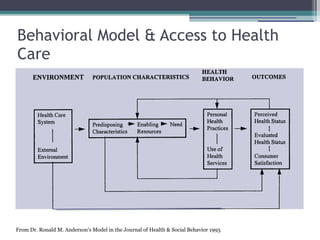
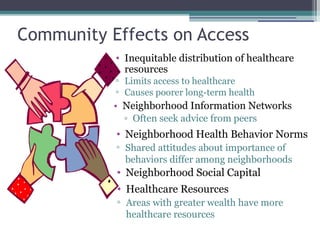
The document discusses how social and environmental factors impact health and access to healthcare. It outlines that where someone lives determines their health based on things like water quality, smoking bans, food access, and healthcare resources. Access to healthcare varies across communities based on race, income, education, insurance status, and disability. A behavioral model shows how predisposing characteristics, enabling factors, and health needs influence healthcare utilization. Neighborhood characteristics like socioeconomic disadvantage, physical environments, and social networks can decrease access to primary care and increase unmet needs. Investing in community prevention and changing neighborhood environments can increase access and produce healthcare savings.