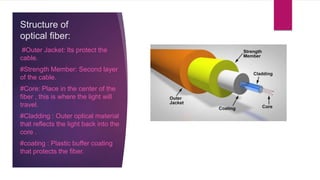
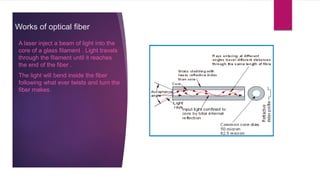
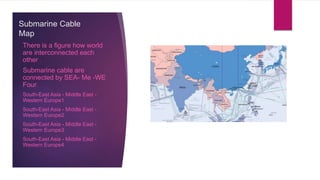
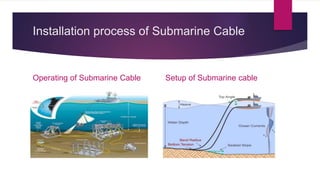
This document discusses different communication media including optical fiber, submarine cables, and wireless networks. It provides details on the structure and workings of optical fiber, including its core, cladding, and protective coatings. Submarine cables are described as cables laid on the ocean floor to carry telecommunications signals across bodies of water. Their modern construction and the process for installing them underwater is outlined. Wireless networks avoid the need for cables by using technologies like radio waves, light, and cellular networks to connect devices over short and long ranges.