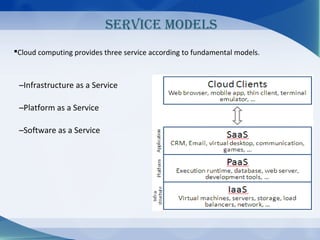
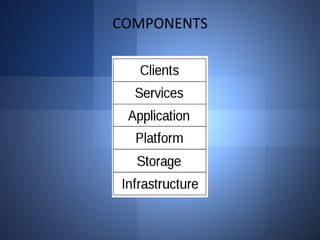
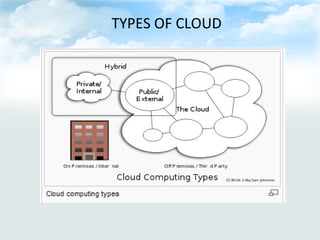
Cloud computing is a model where data and services reside on the internet rather than local servers or personal devices. It provides scalable computing resources and services through a shared network infrastructure. There are three main service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides basic computing and storage resources; Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides development environments; and Software as a Service (SaaS) provides applications delivered over the internet. Cloud computing offers benefits like reduced costs, increased collaboration, and scalability but also security concerns due to data residing externally.