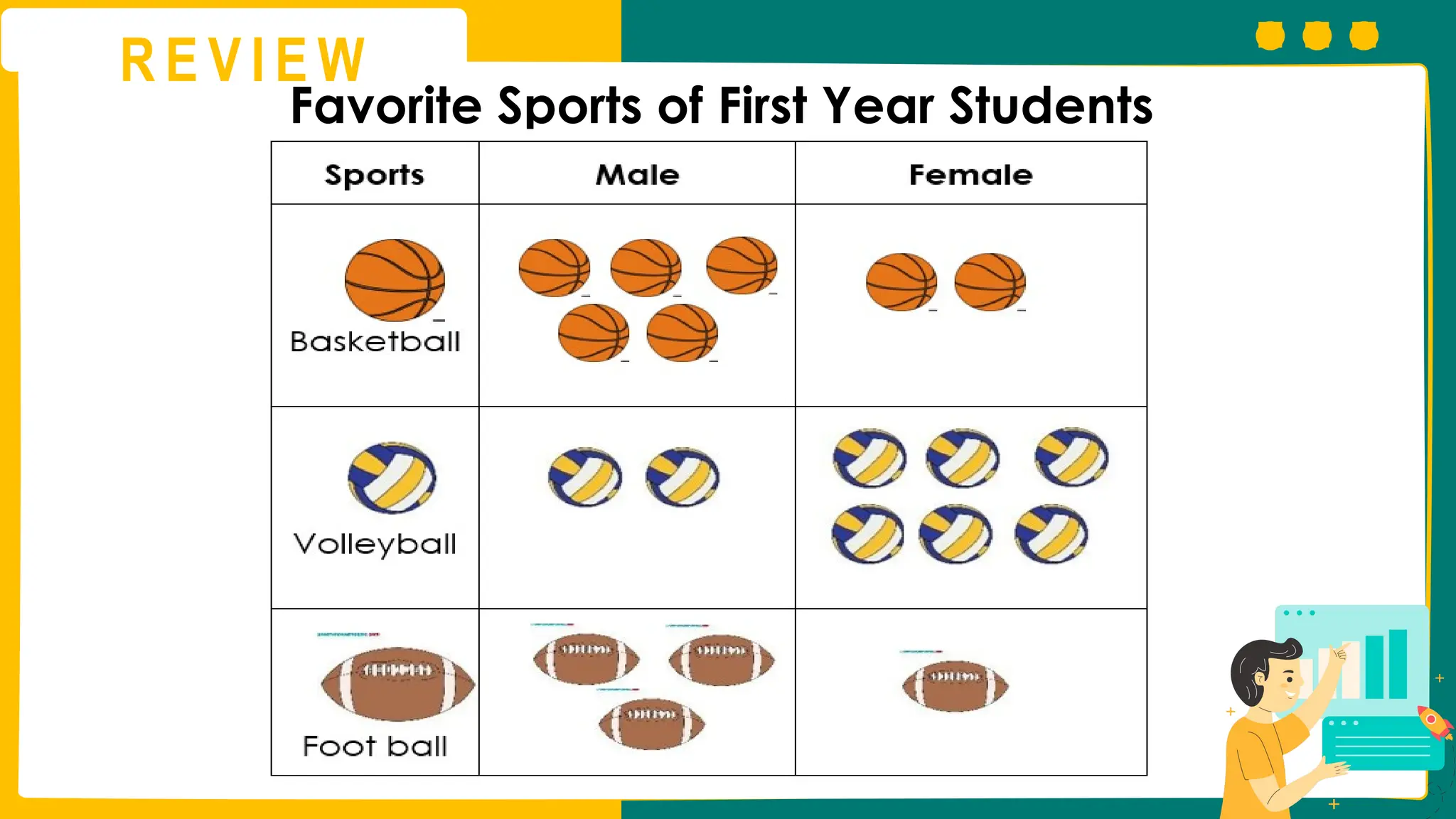
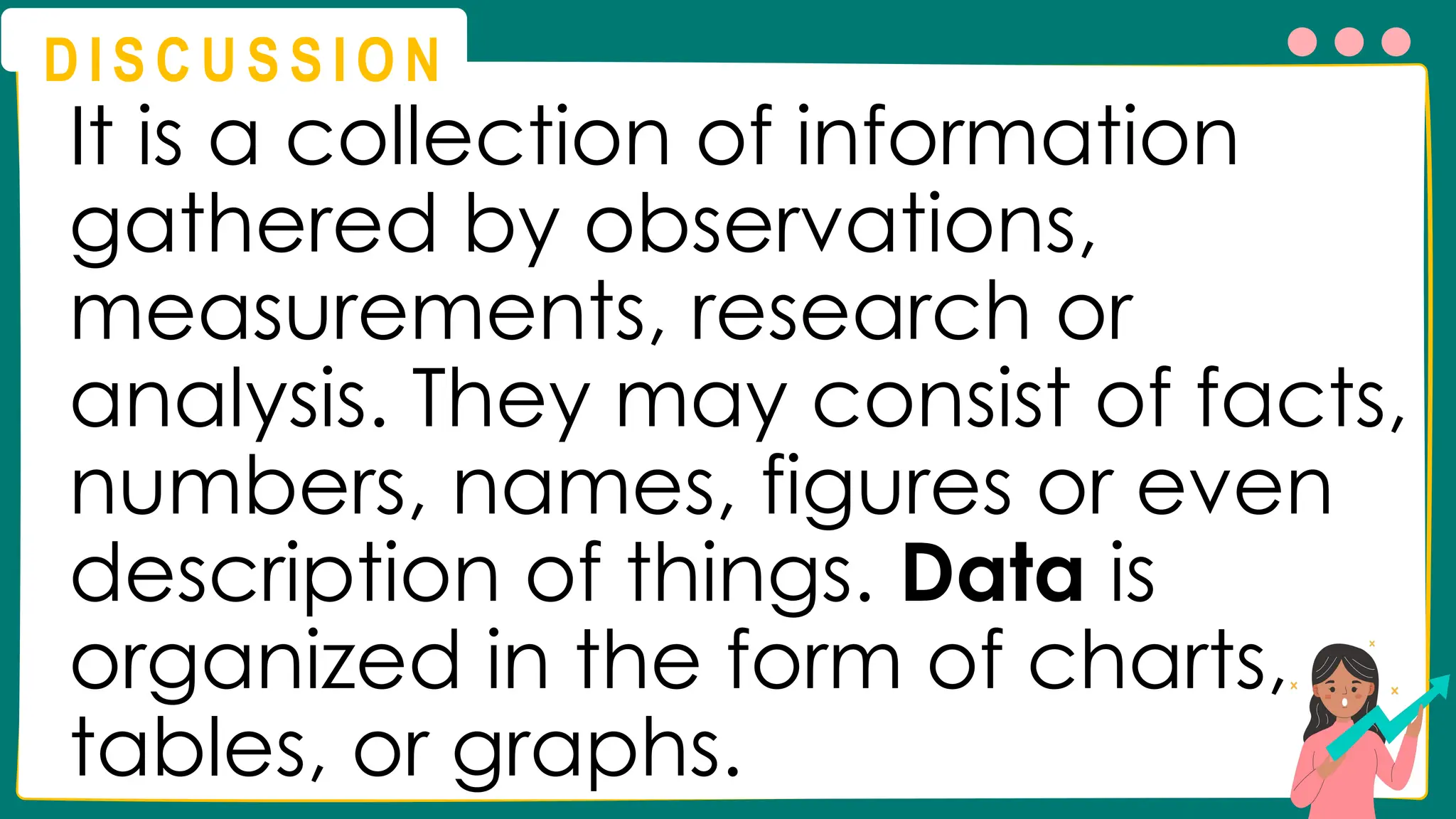
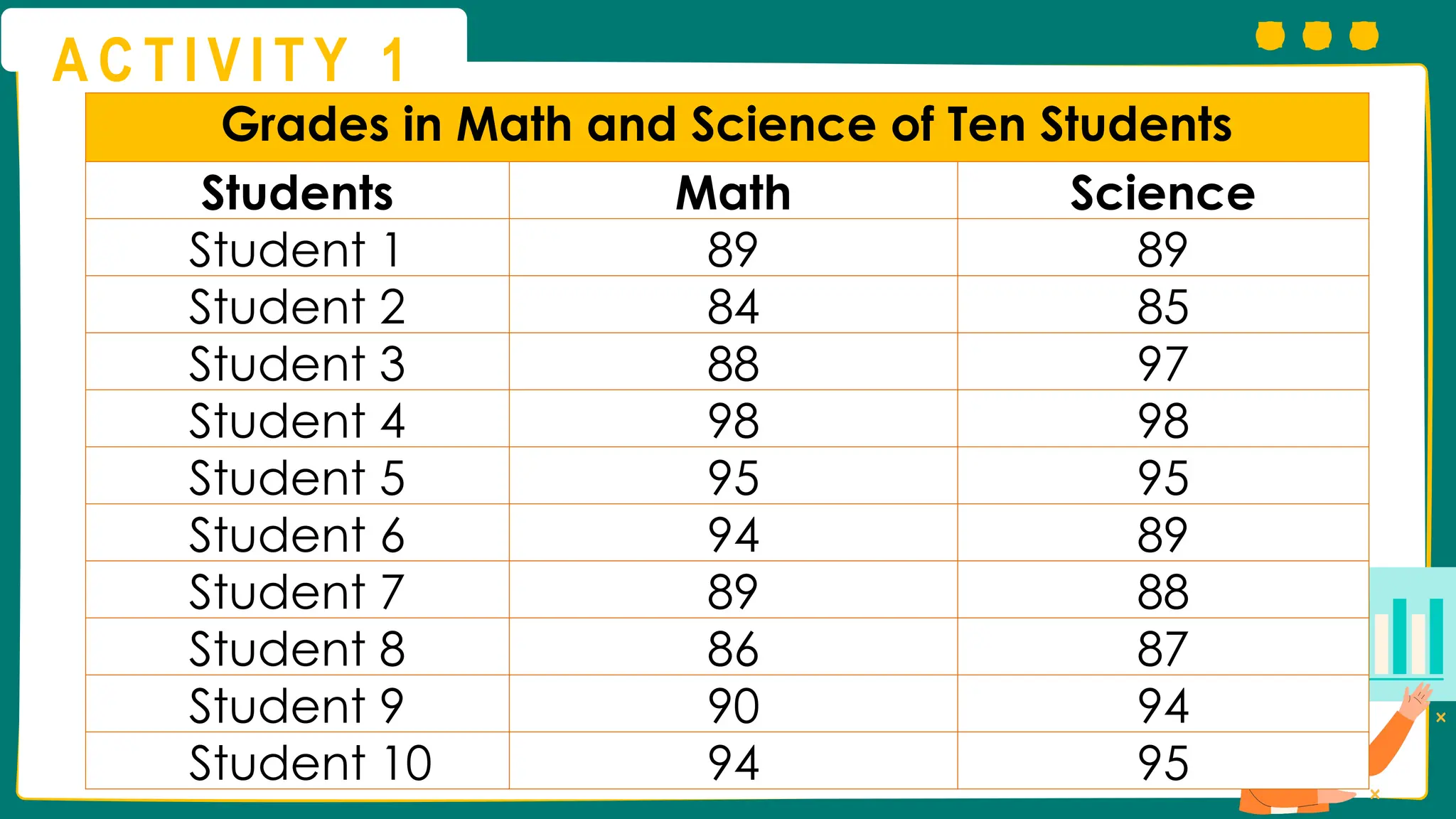
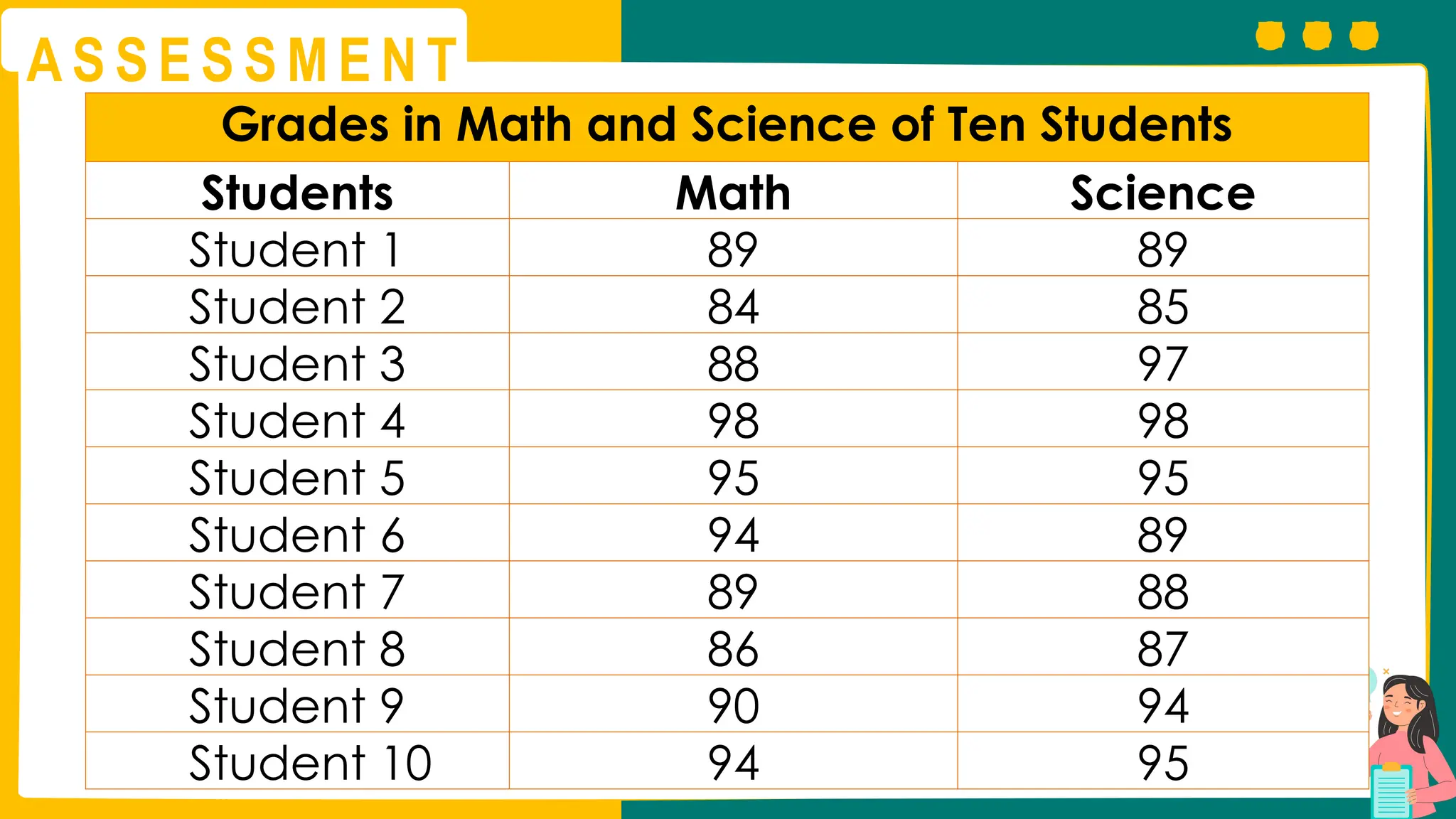
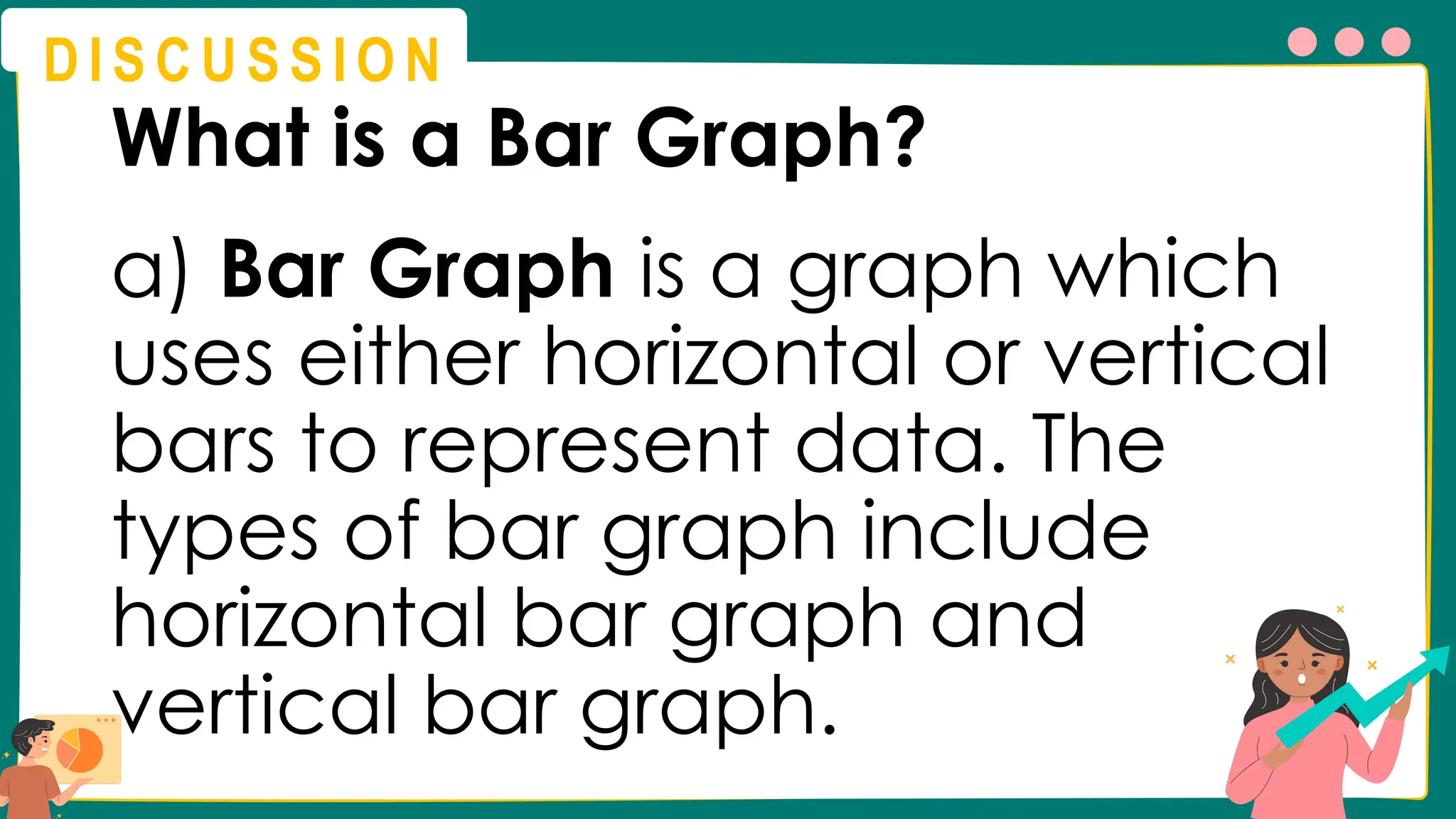
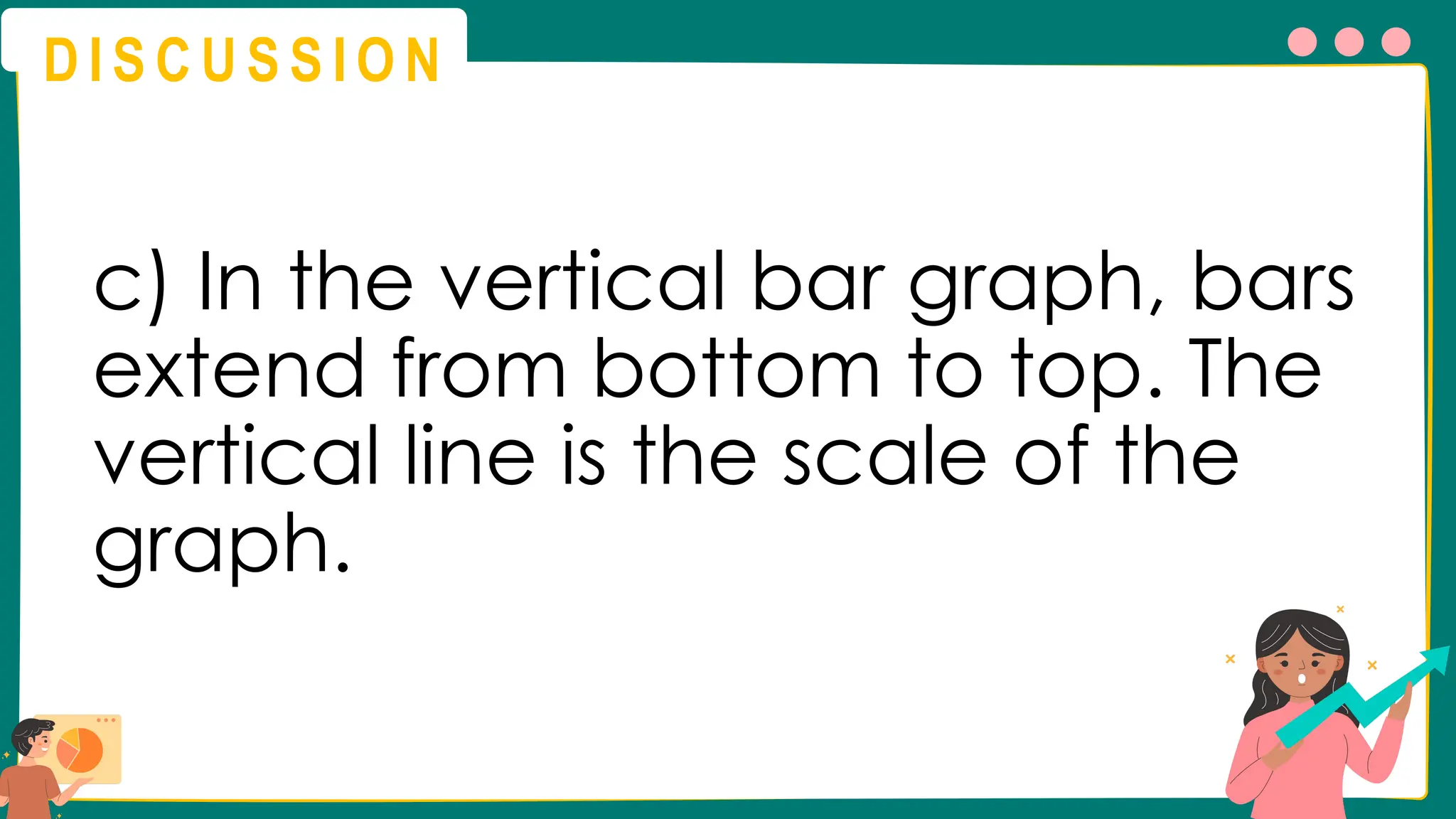
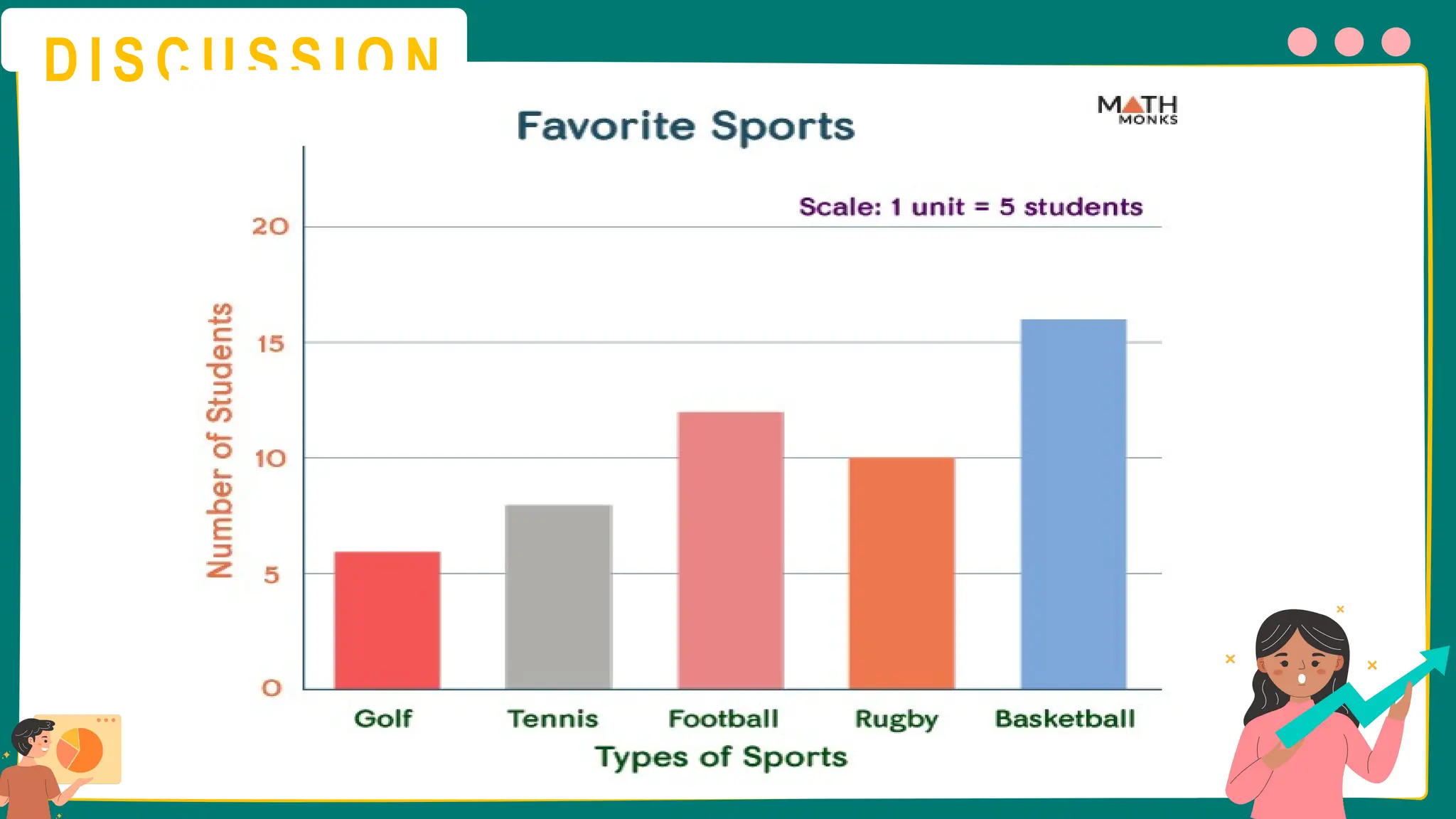
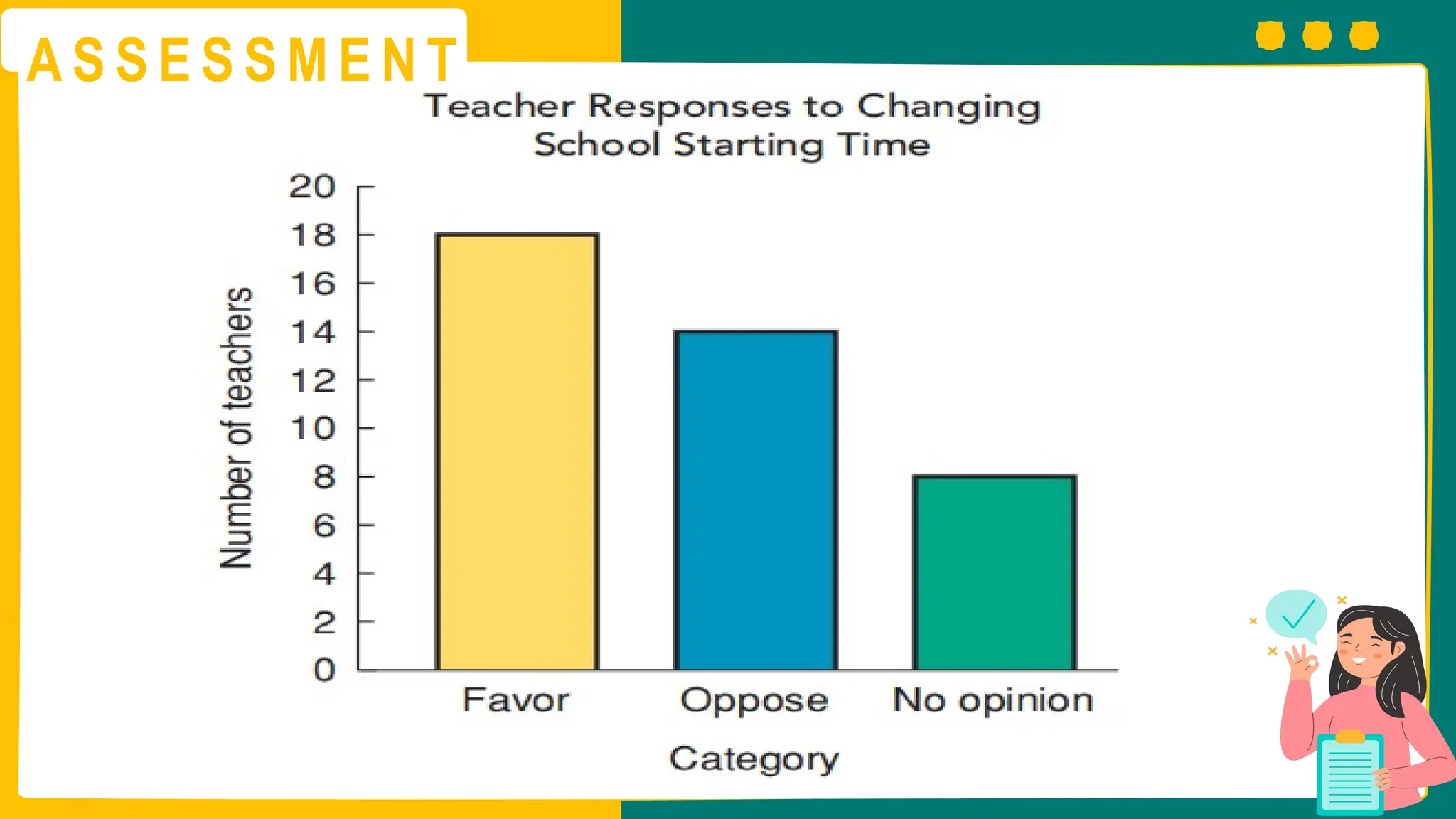
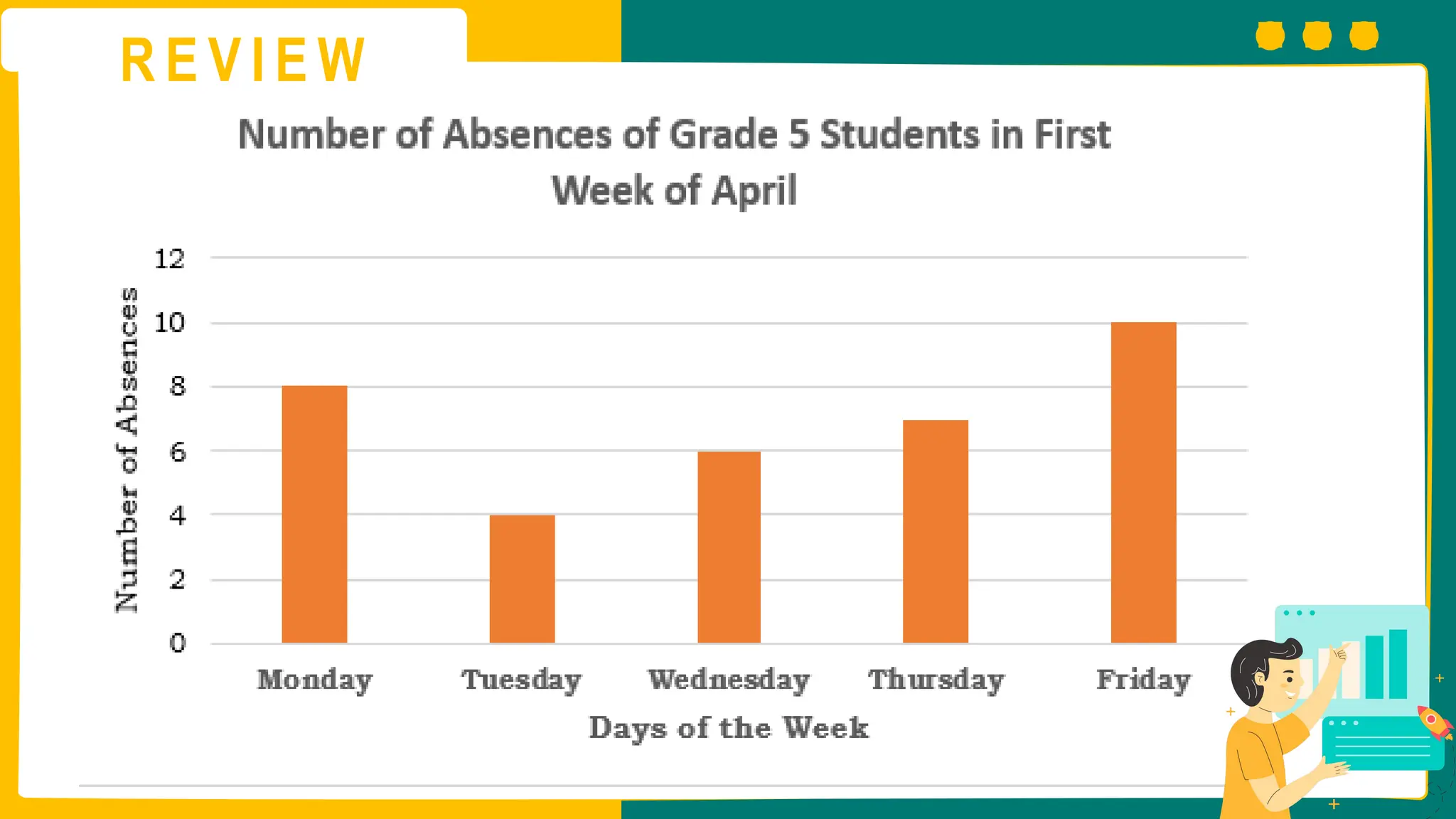
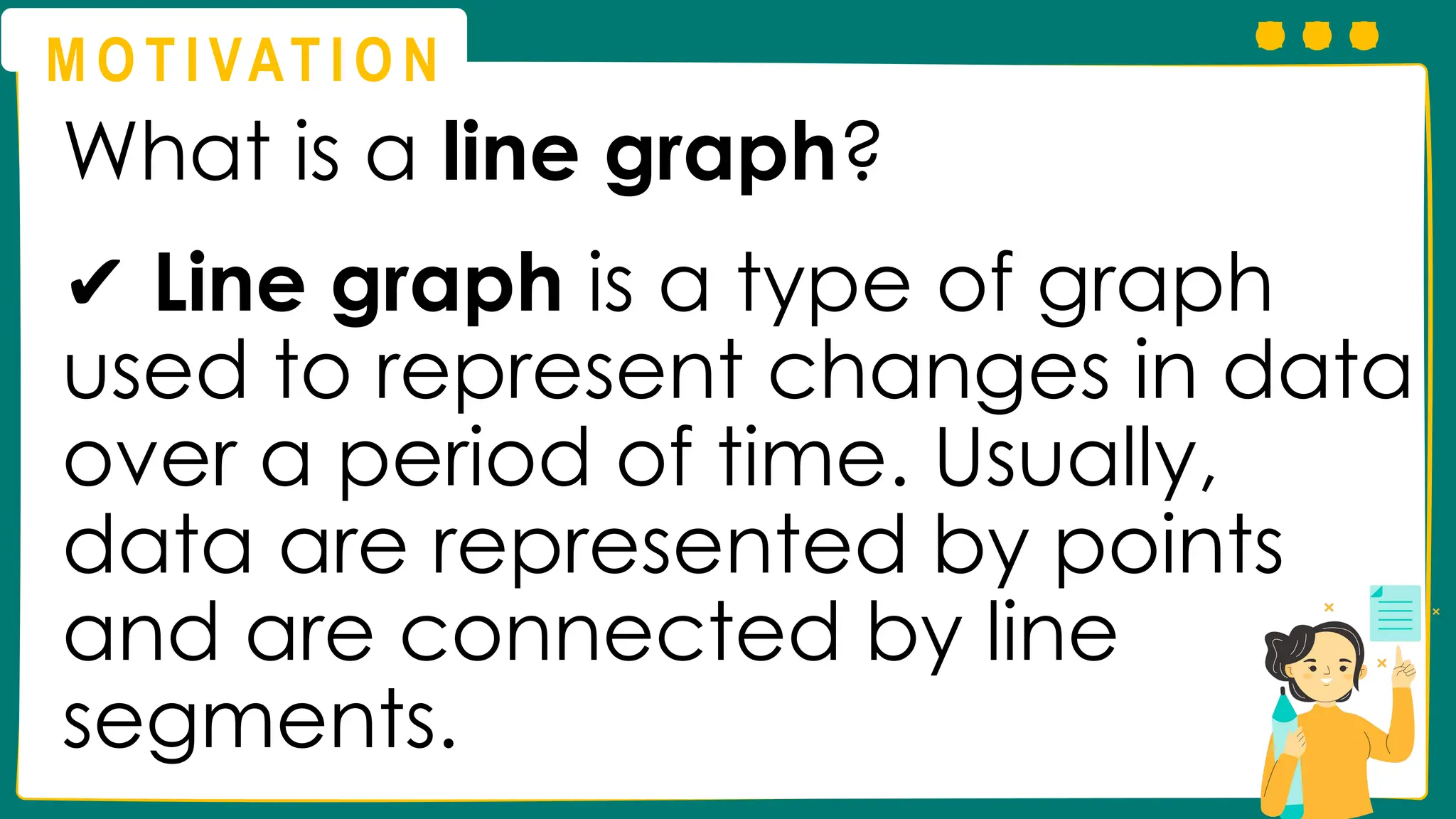
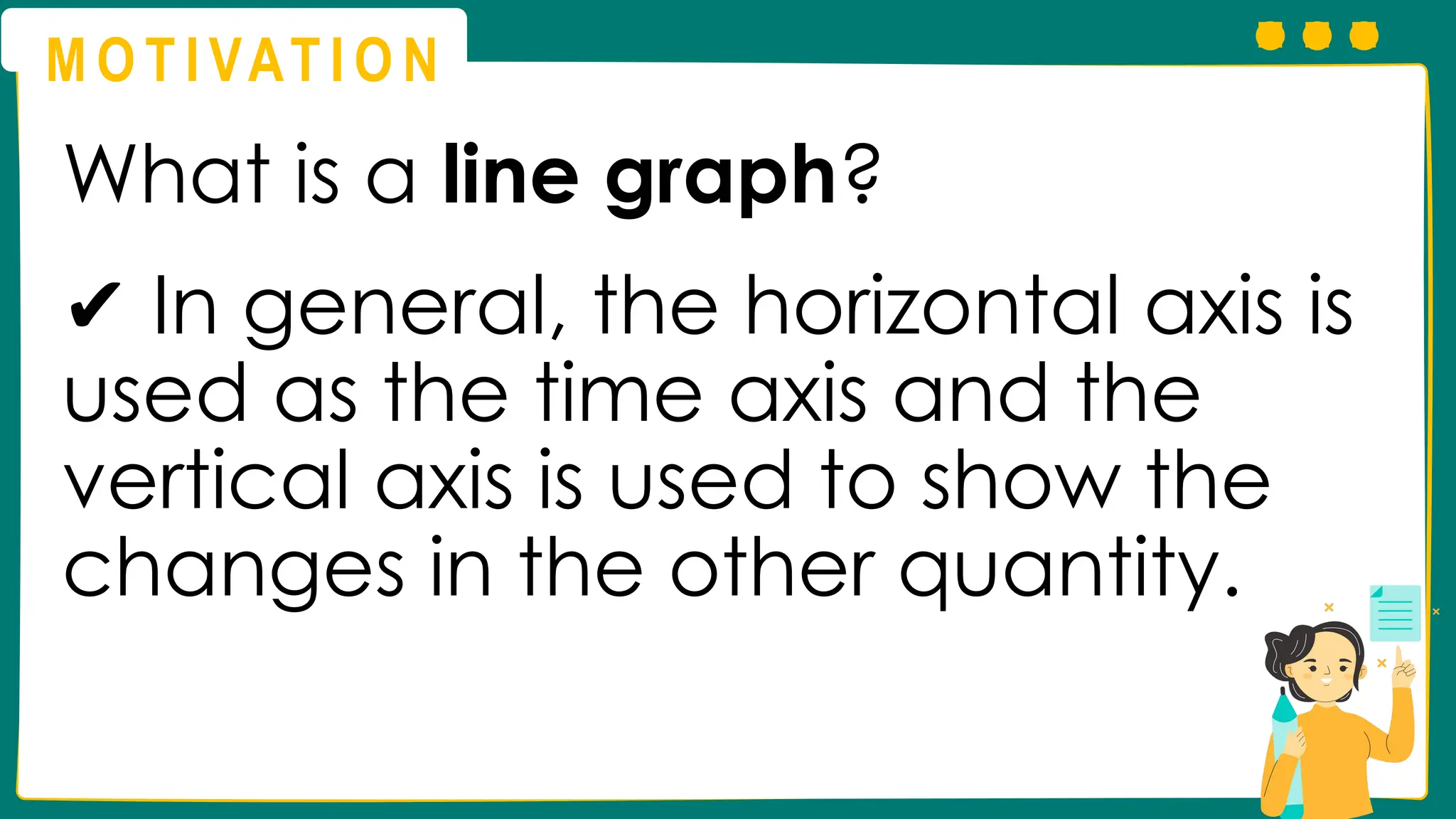
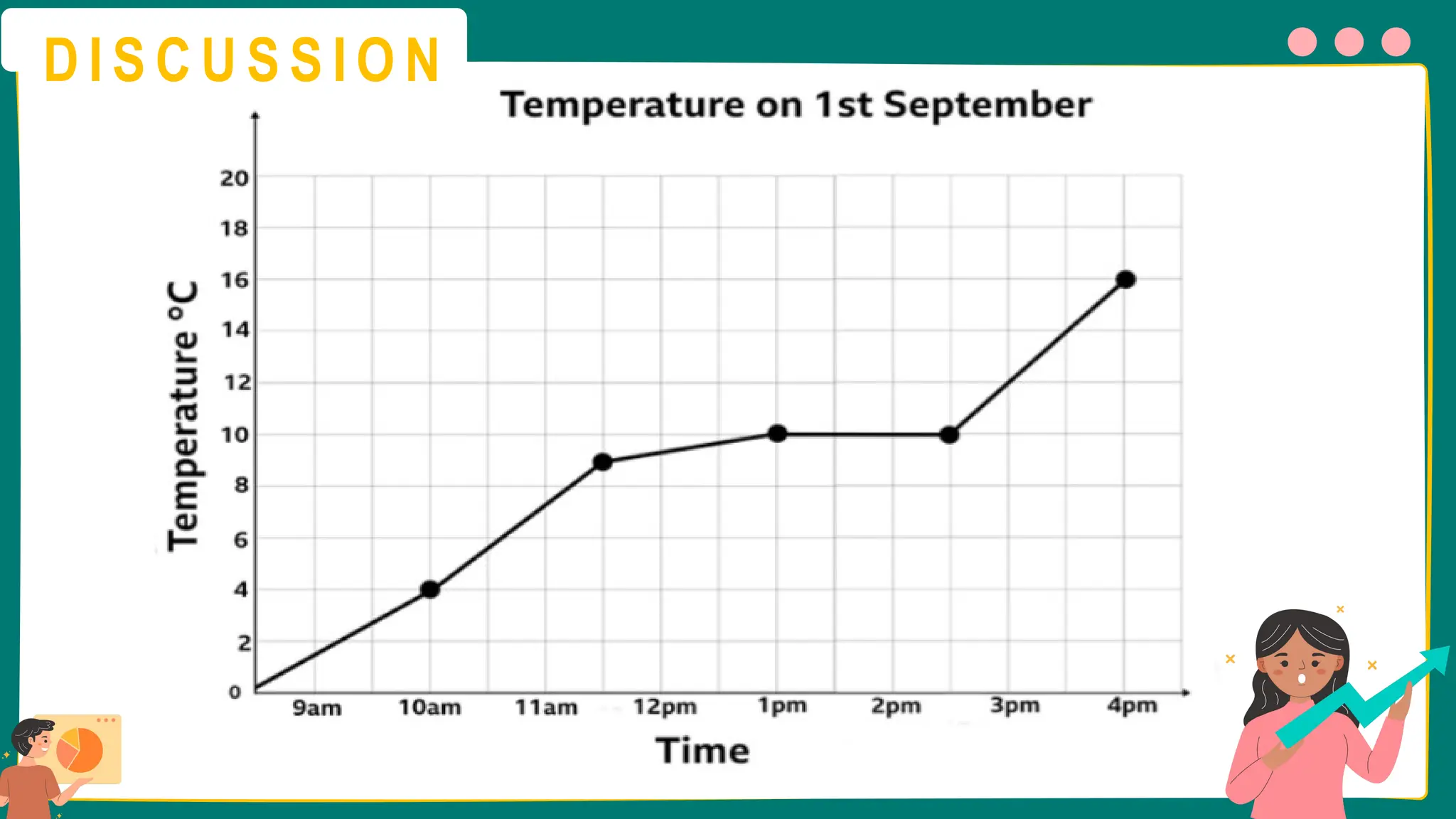
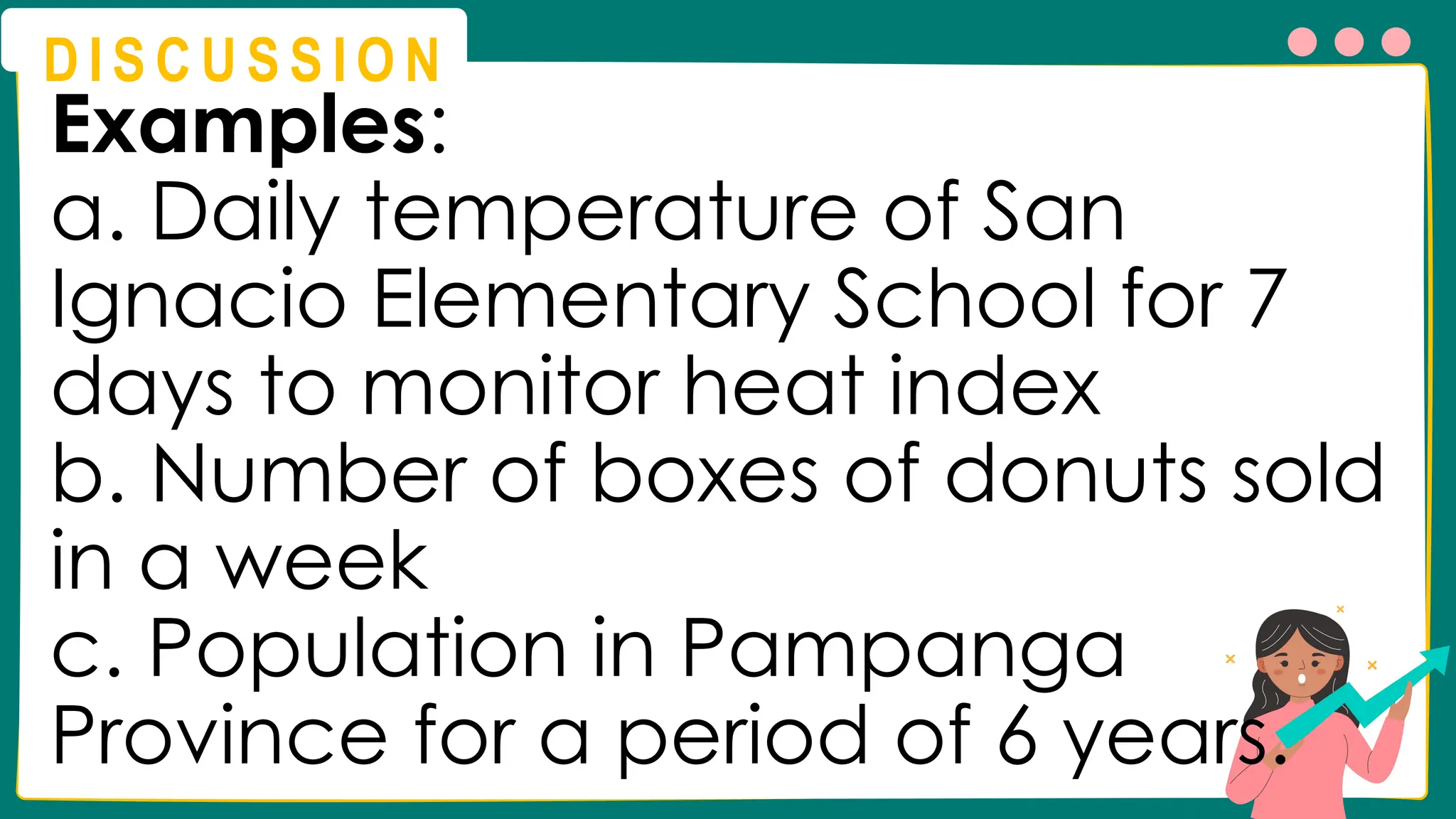
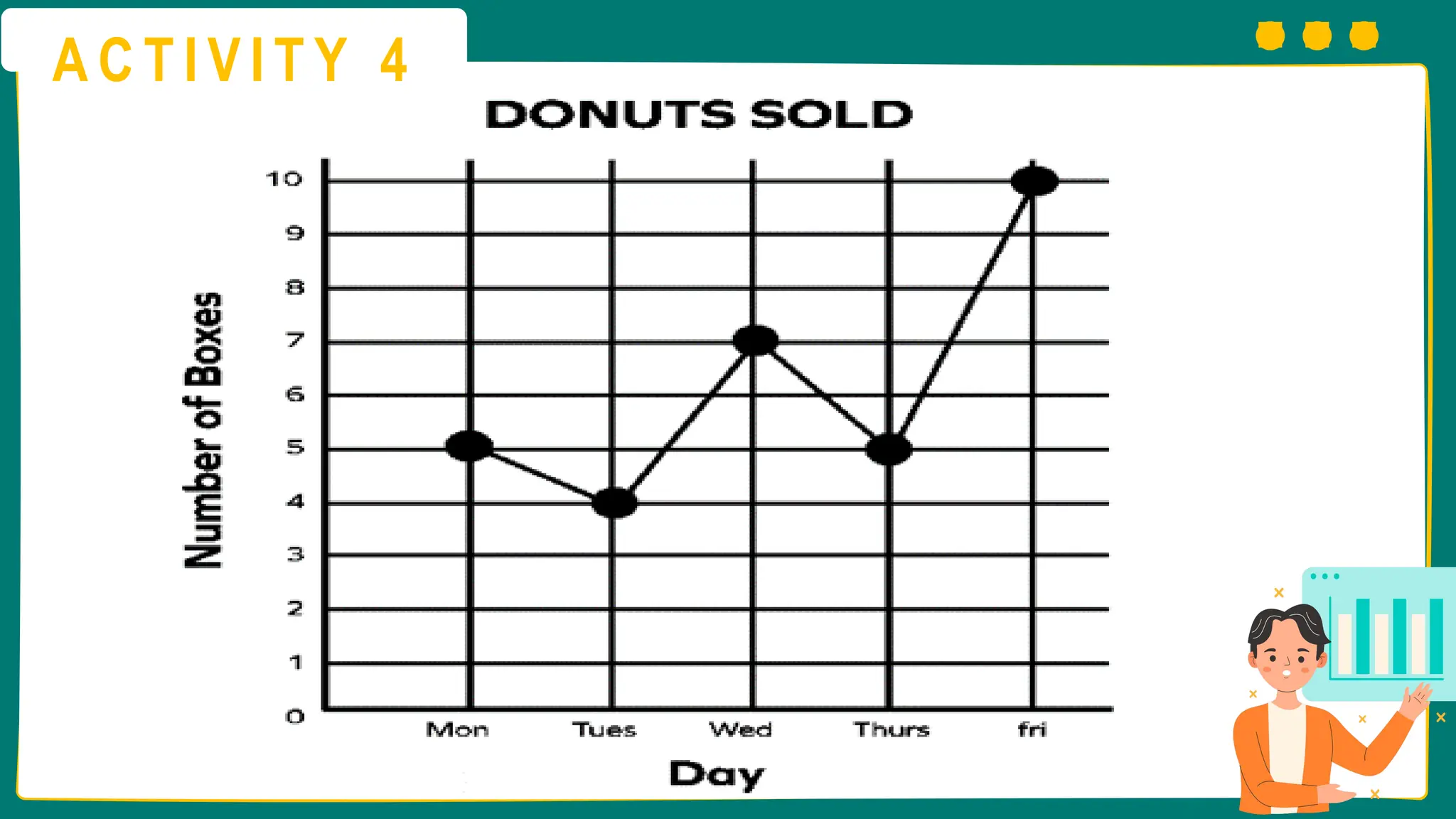
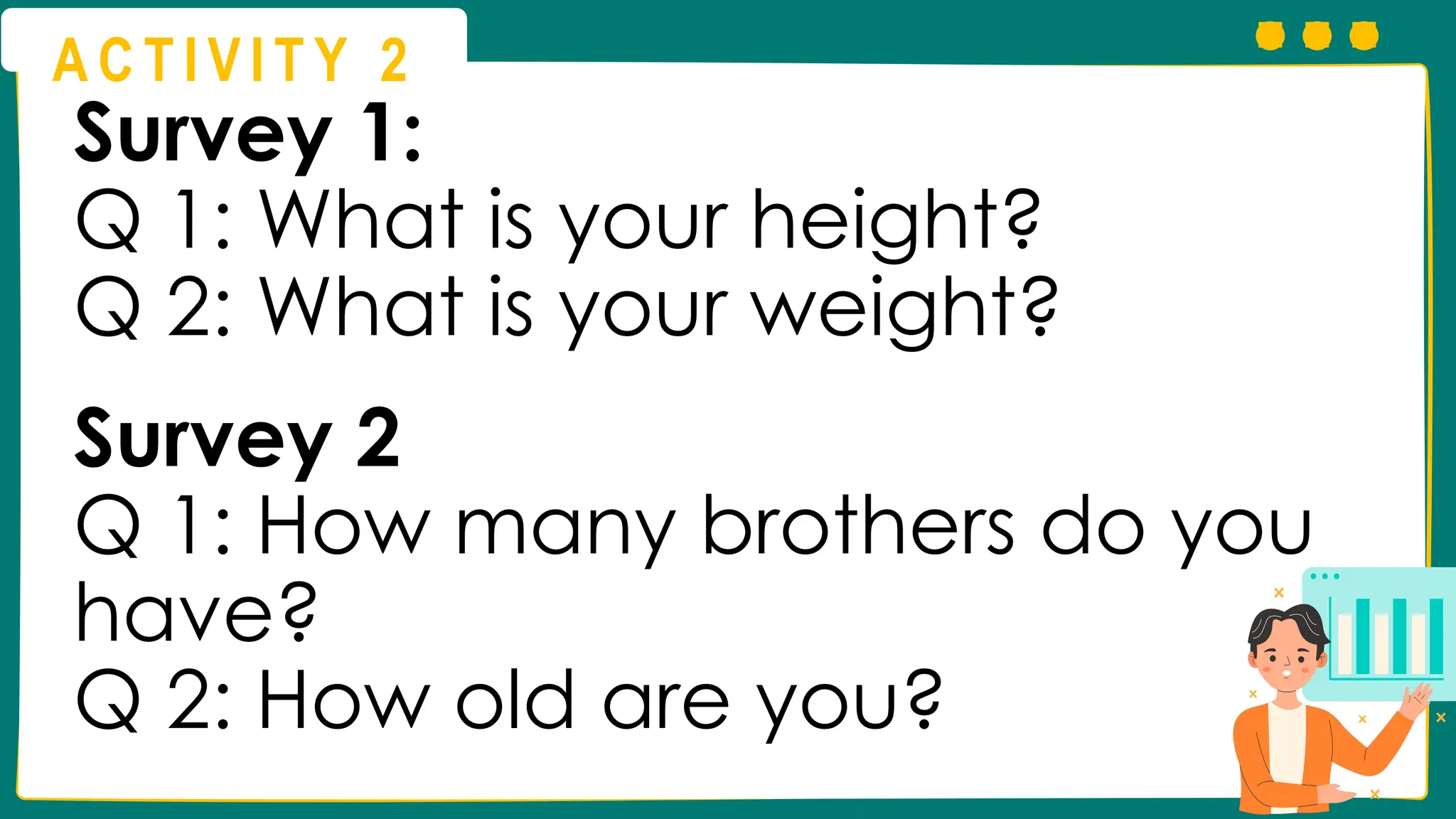This presentation will guide you through the process of collecting bivariate data – that's data with two variables! Learn how to gather information from interviews, questionnaires, and other sources to explore relationships and patterns. We'll make data collection easy and understandable