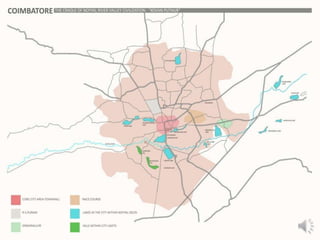
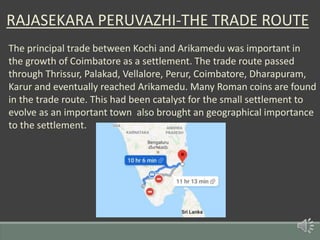
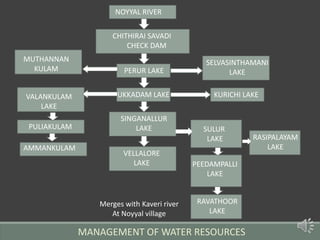
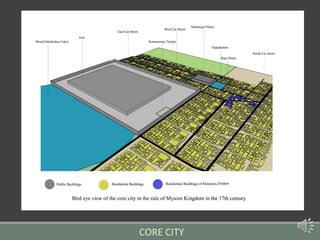
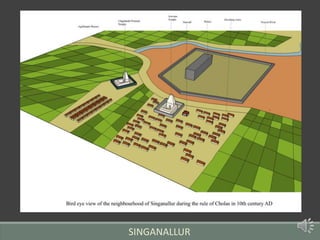
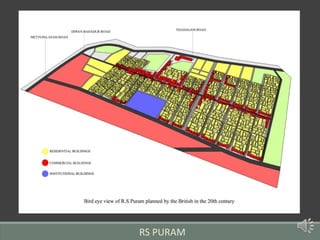
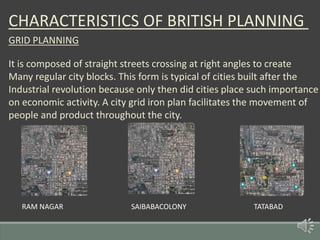
The document summarizes the history of human settlements and planning in Coimbatore, India from its early beginnings to present day. It describes how the city originated as a small settlement near the Noyyal River and gradually expanded over time under different rulers. The core area was initially planned with a radial form centered around a fort and temple. Later, the British introduced grid planning for new neighborhoods during their rule to improve sanitation following a disease outbreak. Today, Coimbatore continues to be influenced by both traditional radial and modern grid-based planning approaches in its urban development.