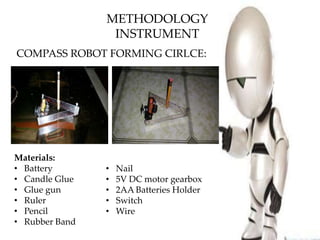
This document discusses circles and how to form circles using a compass robot. It defines what a circle is, listing its key parts like the center, radius, and diameter. It presents the standard equation for a circle centered at the origin (x2 + y2 = r2) and one centered at a point (h,k) ((x - h)2+(y - k)2= r2). The methodology section describes the materials needed for a compass robot, which uses a motor, batteries, and other components to form circles by moving a nail attached to a rubber band.