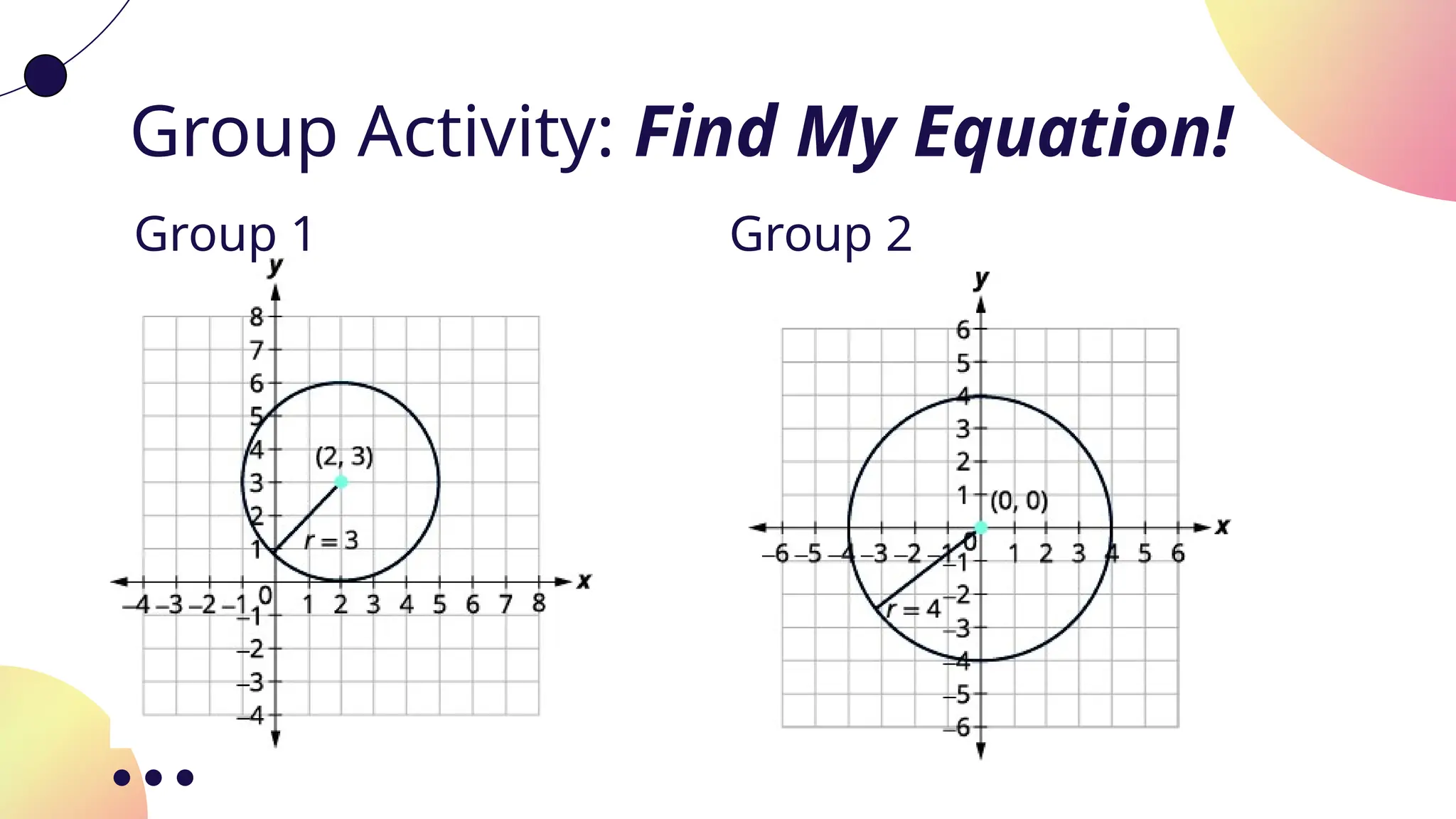
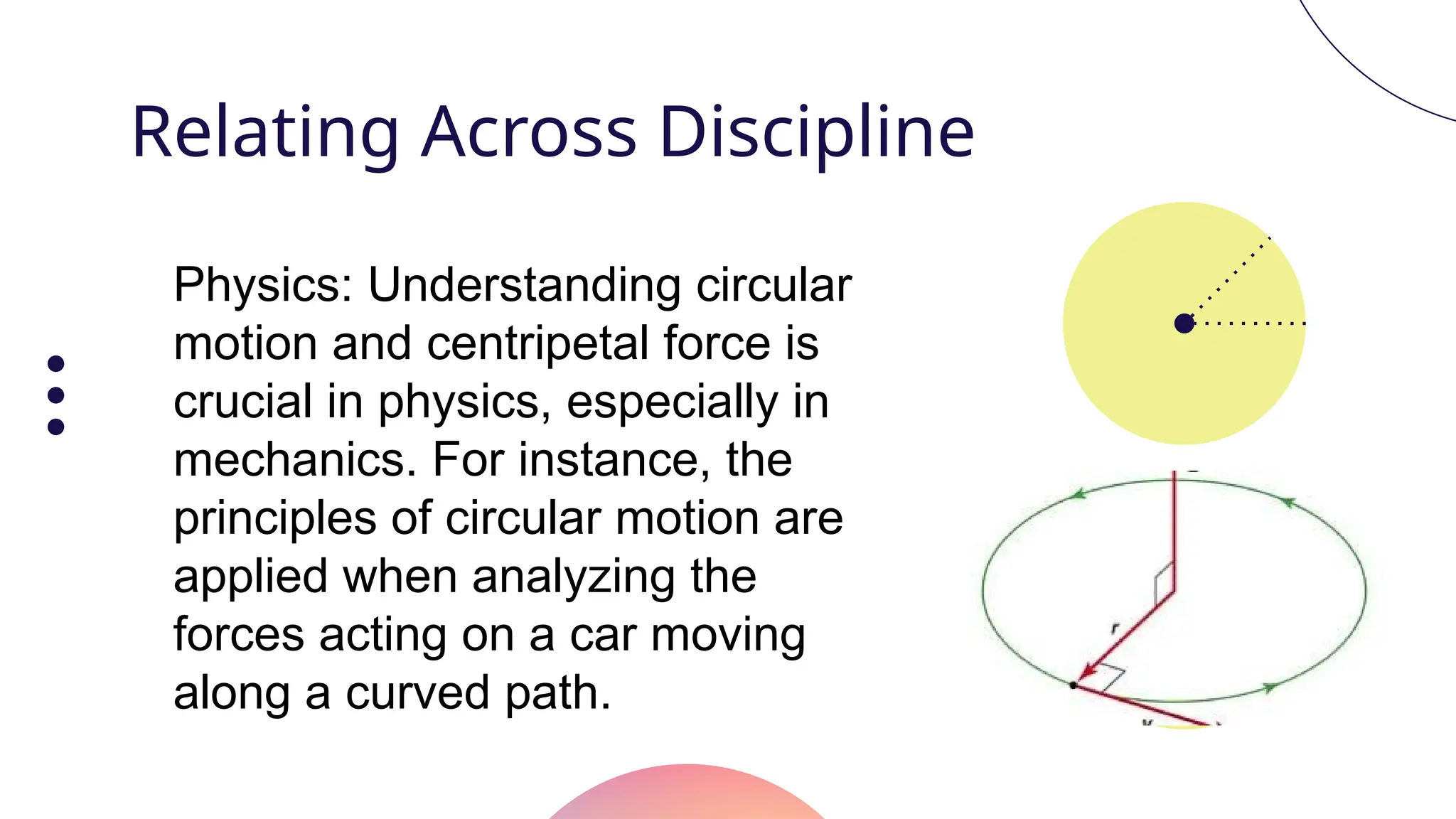
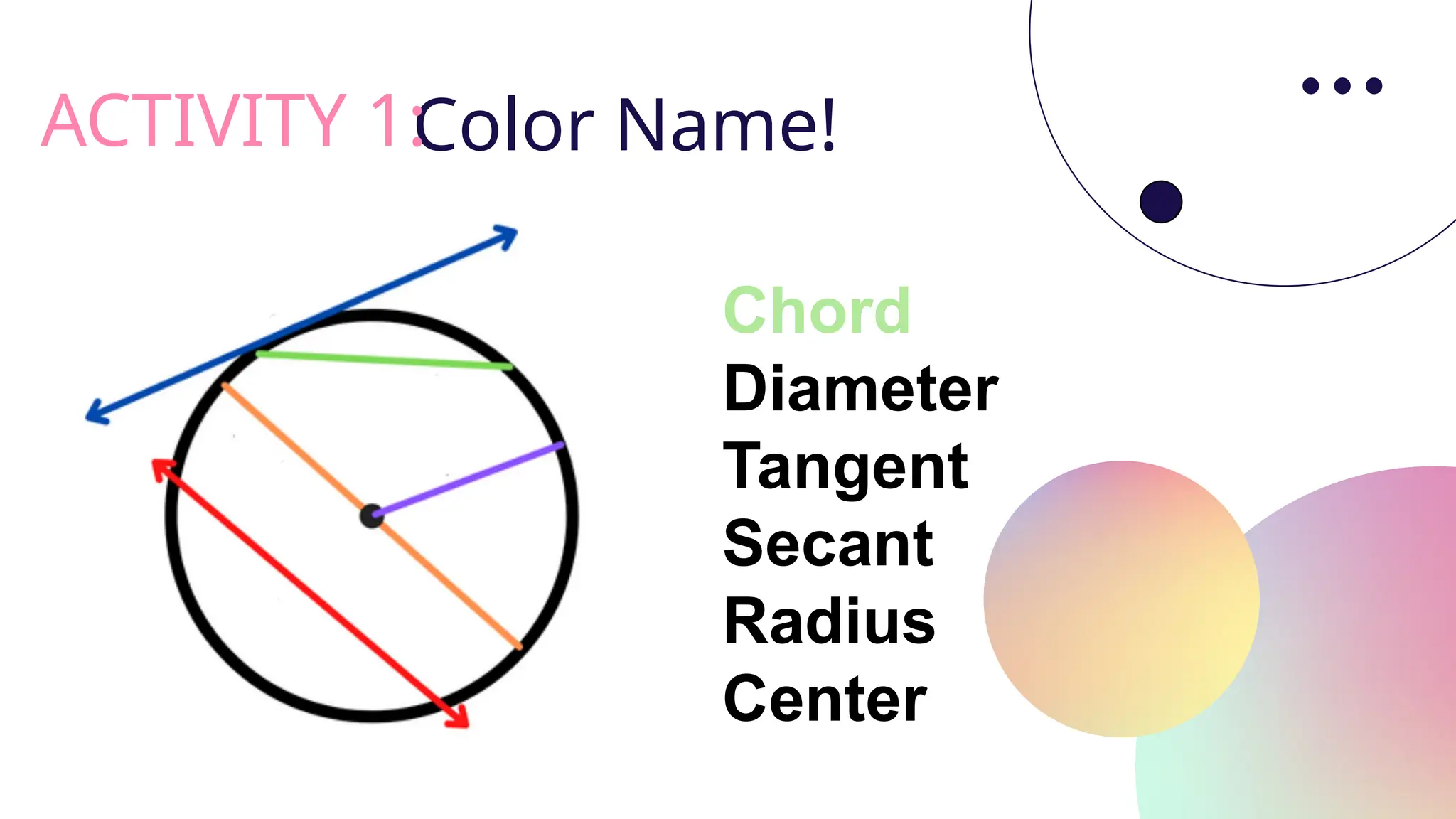
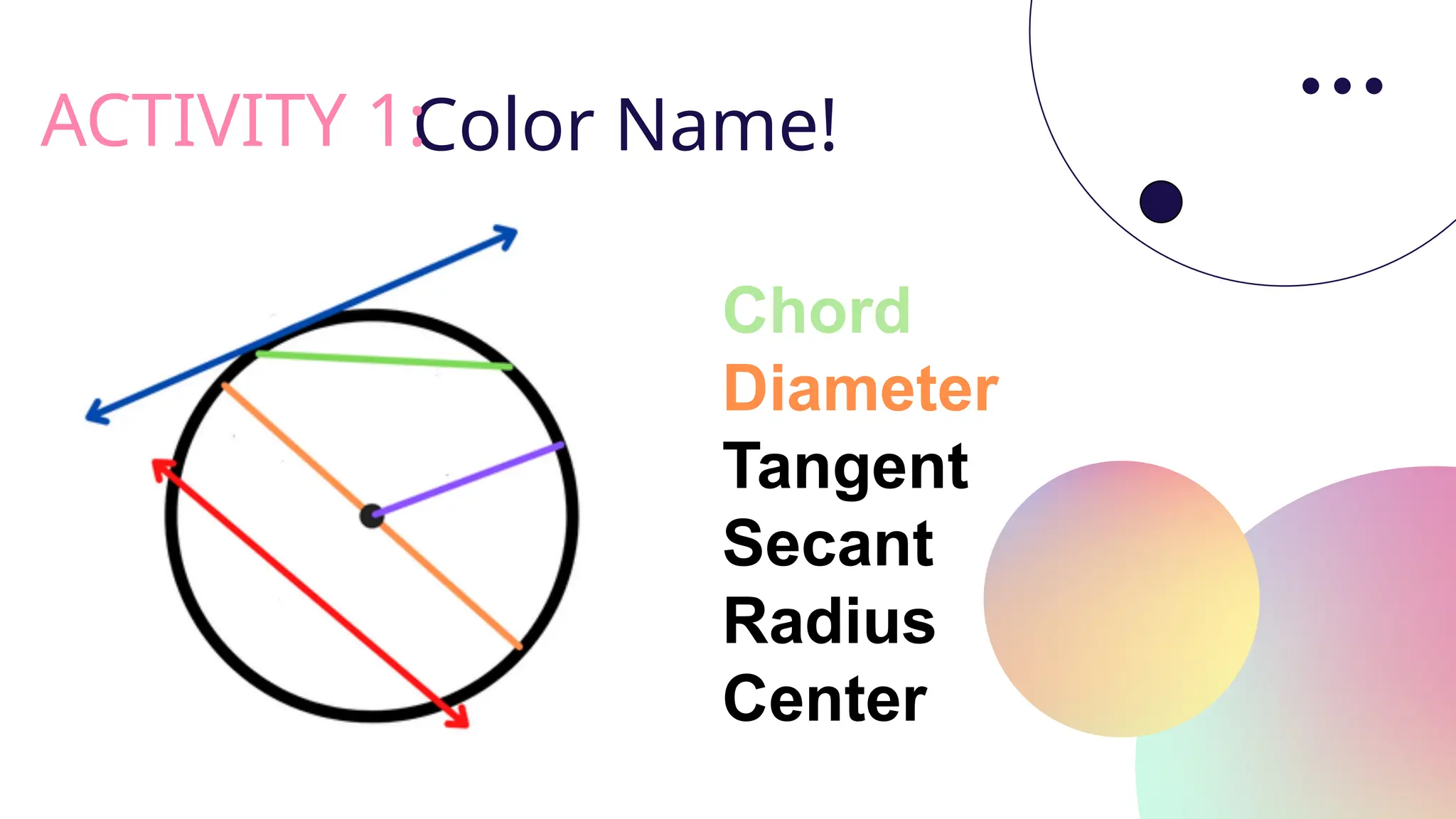
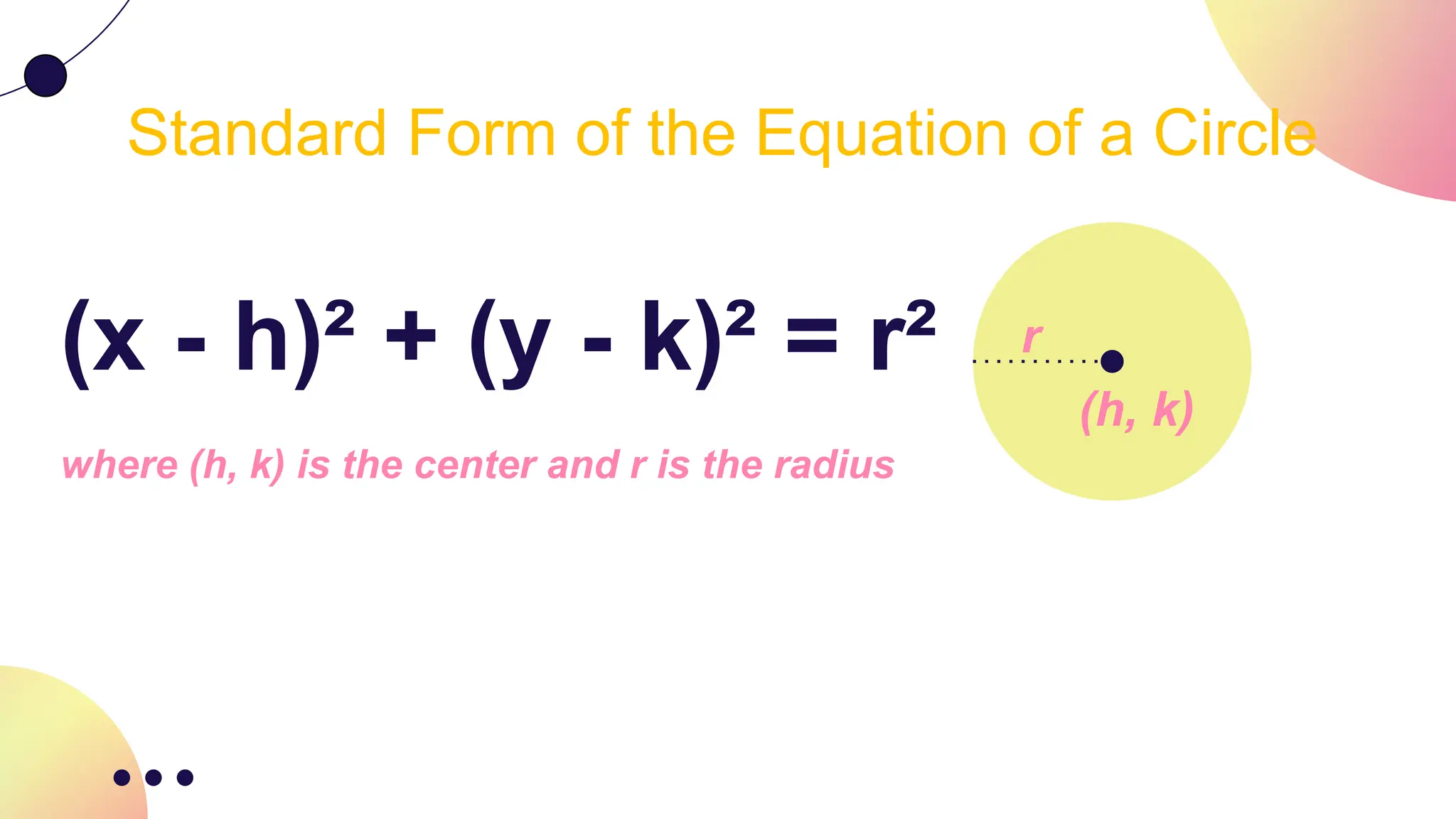
The document provides an overview of circles in pre-calculus, including definitions, properties, and equations of circles with a focus on their significance in mathematics and real-life applications. It includes group activities aimed at helping students understand the concepts better and highlights the relevance of circles in fields like engineering and astronomy. The standard form for the equation of a circle is also presented, along with several examples.











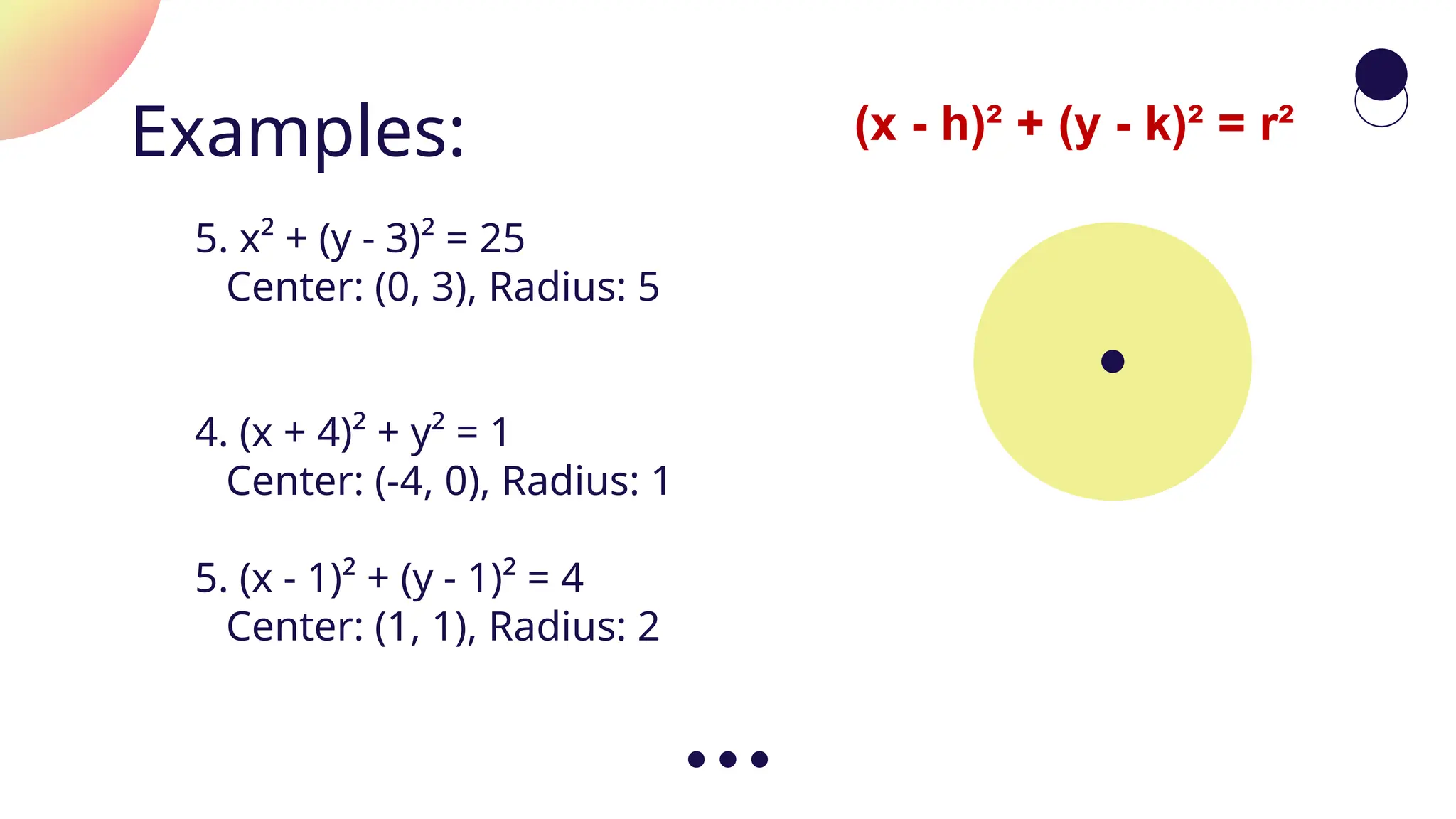
![Examples:
1: Circle with center at (0, 0)
and radius 5:
(x-0)² + (y-0)² = (5)²
x² + y² = 25
2. Circle with center at (3, -2)
and radius 4:
(x - 3)² + [y -(- 2)]² = (4)²
(x - 3)² + (y + 2)² = 16
(x - h)² + (y - k)² = r²
x² + y² = r²](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parts-of-a-circle1-240805031020-c030fd97/75/Pre-calculus_Conic-Sections_Circles-pptx-15-2048.jpg)
![Examples:
3. Center: (0, 0), Radius: 4
(x - h)² + (y - k)² = r²
(x-0²) + (y-0)² = (40) ²
x² + y² = 16
4. Center: (2, -1), Radius: 3
(x - h)² + (y - k)² = r²
(x-2²) + [y-(-1)]² = (3) ²
(x - 2)² + (y + 1)² = 9
(x - h)² + (y - k)² = r²](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parts-of-a-circle1-240805031020-c030fd97/75/Pre-calculus_Conic-Sections_Circles-pptx-16-2048.jpg)