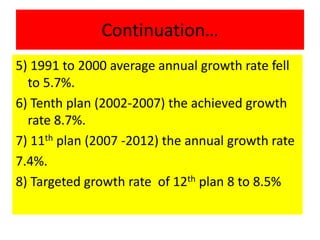
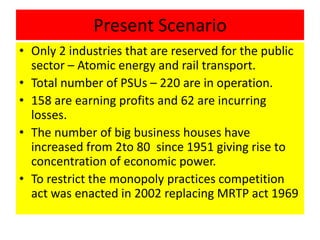
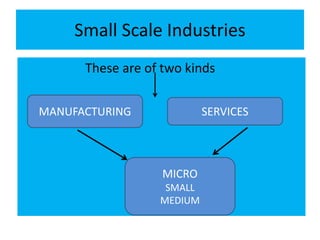
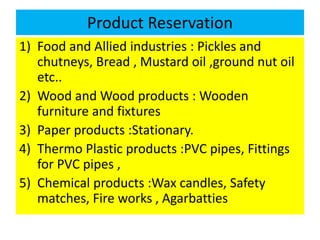
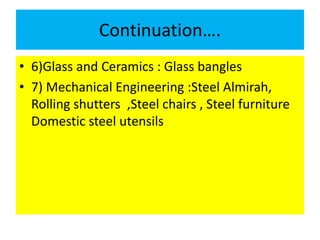
This document discusses large scale and small scale industries in India. It defines large scale industries as those with high capital investment and modern technology, while small scale industries have lower investment and are often household enterprises. Large industries contribute significantly to GDP, exports, and employment. However, they face issues like low capacity utilization and outdated technology. Small industries employ many but struggle with lack of finance, raw materials, infrastructure, and skills. The government supports both sectors through various schemes and product reservations for small industries.