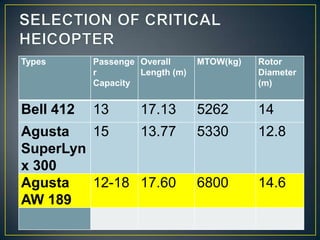
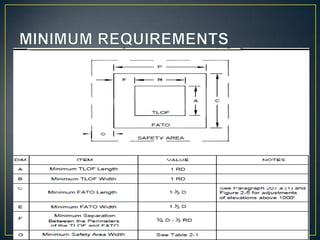
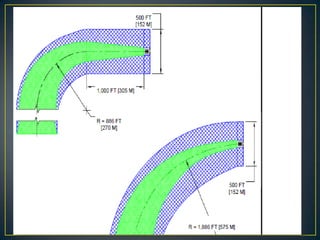
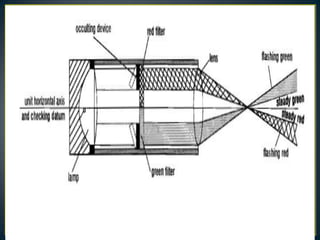
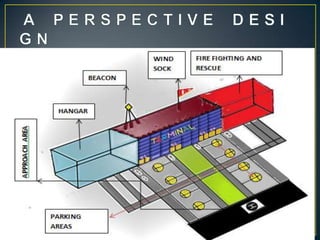
The document details key aspects of heliport design, including site selection and safety requirements for both surface and elevated heliports. It discusses the selection of helicopters, configuration requirements for taxiways and visual aids, and safety considerations, including fire-fighting services and security measures. Additionally, it outlines specifications for various operational needs like lighting, communications, and weather observation systems.