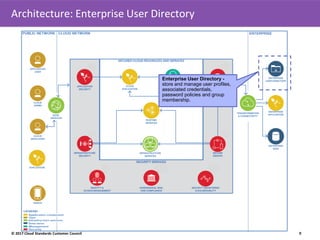
The Cloud Standards Customer Council (CSCC) provides guidance to cloud standards bodies from a customer perspective. This document summarizes a webinar about the CSCC's Cloud Customer Architecture for Securing Workloads on Cloud Services. The webinar discussed key aspects of securing workloads in cloud environments, including identity and access management, infrastructure security, application security, data security, and governance. It also outlined the CSCC's series of cloud customer reference architectures and provided considerations for successfully securing workloads on cloud services.