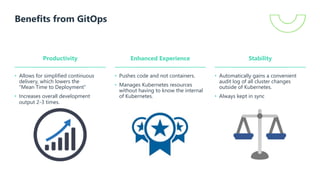
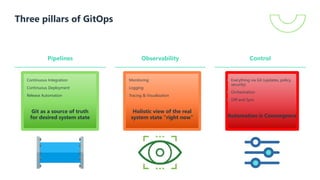
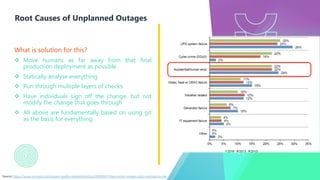
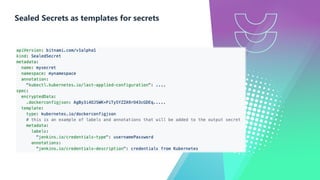
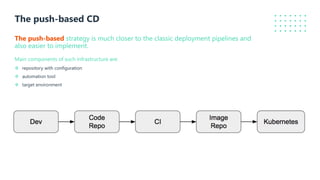
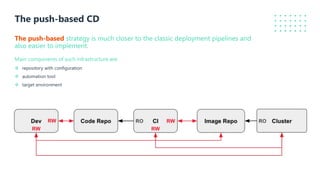
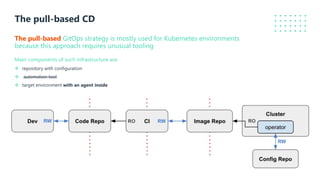
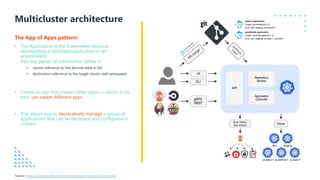
The document presents a detailed overview of GitOps, an operations model designed to enhance deployment speed and development efficiency for cloud-native applications. It outlines the principles of GitOps, including declarative system descriptions and version control via Git, as well as emphasizing the importance of security in CI/CD pipelines. The document also discusses deployment strategies, particularly the push-based and pull-based approaches, providing insights into effective implementation within Kubernetes environments.