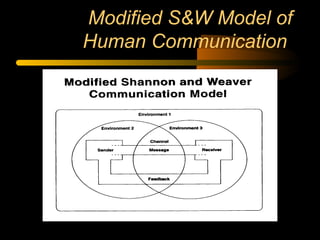
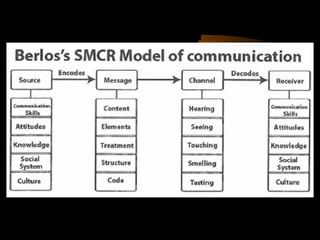
This document discusses several models of communication including the Shannon and Weaver model, a modified Shannon and Weaver model, and Berlo's SMCR model. The Shannon and Weaver model describes the basic elements in a communication process. The modified version adds different types of noise that can interfere. Berlo's SMCR model outlines four key elements - source, message, channel, and receiver - and describes factors that influence each element, such as communication skills, attitudes, knowledge, and culture. Models help simplify and provide an organized framework for understanding complex communication processes.