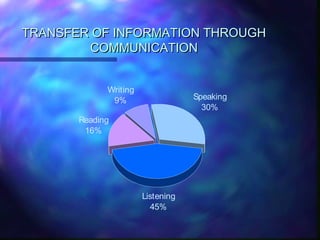
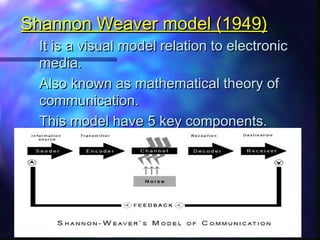
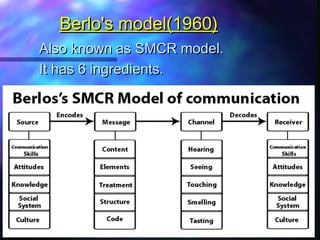
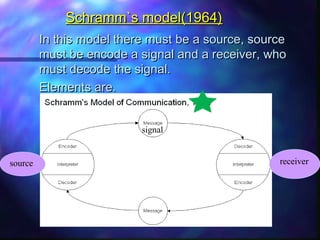
The document discusses communication and provides definitions of communication from various scholars. It describes communication as a dynamic process of sending and receiving messages to share meanings. It also defines different types of communication such as verbal, non-verbal, and levels of communication like interpersonal, intrapersonal, organizational, and mass communication. The document further explains models of communication, principles of effective communication, barriers to communication, and the transfer of information through the communication process.