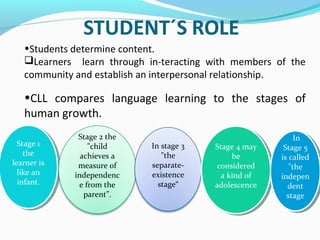
Community Language Learning (CLL) is a language teaching method developed by Charles A. Curran in 1955 that incorporates psychological counseling techniques, focusing on the whole person by considering students’ emotions alongside intellect. In CLL, teachers take on the role of counselors, creating a supportive, non-threatening environment where students can independently choose topics and engage in conversation, fostering fluency and confidence. While it offers advantages like student engagement and elementary independence, challenges include reliance on the teacher and managing varied language levels among students.