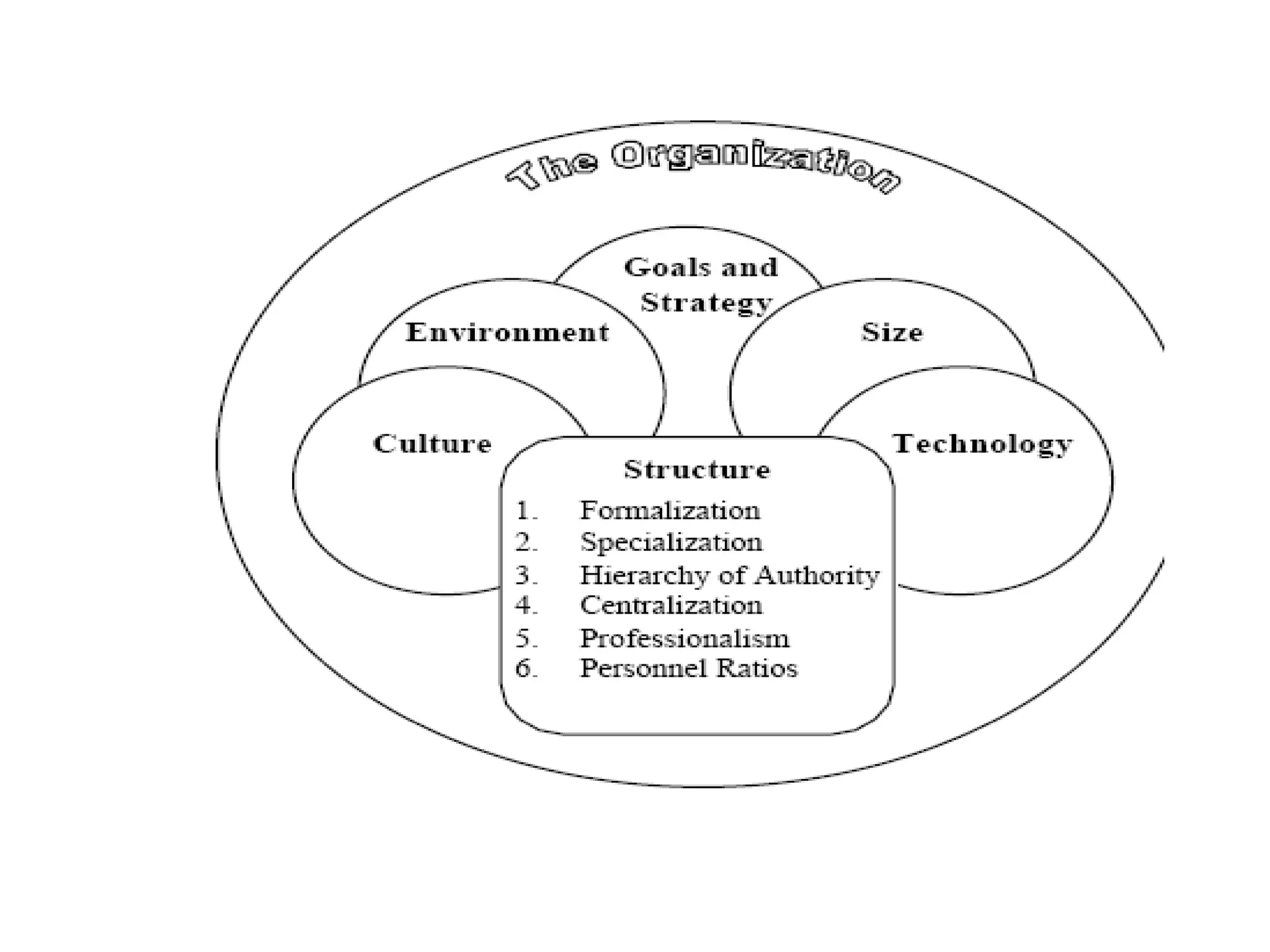
Psychological, semantic, and environmental barriers can hinder effective communication. Psychological barriers include unjust assumptions, a "know-it-all" attitude, snap reactions, indifference, an unwillingness to learn, defensiveness, and fear. Semantic barriers involve word connotations, fluency differences, jargon, and vocabulary level differences. Environmental barriers include issues with time, space, place, and communication medium. Organizations are social entities designed to achieve goals through coordinated activities linked to their external environment. They have formal goals and informal aims as well as formal and informal organizational structures.