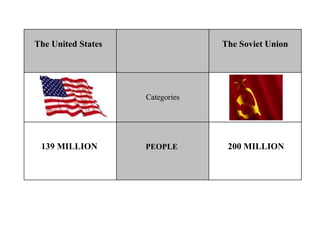
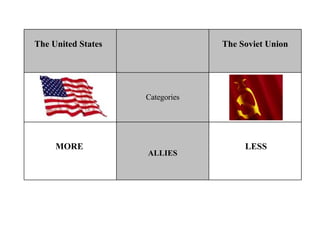
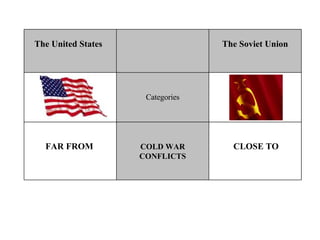
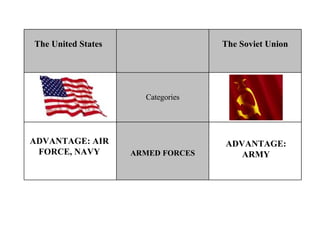
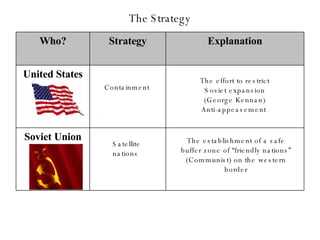
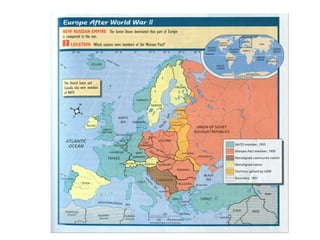
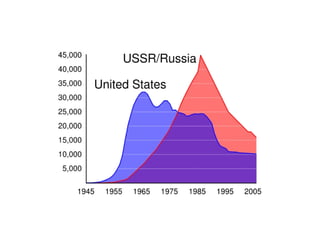
The Cold War was a post-World War II struggle for global power and influence between the United States and Soviet Union that was fought on political and economic fronts rather than through direct military conflict. The two nations had opposing economic systems and forms of government, with the US representing democracy and capitalism while the Soviet Union represented communism and a dictatorship. Both countries engaged in an arms race and developed nuclear weapons during this period, but avoided direct military confrontation and instead waged proxy wars by supporting allies around the world.