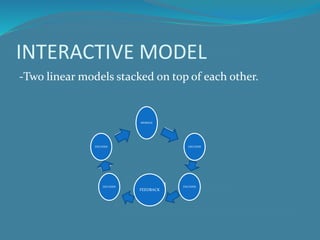
This document defines communication and its key elements. It discusses communication as a process of sharing messages between people across different contexts and cultures. The core elements of communication are the sender, message, encoding, channel, receiver, decoding, and feedback. It also outlines different types of communication models, including the Shannon-Weaver, linear, interactive, and transactional models.