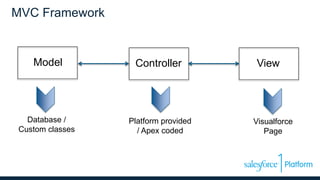
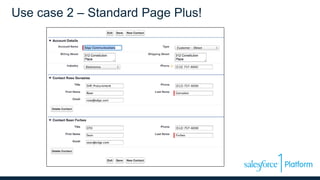
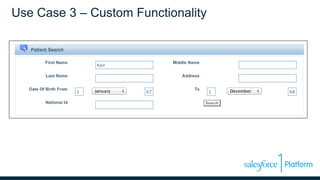
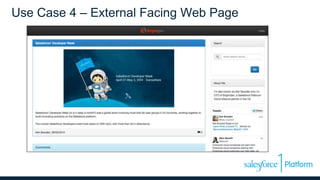
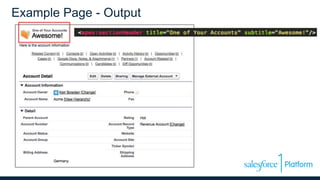
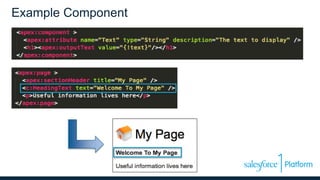
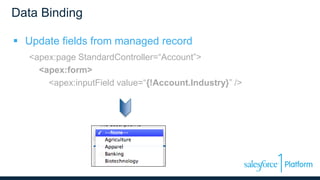
This document discusses coding the Salesforce1 platform user interface using Visualforce. It outlines four use cases for Visualforce: 1) overriding standard pages, 2) adding to standard pages, 3) custom functionality, and 4) external facing web pages. It then demonstrates how to build Visualforce pages using markup, components, data binding, and action binding. The document recommends resources for learning more about Visualforce development.