Embed presentation
Downloaded 40 times


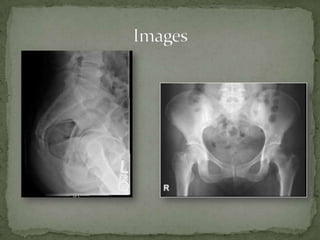
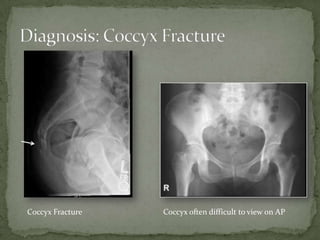


A 56-year-old female presented to urgent care with pain in her tailbone after tripping and landing on her buttocks. On examination, she had tenderness over her sacrum and pain with hip flexion and defecation. A rectal exam also caused significant pain on posterior compression, suggesting a coccyx fracture. Conservative management including analgesics, stool softeners, bed rest, and follow-up in 2-3 weeks was recommended.







