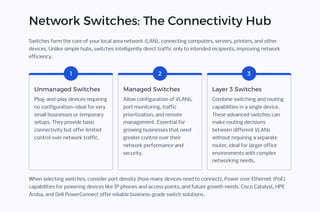
This guide provides an overview of the fundamental network hardware components every business needs to establish a robust IT infrastructure. The goal is to help businesses of all sizes understand what equipment is critical for ensuring connectivity, security, performance, and scalability.