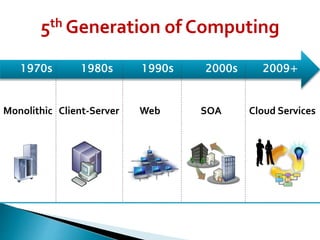
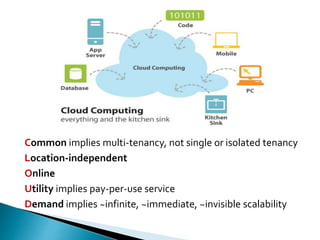
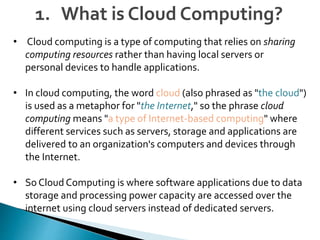
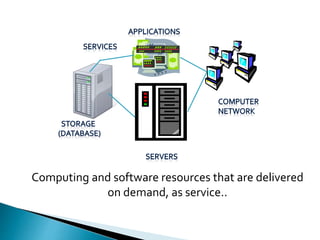
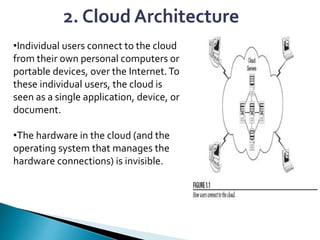
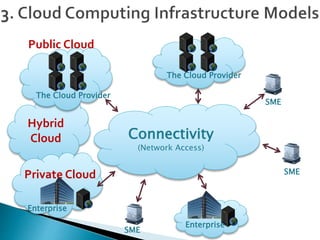
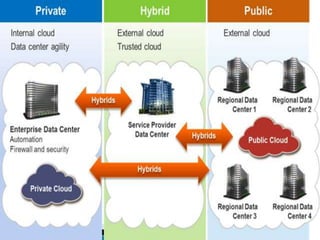
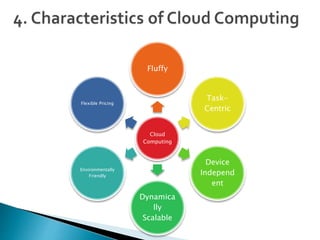
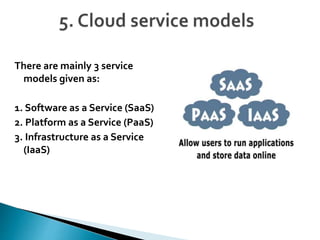
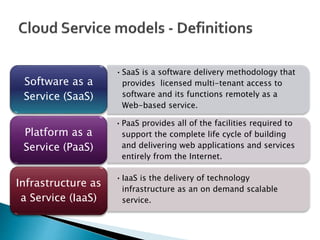
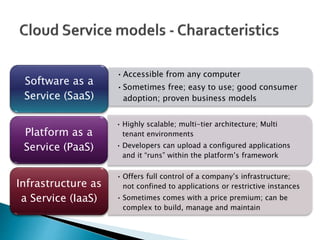
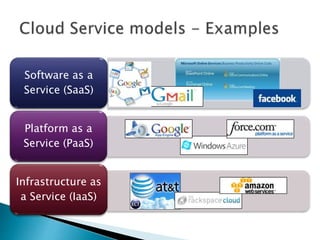
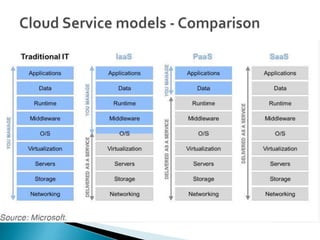
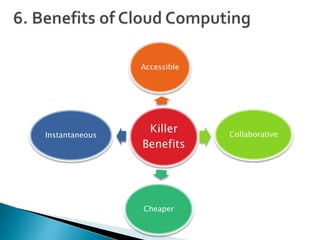
Cloud computing is a type of computing that relies on sharing computing resources over the Internet instead of having local servers or devices handle applications. It allows users to access software, storage, and other computing services from anywhere via cloud servers. There are three main types of cloud services: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) which provides on-demand access to computing infrastructure resources; Platform as a Service (PaaS) which provides platforms and environments for developing and delivering applications; and Software as a Service (SaaS) which provides software applications delivered over the Internet. Cloud computing provides scalable, cost-effective, and collaborative computing resources on demand.