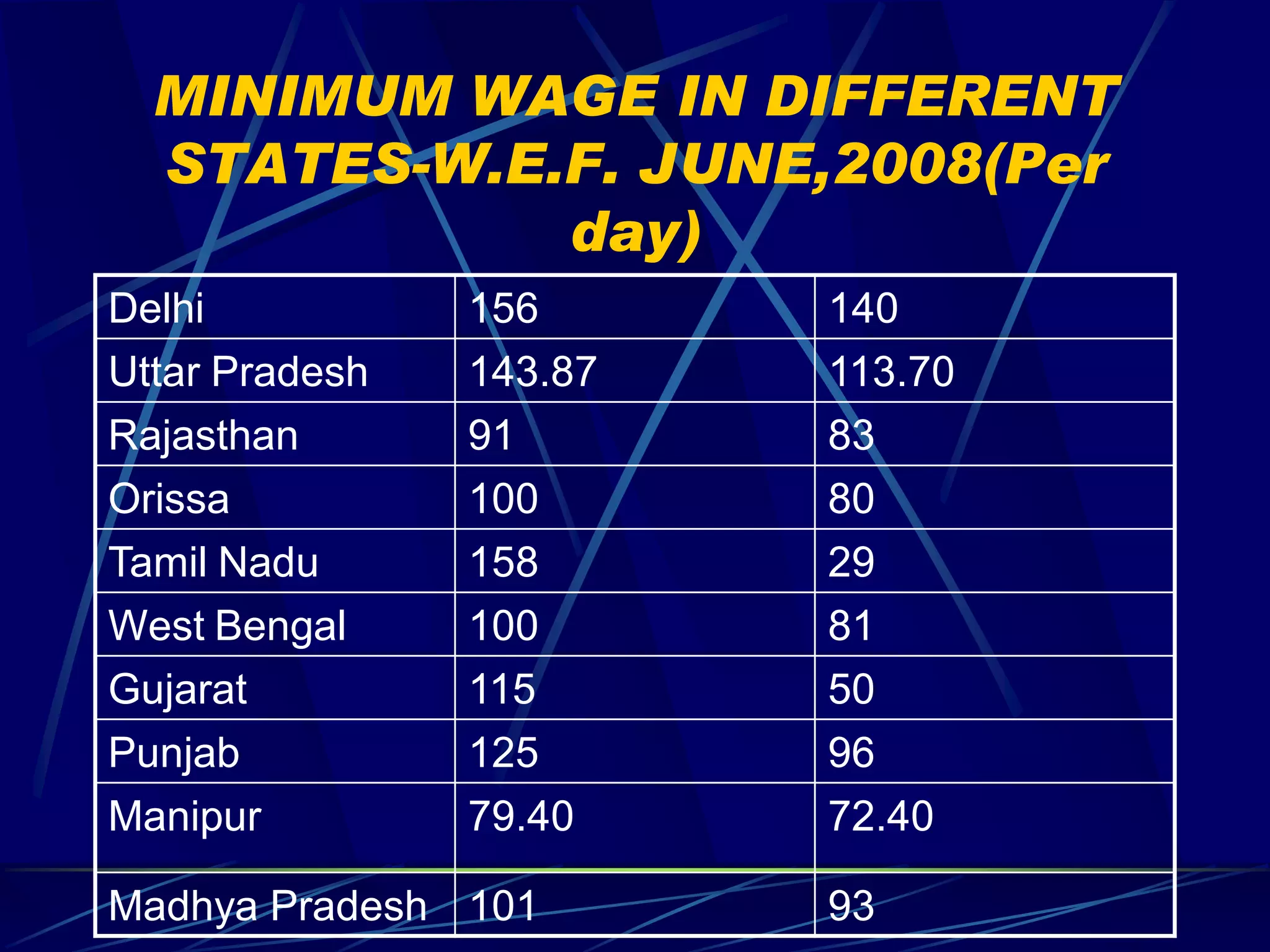
4) Types of minimum wages paid and differentials in compensation based on occupations, firms, regions, industries and individuals.