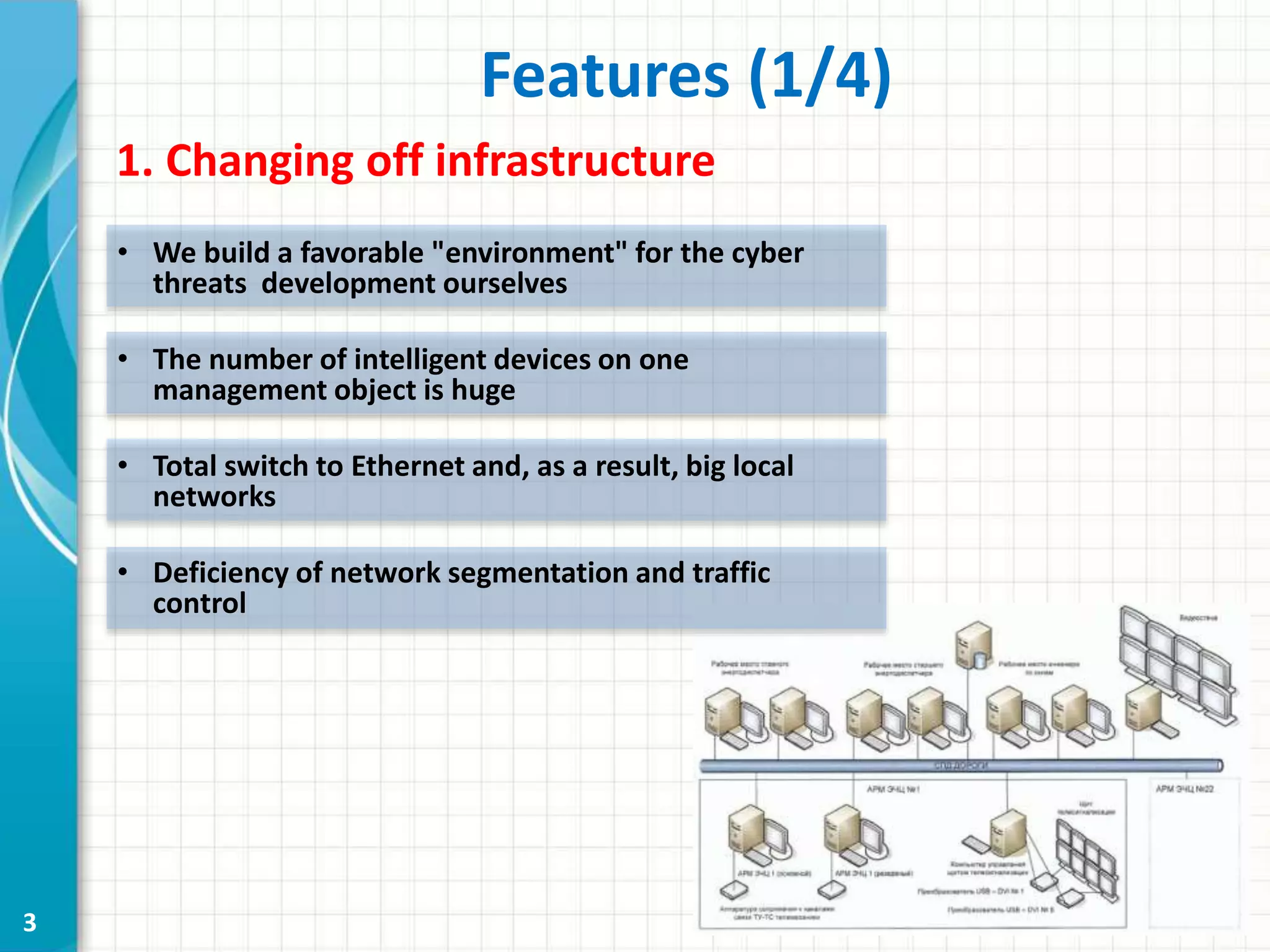
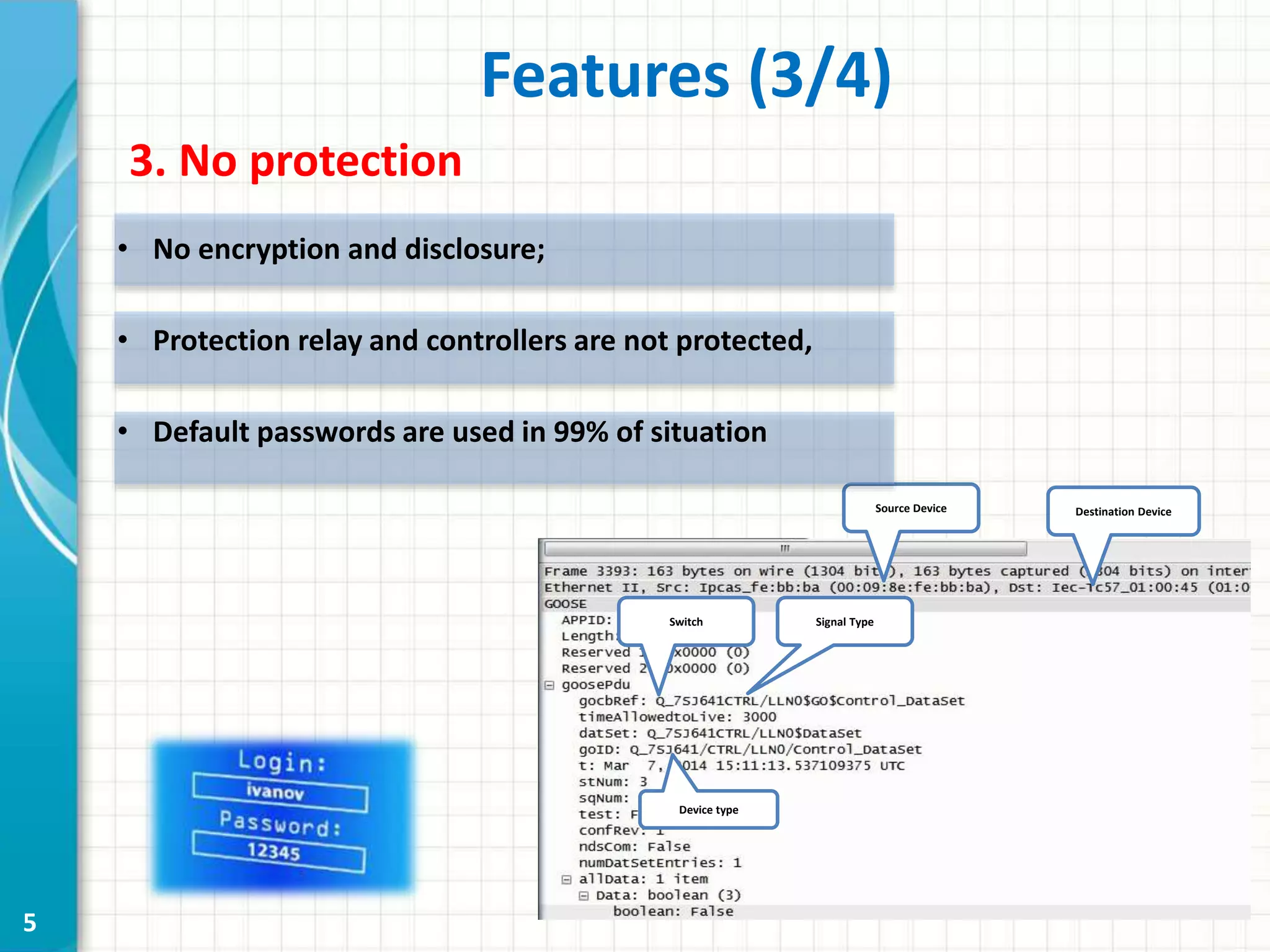
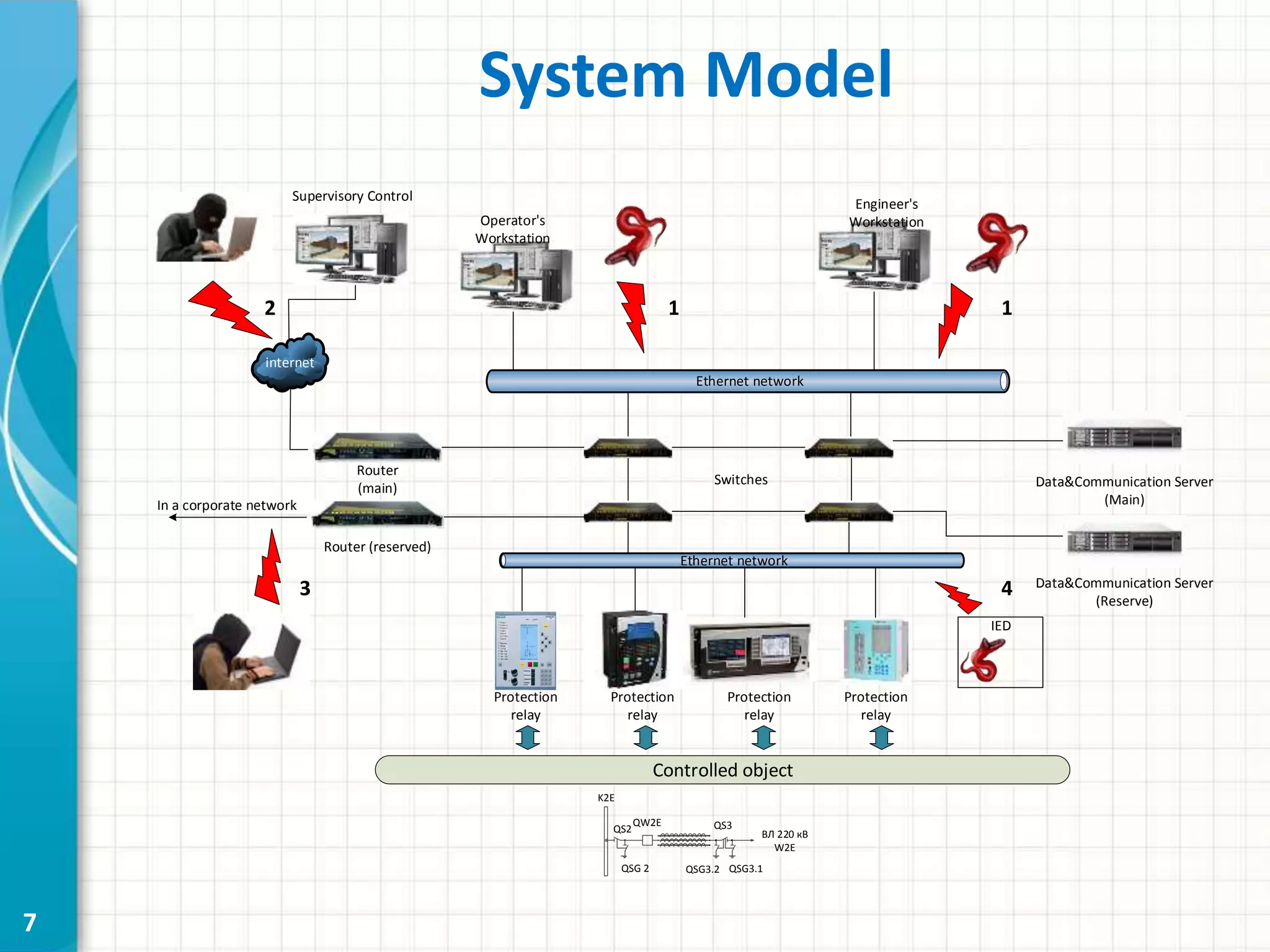
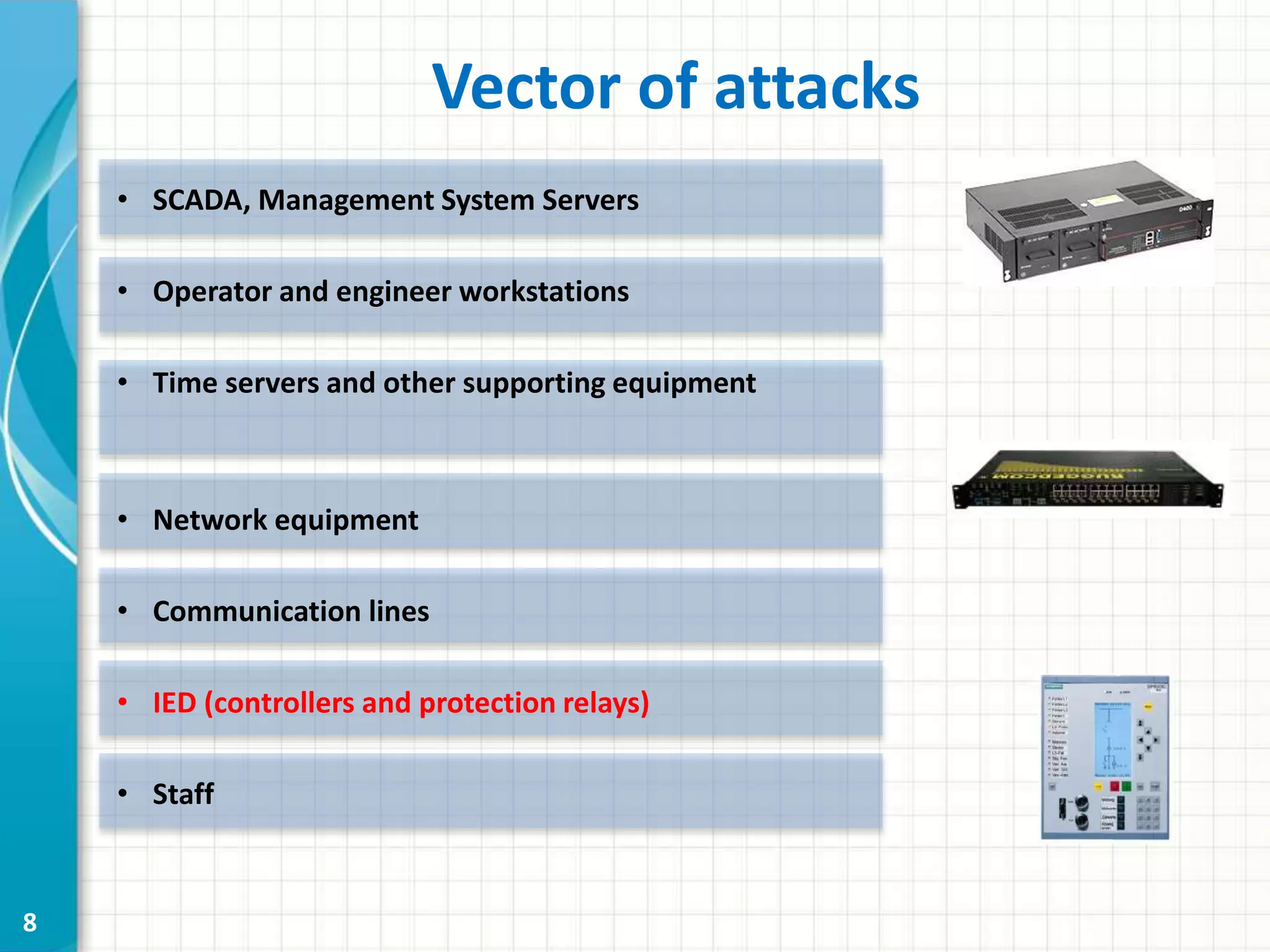
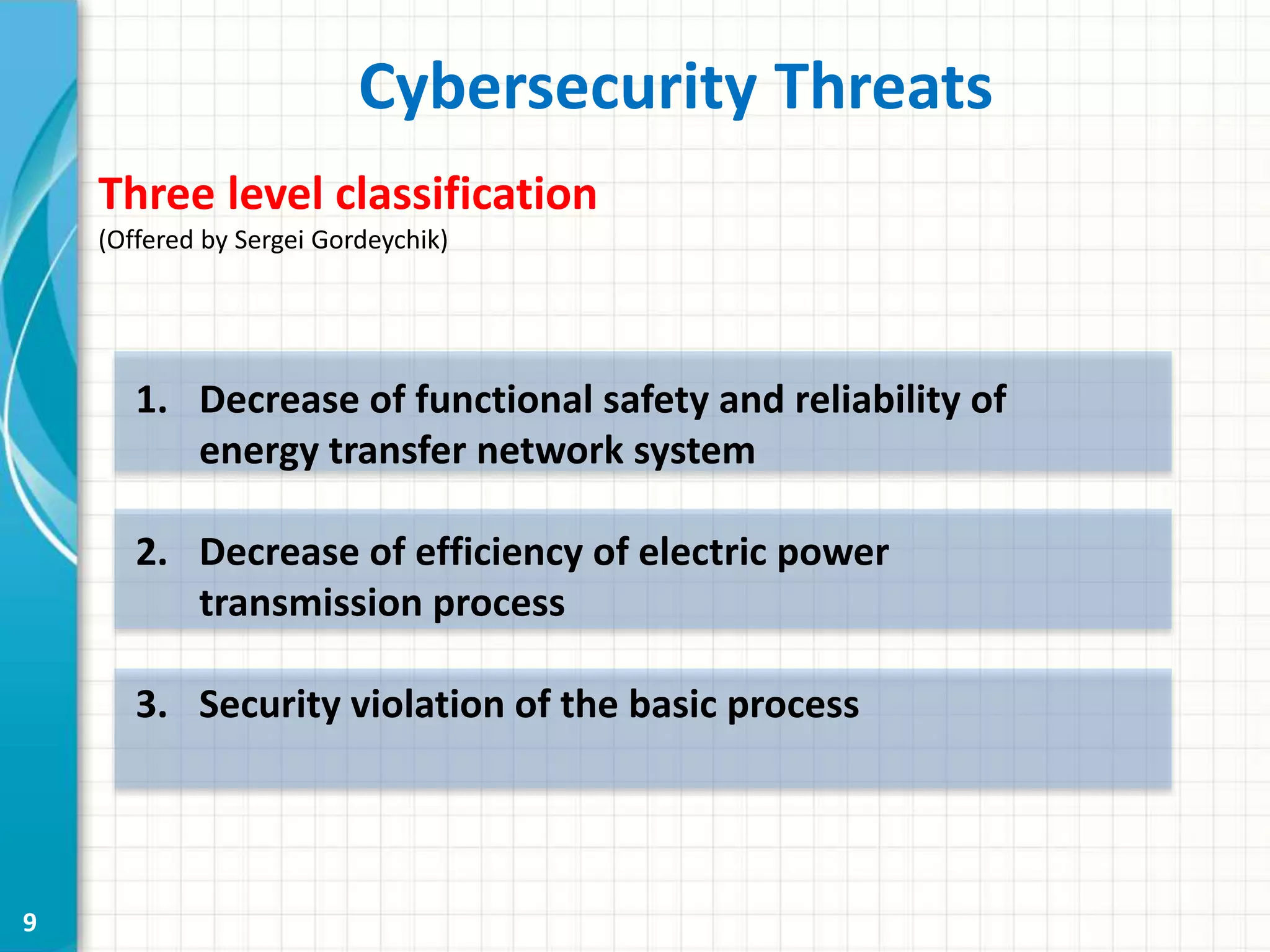
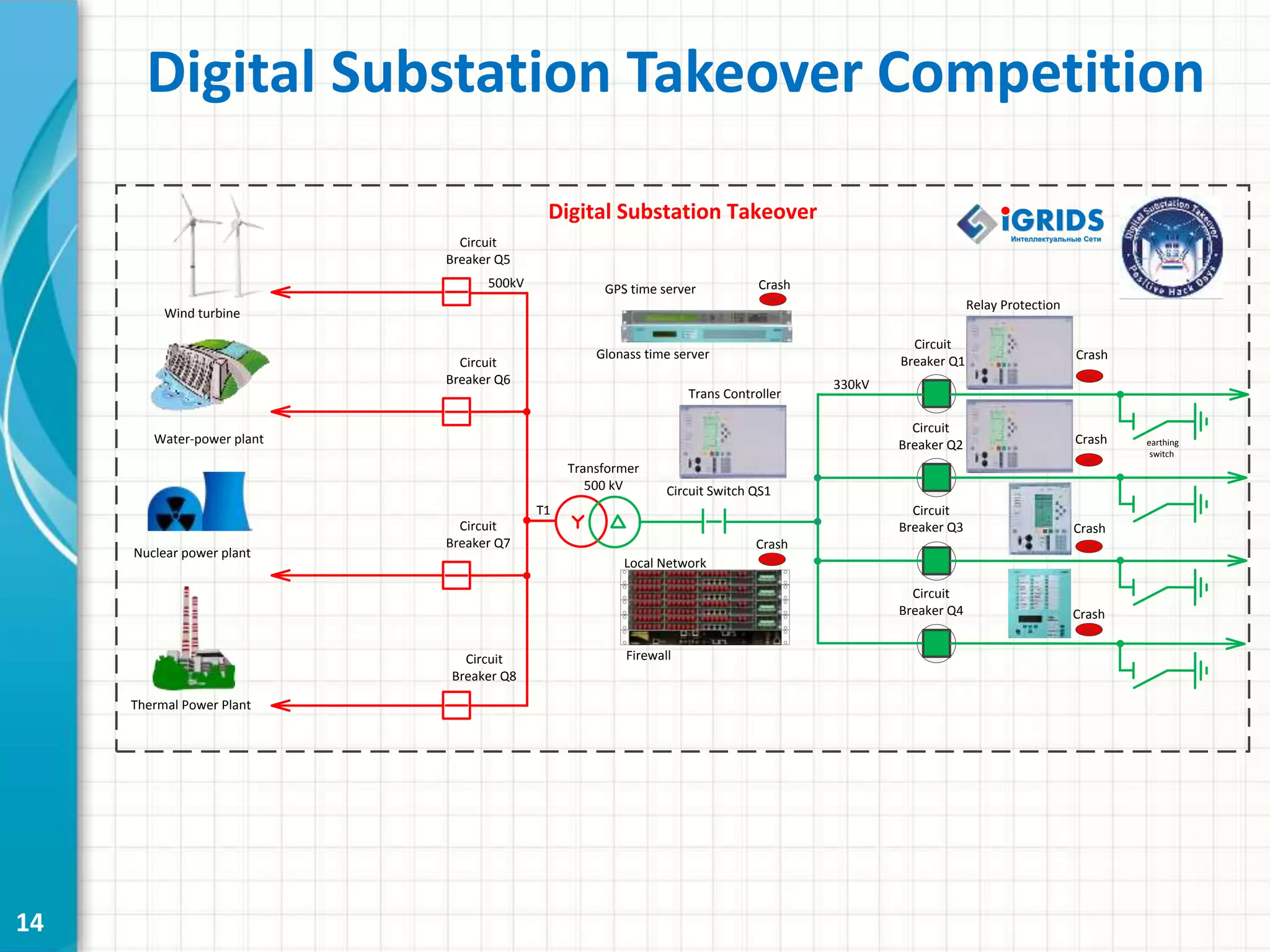
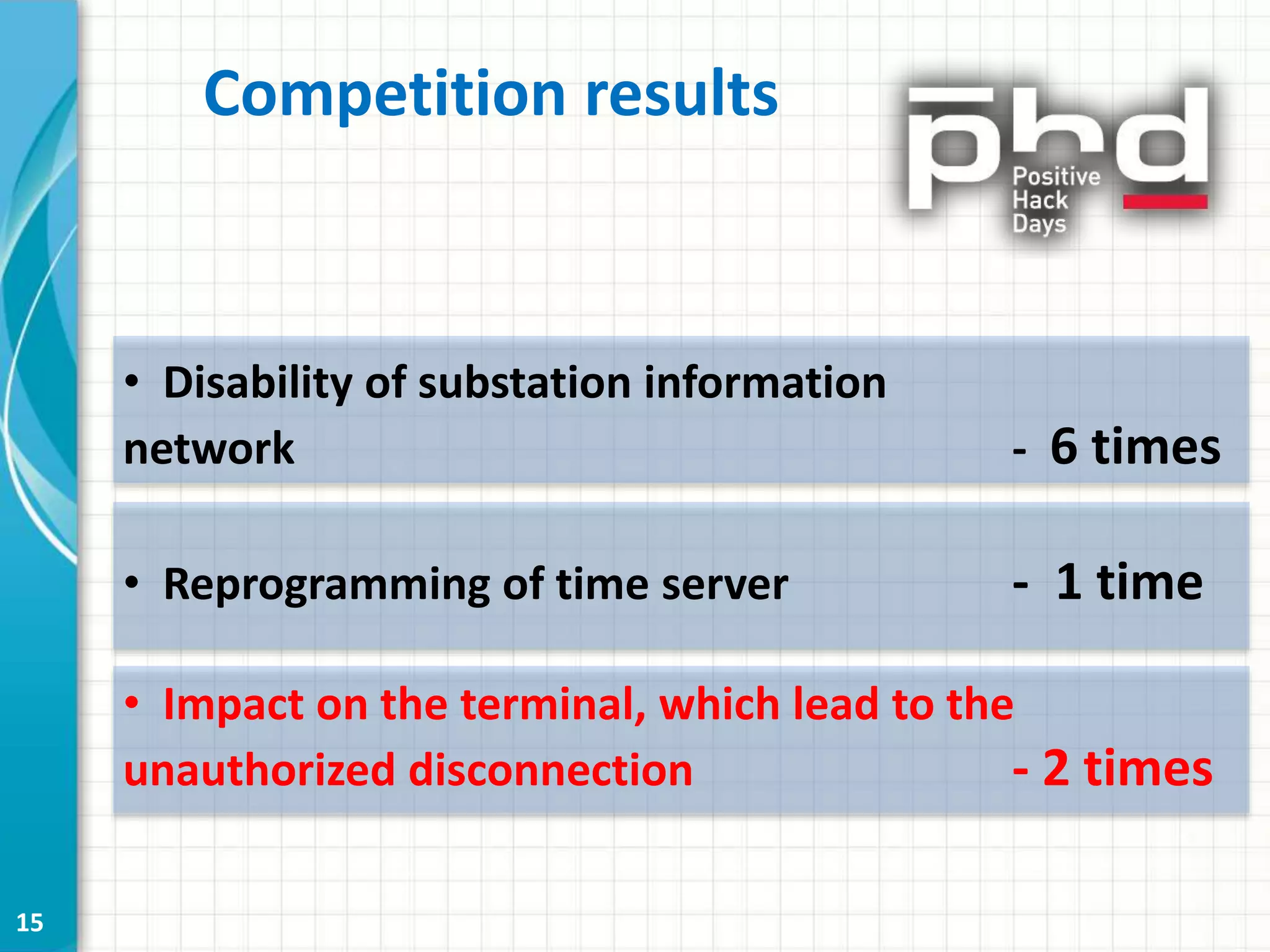
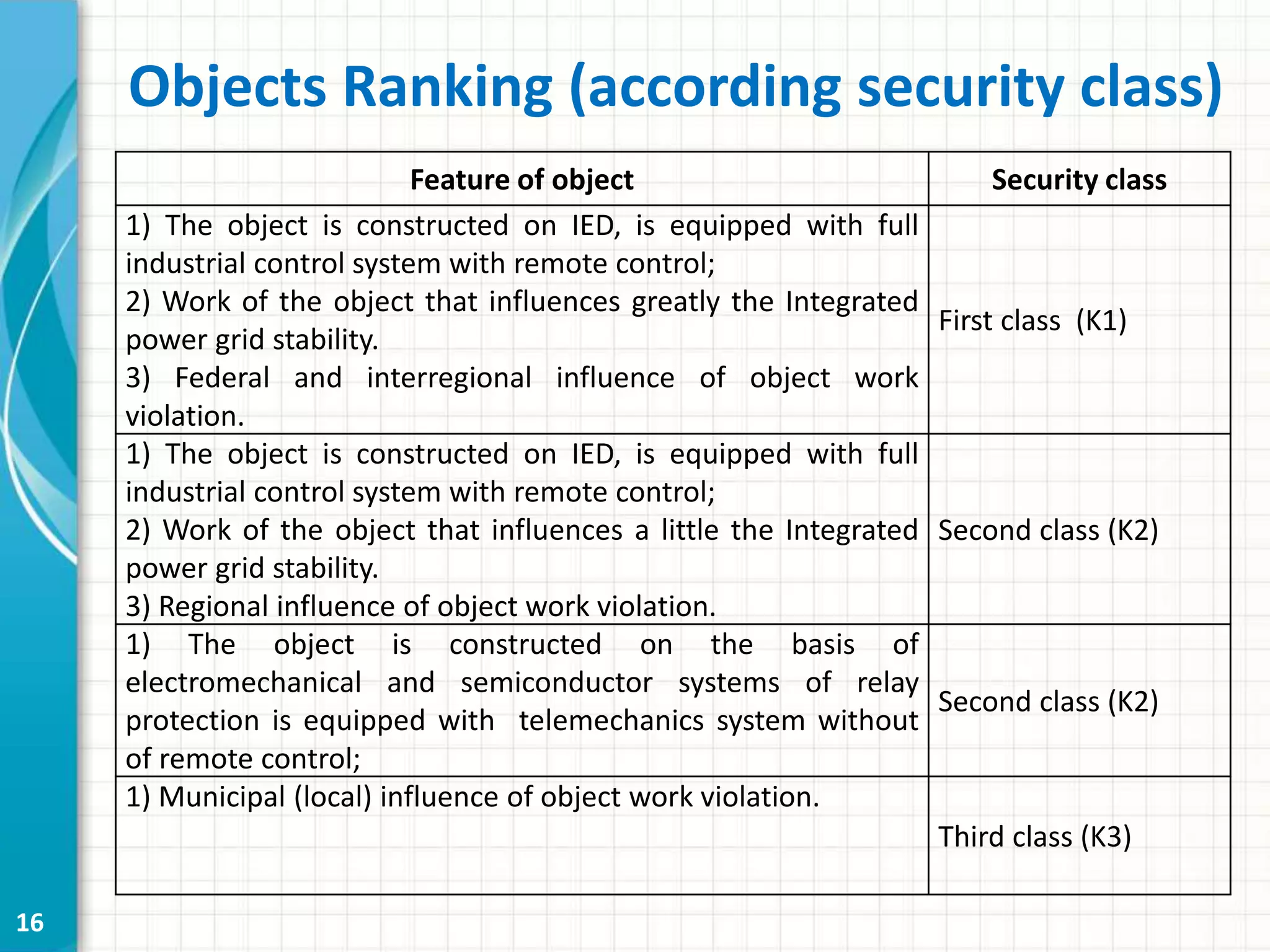
This document discusses cyber security threats to modern power substations. It begins by outlining features of information infrastructures that create opportunities for cyber threats, such as large networks of intelligent devices, lack of network segmentation, and use of unprotected default passwords. It then presents a system model and identifies vectors of potential attacks. Threats are classified into three levels based on their impact: decreasing functional safety and reliability, decreasing transmission efficiency, and violating security of the core transmission process. Examples of possible attacks from a competition are described, such as disabling information networks or reprogramming time servers. Finally, objects are ranked into three security classes based on their impact and influence if compromised.