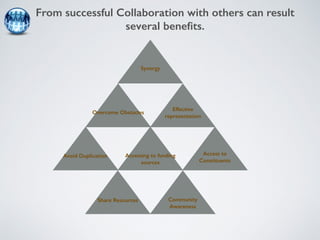
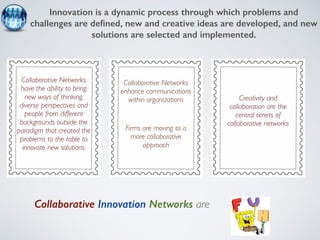
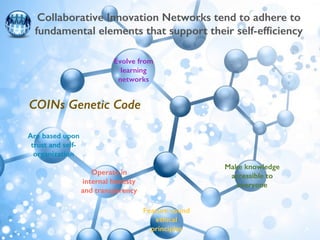
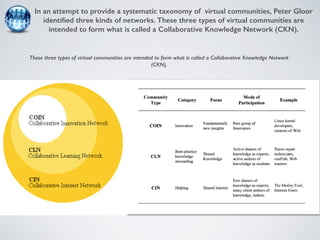
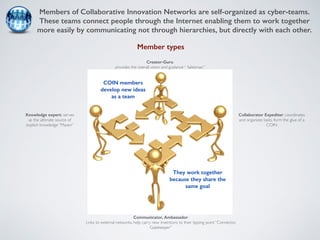
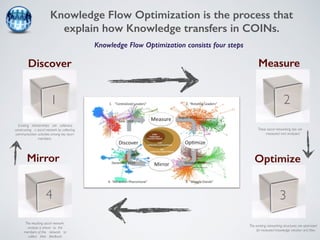
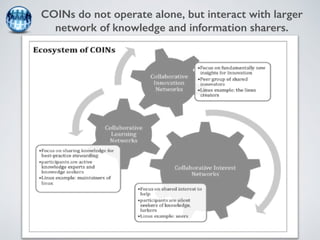
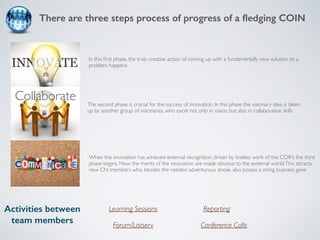
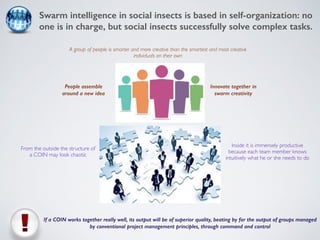
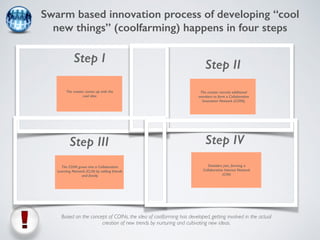
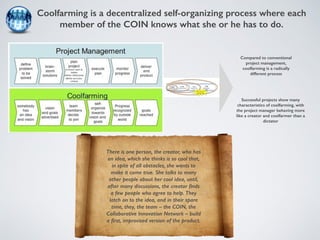
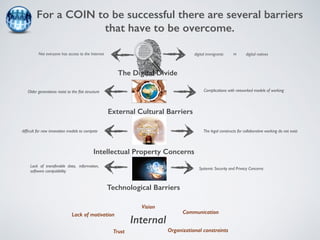
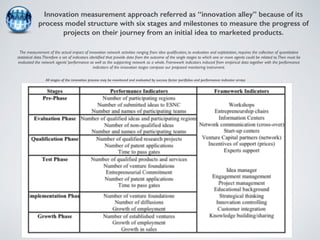
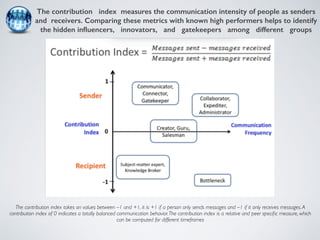
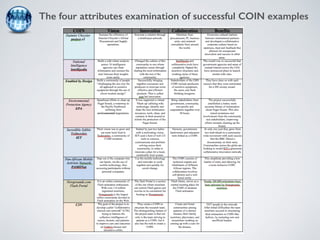
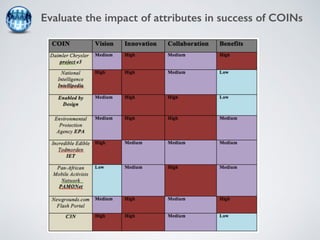
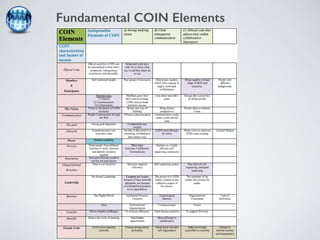
The document discusses collaborative innovation networks (COINs) and their characteristics. It states that COINs are groups of self-motivated people who collaborate online to achieve a common goal by sharing ideas and work. COINs operate with no formal leadership and adhere to principles of open knowledge sharing, reciprocity, transparency and rationality. The success of COINs comes from the collective intelligence that emerges from collaboration between diverse individuals.