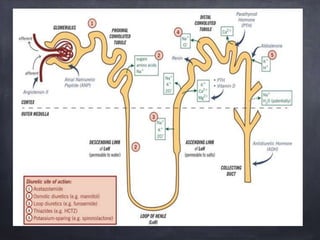
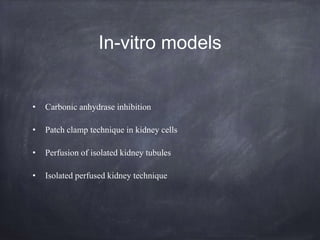
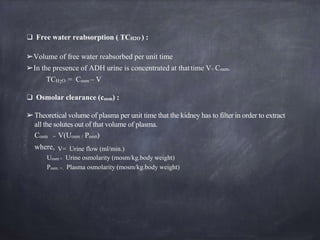This document provides information on various screening methods used to evaluate diuretic and saluretic activity of drugs. It describes metabolic cage studies in rats to measure urine output and electrolyte excretion. The Lipschitz test evaluates diuretic potency in rats by comparing urine volume and sodium excretion after test drug versus urea treatment. Saluretic activity is assessed by measuring sodium and chloride excretion in rats. Clearance studies in dogs provide information on drug site of action by measuring effects on water and electrolyte excretion and clearances. Micropuncture and stop-flow techniques directly examine drug impacts on fluid composition and transport along specific nephron segments.