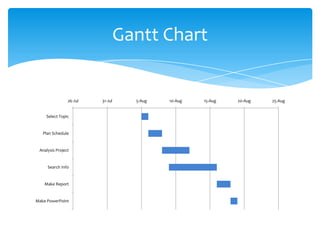
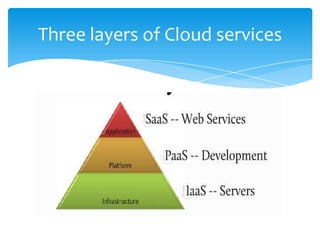
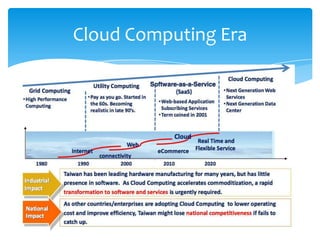
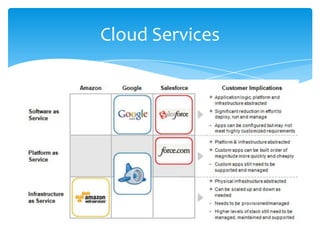
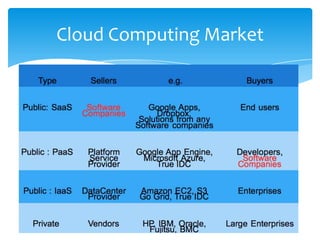
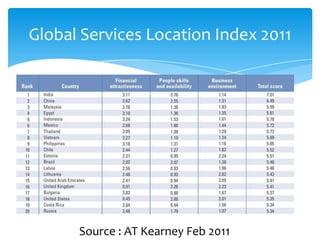
This document discusses cloud computing and its opportunities for telecommunications companies. It provides an overview of cloud computing concepts and categories. It then discusses True IDC, a major cloud computing provider in Thailand, and how it offers infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). The document also outlines opportunities and challenges for telecommunications companies to leverage their network expertise and enterprise relationships to provide cloud services.