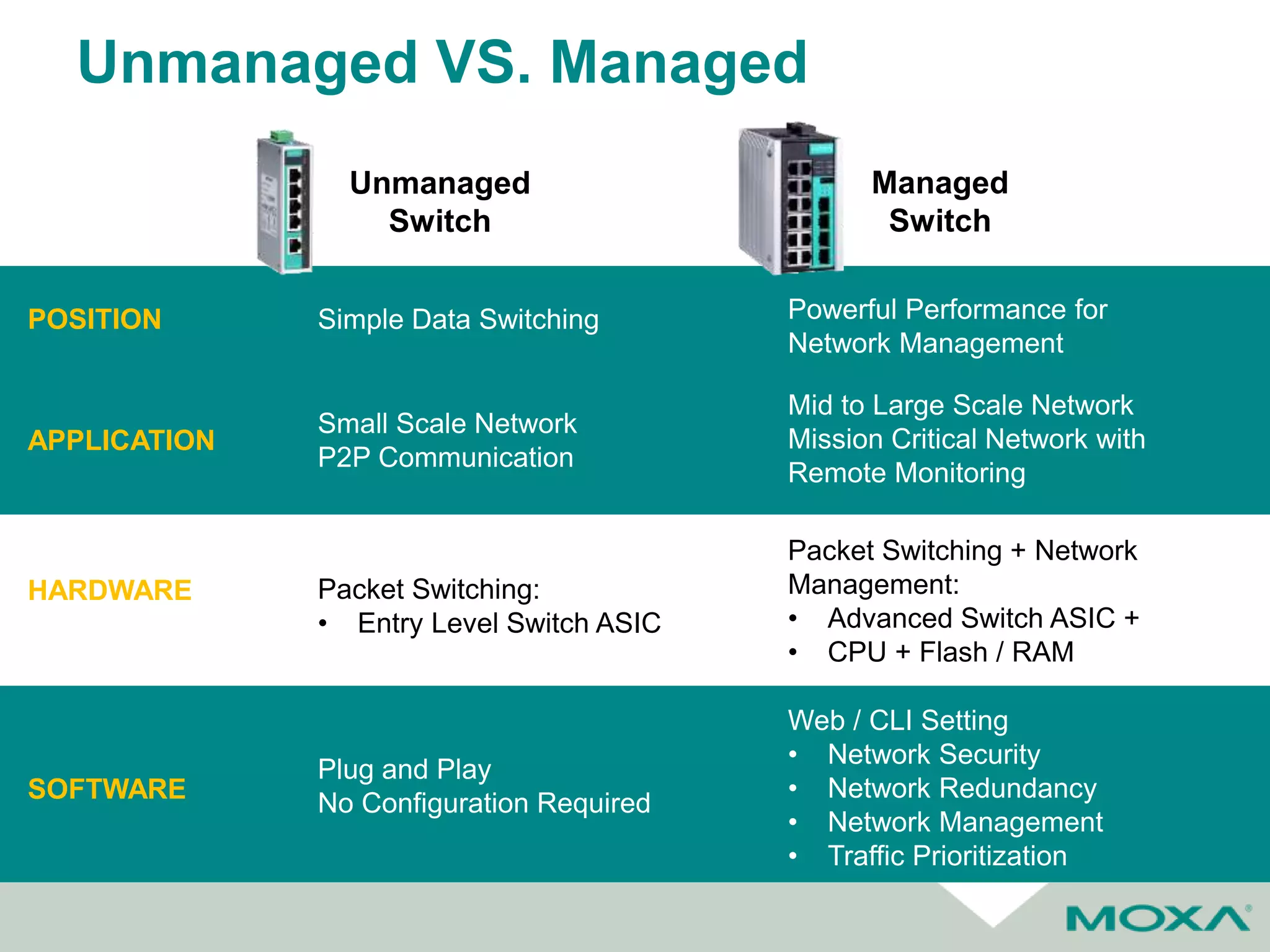
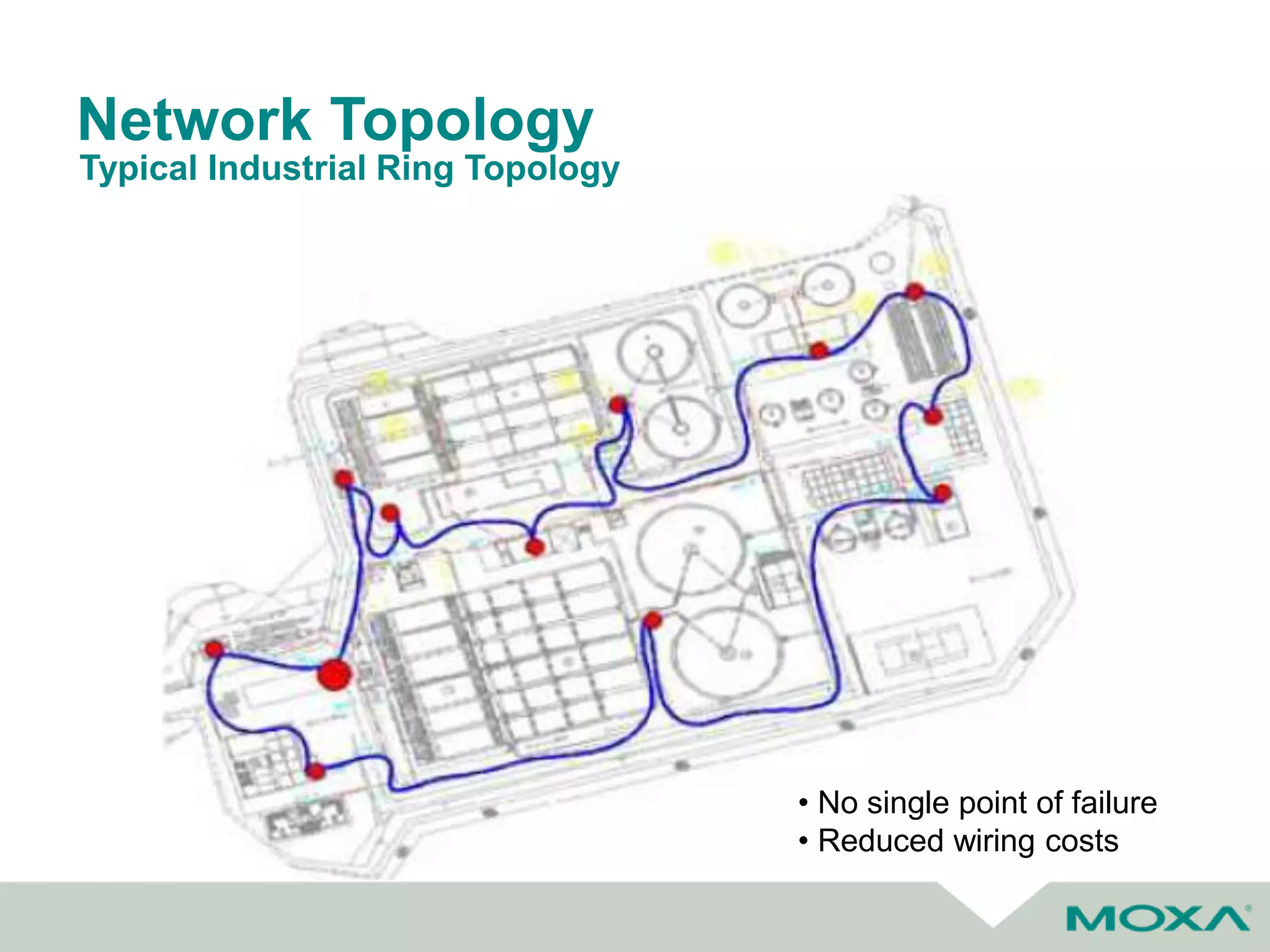
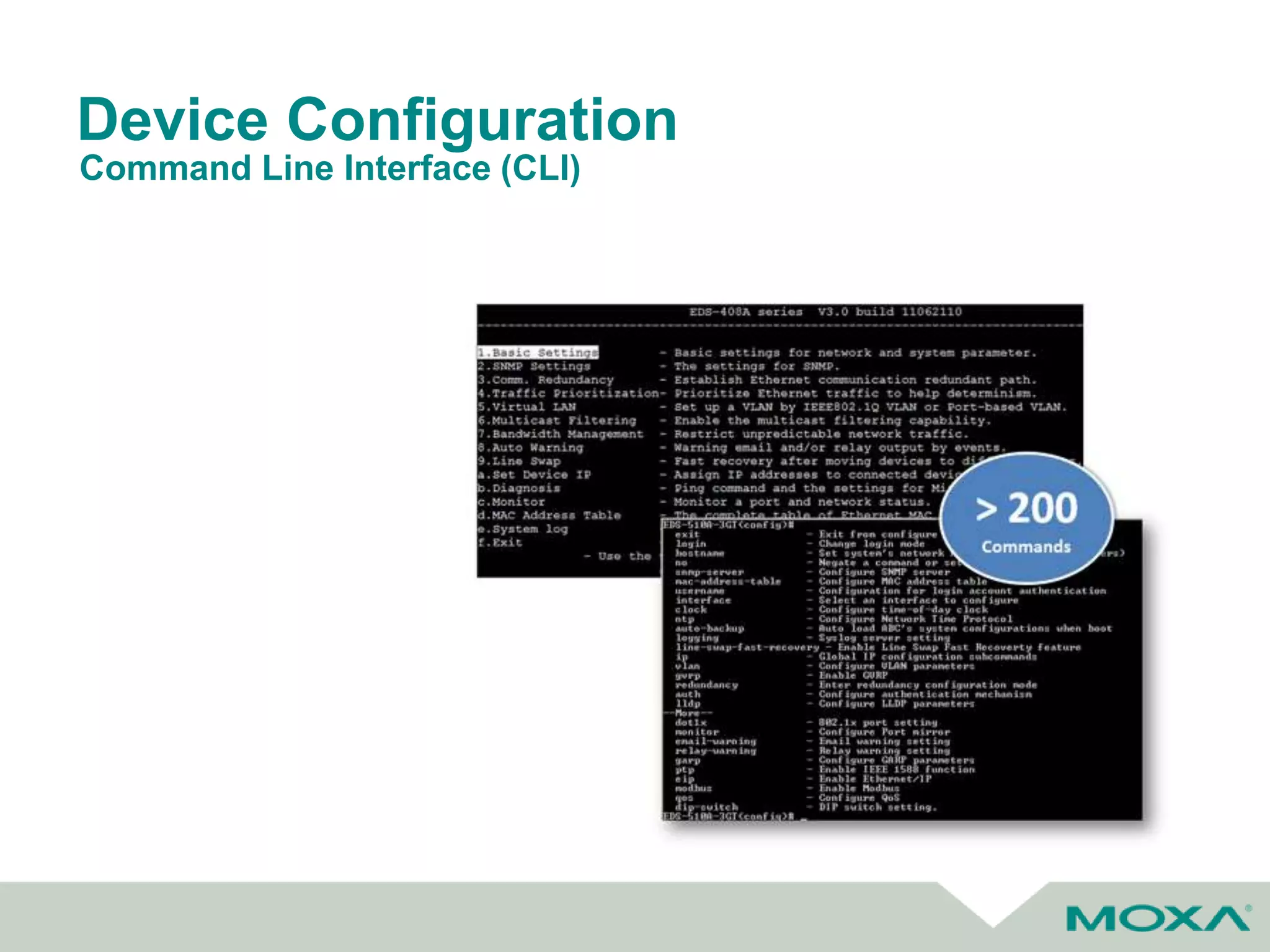
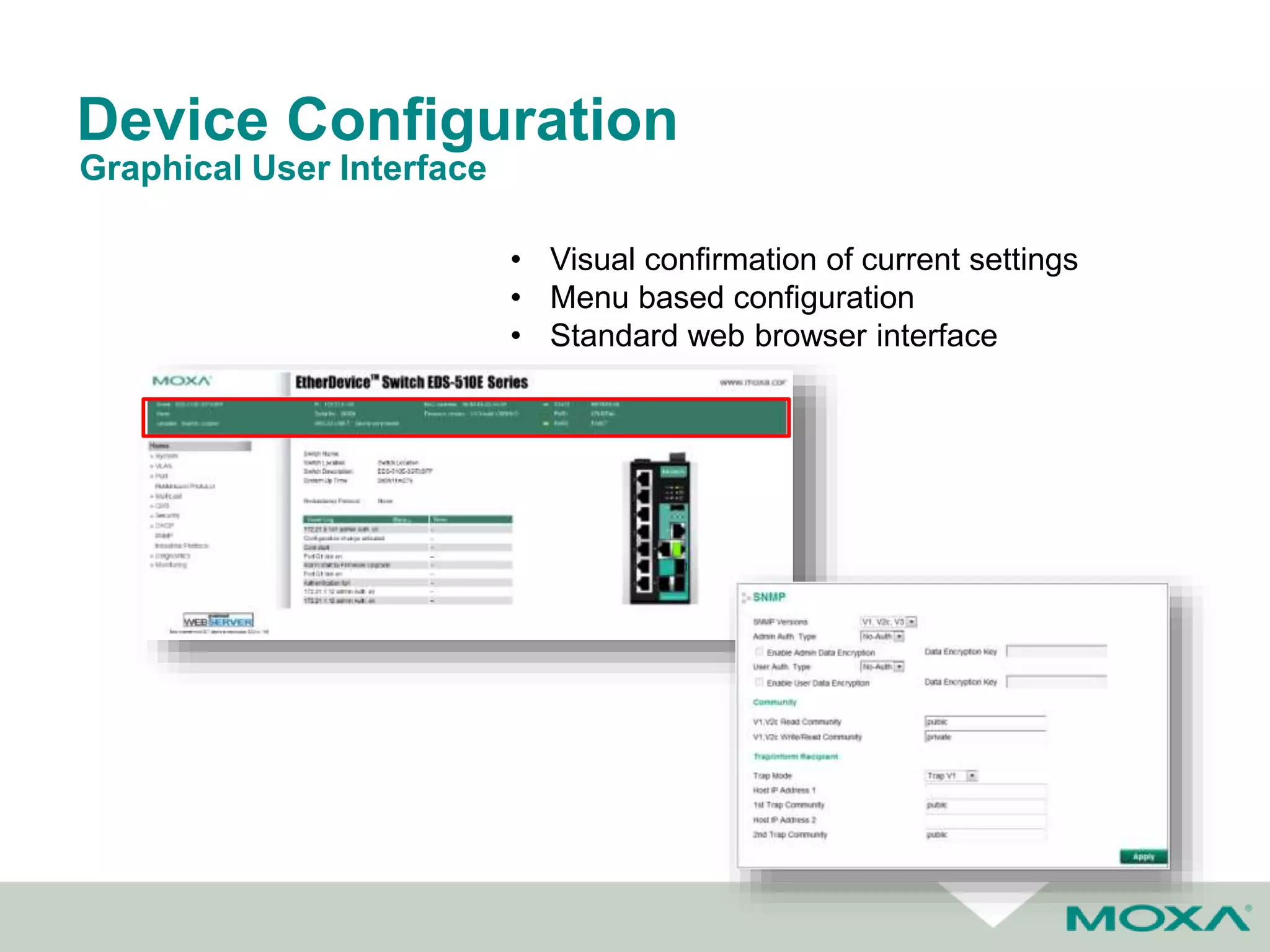
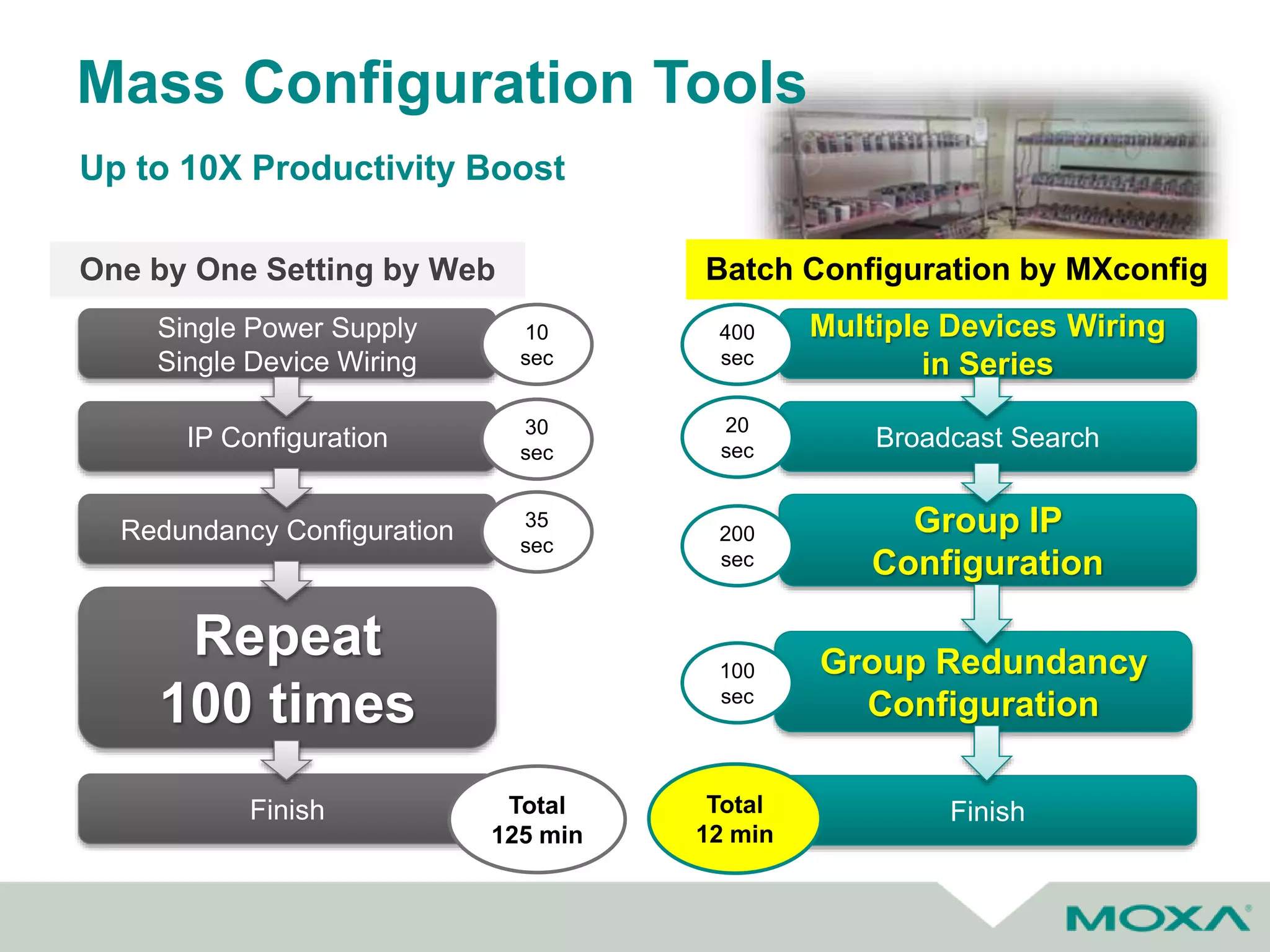
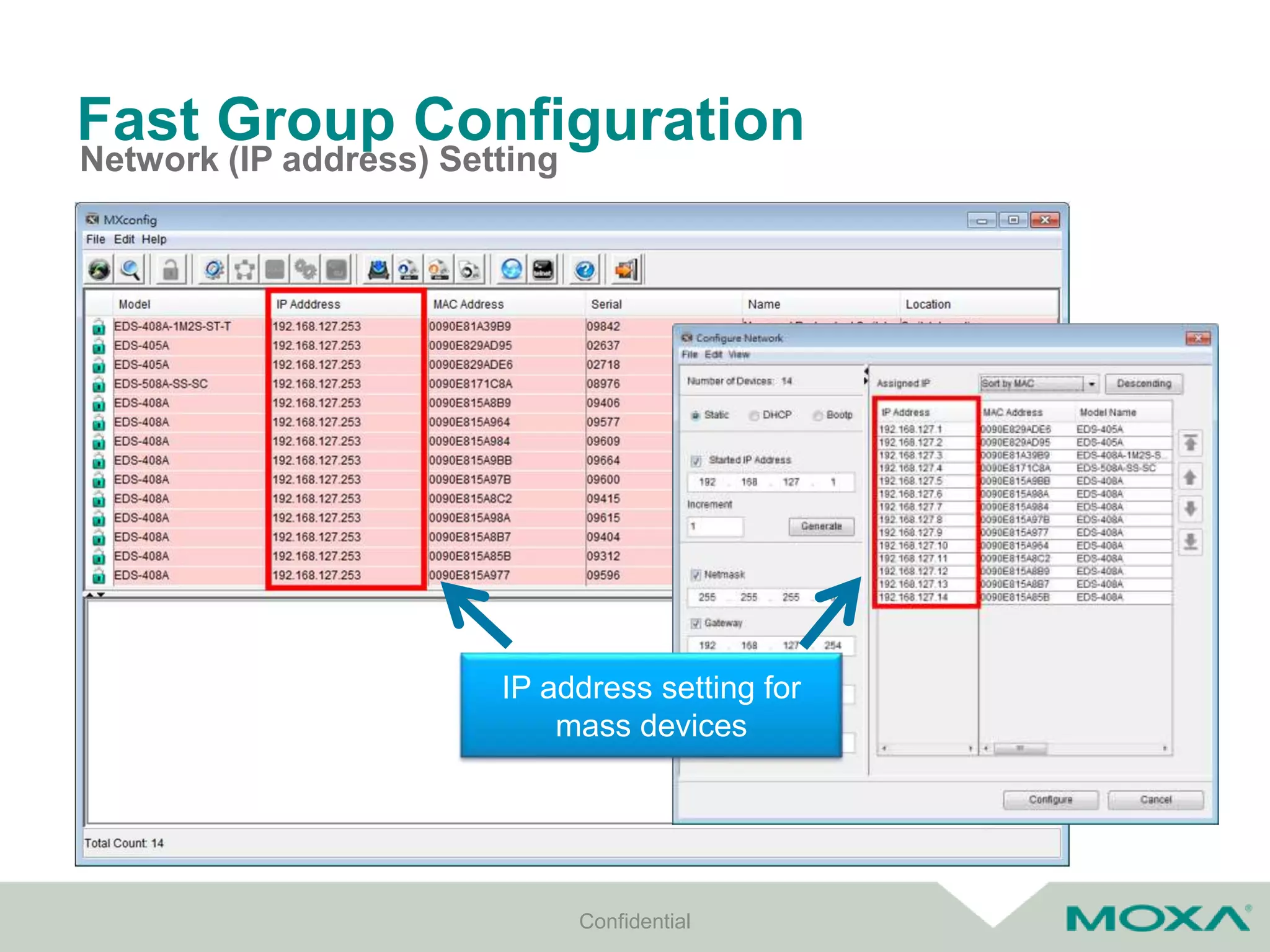
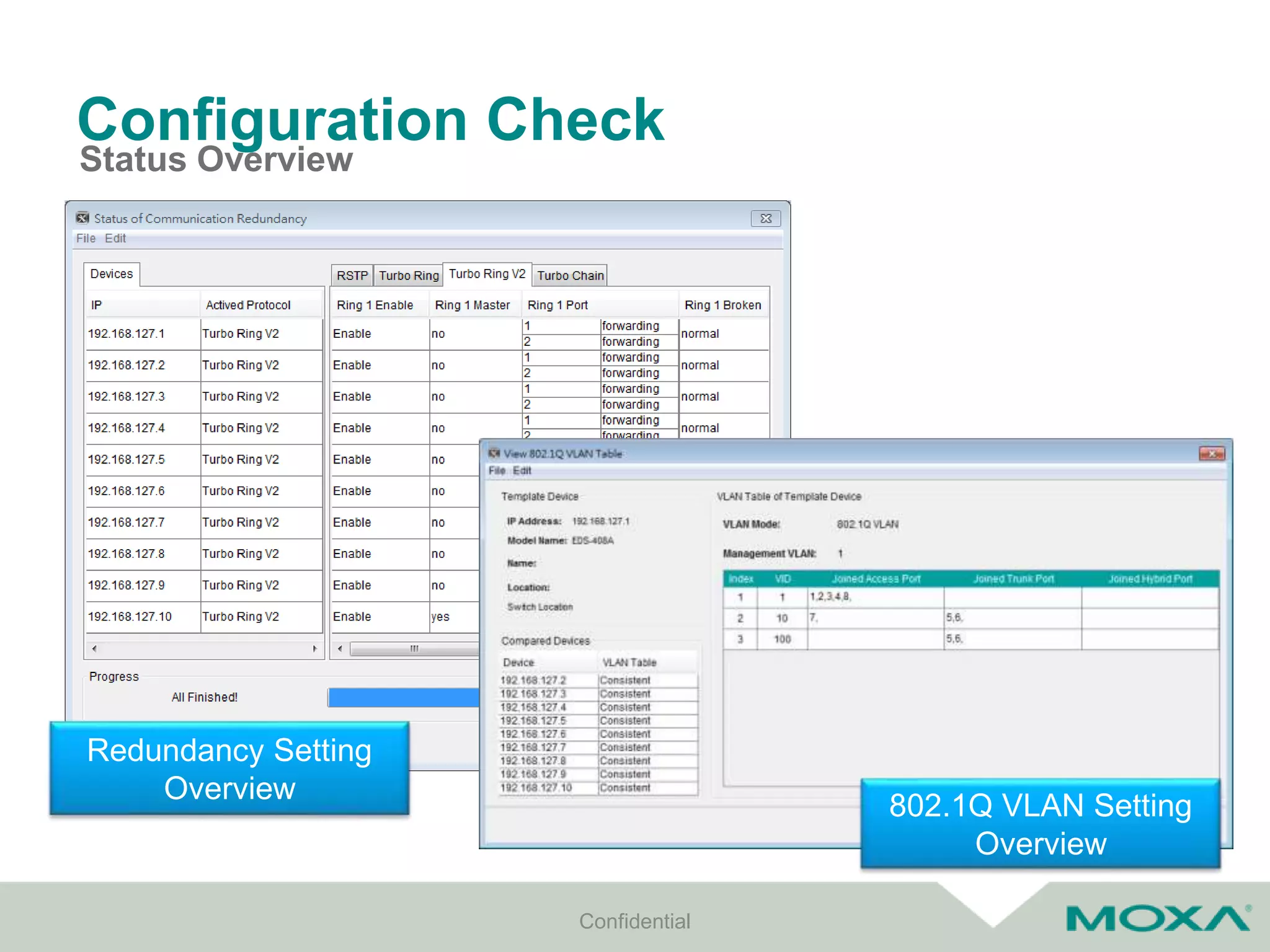
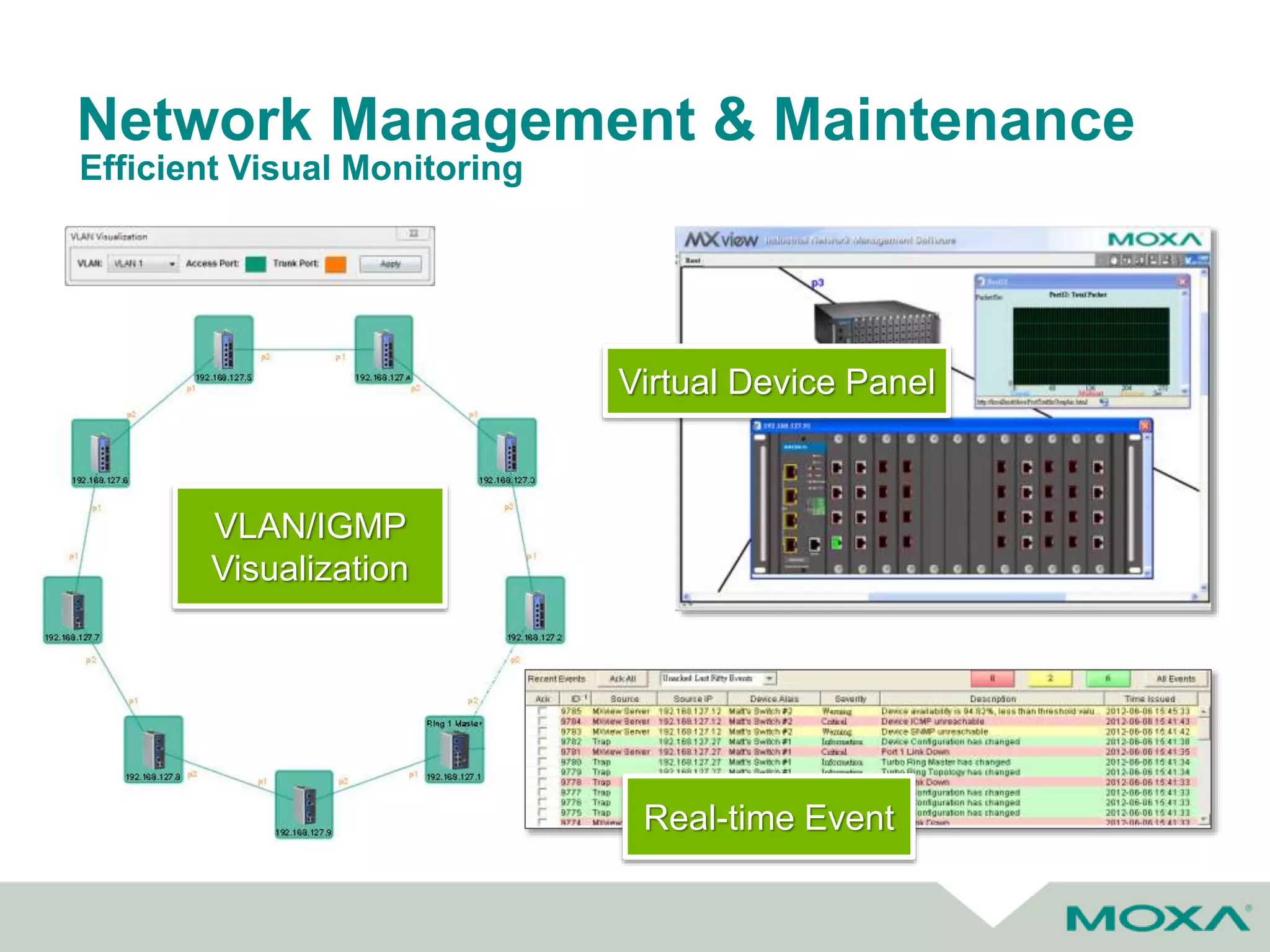
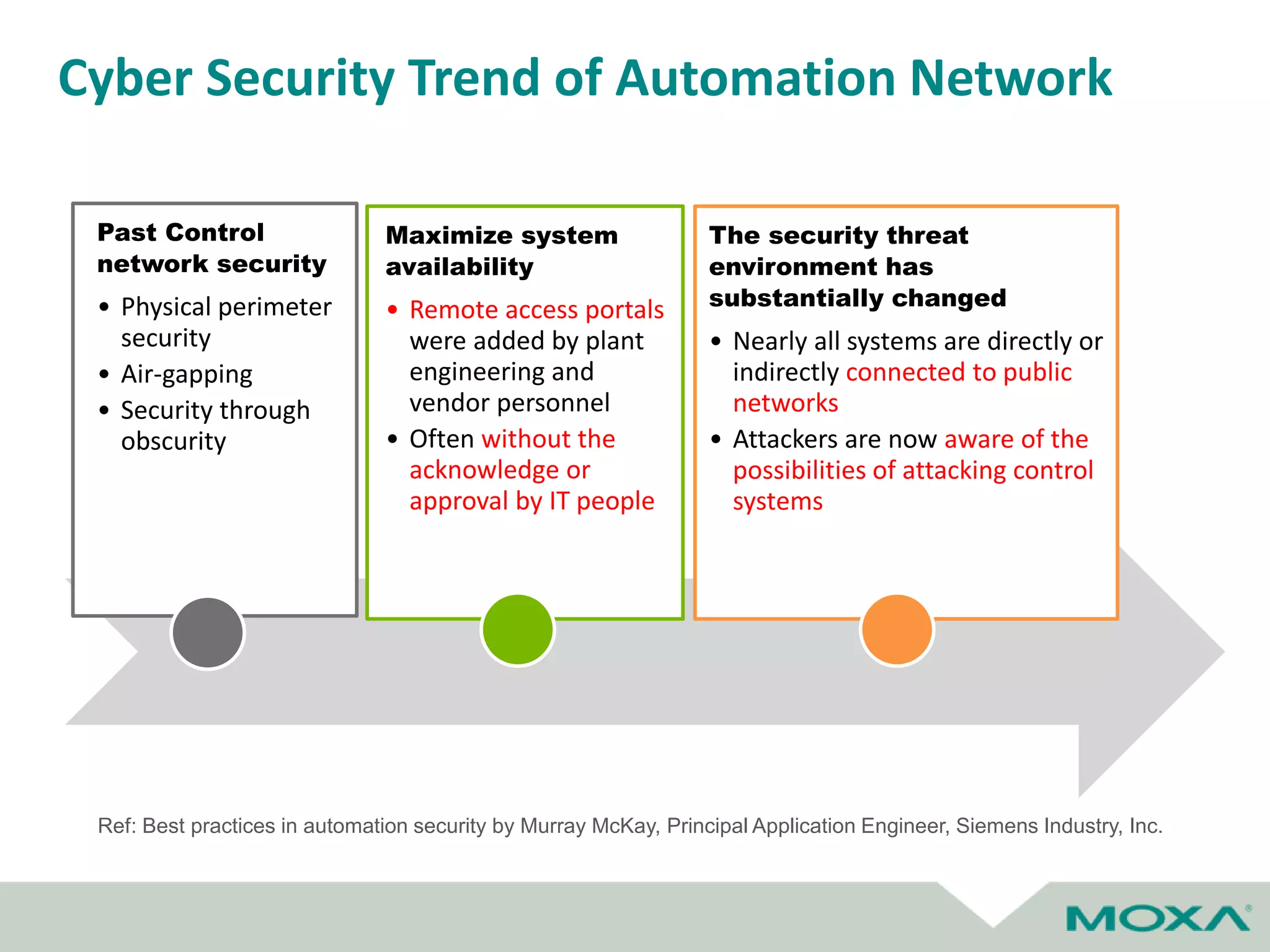
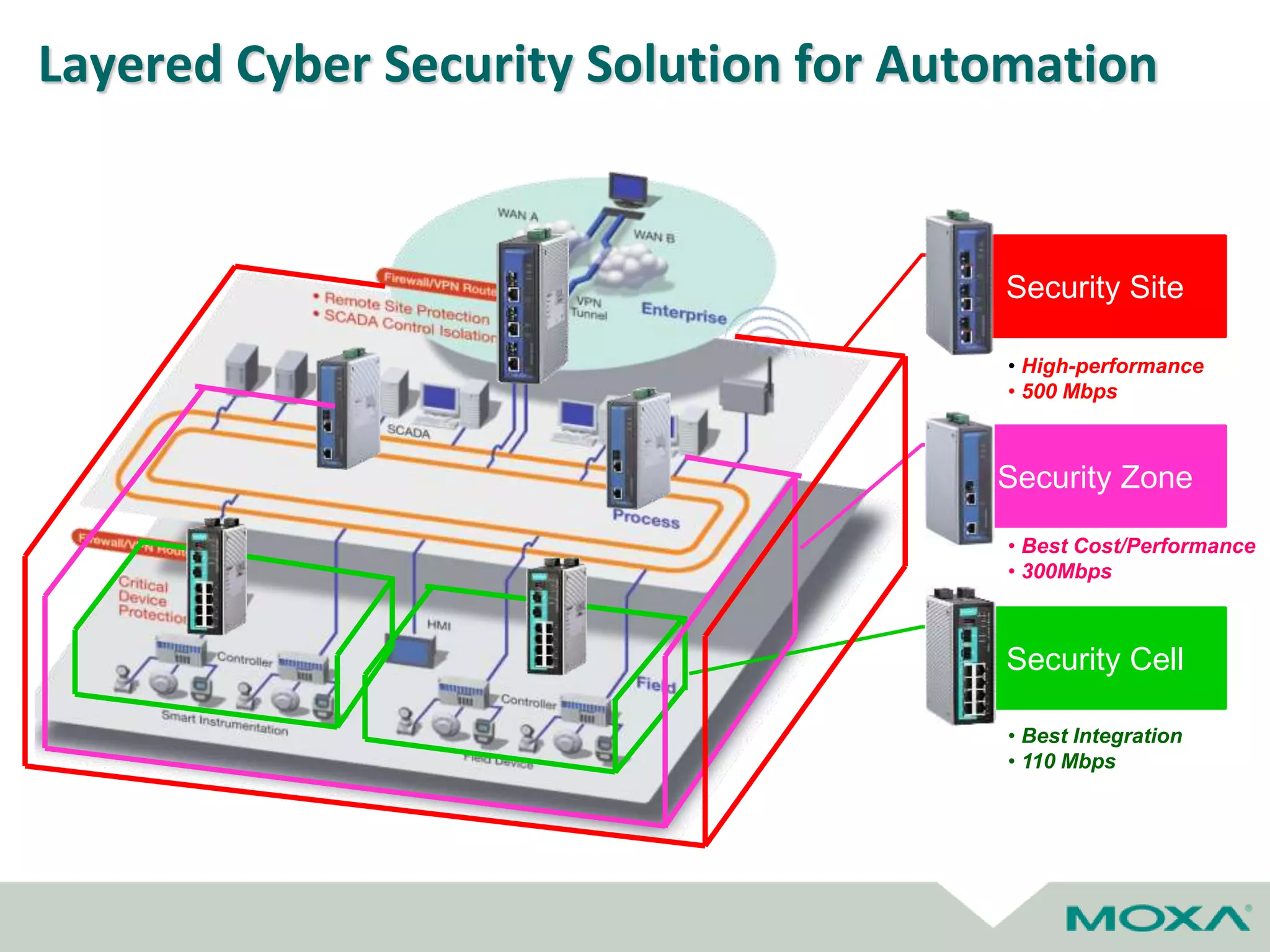
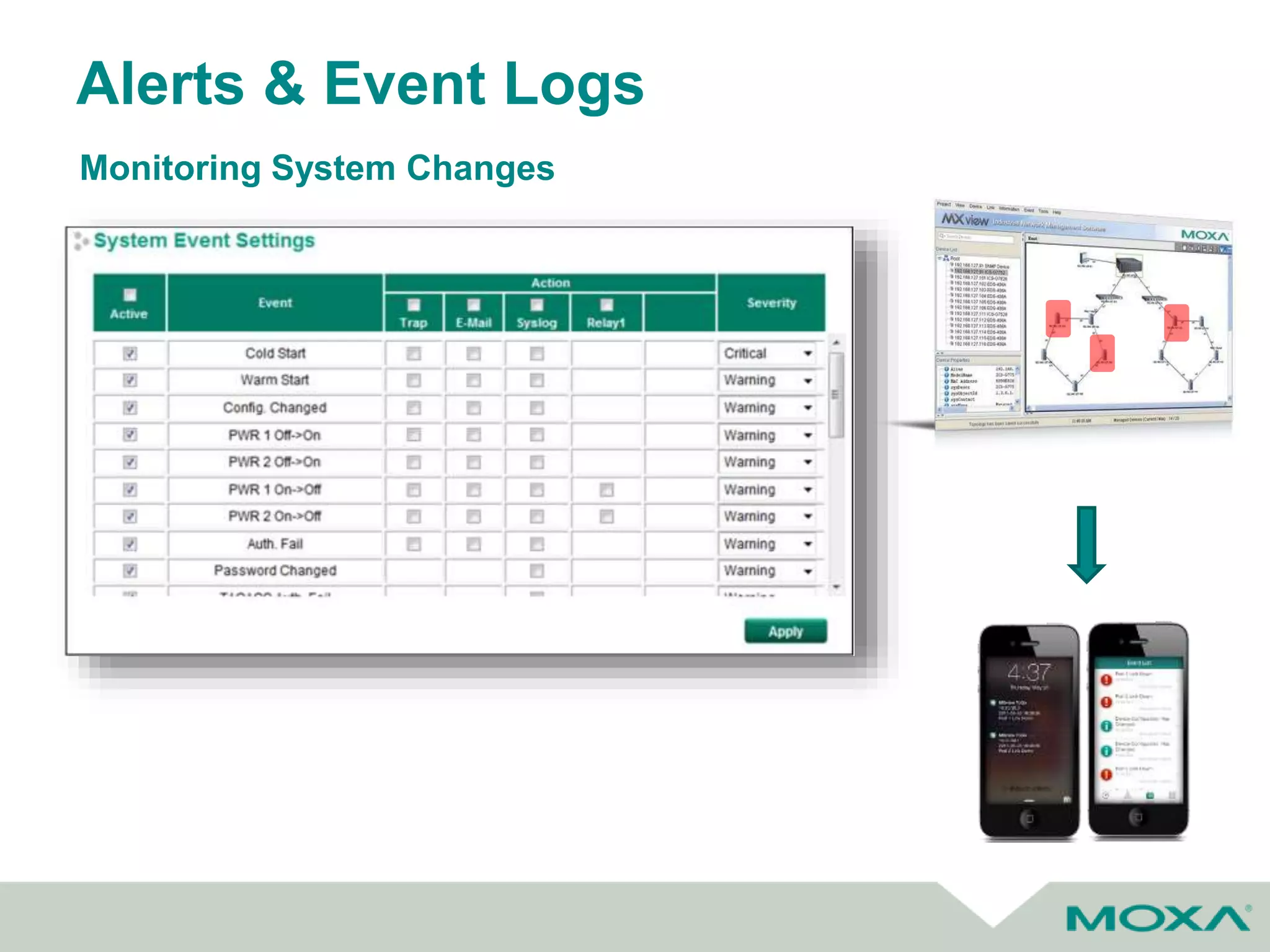
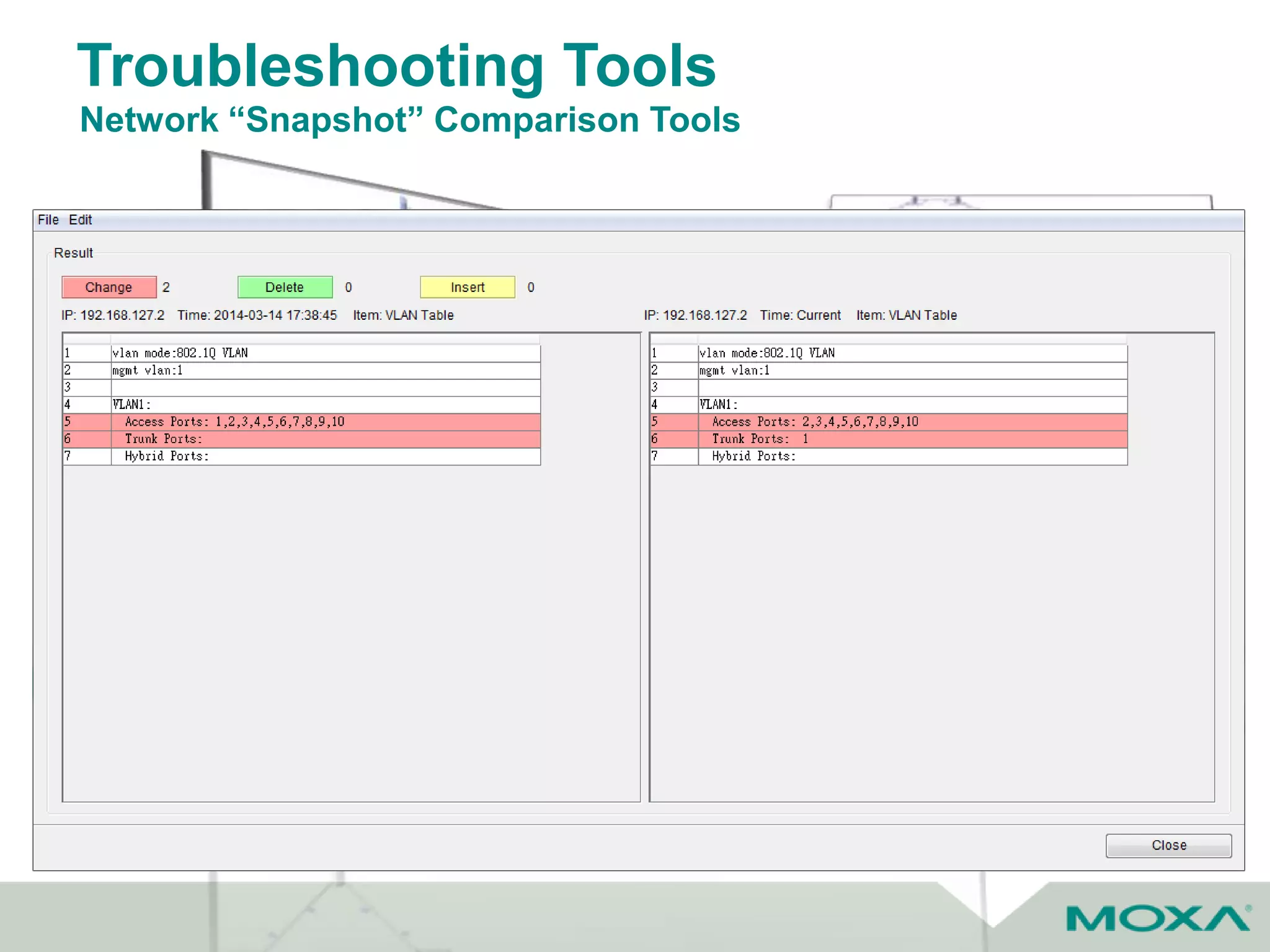
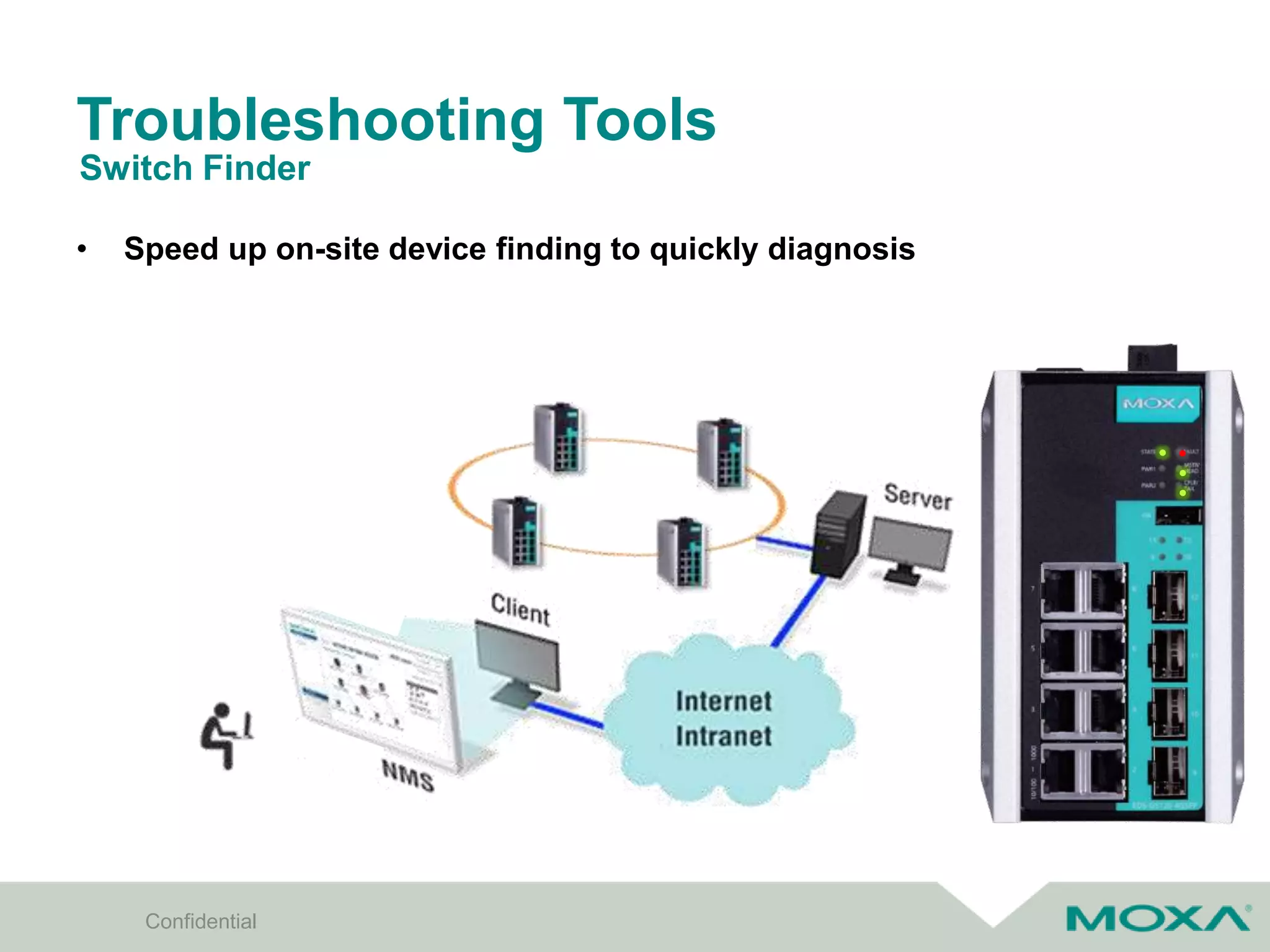
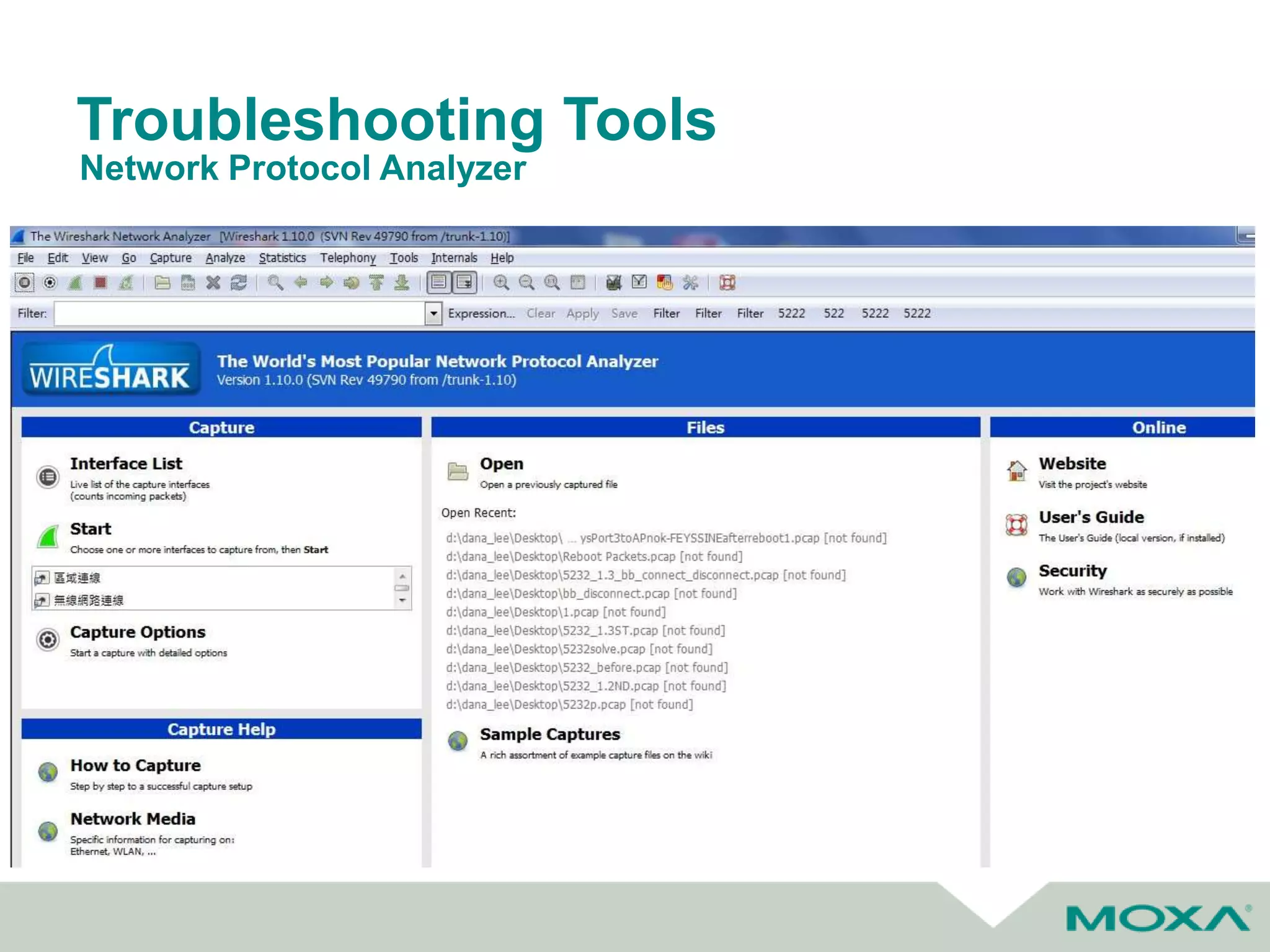
The document outlines best practices for commissioning, managing, and troubleshooting industrial networks, highlighting the unique challenges faced in harsh environments with high availability requirements. It discusses configurations for different network topologies, management tools, and methodologies, emphasizing the importance of security and automation in modern networks. Additionally, it addresses how to minimize downtime through effective monitoring, event management, and troubleshooting techniques.