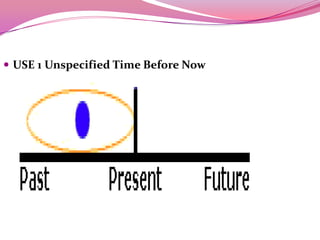
The document discusses various tenses in English, including the present simple tense, present continuous tense, and present perfect tense. The present simple tense is used to express daily routines and habits, often with adverbs of frequency. The present continuous tense refers to actions happening at the moment of speaking. The present perfect tense refers to an action that occurred at an unspecified time before now and is used to discuss experience, change over time, accomplishments, uncompleted actions, and multiple actions at different times. Time expressions can further specify the period being referred to.












![Present perfect tense
[has/have + past participle]
You have seen that movie many times.
Have you seen that movie many times?
You have not seen that movie many times.
[](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tensespresent-140413055437-phpapp01/85/Tenses-present-13-320.jpg)