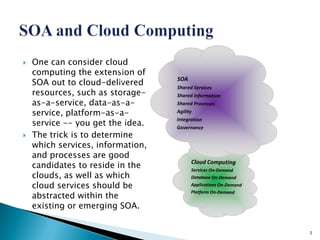
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to shared computing resources like networks, servers, storage, applications and services over the internet. It delivers applications through web browsers and allows for dynamic scaling of resources. Some benefits include reduced costs, increased storage and flexibility compared to traditional computing methods. However, privacy, security, and compliance are concerns that need to be addressed for cloud computing.








![Cloud computing is the delivery of computing as
a service rather than a product.
As cloud computing is achieving increased
popularity, concerns are being voiced about the
security issues
Many universities, vendors and government
organisations are investing in research around the
topic of cloud computing:[91]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloud-ppt-111122083339-phpapp01/85/Cloud-ppt-13-320.jpg)
