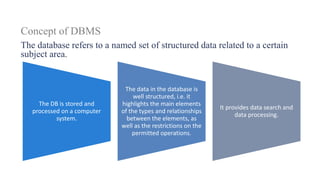
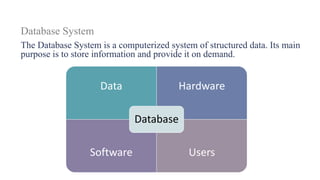
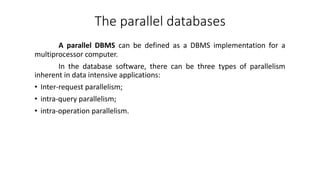
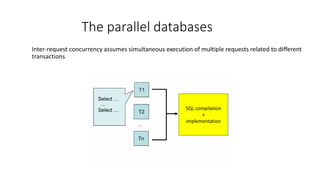
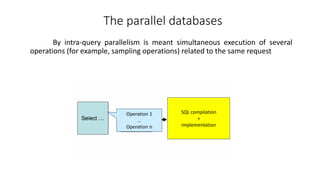
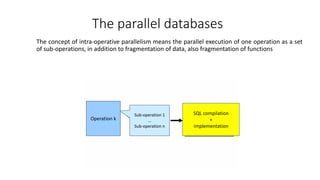
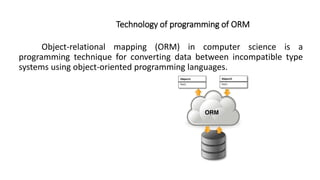
1. The document discusses key concepts related to database systems including the definition of a database, database management systems (DBMS), data models, database classification, data integrity, query optimization, structured query language (SQL), parallel databases, and object-relational mapping (ORM).
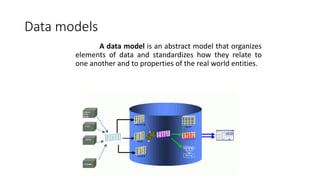
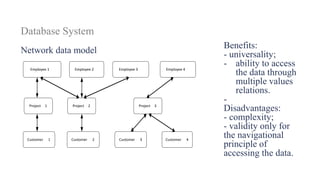
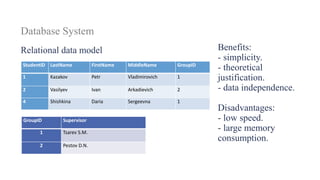
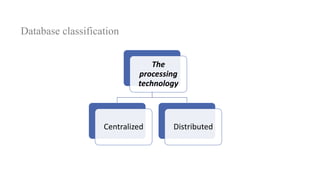
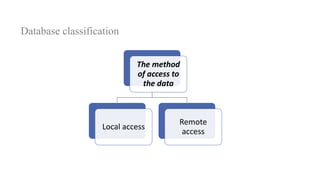
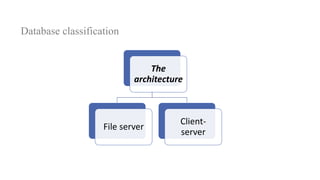
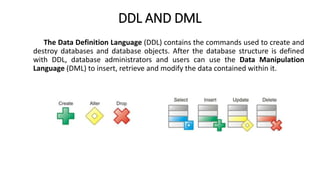
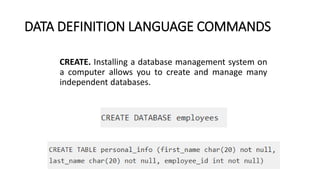
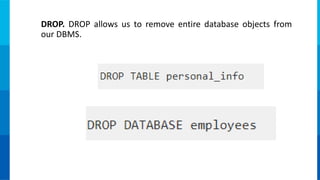
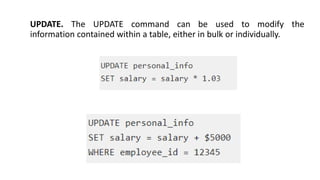
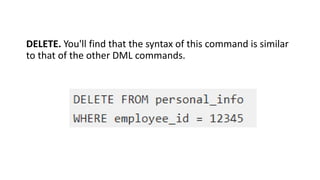
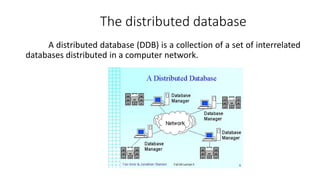
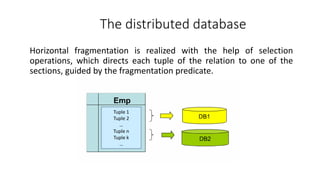
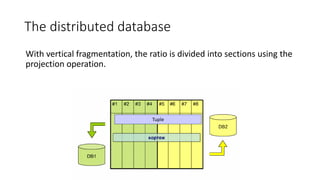
2. It provides details on common data models like hierarchical, network, and relational models. It also describes concepts like database architecture, data definition language, data manipulation language, and distributed databases.
3. Control questions are provided at the end to test understanding of database concepts like the difference between a database and data set, components of a database system, and main elements of a database.