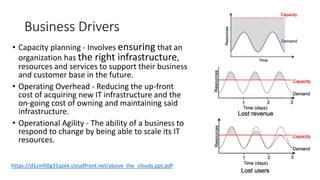
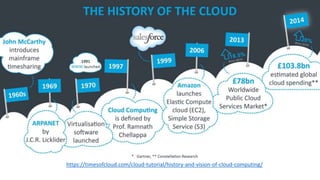
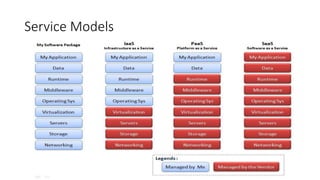
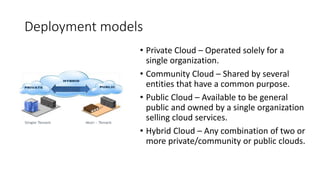
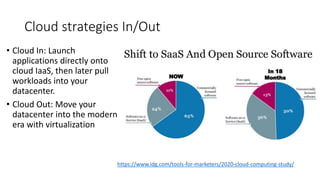
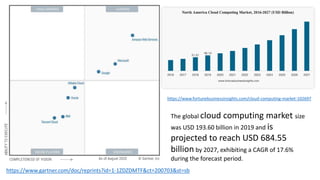
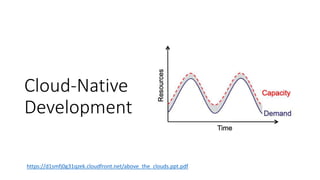
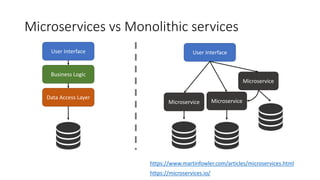
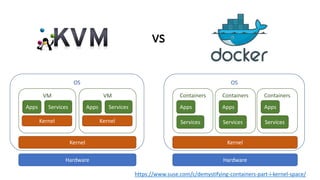
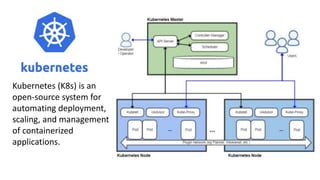
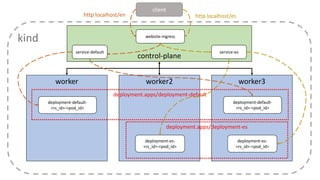
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, covering its business drivers, deployment models (private, community, public, hybrid), and cloud strategies. It highlights the growth of the cloud computing market and emphasizes cloud-native development principles, as well as the differences between microservices and monolithic services. Key topics include infrastructure as code, the twelve-factor app methodology, and the role of Kubernetes in managing containerized applications.