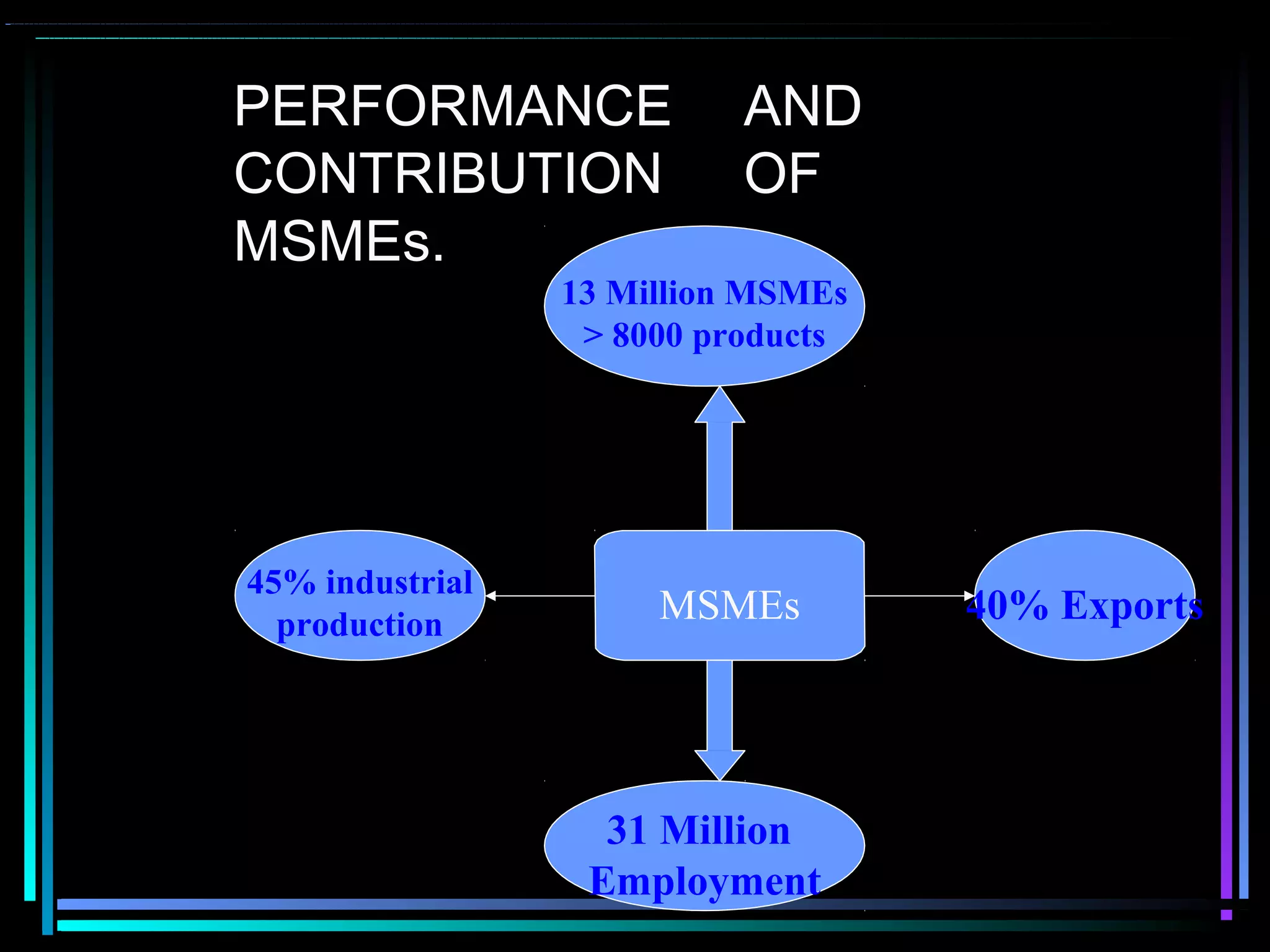
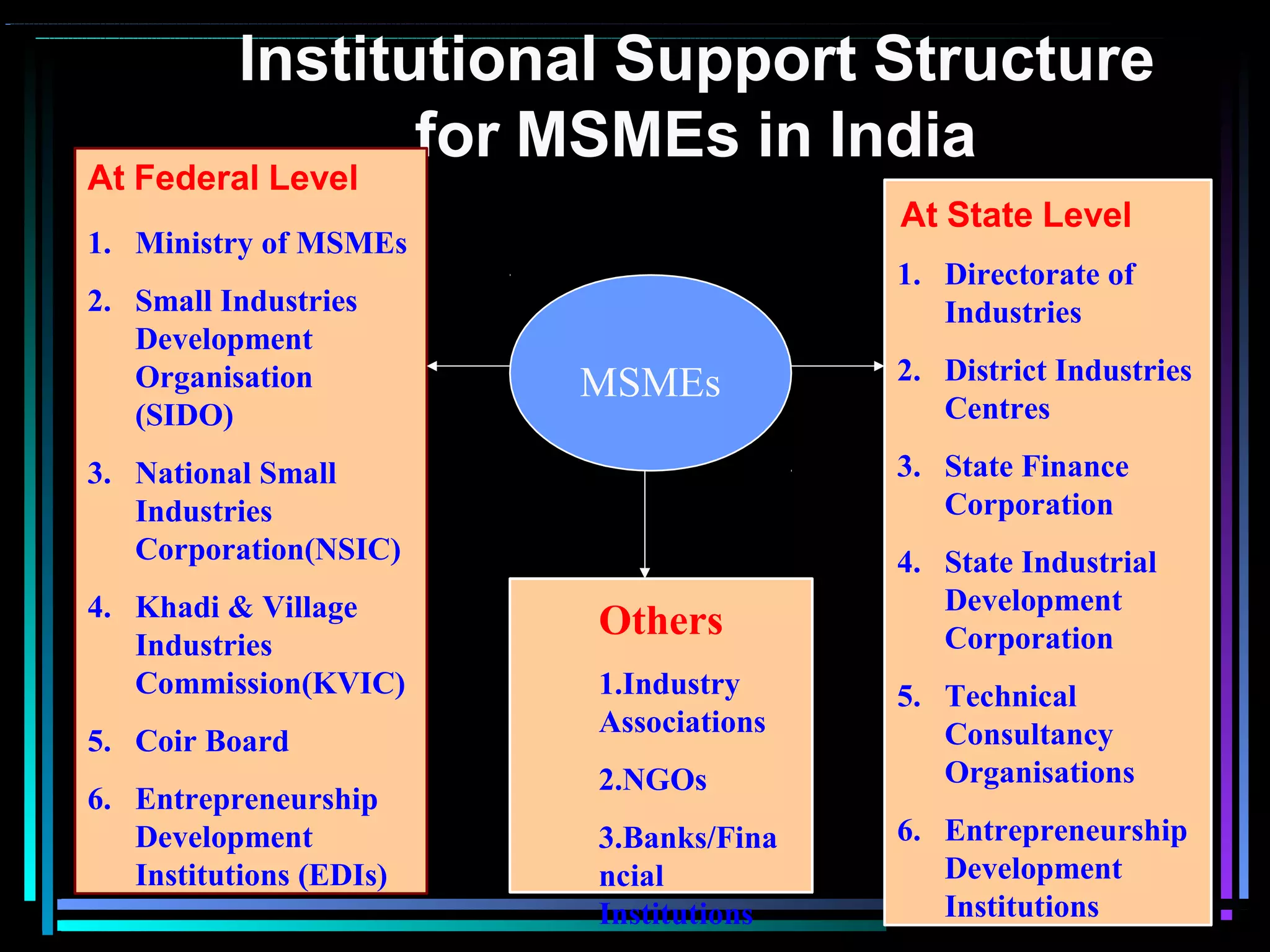
This document defines micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in India based on investment levels. Micro enterprises have investments below 25 lakh rupees, small between 25 lakh and 5 crore rupees, and medium between 5-10 crore rupees. For services, the thresholds are 10 lakh, 2 crore, and 5 crore rupees respectively. MSMEs significantly contribute to India's economy through manufacturing output, exports, and employing over 42 million people. The government supports MSMEs through various schemes including credit support, technology upgradation subsidies, marketing assistance, and cluster development programs. However, MSMEs still face challenges around access to finance, skilled labor,