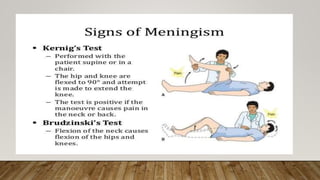
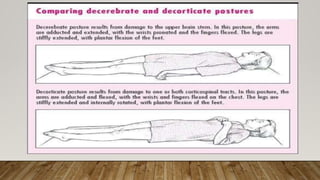
Tuberculous meningitis (TBM) is a severe form of tuberculosis characterized by high morbidity and mortality, primarily affecting young children in areas with high TB prevalence. Diagnosis is challenging and requires a high index of suspicion, with clinical features progressing through three stages leading to neurological deficits. Management includes specific antituberculosis therapy and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and complications, alongside supportive care and health education to prevent transmission.