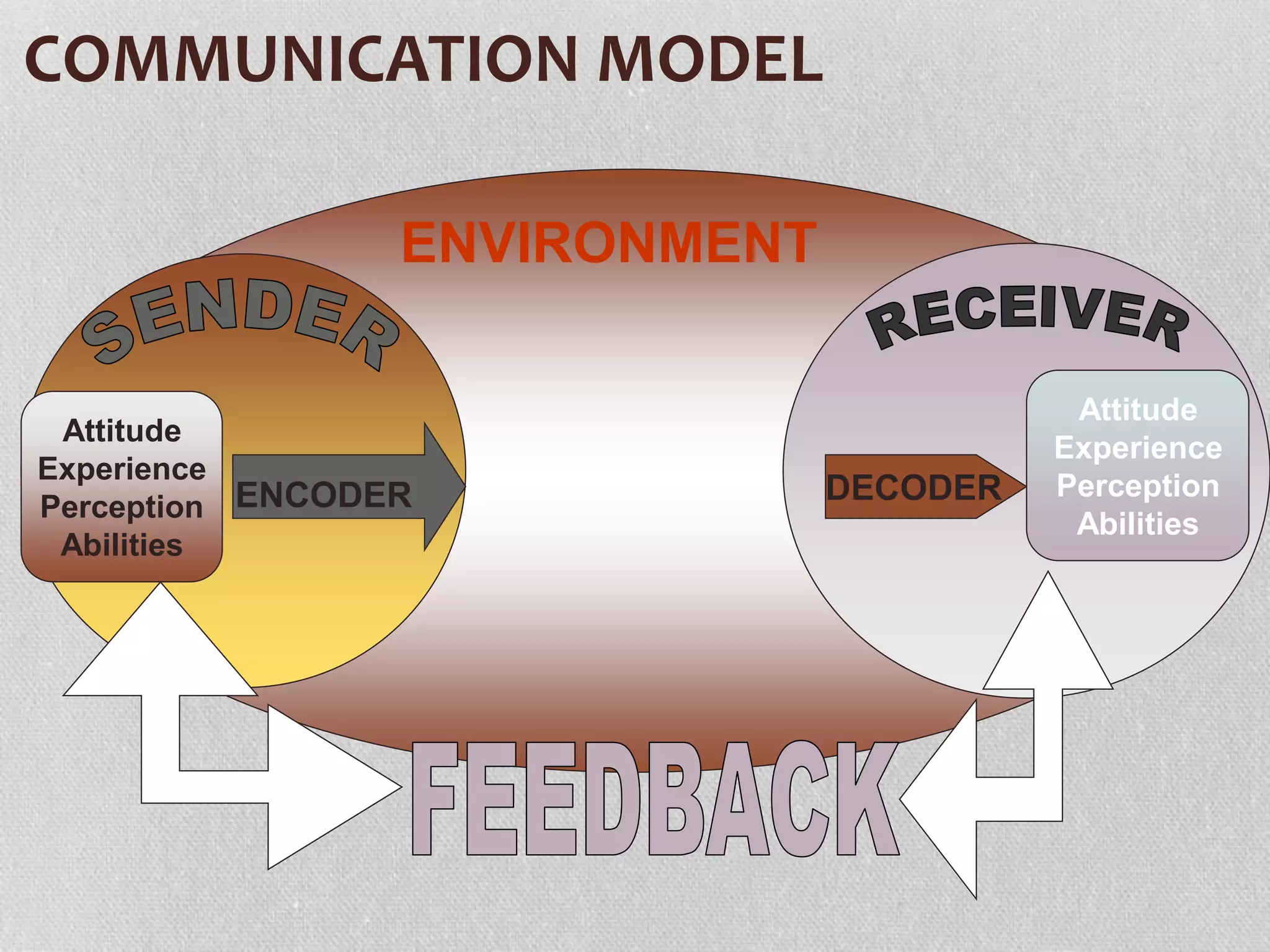
The presentation by Dr. Ahmed Easa outlines the objectives of health education, communication, and counseling, emphasizing the importance of effective communication in healthcare. It details communication models, barriers, and strategies for improving both verbal and non-verbal communication between healthcare providers and patients. Additionally, it explains the components and principles of counseling and health education, highlighting the roles of educators and methods for effective message delivery.